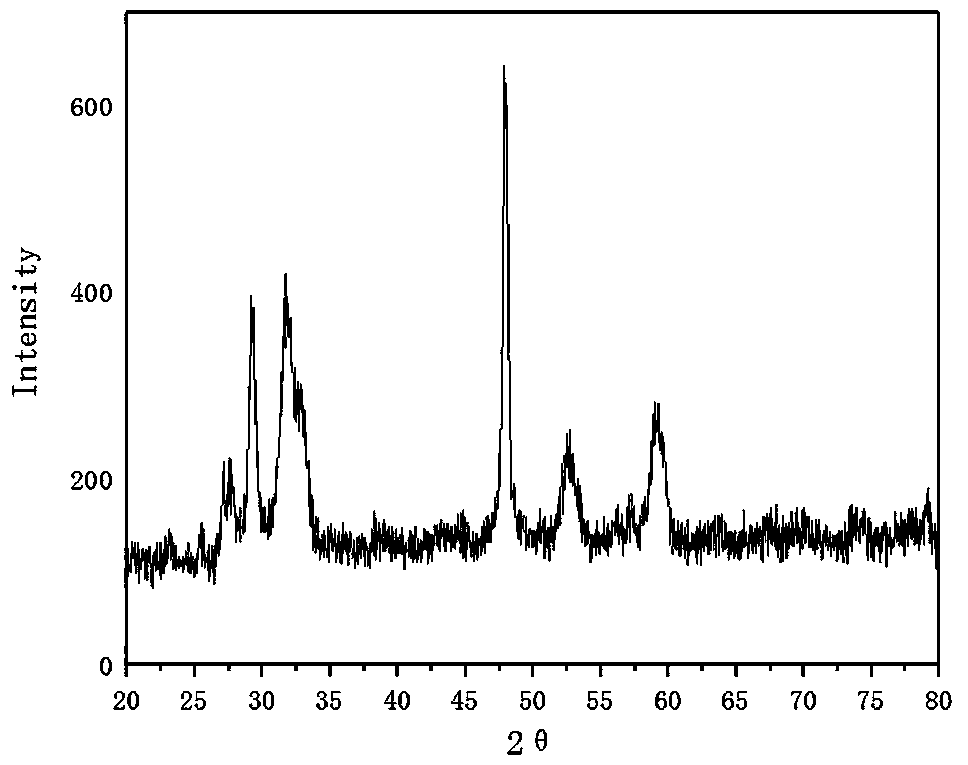
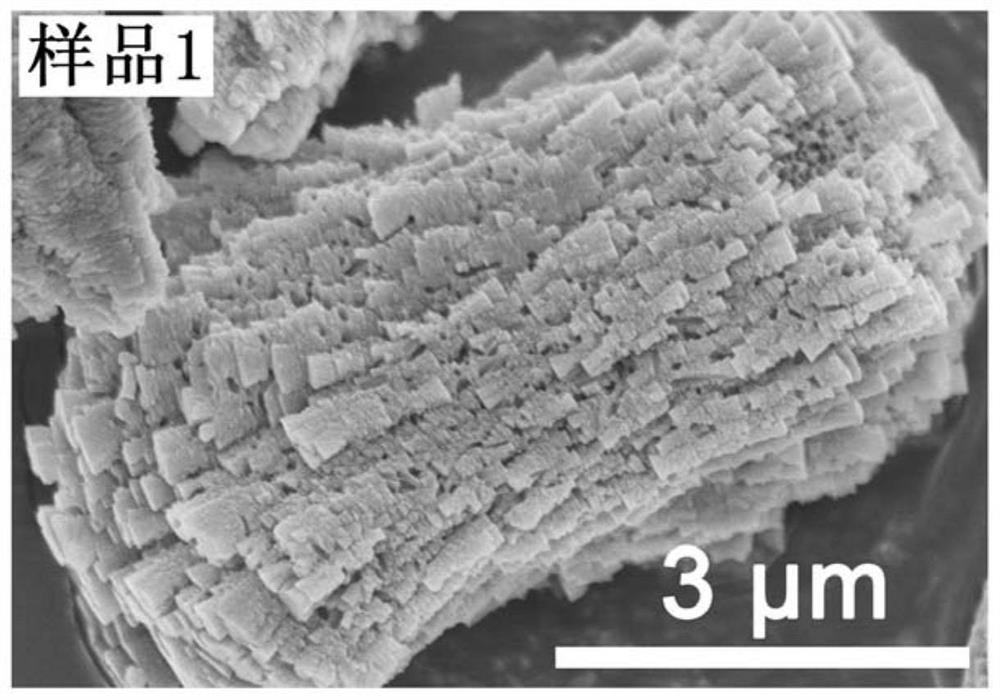
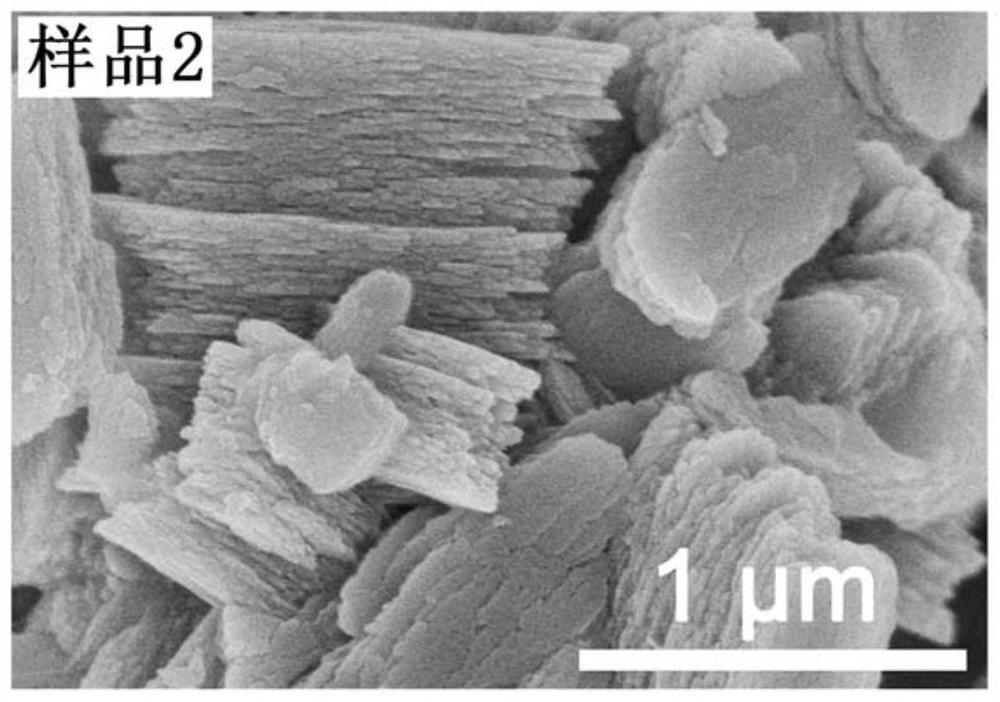
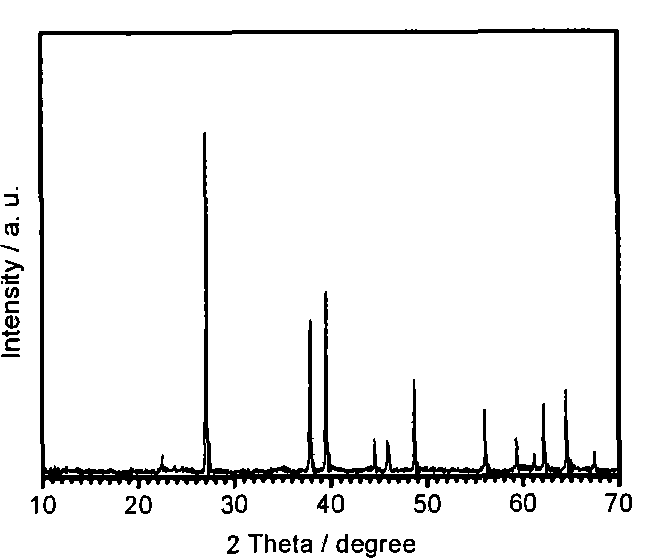
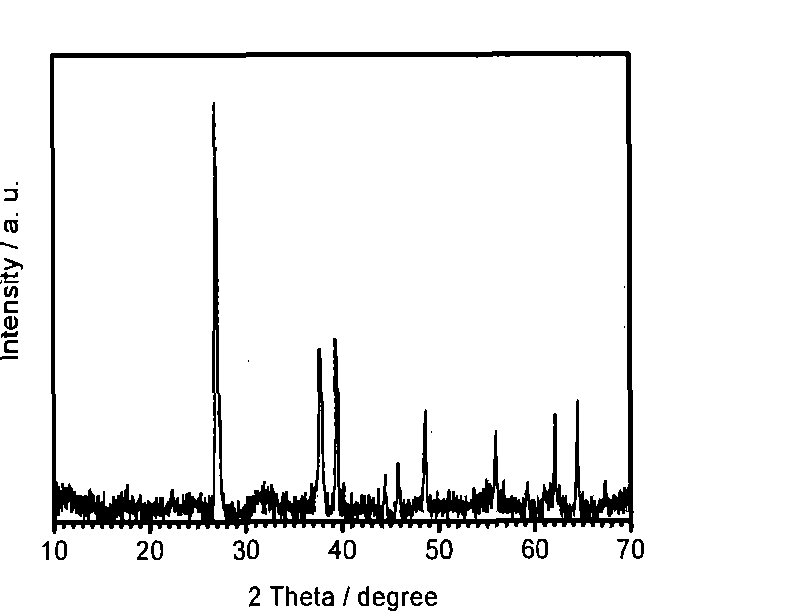
Patents
Literature
39 results about "Anisotropic growth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
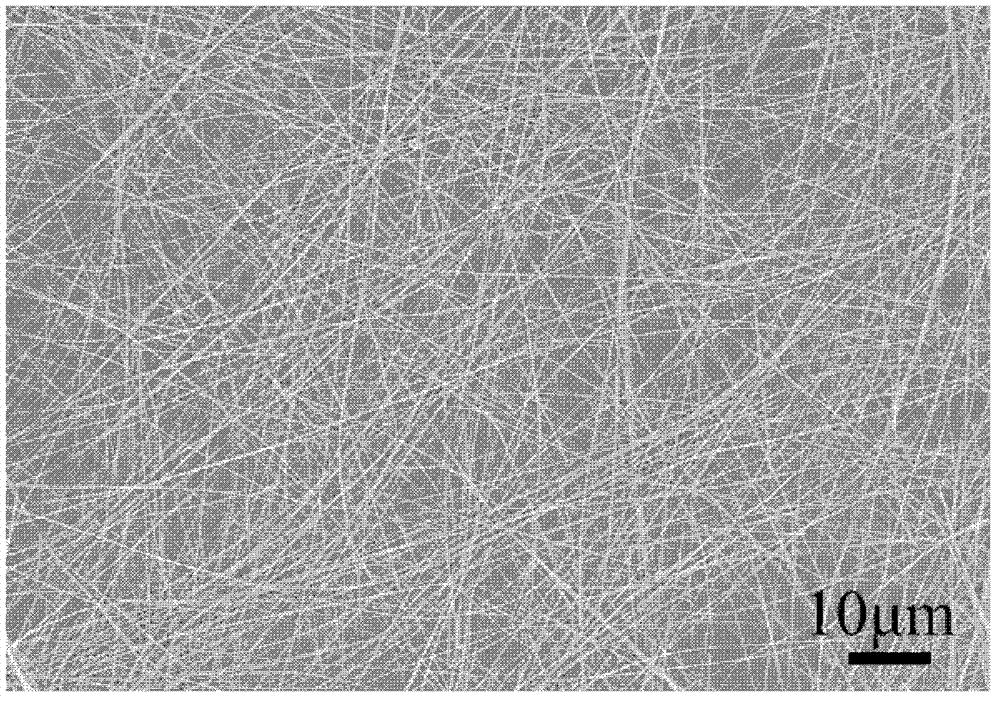
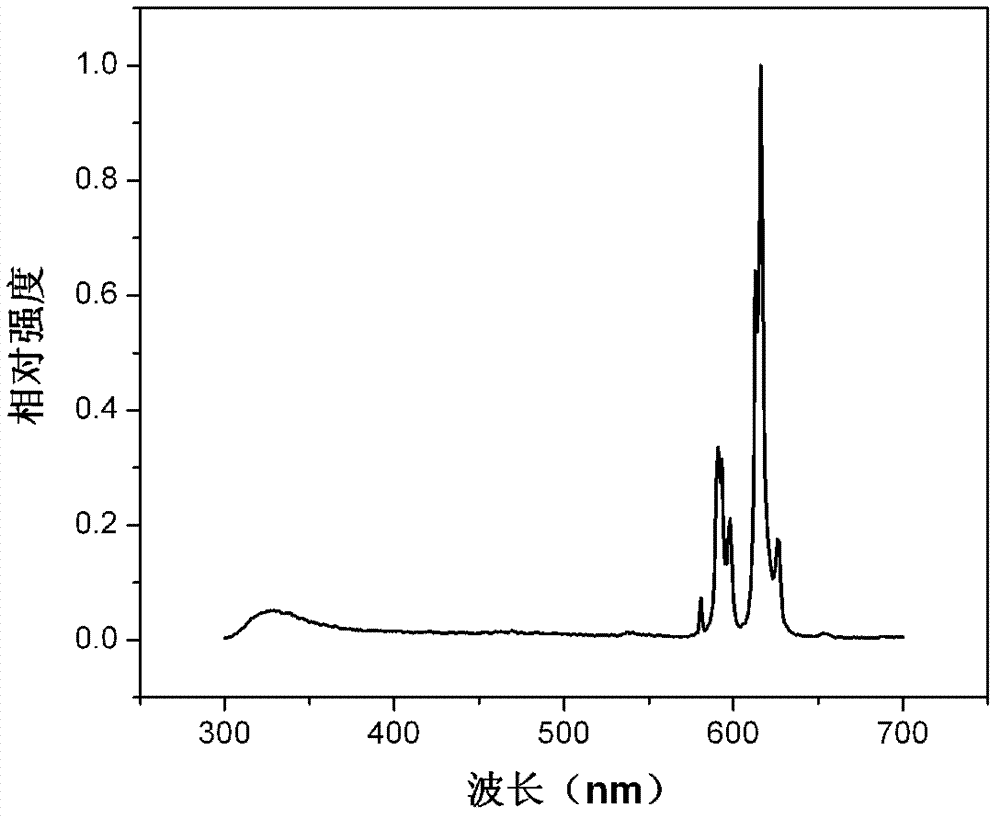
Rare Earth Nanorods
ActiveUS20080279744A1Reduce expenditureMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthNanoparticleRare earth
A process for the production of nanorods containing a rare earth metal is disclosed. The process comprises the steps of: (a) increasing the pH of an aqueous solution of the formula MX3, where M is a trivalent rare earth metal cation and X is a monovalent anion so as to produce a reaction product containing X anions in solution and a precipitate in the form of trivalent rare earth hydroxide nanoparticles of the formula M(OH)3, the nanoparticles having a hexagonal crystal structure; and, (b) ageing the nanoparticles of step (a) in the presence of the reaction product containing X anions in solution so as to cause rod-like anisotropic growth of the nanoparticles and form rare earth hydroxide nanorods.
