A universal two-dimensional rare earth MOFs material and its solvent-free chemical exfoliation method and application
A universal, solvent-free technology, which is applied in the analysis of materials, material analysis by electromagnetic means, material analysis by optical means, etc., can solve the problems of harsh synthesis conditions, achieve simple synthesis methods, relatively mild conditions, and produce high rate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
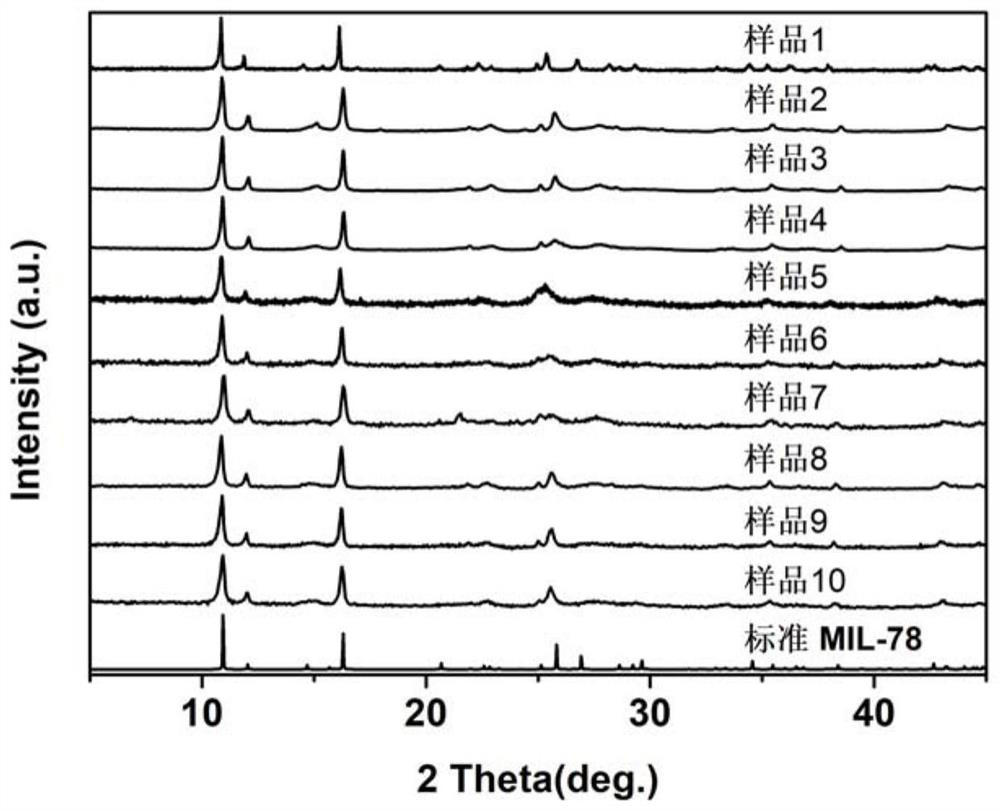
[0047] A kind of solvent-free chemical exfoliation method of TEAB quaternary ammonium salt-assisted, hierarchical structure bulk rare earth MOFs material, comprises the following steps:
[0048] (1) Eu(NO 3 ) 3 .6H 2 O, trimesic acid and TEAB were mixed in a molar ratio of 1:1:5, and ground for 5 minutes to obtain a mixture;
[0049] (2) Put the mixture in step (1) into a polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, and heat it for 48 hours at a temperature of 160° C. to obtain a product with a hierarchical block shape;
[0050] (3) After the product obtained in step (2) was cooled to room temperature, it was washed with distilled water and ethanol three times in sequence, and then dried at 60°C for 2 hours to obtain a Eu-MOFs material sample, which was named sample 1.
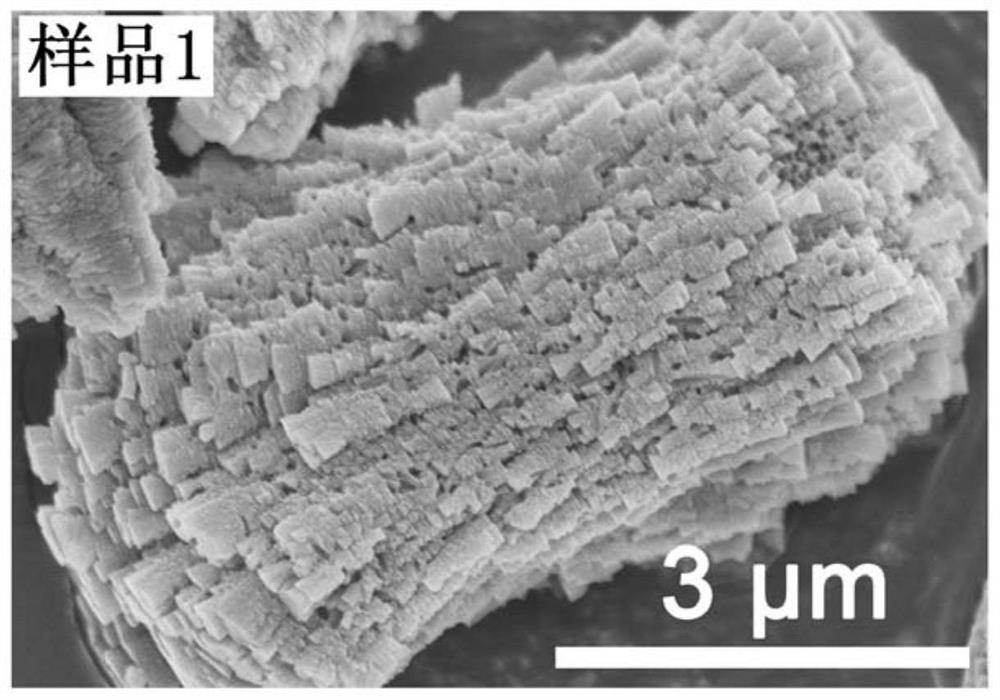
[0051] see figure 2 , the crystal morphology of the Eu-MOFs material obtained in this example is a hierarchical structure block, and the average crystallite size of the Eu-MOFs material is about 10 μm.
