Method for connecting skutterudite thermoelectric material and electrode by using high-thermal-stability alloy composite intermediate layer
A technology of composite intermediate layer and thermoelectric material, which is used in the manufacture/processing of thermoelectric devices, thermoelectric device parts, welding equipment, etc. The effect of high thermal stability and simple process control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
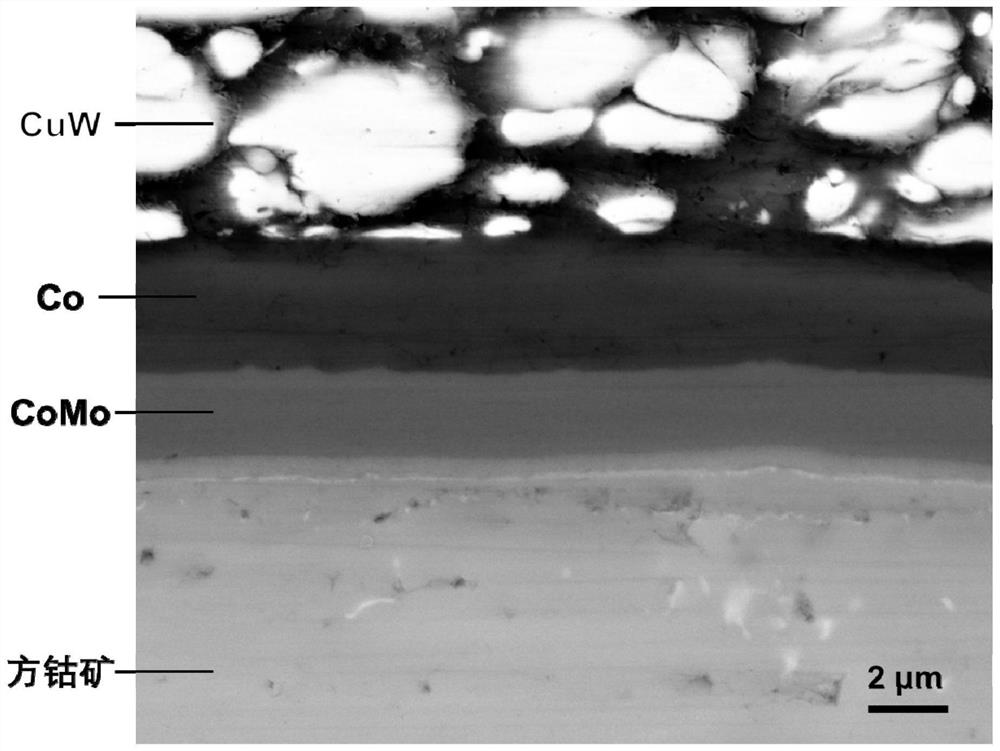
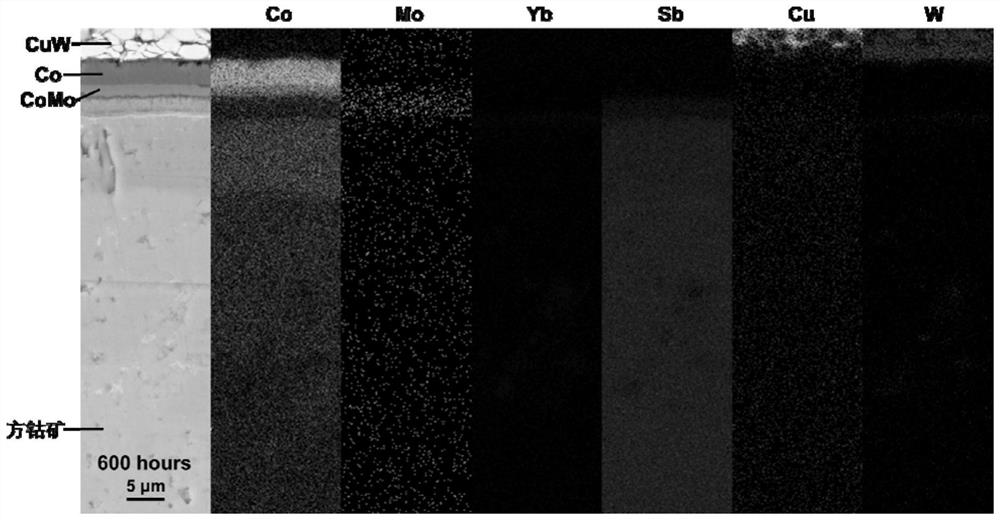
[0019] Specific implementation mode 1: In this implementation mode, the method of connecting skutterudite thermoelectric materials and electrodes with a high thermal stability alloy composite intermediate layer is carried out according to the following steps:
[0020] 1. Clean the surface to be welded of the cobalt ore thermoelectric material and the electrode;
[0021] 2. Use electroplating or physical vapor deposition to prepare an intermediate connecting layer on the surface of the electrode, and prepare a diffusion barrier layer on the surface of the intermediate connecting layer; or prepare an intermediate connecting layer on the surface of the electrode, and prepare a diffusion barrier layer on the surface of the skutterudite thermoelectric material or prepare a diffusion barrier layer on the surface of the skutterudite thermoelectric material, and prepare an intermediate connection layer on the surface of the diffusion barrier layer; then stack the obtained electrode and...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0029] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that the cleaning process described in Step 1 is as follows: first, rinse with absolute ethanol, then place in acetone for ultrasonic cleaning for 5-30 minutes, and finally air-dry.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0030] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the electrode described in step 1 is a metal electrode or an alloy electrode;
[0031] The metal electrode material is Cu, Ni, Fe, Co or Cr;
[0032]The material of the alloy electrode is Cu-based alloy, Ni-based alloy, Fe-based alloy, Co-based alloy or Cr-based alloy;
[0033] The Cu-based alloy is CuW or CuMo; the Ni-based alloy is NiW, NiMo or NiCr; the Fe-based alloy is FeW, FeMo, FeCr or FeCoNi; the Co-based alloy is CoW, CoMo, CoCr, CoNi or CoFe; the Cr-based alloy is CrW, CrMo, CrCoNi or CrFeNi.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Contact resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com