Owner:ADVANCED NANO TECH
Rare earth nanorods
ActiveUS7943106B2Reduce expenditureMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthRare-earth elementAnisotropic growth
A process for the production of nanorods containing a rare earth metal is disclosed. The process comprises the steps of: (a) increasing the pH of an aqueous solution of the formula MX3, where M is a trivalent rare earth metal cation and X is a monovalent anion so as to produce a reaction product containing X anions in solution and a precipitate in the form of trivalent rare earth hydroxide nanoparticles of the formula M(OH)3, the nanoparticles having a hexagonal crystal structure; and, (b) ageing the nanoparticles of step (a) in the presence of the reaction product containing X anions in solution so as to cause rod-like anisotropic growth of the nanoparticles and form rare earth hydroxide nanorods.
Owner:ADVANCED NANO TECH
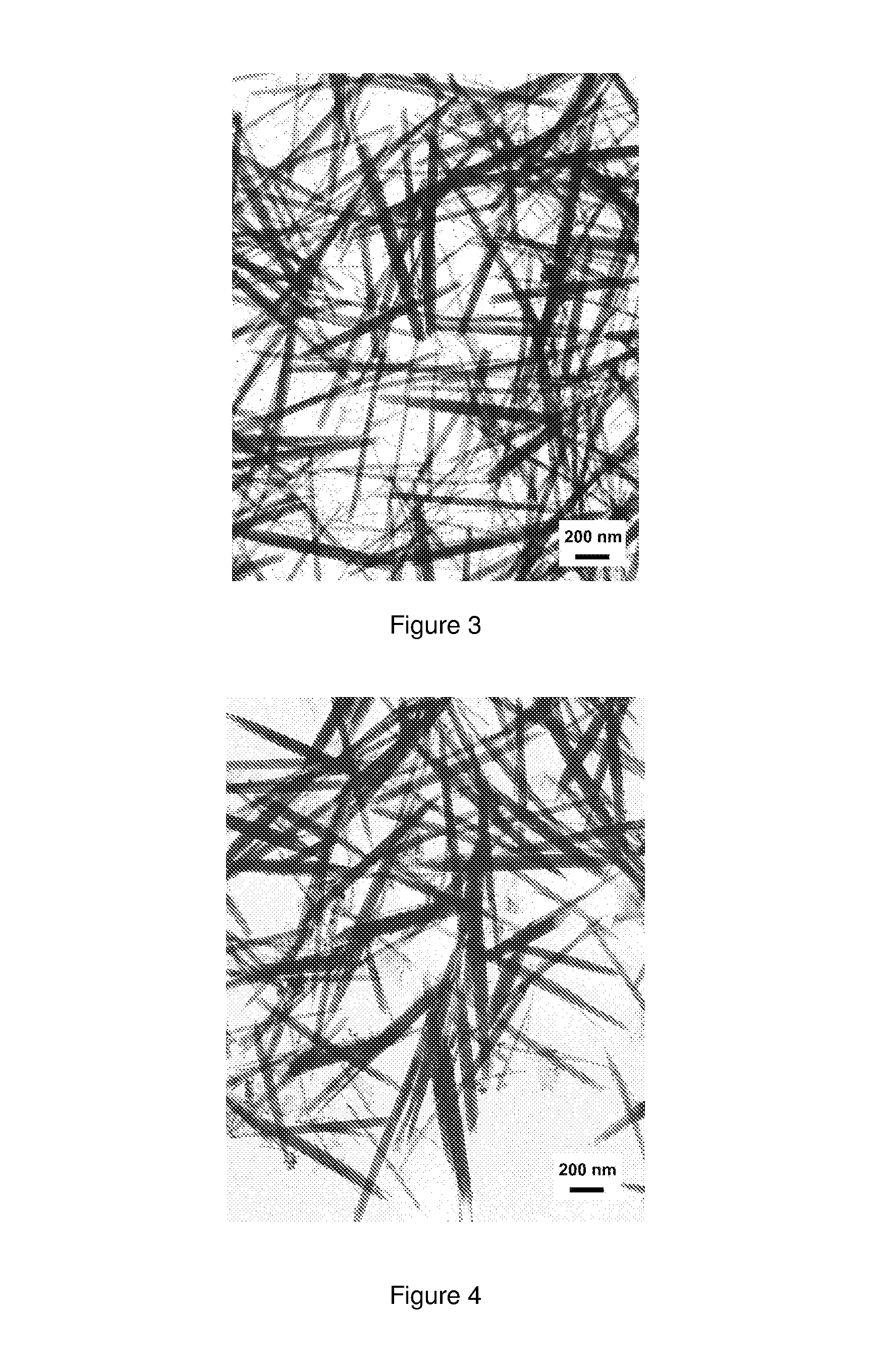
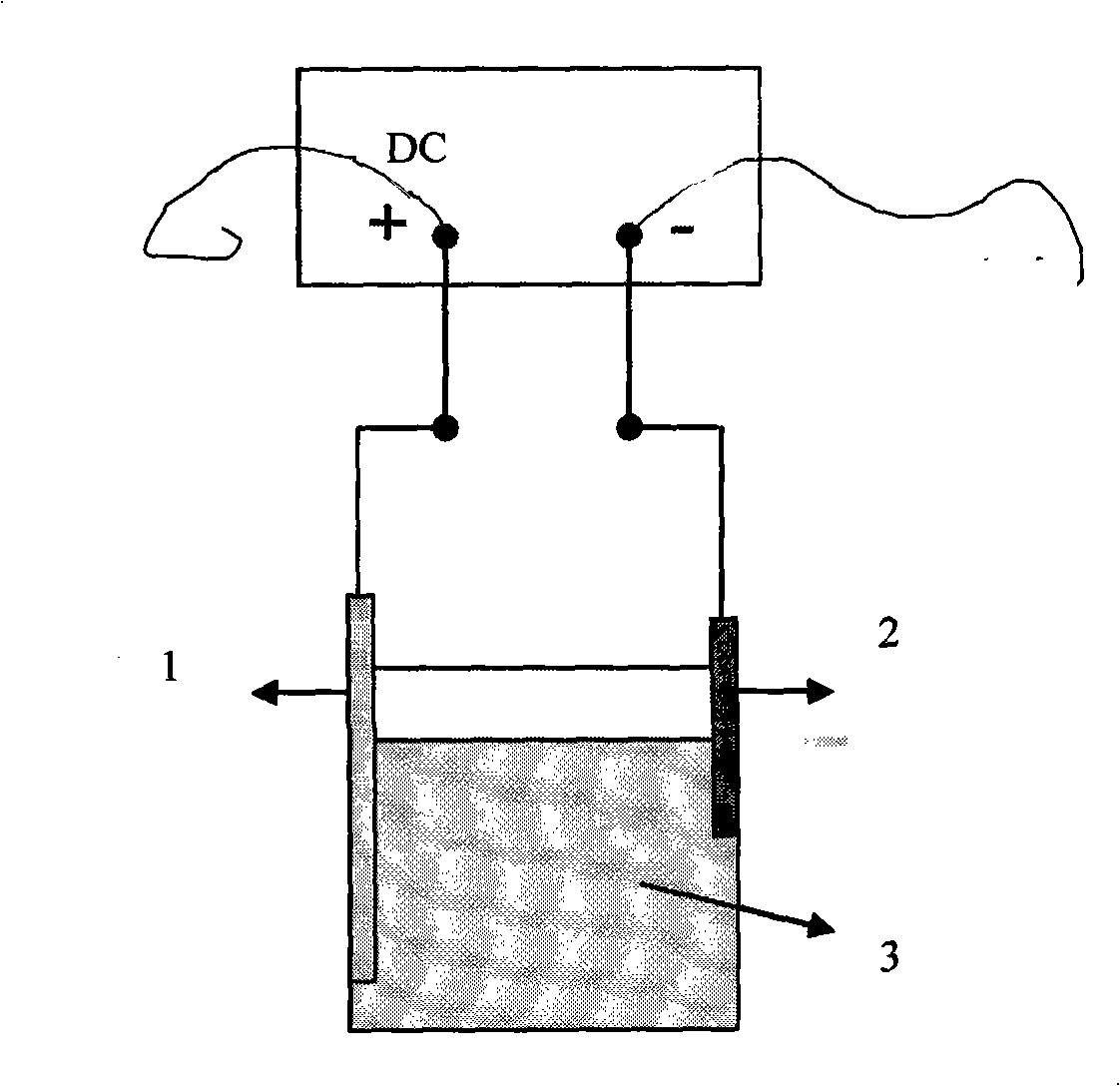
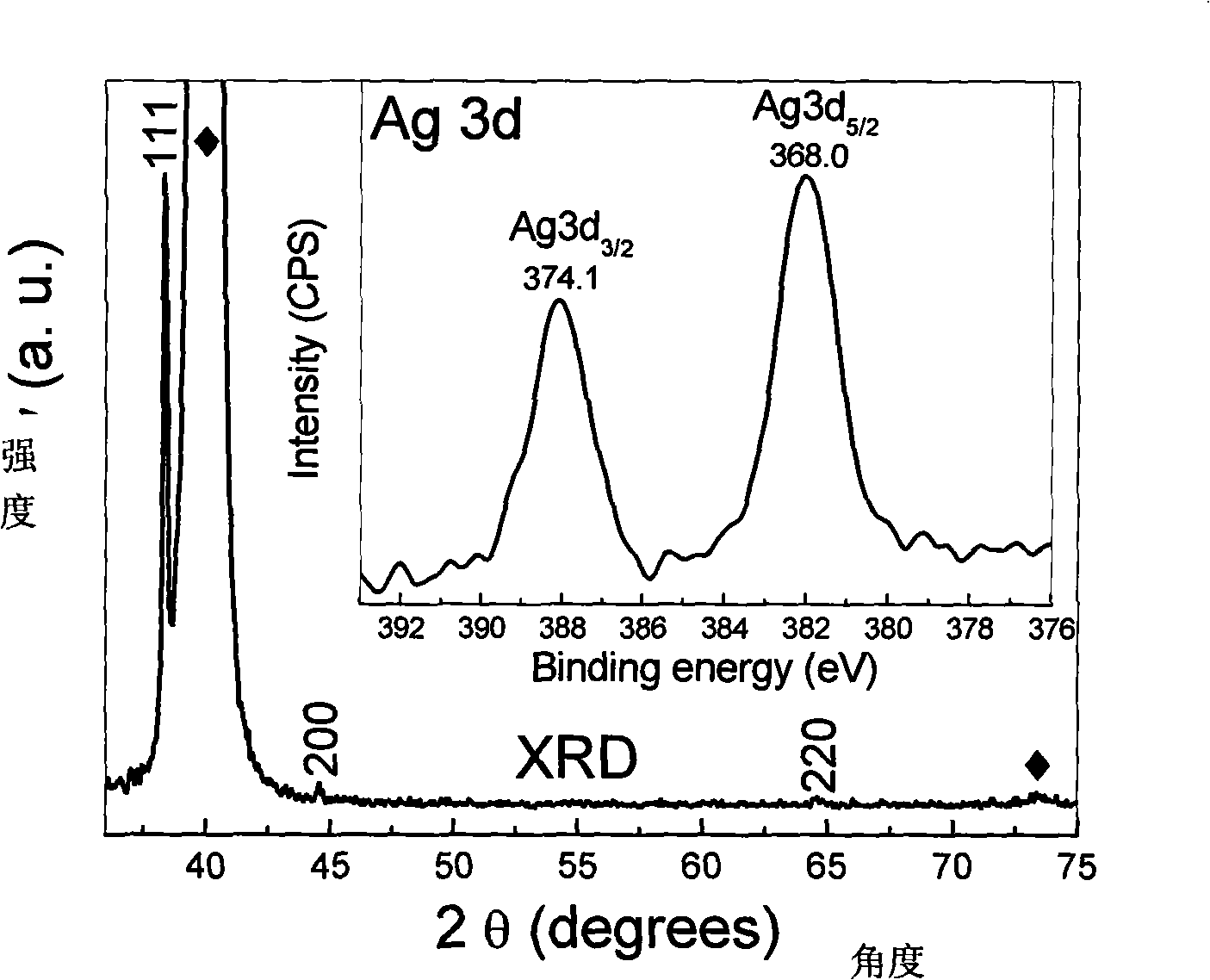
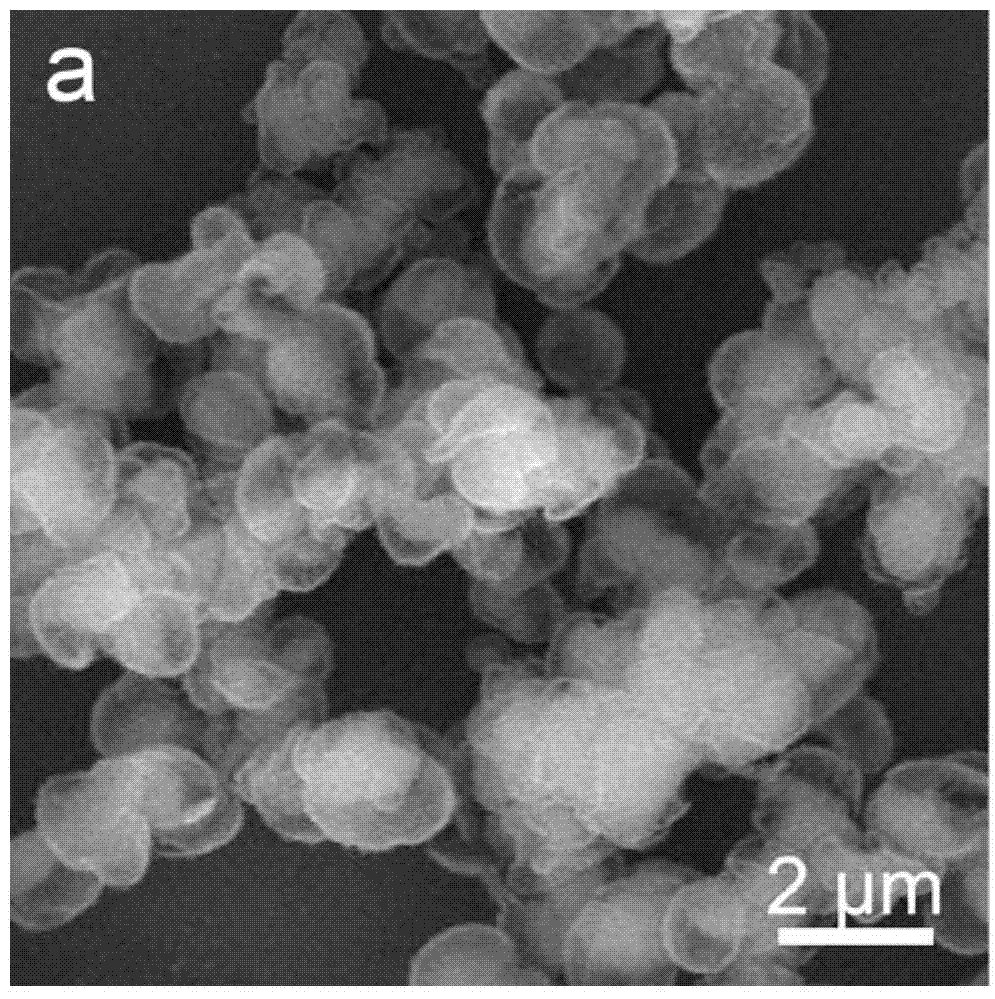
Synthetic method of load type floriform silver nanostructured material
The invention discloses a synthesizing method of a loading flower-shaped nano silver structural material, which is characterized in that a silver plate with high purity is taken as an anode, a platinum film electrode is taken as a cathode, a silver nitrate solution with the concentration of 0.003 to 0.01 mol / L is taken as an electrolytic solution, and the volume of the electrolytic solution is 20 to 100 mL; the range of constant voltage is adjusted to be 50 to 200 mV during electrolytic deposition, and the time of the electrolytic deposition lasts for 2 to 15 minutes; the cathode of the loading nano silver structural material is repeatedly rinsed by deionized water after the reaction, and then dried in nitrogen. The synthesizing method of the loading flower-shaped nano silver structural material realizes the growth anisotropy of crystal, leads the size and the microstructure of the nano metallic structure to be controllable, does not need any addition agent and electrode surface modification, and achieves simple control of appropriate voltage and concentration of the electrolytic solution; the synthesizing method is ultra-simple, and has convenient operation, easy-separated products and high purity and well industrial application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for preparing transition metal oxide microspheres with controllable morphology
ActiveCN104743609ASimple stepsExperimental conditions are easy to controlMaterial nanotechnologyManganese oxides/hydroxidesMicrosphereControllability
The invention discloses a method for preparing transition metal oxide microspheres with controllable morphology. According to the method for preparing the transition metal oxide microspheres, the transition metal oxide microspheres are produced according to the steps of introducing catechol compounds into a reaction system and then performing simple hydrothermal reaction, and preferably, a morphology control agent can also be added in the hydrothermal reaction system to control the morphology of the transition metal oxide microspheres. According to the method for preparing the transition metal oxide microspheres with controllable morphology disclosed by the invention, the transition metal oxide microspheres with controllable morphology are produced by adding a special morphology control agent into the hydrothermal reaction system to control the anisotropic growth of the material, not only the technology is simple, the controllability is good and the yield is high, but also the product produced according to the method has uniform size, larger specific surface area and high reaction activity and is suitable for large-scale preparation.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Method for preparing polycrystal texture ceramic material
InactiveCN1850725AQuality improvementImprove performanceElectromechanical coupling coefficientElectric breakdown
This invention relates to polycrystal texture ceramic material preparation method, it includes preparation technique principle and corresponding technique method. Diffusion route of ion and polar particle in high temperature field can be affected by electrostatic field, the characteristic is used to induct crystal nucleus growth process and reinforce anisotropy growth to form texture polycrystal material. Different strength orientation electric field is applied, and the strength is related to material system different component, core forming and crystal growth speed, anisotropy radius-thickness ratio expected, and electric breakdown strength of environment and materials. The anisotropy growth of polusrystal texture made is appreciable, polyspinal deformity is uniform, breaking tenacity and fracture toughness of material on wishful direction can be improved. Directed dielectric property can be great improved, and material piezoelectric constant and electromechanical conpling factor can be improved, dielectric loss can be reduced.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