Embodiment 2
[0053] A kind of solvent-free chemical exfoliation method of TPAB quaternary ammonium salt-assisted, hierarchical structure bulk rare earth MOFs material, comprises the following steps:
[0054] (1) Eu(NO 3 ) 3 .6H 2 O, trimesic acid and TPAB are mixed in a molar ratio of 1:1:5, and ground for 10 minutes to obtain a mixture;
[0055] (2) Put the mixture in step (1) into a polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, and heat it for 48 hours at a temperature of 160° C. to obtain a product with a hierarchical block shape;
[0056] (3) After the product obtained in step (2) was cooled to room temperature, it was washed with distilled water and ethanol three times in sequence, and then dried at 60°C for 2 hours to obtain a Eu-MOFs material sample, which was named sample 2.
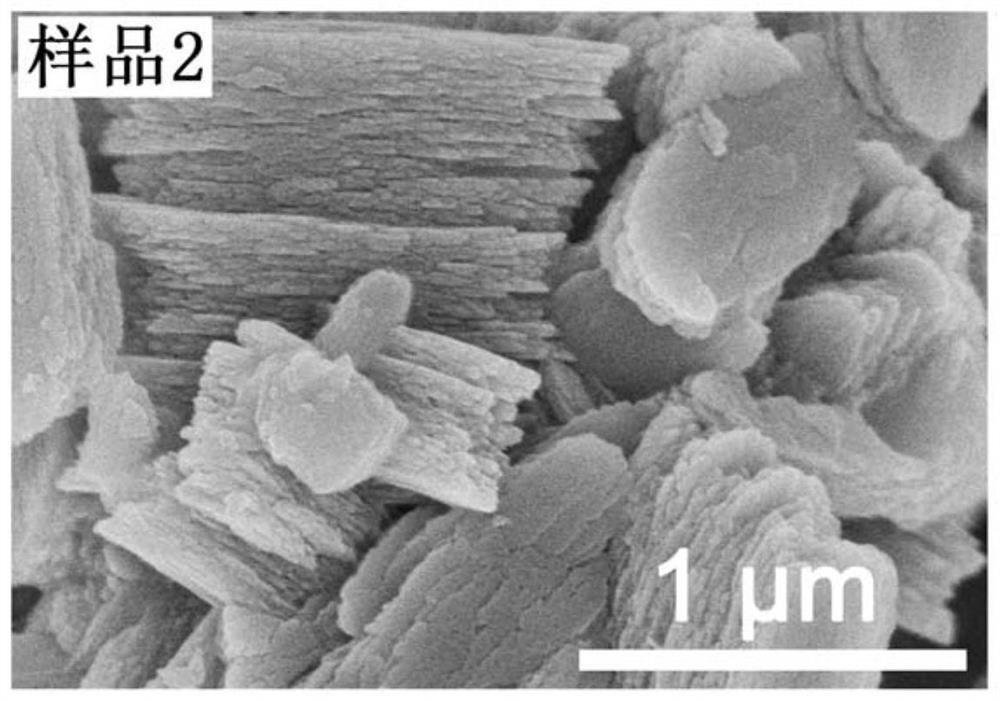
[0057] see image 3 , the crystal morphology of the Eu-MOFs material obtained in this example is a hierarchical structure block, and the average crystallite size of the rare earth Eu-Fs material is about 3 μm.
Embodiment 3
[0059] A kind of solvent-free chemical exfoliation method of TBAB quaternary ammonium salt assisted, accordion-shaped rare earth MOFs material, comprises the steps:
[0060] (1) Eu(NO 3 ) 3 .6H 2 O, trimesic acid and TBAB were mixed in a molar ratio of 1:1:5, and ground for 6 minutes to obtain a mixture;
[0061] (2) Put the mixture in step (1) into a polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, and heat it for 48 hours at a temperature of 160° C. to obtain a product with an organ-shaped appearance;
[0062] (3) After the product obtained in step (2) was cooled to room temperature, it was washed with distilled water and ethanol three times in sequence, and then dried at 60°C for 2 hours to obtain a Eu-MOFs material sample, which was named sample 3.
[0063] see Figure 4 , the crystal morphology of the Eu-MOFs material obtained in this example is accordion-shaped, and the average size of the crystallites of the Eu-MOFs material is about 6 μm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com