Screening method of high-temperature stable lignin for storage battery
A high-temperature stability and screening method technology, applied in the direction of color/spectral characteristic measurement, etc., can solve the problems of inability to scientifically determine the correlation of high-temperature resistance performance of lignin batteries, many factors affecting batteries, and short high-temperature treatment time, etc., to achieve the stage change process Comprehensive evaluation, excellent cold start performance, good high temperature stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
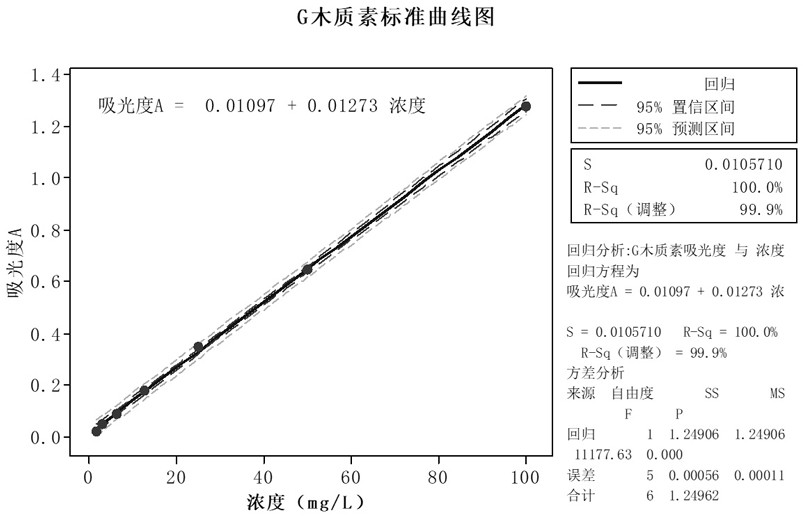
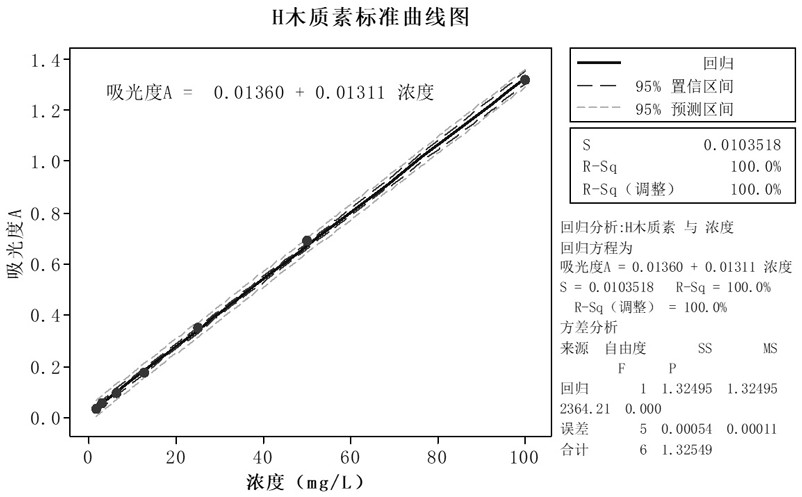
[0050] (1) Select two lignosulfonate products H and G, and prepare lignin concentrations of 100mg / L, 50mg / L, 25mg / L, 12.5mg / L, 6.25mg / L in 4g / L NaOH solution respectively L, 3.125mg / L, 1.5625mg / L series of standard solutions, the balance adopts an analytical balance, and a volumetric flask is used to constant volume; the standard curve is as attached figure 1 , 2 shown;
[0051] (2) Use a UV-visible spectrophotometer to test the full-wavelength ultraviolet light, record the ultraviolet absorption value A at the maximum absorption wavelength, and use the concentration and light absorption value to draw the standard curve A=aC+b of this lignin in an alkaline solvent. R 2 >99.9%, where A is the absorbance, C is the concentration, the unit is mg / L, a and b are the values obtained by linear simulation;
[0052] The standard curve equation of lignin G in this UV standard curve test is: A=0.01097+0.01273C, where A represents the absorbance value, C represents the concentration o...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Select two kinds of alkali lignin products W and J, measure their standard curve in DMF complete solution, select 1.19g / cm3 for high temperature test electrolyte density 3 , the ambient temperature is selected to be 75°C, the test cycle is selected to be 30 days, and other operating steps are the same as in Example 1; the corresponding daily dissolution rate and daily decomposition rate data are calculated according to the concentration value, and the results are shown in Table 2 and attached Figure 5 , 6 shown.
[0061]
[0062] W lignin is more soluble than J lignin at high temperature, and its decomposition rate is lower. The results show that W lignin is more stable than J lignin at high temperature of 75 °C.
Embodiment 3
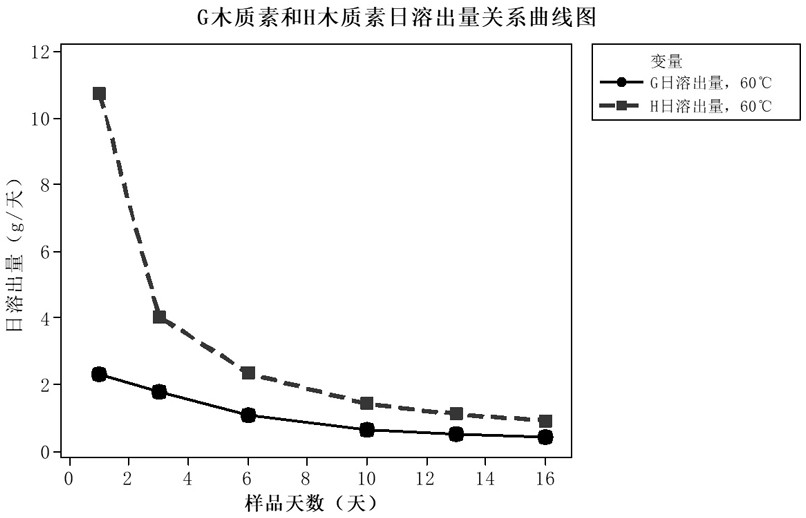
[0064] Choose a kind of benzene sulfonate expansion agent product T and a kind of naphthalene sulfonate expansion agent product N, measure its 1.19g / cm 3 For the standard curve in sulfuric acid solution, the density of the electrolyte for high temperature testing is 1.19g / cm 3 , the ambient temperature is selected at 60°C, the test period is selected at 15 days, and other operating steps are the same as in Example 1; the corresponding daily dissolution rate and daily decomposition rate data are calculated according to the concentration value, and the results are shown in Table 3 and attached Figure 4 shown.
[0065]
[0066] The daily dissolution rate of T synthetic expansion agent and N synthetic expansion agent is close, but the decomposition rate of T synthetic expansion agent is larger than that of N synthetic expansion agent under the same test environment. more stable.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com