High density ceramic matrix composite material, preparation method and application thereof
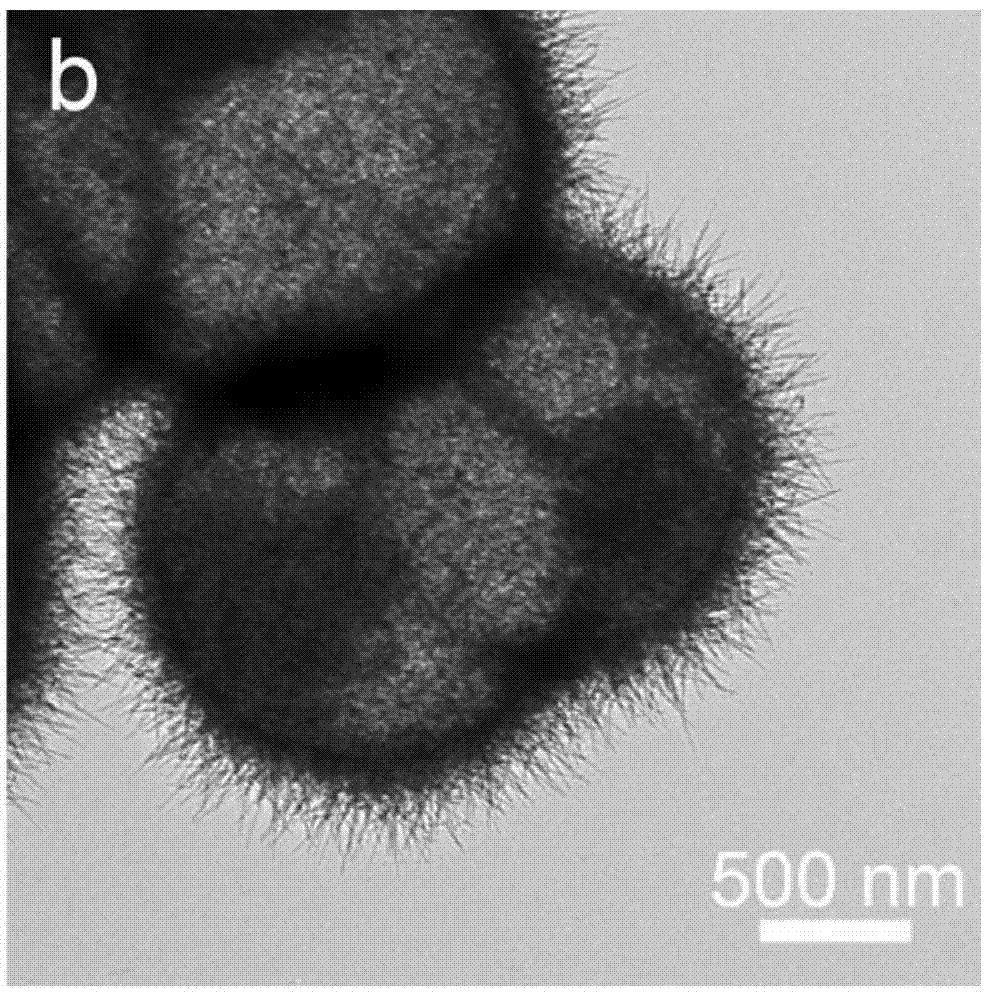
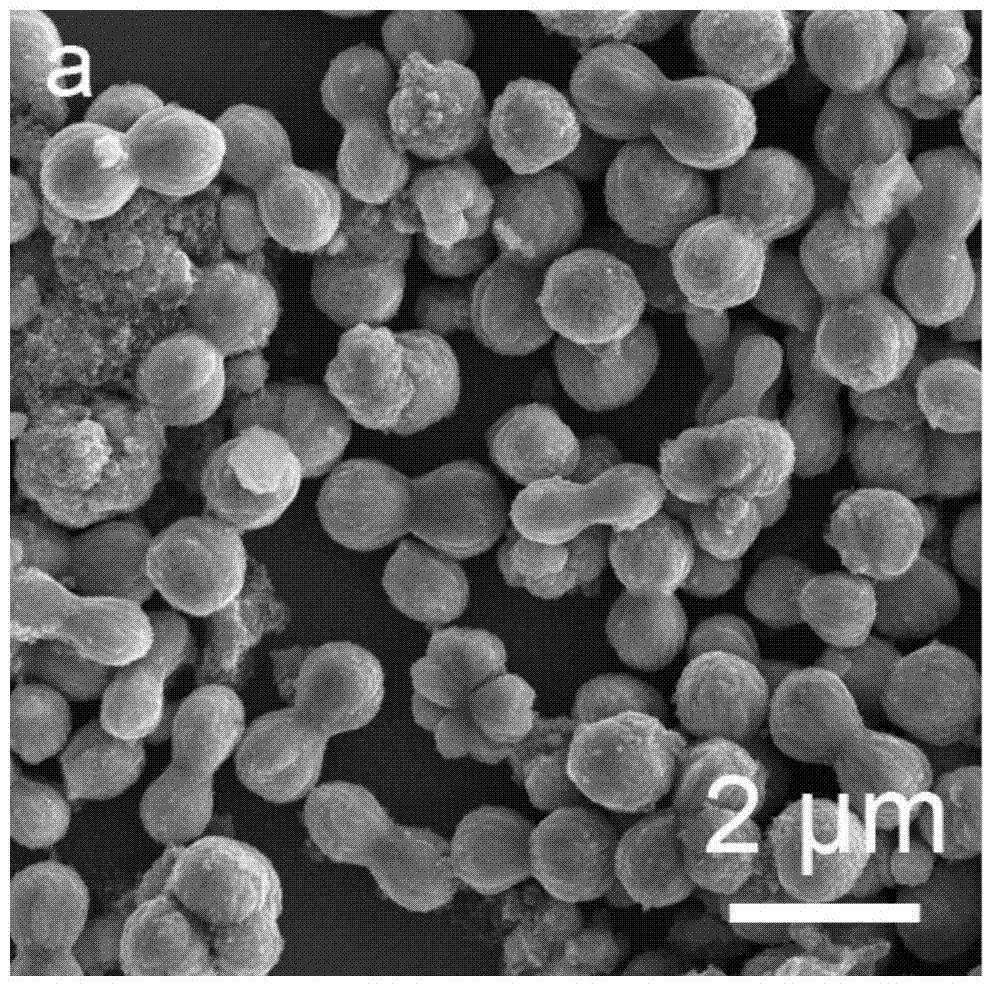
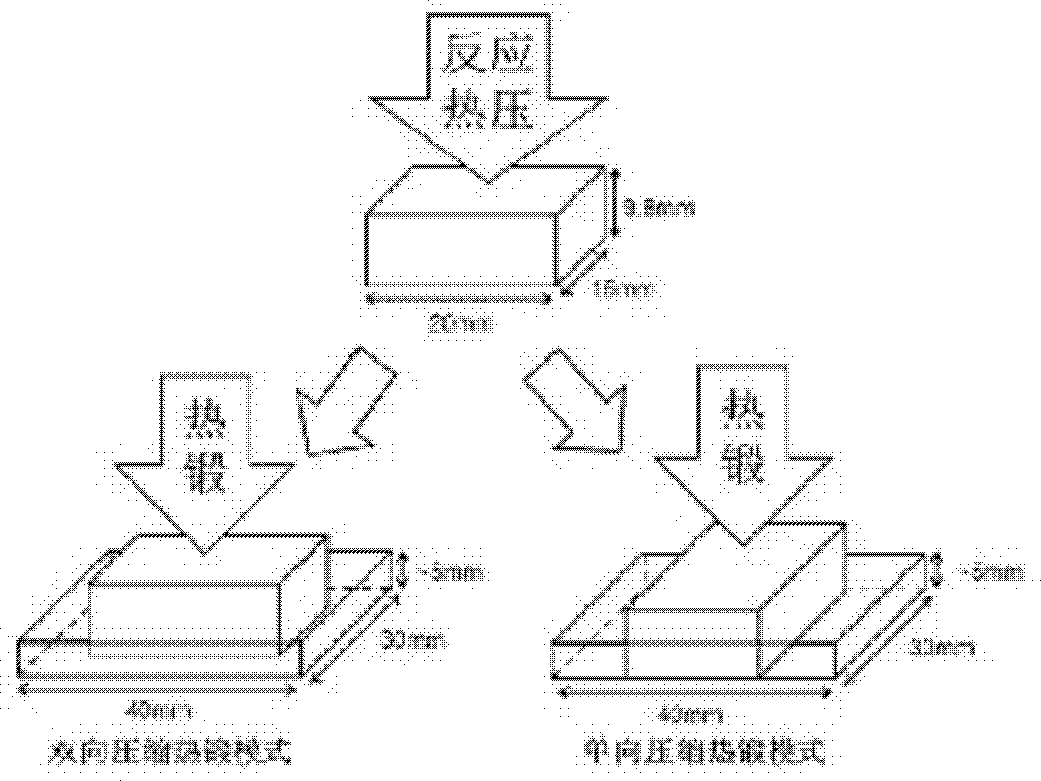
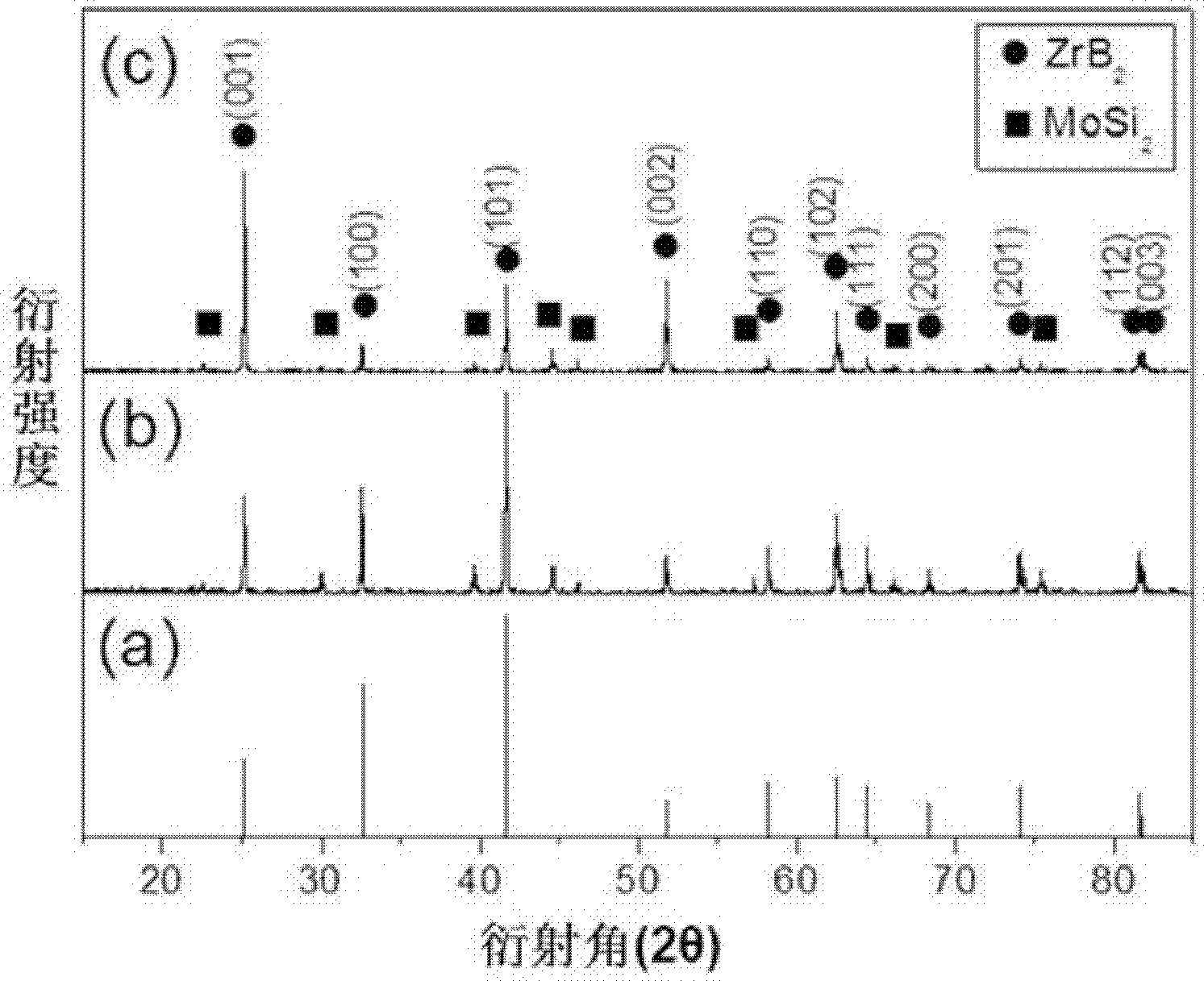
The invention discloses a high density ceramic matrix composite material, a preparation method and application thereof. A zirconium diboride-zirconium disilicide-tungsten carbide ceramic matrix composite material is prepared from zirconium diboride powder, zirconium disilicide and tungsten carbide with purity of greater than 98% by a two-step hot pressing sintering process. Specifically, the mass fraction of zirconium diboride powder is 75-90%, and the adding of high content zirconium diboride into the ceramic matrix composite material is in favor of improving the physical and chemical performance of the composite material. The mass fraction of zirconium disilicide is 10-15%, and the adding of the zirconium disilicide with the mass fraction into the ceramic matrix composite material can significantly lower the sintering temperature of the material. The mass fraction of tungsten carbide is 0-10%, the added tungsten carbide can promote the anisotropic growth of crystal grains in the material. The grain size of the three original powder is 1-5 microns, and the grain size in the range is conducive to uniform mixing of each phase. The material provided by the invention can be used as a surface heat insulation layer of hypersonic flight vehicles, and has the characteristics of high density and high mechanical properties.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing polar microcrystalline glass
This invention relates to a method for manufacturing polar glass ceramic. The method comprises: (1) mixing raw material micropowder with 0-15 wt.% of melting agent and 0-15 wt.% of seed crystal powder, and putting into a crucible; (2) placing the crucible in a high-temperature electric furnace, melting, taking out, molding and cooling to form ordinary glass; (3) cutting into a certain shape, polishing, putting into the high-temperature zone of an ordinary high-temperature electric furnace or a temperature-gradient electric furnace, placing electrodes on both sides of the glass or the crucible, and crystallizing at a medium temperature; (4) simultaneously applying a DC electric field to assist orientation crystallization; (5) cooling and shaping to obtain the final product. The method is reliable, and easy to control. The polar ceramic glass has high crystallization volume fraction, high orientation degree, and stable quality.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Textured boride base ultra-high temperature ceramic material and its preparation method
The invention discloses a textured boride base ultra-high temperature ceramic material and its preparation method. The ceramic material is a boride-silicide base composite material and is prepared from raw materials of group IVB metal, boron, silicon and transition metal. In addition, the microstructure of the composite material contains boride crystal grains of anisotropic grain growth and directional arrangement. The ceramic material is prepared by the following steps of: firstly performing reactive hot-pressing sintering to prepare densified boride base ceramic with the anisotropy crystal grain microstructure, and carrying out microstructure modulation on the ceramic which has undergone reactive hot-pressing sintering by a hot forging method to realize directional arrangement of the crystal grains of anisotropic grain growth. Therefore, the textured boride base ultra-high temperature ceramic material with the anisotropic grain growth crystal grain microstructure is obtained. According to the invention, relative density of the obtained ceramic material is greater than 98%; Lotgering orientation factor f (001) can reach up to 0.91; and its oxidation resistance, thermal conductivity and other properties all show obvious anisotropy.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving lithium battery negative electrode rate performance through magnetic effect
InactiveCN108417839AImproved electrode rate performanceImproved magnification performanceCell electrodesInternal resistanceElectrical battery
