Low-energy-consumption and low-Al-content recovery method for lithium iron phosphate positive plate
A technology for lithium iron phosphate and recovery methods, which is applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, positive electrodes, battery recovery, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable industrial application, high calcination temperature, and high recovery energy consumption, so as to shorten calcination time and reduce calcination The effect of temperature and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] A method for recovering lithium iron phosphate cathode sheet with low energy consumption and low Al content, comprising the following steps:
[0049] S1. Use a crusher to crush the lithium iron phosphate cathode sheet to be recovered into coarse particles, and control the particle size to about 5-10 mm to obtain a crushed material;
[0050] S2. Use a roller furnace to put a broken material in N 2 Calcining under the atmosphere, set the temperature of the holding zone to 450°C, the heating time is 2h, the holding time is 1h, and after cooling to below 95°C, it is released from the furnace to obtain the calcined material;
[0051] S3. Grinding the calcined material with a pulverizer into a powder with a particle size D50 between 50 and 80 μm to obtain a secondary crushed material;
[0052] S4. Classify the secondary crushed material with an airflow classifier, screen out the Al element therein, and obtain a lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material with a low Al...
Embodiment 2~6 and comparative example 1~7
[0055] Compared with Example 1, the recovery method of lithium iron phosphate positive electrode sheet provided by Examples 2-6 and Comparative Examples 1-7 with low energy consumption and low Al content is different in that the calcination temperature and time in step S2 are as shown in the table 1, and Comparative Examples 1 to 4 and Comparative Example 6 cancel the S3 step, and the others are substantially the same as in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0056] Preparation conditions and Al content of Table 1 Examples 1-6 and Comparative Examples 1-7
[0057]
[0058]
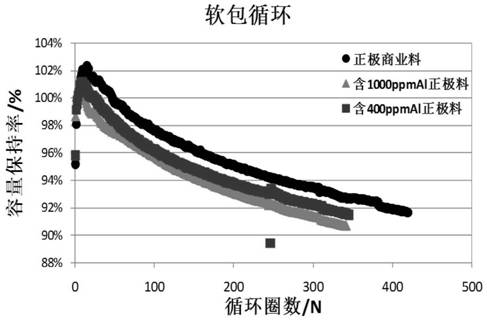
[0059] Table 2 Comparison of internal resistance of batteries with different Al impurity contents
[0060]
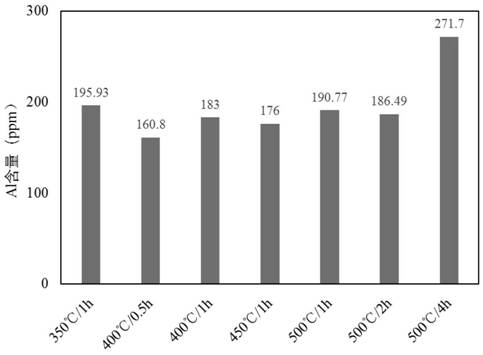
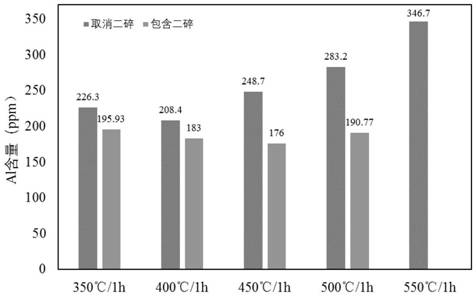
[0061] From Table 1 and Figure 3-4 It can be seen that when the calcination temperature of S2 is higher than 500°C, or the holding time of S2 exceeds 2h, the Al content of the product exceeds 200ppm, and with the increase of temperature, the Al content tends to increase. In ad...
Embodiment 7~9 and comparative example 8
[0064] Compared with Example 1, the recovery method of low energy consumption and low Al content of the lithium iron phosphate positive electrode sheet provided in Examples 7-9 and Comparative Example 8 is different in that the particle size of the first crush and the D50 of the second crush are shown in Table 3 , and others are substantially the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0065] Table 3 Preparation conditions and Al content of Examples 7-9 and Comparative Example 8
[0066] sample Particle size(mm) Secondary crushed material D50(μm) Al content / ppm Example 7 1~5 50~80 196 Example 8 10~15 50~80 174 Example 9 5~10 80~100 207 Comparative example 8 5~10 30~50 234
[0067] It can be seen from Table 3 that when the particle size of step S1 is between 1-15 mm, if the D50 of S3 exceeds 80 μm or is lower than 50 μm, the Al content of the obtained product will exceed 200 ppm. Only when the particle...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com