Textured boride base ultra-high temperature ceramic material and its preparation method
An ultra-high temperature ceramic and boride technology, which is applied in the field of textured boride-based ultra-high temperature ceramic materials and its preparation, can solve the problem of low mechanical properties of boride-based ceramics, and achieve improved performance, obvious thermal conductivity, high The effect of the degree of texture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
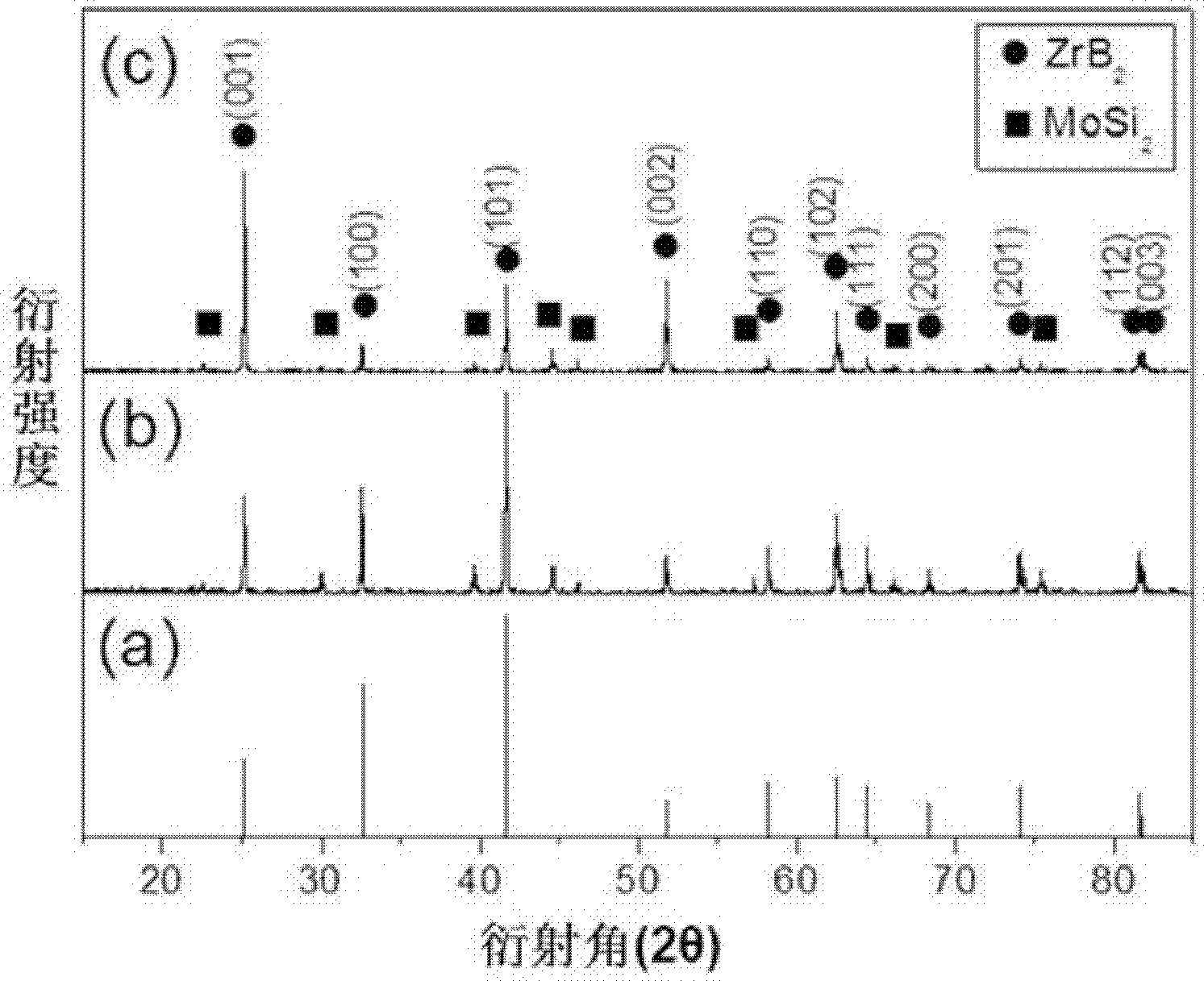
[0037] For the preparation of ZrB 2 -5mol%MoSi 2 Composite ceramics, weighing 45.612 grams of Zr powder, 10.811 grams of B powder, 2.399 grams of Mo powder and 1.404 grams of Si powder.
[0038] With acetone as solvent, at a speed of 560 rpm, with ZrO 2 The balls and planets were milled for 8 hours, and the resulting slurry was dried by rotary evaporation to obtain a uniformly mixed powder.