The invention provides a method for improving lithium battery negative electrode rate performance through a magnetic effect. A one-dimensional negative electrode material is adopted for loading ferrofluid and ferrite materials to form an oriented structure under a magnetic field, and by vertical combination with a copper current collector, a negative electrode in a three-dimensional dense array structure is formed. The problem of lithium ion intercalation difficulty caused by excessively high internal resistance resulted from anisotropic growth of the negative electrode of a traditional lithium battery negative electrode material in a lithium ion de-intercalation process is solved; by combination of the ferrite materials, the ferrofluid and the negative electrode through van der Waals force, the negative electrode material is vertically combined on the surface of the copper current collector in an oriented manner under the action of the magnetic field to form the three-dimensional dense array, active points of the material can be exposed more completely, a lithium ion transmission passage is formed, de-intercalation and migration performances of lithium ions in the negative electrode material are effectively improved, the battery rate performance is improved, and improving electrical performances of the negative electrode material through control of the negative electrode structure instead of components is realized.
Owner:CHENDU NEW KELI CHEM SCI CO LTD
Method for preparing hexagonal copper sulfide nano-sheets
ActiveCN108529661ASave raw materialsEasy to operateMaterial nanotechnologyCopper sulfidesSolventCopper sulfide
The invention belongs to the field of nano-material preparation, and particularly discloses a method for preparing hexagonal copper sulfide nano-sheets. The method includes steps of mixing copper saltand long-chain alkylamine with each other, heating and vacuumizing the copper salt and the long-chain alkylamine to dissolve the copper salt and the long-chain alkylamine and carrying out complexation on copper ions and amino to form reaction liquid A; heating and dissolving powdered sulfur and long-chain alkylamine to form reaction liquid B; adding the reaction liquid B into the reaction liquidA to form mixed solution; carrying out reaction, then adding absolute ethyl alcohol into the mixed solution to dissolve copper sulfide nano-sheets out from solution, and centrifugally washing and drying dissolved substances by the aid of absolute ethyl alcohol to obtain the copper sulfide nano-sheets with hexagonal structures. The method has the advantages that the long-chain alkylamine is used asa structure-directing agent and a solvent, accordingly, growth of copper sulfide nano-crystals can be effectively controlled in reaction procedures, excellent directing effects can be realized for anisotropic growth of the hexagonal copper sulfide nano-sheets, and excellent protective media further can be provided to the morphological regularity of the hexagonal copper sulfide nano-sheets.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Preparation of Metal Nanowire Decorated Carbon Allotropes
In the method of embodiments of the invention, the metal seeded carbon allotropes are reacted in solution forming zero valent metallic nanowires at the seeded sites. A polymeric passivating reagent, which selects for anisotropic growth is also used in the reaction to facilitate nanowire formation. The resulting structure resembles a porcupine, where carbon allotropes have metallic wires of nanometer dimensions that emanate from the seed sites on the carbon allotrope. These sites are populated by nanowires having approximately the same diameter as the starting nanoparticle diameter.
Owner:NASA
Method for preparing glass ceramics
The invention relates to a preparation method for glass ceramics. The preparation steps are as follows: firstly, selecting a raw material micro powder for forming glass ceramics, then adding an agent of fusion with weight percentage of 0-15%, and then adding a network modifier or crystal seed powder with weight percentage of 0-15%, performing even mixing, putting the mixture into a crucible, then performing melting at high temperature in a high-temperature electric furnace, taking out an obtained product and then pouring the obtained product into a mould and performing moulding and cooling, so as to obtain ordinary glass; secondly, cutting the glass into desired shapes and polishing the surface, then putting the polished glass in a high temperature work area of a common high-temperature electric furnace or ladder gradient-temperature electric furnace, placing electrodes onto parallel upper and lower surfaces of the glass or the crucible, applying a direct current electric field to assist directional crystallization treatment during crystallization of glass at medium temperature, wherein the electrostatic potential of the electric field is used as an auxiliary method to control grain nucleation and anisotropic growth; and thirdly, after the crystallization process is finished, performing cooling to form polar glass ceramics with the characteristics of a high devitrification volume fraction and high grain orientation. The method has the advantages of novel principle, reliable process, easy control as well as stable and reliable quality.
Owner:尤世元
Monoclinic phase vanadium dioxide nanowire and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106395901AEvenly distributedHigh crystallinityNanotechnologyVanadium oxidesVanadium dioxideNanowire
The invention discloses a method for preparing a monoclinic phase vanadium dioxide nanowire. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a vanadium source, stearic acid and water, carrying out a hydrothermal reaction on the obtained mixed solution, sequentially centrifuging, washing and drying the obtained product after the hydrothermal reaction is completed, thereby obtaining the monoclinic phase vanadium dioxide nanowire. By utilizing the dual effects of inducing anisotropic growth of crystals through a reducing agent and a surfactant in the stearic acid, the monoclinic phase vanadium dioxide nanowire with thermal induced phase transition property can be prepared in a one-step process, the preparation process is simple, complicated equipment is not needed, the production cost is low, the reaction conditions are easy to control, and large-scale industrial production is easily realized; and moreover, the monoclinic phase vanadium dioxide nanowire is uniform in distribution and high in crystallinity and can be applied to the fields of smart windows, photoelectric switches, camouflage and stealth, infrared detection devices and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Preparation methods of controllable arrayed nanowires and FET (field effect transistor) comprising controllable arrayed nanowires
ActiveCN104485284APrecise control cyclePrecisely control the quantitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesAnisotropic growthNanowire
The invention discloses a preparation method of controllable arrayed nanowires and a preparation method of an FET (field effect transistor) comprising the controllable arrayed nanowires. According to the preparation method of the controllable arrayed nanowires and the preparation method of the FET comprising the controllable arrayed nanowires, materials with anisotropic growth rates of growing materials in different crystal orientations in epitaxial growth are selected as substrates, so that growth of the nanowires is realized; configurations and diameters of the patterned substrates are designed, so that cycles, the number, lengths and diameters of the arrayed nanowires can be controlled accurately, and different FET requirements can be met; growth conditions of group-VI-rich or group-V-rich atoms realize the surface inhibition effect, isotropic migrations of the metal atoms on surfaces are reduced, and growth of the nanowires is facilitated; the FET comprising the controllable arrayed nanowires can be prepared with a traditional semiconductor device preparation technology, the technology is simple, the controllability is high, the cost is low, and mass production can be realized.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Rare earth complex nanobelt and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102617619AUniform shape and sizeGood dispersionPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsAnisotropic growthRare earth ions
The invention discloses a rare earth complex nanobelt and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises enabling rare earth nitrate to react with phthalic acid, performing deprotonation of carboxyl of phthalic acid by adjusting the pH value of a solution, achieving coordinate bond between rare earth ions and phthalic acid, generating massive crystal nucleuses, enabling crystal nucleuses to achieve anisotropic growth in a polar solvent environment, and obtaining the rare earth complex nanobelt with the chemical formula to be RE4(1,2-BDC)6(H<2>O)2-nH<2>O or RE4(1,2-BDC)6(H<2>O)2-nH<2>O: xLn3+. Due to the fact that the pH value is 5.5-6.5, complete deprotonation of carboxyl of phthalic acid under the pH value is achieved, rare earth hydroxide is not formed, the solution is in a hypersaturated state, massive crystal nucleuses are generated rapidly, anisotropic growth is achieved so that a belt-shaped structure is formed, and block-shaped crystal caused by slow growth is avoided. Experimental results show that the width of the rare earth complex nanobelt is 100-150nm, the thickness of the rare earth complex nanobelt is 10-20nm, and the length of the rare earth complex nanobelt is over hundreds of microns.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rhenium disulfide nanosheet used for hydrogen evolution reaction, and preparation method and applications thereof
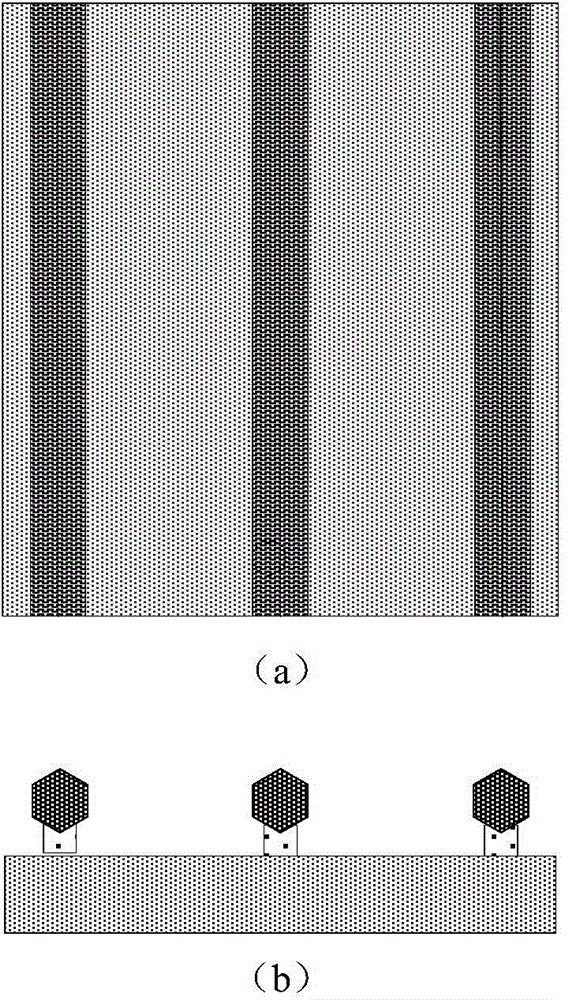
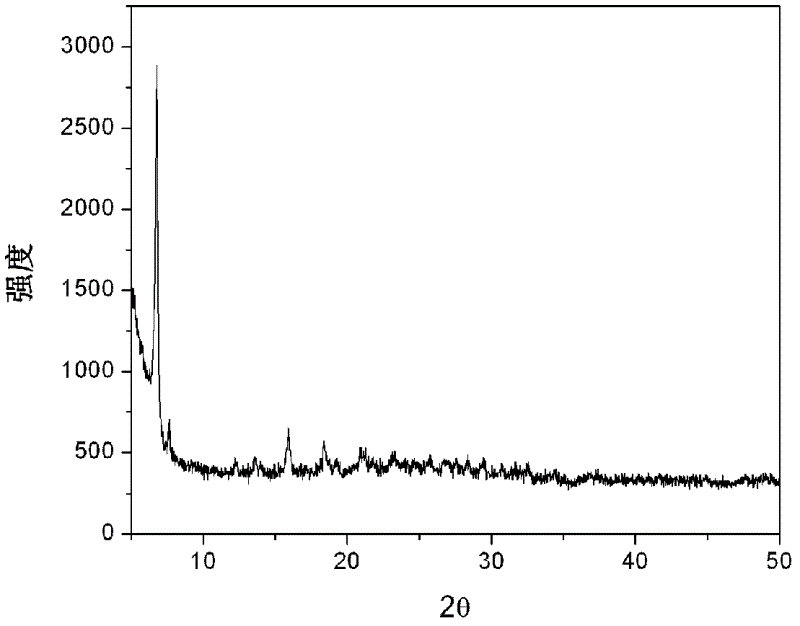
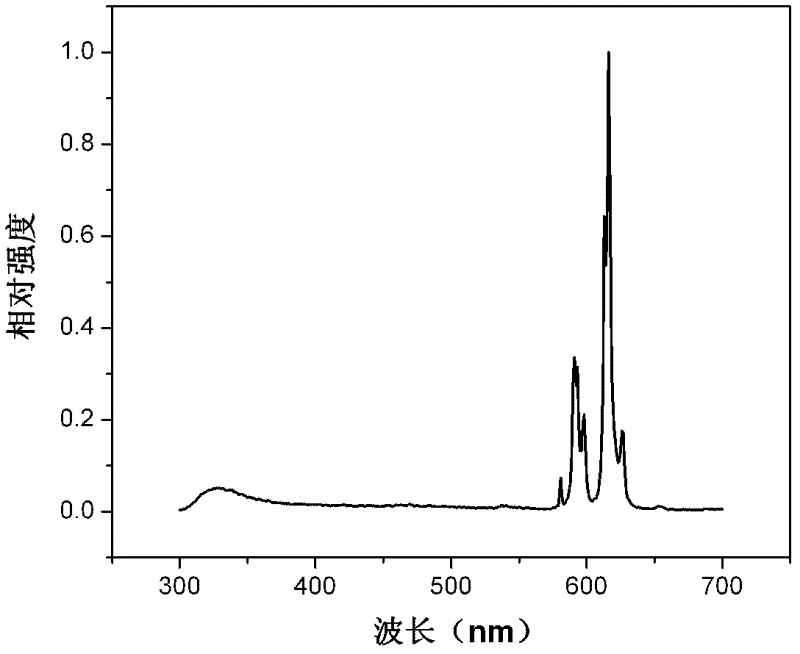
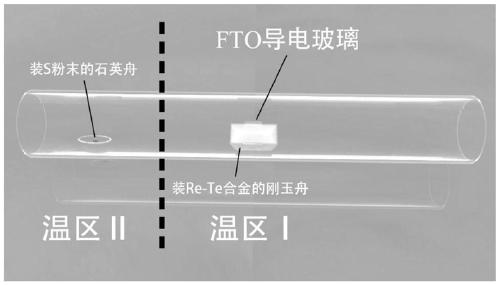
The invention belongs to the technical field of nanometer material, and discloses a rhenium disulfide nanosheet used for hydrogen evolution reaction, and a preparation method and applications thereof.According to the preparation method, Re-Te co-molten alloy and sulfur powder are taken as raw materials, FTO electro-conductive glass is taken as a substrate, chemical vapor deposition is adopted, atinert atmosphere, the Re-Te co-molten alloy is introduced into a quartz tube, is heated to 450 to 500 DEG C in a constant temperature zone I for thermal insulation treatment; the sulfur powder is placed on a carrier gas upstream end of the same quartz tube, and is heated to 120 to 170 DEG C in a constant temperature zone II for thermal insulation treatment, so that Re steam in the Re-Te co-moltenalloy and sulfur steam are reacted, and anisotropic growth on the FTO substrate is realized to obtain a finished product. According to the rhenium disulfide nanosheet, ReS2 nanosheets are verticallyarranged on the FTO substrate, the edges of the ReS2 nanosheets possess a large amount of electrochemical active sites for combination with the FTO substrate, the rhenium disulfide nanosheet can be taken as a hydrogen evolution reaction electrode, and is promising to be used in catalytic hydrogen production field.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation of metal nanowire decorated carbon allotropes
In the method of embodiments of the invention, the metal seeded carbon allotropes are reacted in solution forming zero valent metallic nanowires at the seeded sites. A polymeric passivating reagent, which selects for anisotropic growth is also used in the reaction to facilitate nanowire formation. The resulting structure resembles a porcupine, where carbon allotropes have metallic wires of nanometer dimensions that emanate from the seed sites on the carbon allotrope. These sites are populated by nanowires having approximately the same diameter as the starting nanoparticle diameter.
Owner:NASA
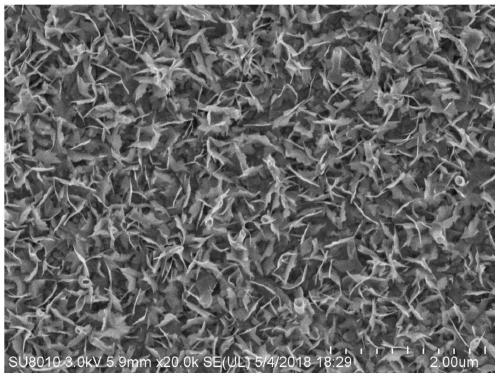
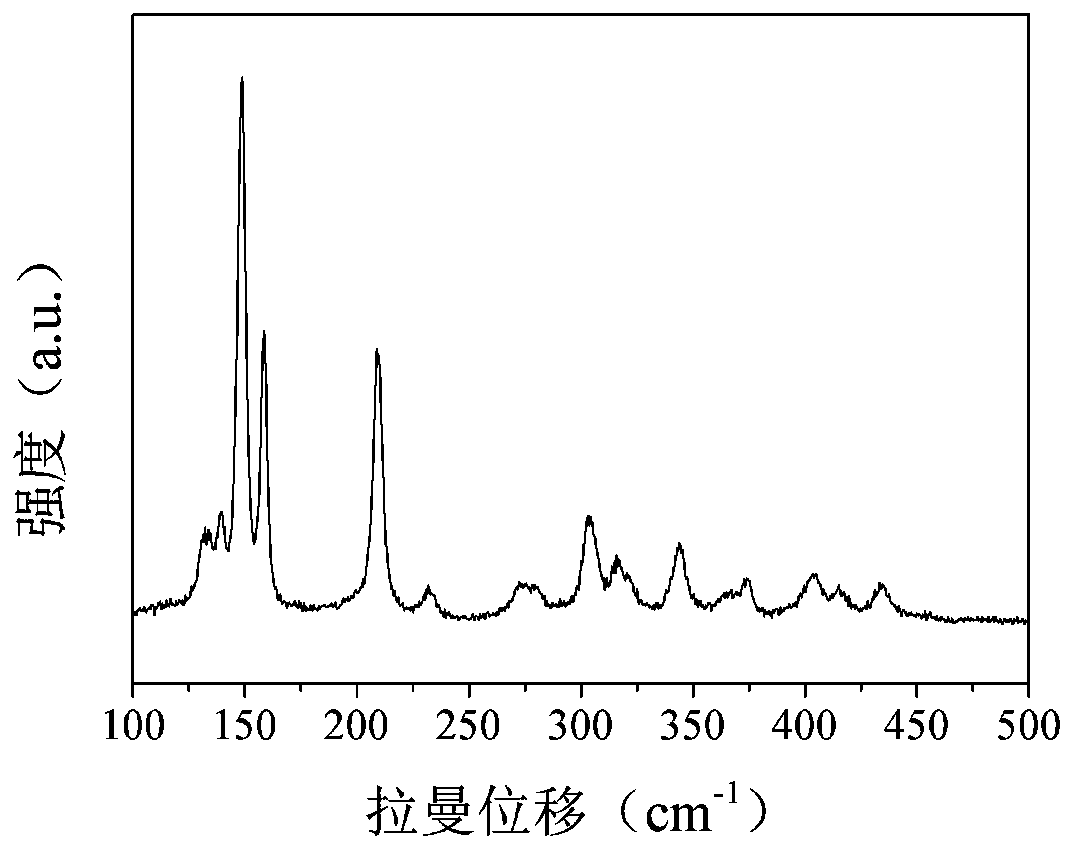
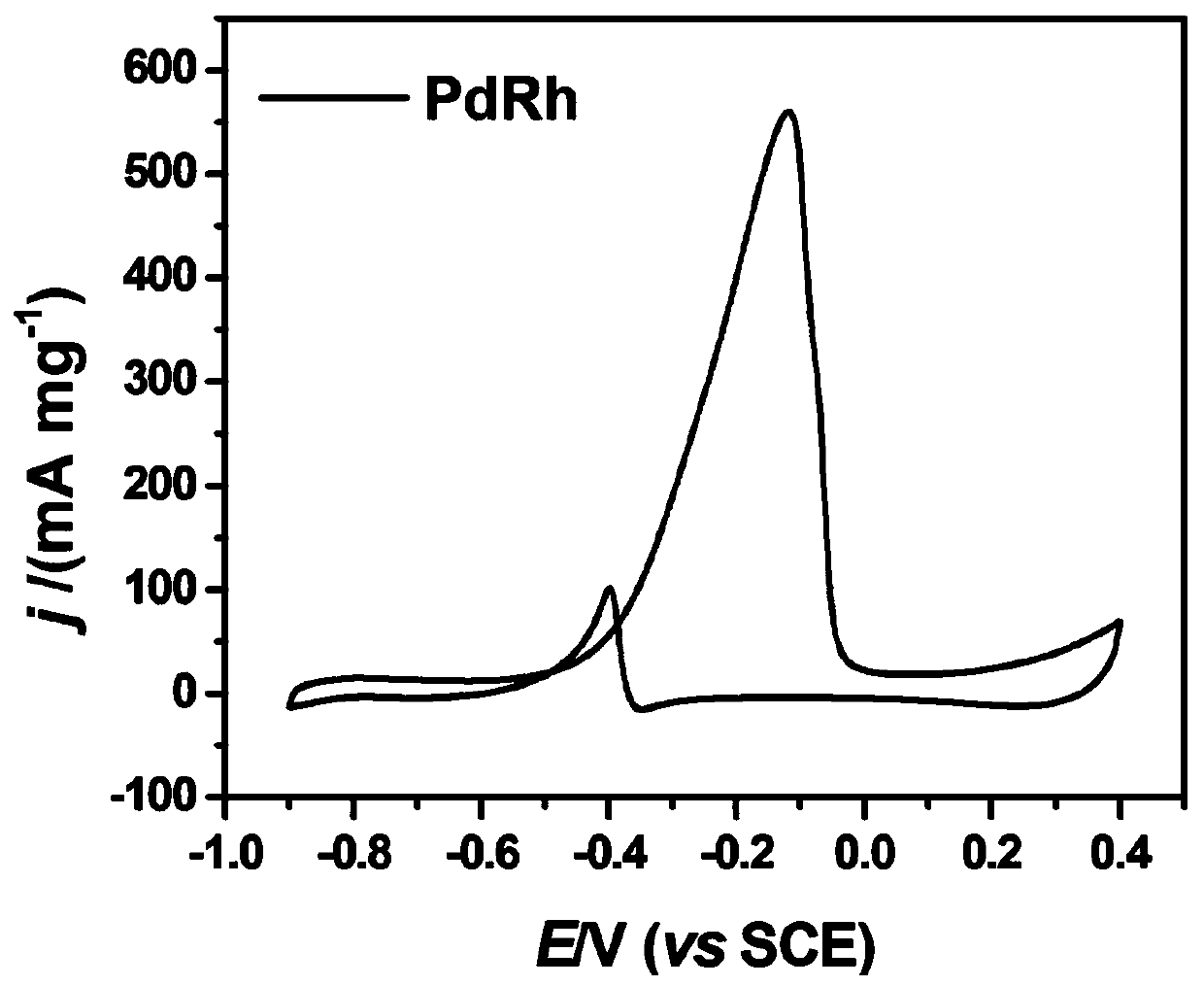
Preparation method of PdRh alloy electrocatalyst for fuel cell and application
ActiveCN110416563AHigh activityImprove catalytic performanceMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesReaction ratePotassium
The invention provides a preparation method of a PdRh alloy electrocatalyst for a fuel cell, and the method comprises the following steps: weighing P123, dissolving the P123 in deionized water, addinga complexing agent PEI, performing stirring, and adding a formaldehyde solution to obtain a mixed solution A; dissolving potassium chloropalladate and rhodium chloride powder in deionized water to obtain an orange-yellow solution B; dropwise adding the orange-yellow solution B into the mixed solution A, and obtaining a precursor solution after the solution is completely changed into a grey blackturbid solution; transferring the precursor liquid into a polytetrafluoroethylene high-pressure reaction kettle at room temperature, and putting the polytetrafluoroethylene high-pressure reaction kettle into a drying oven for reaction; after the reaction is finished, performing the natural cooling to the room temperature, and performing centrifugal washing to obtain the fuel cell PdRh alloy electrocatalyst. According to the method, the PEI is used as a complexing agent and complexed with precursor ions, so the reaction rate is decreased, and the anisotropic growth of the PdRh alloy has a moreopen structure. The prepared alloy catalyst has good methanol oxidation performances, and has a wide development prospect in direct methanol fuel cells.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Method for preparing a light-sensitive emulsion having (100) tabular grains rich in silver chloride
InactiveUS6083678AImprove homogeneityPrevent fadingX-ray/infra-red processesSilver halide emulsionsUltrafiltrationDislocation
A method has been described for preparing a light-sensitive silver halide photographic emulsion comprising performing at least three distinct precipitation steps in an aqueous medium into a reaction vessel, followed by desalting by means of flocculation and washing or by means of ultrafiltration, said emulsion comprising a colloidally stabilizing binder and {100} tabular silver halide grains containing at least 50 mole % of silver chloride, wherein at least 60% by number of all grains is provided by said tabular grains, and wherein said tabular grains exhibit an average aspect ratio of at least 2, an average thickness of at most 0.25 mu m with a variation coefficient of at most 0.25, and an average equivalent circular crystal diameter of 0.3 mu m or more with a variation coefficient of at most 0.20; said three distinct precipitation steps being a nucleation step and two growth steps, said method being further characterized by introducing after ending the said nucleation step one or more crystal dislocation(s) onto nuclei formed in the said nucleation step in order to provide anisotropic growth of the said nuclei into {100} tabular grains, wherein introducing said crystal dislocation(s) is performed within a time taking no longer than the time required to perform a first physical ripening step after the nucleation step in order to get a number of dislocation lines of less than 5, in one and the same crystallographic plane, and wherein said physical ripening step between introducing said dislocation(s) and growing the nuclei having said dislocation(s) in a first growth step proceeds within a time interval from 2 to 10 minutes, and more preferably from 5 to 10 minutes.