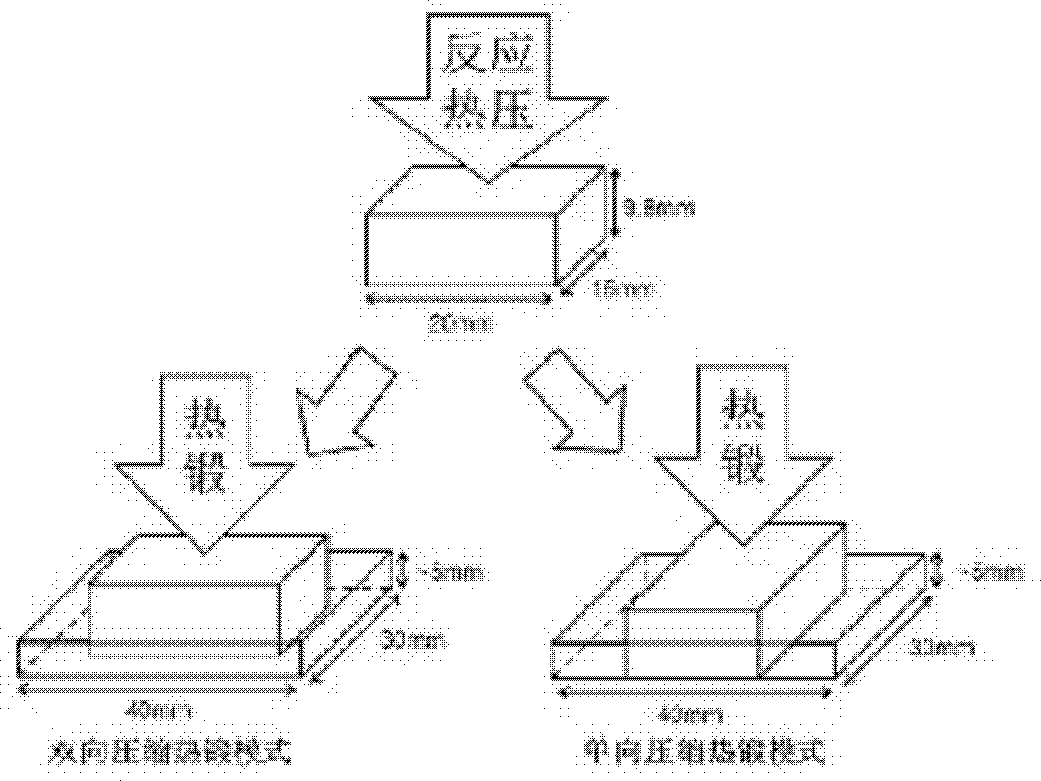
[0039] Put the uniformly mixed powder in a graphite mold (37mm×30mm) coated with BN on the inner wall surface, and carry out reaction hot pressing sintering in vacuum: the heating rate during sintering is 10°C / min, and the temperature is raised to 1550°C and kept for 30 minutes , and then apply a pressure of 20 MPa, while raising the temperature to 1800° C. at a heating rate of 10° C. / min and keep it warm for 1 hour.
[0040] Cut the sample prepared by reactive hot pressing sintering (40mm×30mm×9.8mm before cutting, 20mm×15mm×9.8mm after cutting), and then place it in a graphite mold (...
Embodiment 2
[0043] For the preparation of ZrB 2 -19mol% MoSi 2 Composite ceramics, weighing 45.612 grams of Zr powder, 10.811 grams of B powder, 9.114 grams of Mo powder and 5.336 grams of Si powder.
[0044] The powder was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, sintered by reactive hot pressing and hot forged.
[0045] The relative density of the sample after hot forging is 98.9%. The Lotgering orientation factors f(00l) of samples before and after hot forging were 0.12 (before hot forging), 0.59 (bidirectional compression hot forging), and 0.64 (unidirectional compression hot forging). Bending strength of the sample before hot forging: vertical to the hot forging direction, 595MPa; parallel to the hot forging direction, 531MPa. The bending strength of the sample after bidirectional compression hot forging: vertical hot forging direction, 845MPa; parallel hot forging direction, 691MPa. The bending strength of the sample after unidirectional compression hot forging: perpendicula...
Embodiment 3
[0047] For the preparation of ZrB 2 -50mol% MoSi 2 Composite ceramics, weighing 45.612 grams of Zr powder, 10.811 grams of B powder, 23.985 grams of Mo powder and 14.043 grams of Si powder.
[0048] The powder was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, sintered by reactive hot pressing and hot forged.
[0049] The relative density of the sample after hot forging is 99.5%. The Lotgering orientation factors f(00l) of samples before and after hot forging were 0.16 (before hot forging), 0.70 (bidirectional compression hot forging), and 0.73 (unidirectional compression hot forging). Bending strength of the sample before hot forging: vertical to the hot forging direction, 520MPa; parallel to the hot forging direction, 467MPa. The bending strength of the sample after bidirectional compression hot forging: vertical hot forging direction, 789MPa; parallel hot forging direction, 659MPa. The bending strength of the sample after unidirectional compression hot forging: perpendicu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com