Owner:AGFA GEVAERT AG
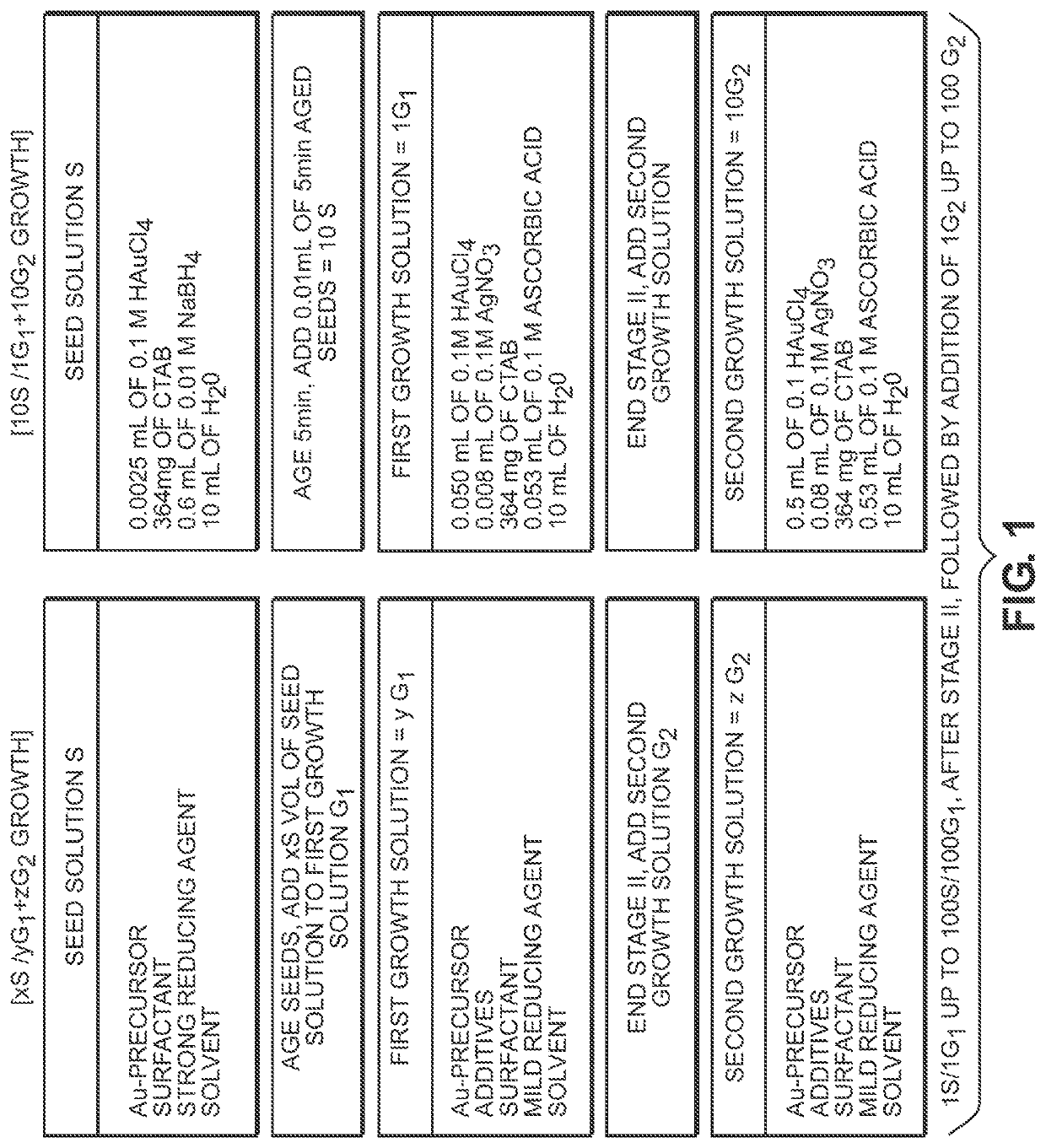
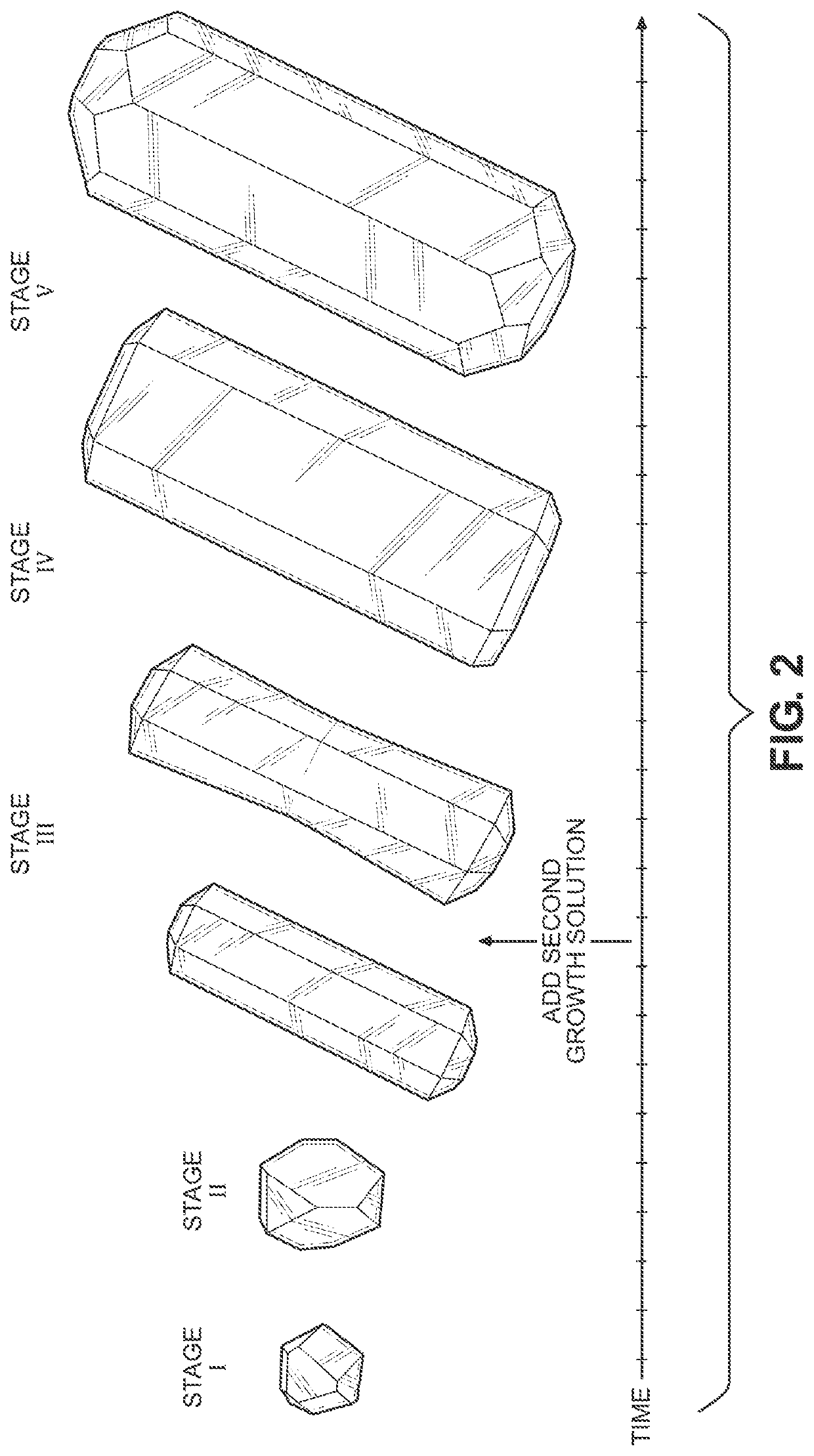
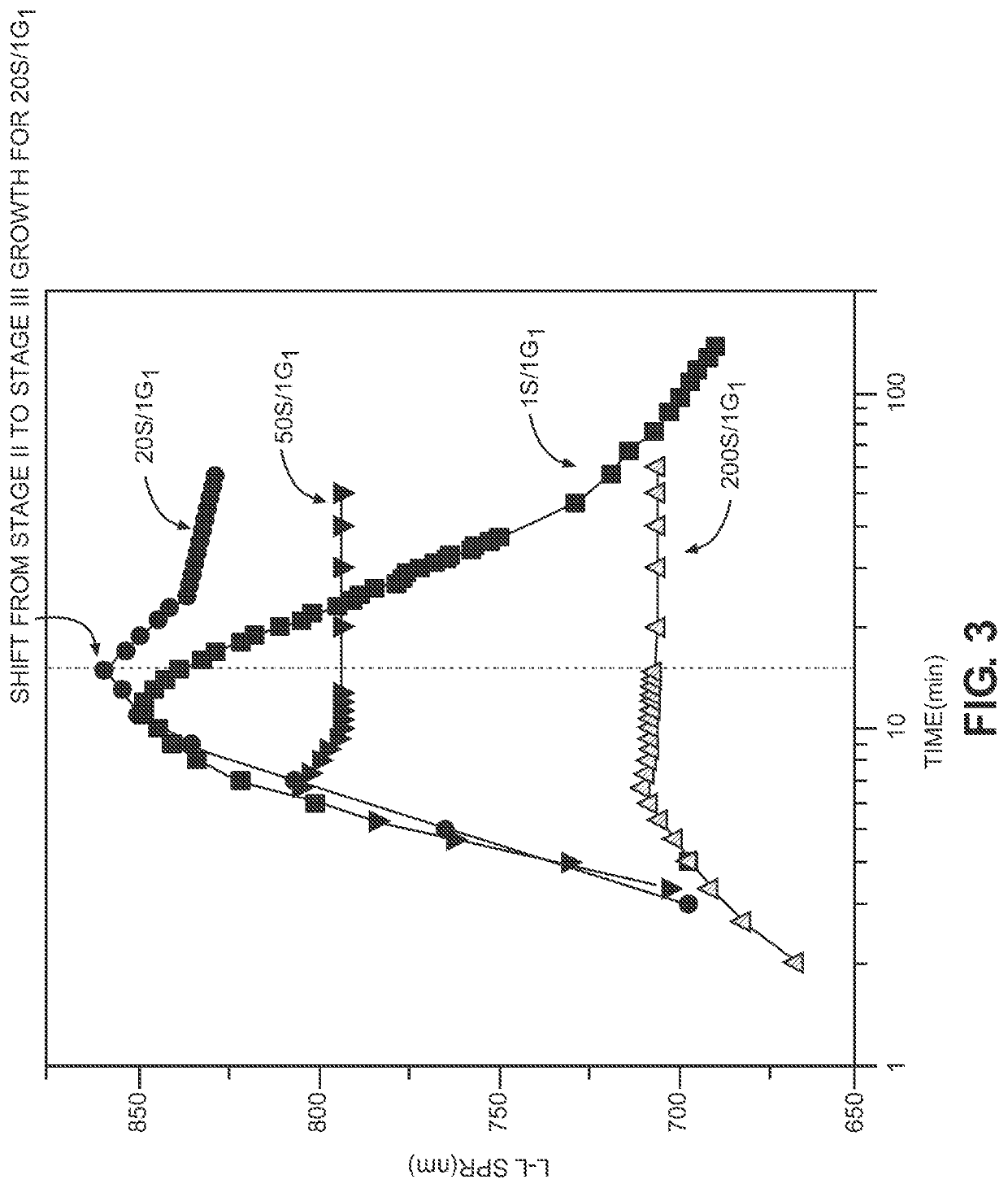
Concentrated synthesis of monodispersed gold nanorods
A method for synthesizing nanostructures includes introducing a solution of seed crystals into an initial growth solution to form a nanostructure synthesis mixture. The initial growth solution includes a precursor material and a reducing agent in a surfactant solution. Growth of nanostructures in the nanostructure synthesis mixture is monitored during a period of anisotropic growth of the nanostructures to determine a shift from stage II growth of the nanostructures to stage III growth of the nanostructures. The shift from stage II growth to stage III growth is identified, and after identifying the shift, a second growth solution is added to the nanostructure synthesis mixture coincident in time with the shift. The second growth solution includes the precursor material and the reducing agent in the surfactant solution.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Universal two-dimensional rare earth MOFs material, solvent-free chemical stripping method and application thereof
ActiveCN112266485AThe synthesis method is simpleHigh yieldMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansAnisotropic growthPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a universal two-dimensional rare earth MOFs material, a solvent-free chemical stripping method and application thereof. According to the invention, different quaternary ammonium salts are used as a morphology regulator and an intercalation stripping agent, and under a solvent-free state, a mechanical grinding method and heating treatment in a reaction kettle are carried outin sequence so as to achieve effective regulation and control of the rare earth MOFs material from a 3D block shape to a 2D two-dimensional sheet shape are realized; in the process, the quaternary ammonium salt is attached to the surface of the rare earth MOFs material, anisotropic growth of the rare earth MOFs material is caused, and then the ultrathin MOF nanosheet is formed; and the synthesismethod of the rare earth MOFs material provided by the invention is simple and convenient, high in yield and relatively mild in condition, meets the requirements of the 2D rare earth MOFs material onmaterial performance in fluorescence and sensing application, and further has a large-scale production prospect.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for synthesizing monocrystal bismuth nano-wire with intense magnetic field abduction
InactiveCN101314183BHigh crystallinityIncrease productionPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsNanowireSingle crystal
The invention discloses a method for thermally synthesizing a single-crystal bismuth nanowire by solvent in a magnetic field. By utilizing the characteristic of anisotropic growth induced by the magnetic field, the single-crystal bismuth nanowire is produced through a polyhydroxy reduction reaction between sodium bismuthate and glycol. The whole reaction process is performed in the magnetic field, and the Bi nanowire produced by the synthesis has a diameter of 40 nanometers and a length of between 10 and 50 microns. The method is simple, convenient and safe, and has high repeatability, high output, and good product crystallinity; and the bismuth nanowire produced by the synthesis can be widely used in the fields such as physics, chemistry, material, micro-electronics and so on. The methodalso provides a novel idea and a novel means for materials which are disadvantageous to grow into nanowires.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
A kind of high density ceramic matrix composite material and its preparation method and application
The invention discloses a high density ceramic matrix composite material, a preparation method and application thereof. A zirconium diboride-zirconium disilicide-tungsten carbide ceramic matrix composite material is prepared from zirconium diboride powder, zirconium disilicide and tungsten carbide with purity of greater than 98% by a two-step hot pressing sintering process. Specifically, the mass fraction of zirconium diboride powder is 75-90%, and the adding of high content zirconium diboride into the ceramic matrix composite material is in favor of improving the physical and chemical performance of the composite material. The mass fraction of zirconium disilicide is 10-15%, and the adding of the zirconium disilicide with the mass fraction into the ceramic matrix composite material can significantly lower the sintering temperature of the material. The mass fraction of tungsten carbide is 0-10%, the added tungsten carbide can promote the anisotropic growth of crystal grains in the material. The grain size of the three original powder is 1-5 microns, and the grain size in the range is conducive to uniform mixing of each phase. The material provided by the invention can be used as a surface heat insulation layer of hypersonic flight vehicles, and has the characteristics of high density and high mechanical properties.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
A selenide nanorod, its preparation method and its prepared photodetector
ActiveCN110429148BLow viscosityImprove liquidityMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureMolten stateSpectral response
The invention discloses a selenide nanorod, a preparation method thereof and a photodetector prepared thereof, belonging to the field of preparation of nanometer semiconductors. Including the following steps: KOH, SeO 2 Powder, AgNO 3 and In(NO 3 ) 3 Dissolving in a non-coordinating solvent and a small amount of ethylenediamine, under the protection of an inert gas, at a temperature of 200-240° C., stirring vigorously, and keeping warm for 12-24 hours, to prepare selenide nanorods. The hydroxide ions of the alkali in the molten state are separated into and, and then under the dilution of the non-coordinating solvent, the viscosity is reduced and the fluidity is improved. In such an alkaline environment of the molten alkali, In 2 Se 3 Form the crystal nuclei of the wurtzite structure, and finally through the competitive adsorption of ethylenediamine molecules on the crystal faces in the reaction mixture, induce the growth direction, and promote the growth direction of In 2 Se 3 The nuclei continue to adsorb and grow anisotropically and in small amounts. The problem of low spectral responsivity and external quantum efficiency of the detector due to low intrinsic conductivity in actual use is solved.
Owner:南京倍格电子科技有限公司
A universal two-dimensional rare earth MOFs material and its solvent-free chemical exfoliation method and application
ActiveCN112266485BThe synthesis method is simpleHigh yieldMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansAnisotropic growthPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a universal two-dimensional rare earth MOFs material and its solvent-free chemical stripping method and application. By using different quaternary ammonium salts as morphology modifiers and intercalation stripping agents, in a solvent-free state, Through the mechanical grinding method and the heat treatment in the reactor, the effective regulation of the morphology of the rare earth MOFs material from 3D bulk to 2D two-dimensional sheet is realized. During this process, the quaternary ammonium salt is attached to the surface of the rare earth MOFs material, leading to the anisotropic growth of the rare earth MOFs material, and then forming ultrathin MOF nanosheets. The synthesis method of the rare earth MOFs material provided by the present invention is not only simple, high yield, and relatively mild conditions, but also meets the material performance requirements of 2D rare earth MOFs materials in fluorescence and sensing applications, and has the prospect of large-scale production.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
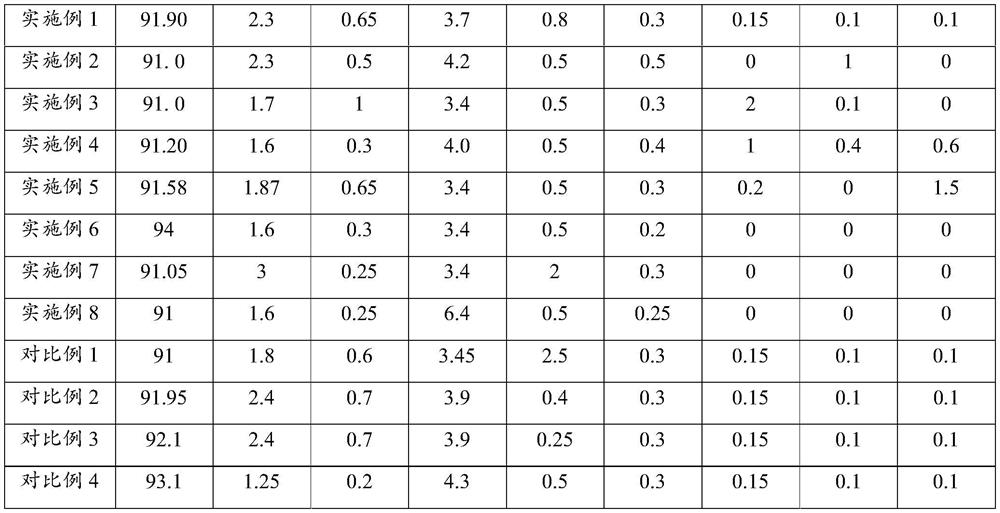
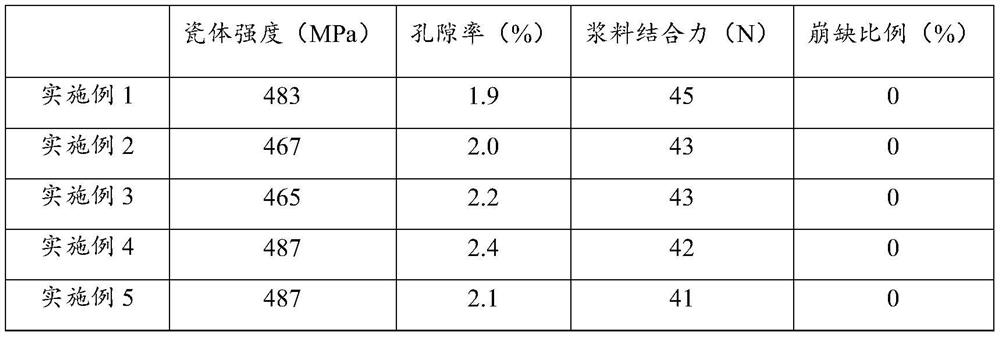
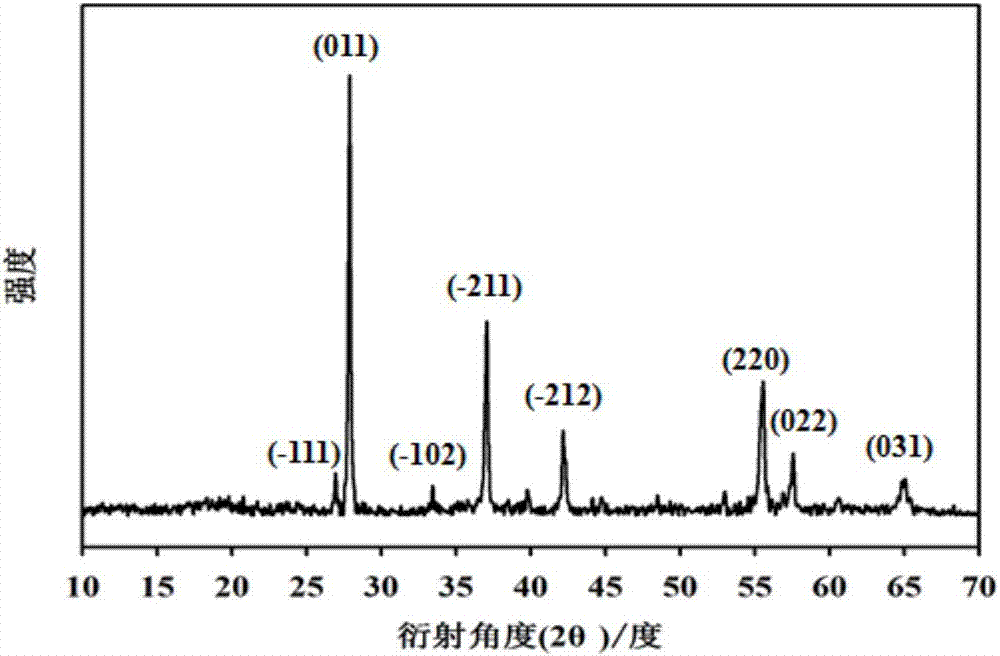
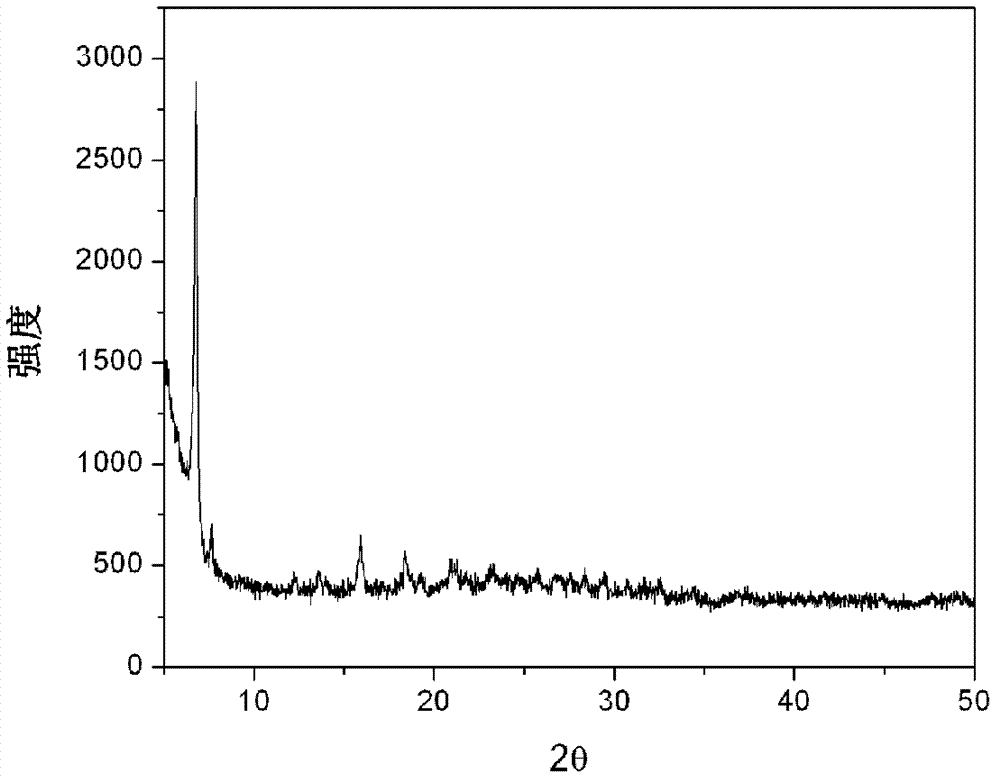
A kind of ceramic packaging base material composition and its application
ActiveCN110922172BPromote anisotropyChanging and adding extensions to the pathAnisotropic growthCrazing
The invention relates to a ceramic packaging base material composition, which comprises the following components in mass percentage: 1.6%-3.0% of silicon dioxide, 3.4%-6.4% of dichromium trioxide, and 0.25% of calcium oxide ~1%, molybdenum 0.2%~0.5%, manganese dioxide 0.5%~2%, and the balance is alumina. The present invention is by adding appropriate MnO in the ceramic raw material 2 , promote the anisotropic growth of crystal grains, form long rod-shaped crystals, cause the cracks in the ceramic package base to shift, change and increase the path of crack propagation, thereby passivating the propagation of cracks; at the same time, reduce the liquid in the sintering process Compared with the ratio, the reduction of amorphous phase aggregates in the ceramic body to form stress failure points. Therefore, the ceramic packaging base of the present invention does not have problems such as chipping when the grinding wheel is cut into pieces.
Owner:CHAOZHOU THREE CIRCLE GRP
A kind of monoclinic vanadium dioxide nanowire and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN106395901BEvenly distributedHigh crystallinityNanotechnologyVanadium oxidesVanadium dioxideNanowire
The invention discloses a method for preparing a monoclinic phase vanadium dioxide nanowire. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a vanadium source, stearic acid and water, carrying out a hydrothermal reaction on the obtained mixed solution, sequentially centrifuging, washing and drying the obtained product after the hydrothermal reaction is completed, thereby obtaining the monoclinic phase vanadium dioxide nanowire. By utilizing the dual effects of inducing anisotropic growth of crystals through a reducing agent and a surfactant in the stearic acid, the monoclinic phase vanadium dioxide nanowire with thermal induced phase transition property can be prepared in a one-step process, the preparation process is simple, complicated equipment is not needed, the production cost is low, the reaction conditions are easy to control, and large-scale industrial production is easily realized; and moreover, the monoclinic phase vanadium dioxide nanowire is uniform in distribution and high in crystallinity and can be applied to the fields of smart windows, photoelectric switches, camouflage and stealth, infrared detection devices and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Rare earth complex nanobelt and its preparation method
InactiveCN102617619BUniform shape and sizeGood dispersionPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsProtonationAnisotropic growth
The invention discloses a rare earth complex nanobelt and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises enabling rare earth nitrate to react with phthalic acid, performing deprotonation of carboxyl of phthalic acid by adjusting the pH value of a solution, achieving coordinate bond between rare earth ions and phthalic acid, generating massive crystal nucleuses, enabling crystal nucleuses to achieve anisotropic growth in a polar solvent environment, and obtaining the rare earth complex nanobelt with the chemical formula to be RE4(1,2-BDC)6(H<2>O)2-nH<2>O or RE4(1,2-BDC)6(H<2>O)2-nH<2>O: xLn3+. Due to the fact that the pH value is 5.5-6.5, complete deprotonation of carboxyl of phthalic acid under the pH value is achieved, rare earth hydroxide is not formed, the solution is in a hypersaturated state, massive crystal nucleuses are generated rapidly, anisotropic growth is achieved so that a belt-shaped structure is formed, and block-shaped crystal caused by slow growth is avoided. Experimental results show that the width of the rare earth complex nanobelt is 100-150nm, the thickness of the rare earth complex nanobelt is 10-20nm, and the length of the rare earth complex nanobelt is over hundreds of microns.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
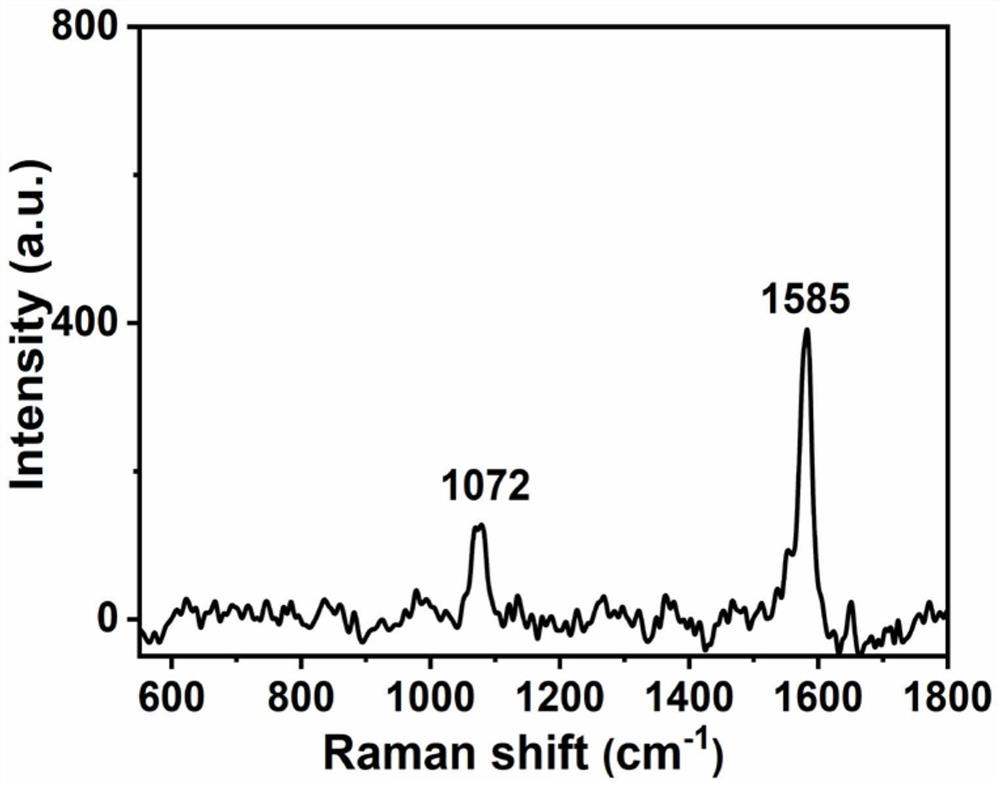
Preparation method and application of red phosphorus/gold nanoflower composite material
PendingCN114018894APromote enrichmentTightly boundMaterial nanotechnologyRaman scatteringBenzoic acidMaterials science
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a red phosphorus / gold nanoflower composite material. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) preparing nano red phosphorus by adopting a hydrothermal method; (2) preparing red phosphorus / gold nanoparticles by adopting an in-situ deposition method; and (3) preparing the red phosphorus / gold nano-flower composite material by adopting an anisotropic growth strategy: sequentially adding 1ml of the red phosphorus / gold nano-particle aqueous solution prepared in the step (2), 5ml of a 4-mercaptobenzoic acid solution and 12.5 ml of an ascorbic acid solution into 2.5 ml of a chloroauric acid solution, slightly shaking, enabling the mixture to react for 30 minutes, then washing with deionized water and ethanol for several times, and removing the modified 4-mercaptobenzoic acid molecules by photocatalysis to obtain the red phosphorus / gold nanoflower composite material. The red phosphorus / gold nanoflower composite material can be used for preparing a sandwich immune structure for detecting tumor markers, and has the advantage that the detection sensitivity of the tumor markers is improved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
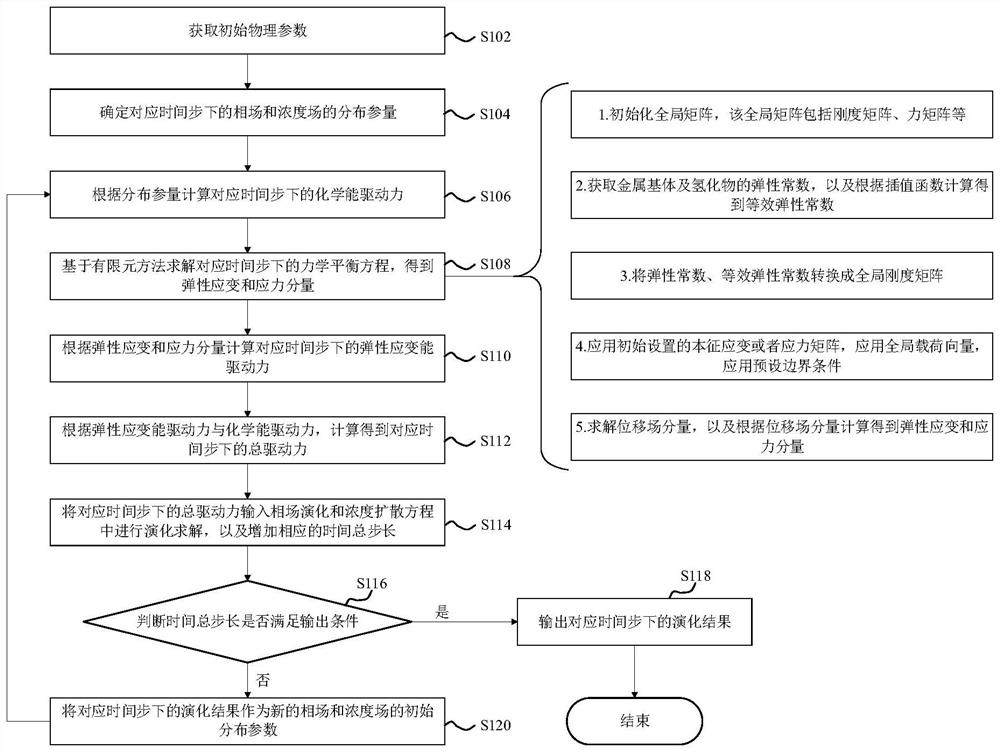
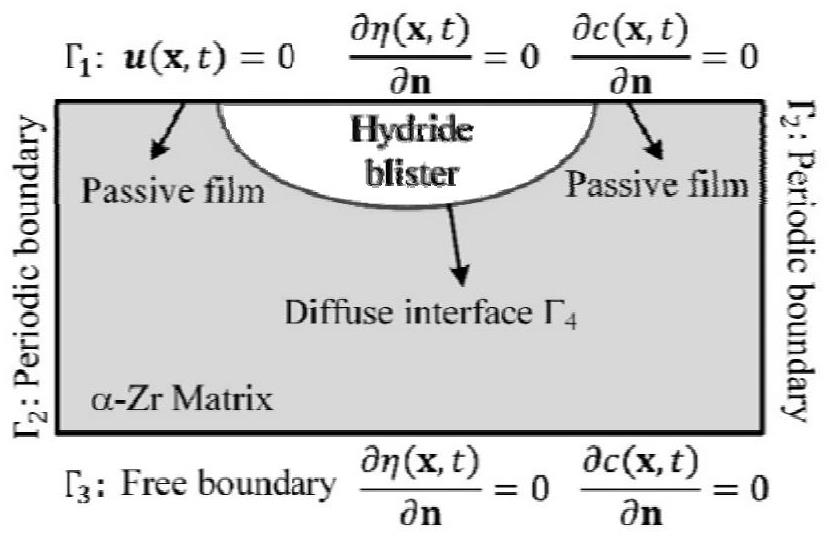
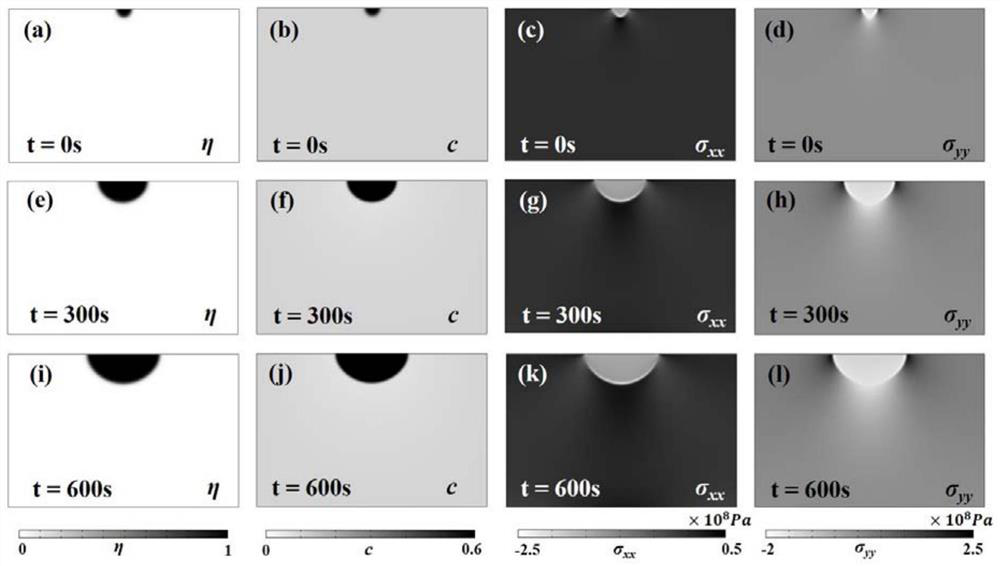
Method and device for simulating metal surface hydrogenation spot corrosion morphology evolution
ActiveCN114330053AShow growth featuresAvoid the problem of periodicization of non-periodic physical parametersDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsMetallic materialsMechanical equilibrium
The invention discloses a method and device for simulating metal surface hydrogenation spot corrosion morphology evolution, and the method comprises the steps: building a hydrogenation spot corrosion phase field model coupled with anisotropic elastic energy through employing an anisotropic elastic constant, and constructing an equivalent elastic constant through employing an interpolation function method to represent the non-uniformity of a system; the method is suitable for anisotropic metal materials, can simulate the morphology difference caused by elastic anisotropic growth of the metal materials, and better shows the growth morphology characteristics of hydrogenation point corrosion; in the pitting corrosion phase field model, a finite element method is adopted to solve a mechanical equilibrium equation of a non-periodic boundary condition, and the problem of non-periodic physical parameter periodicity caused by Fourier transform solving of a periodic elastic field can be avoided.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS & COMPUTATIONAL MATHEMATICS +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com