Preparation of phosphate radical-responsive carbon quantum dots and application of phosphate radical-responsive carbon quantum dots in fingerprint fluorescence recognition
A technology of carbon quantum dots and fluorescence recognition, which is applied in the direction of fluorescence/phosphorescence, nano-carbon, luminescent materials, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable large-scale production and application, and achieve the effect of low cost, simple preparation process and good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] 1. Add 50mL of ultrapure water to a 100mL beaker, then add 0.15mmol of 1,2,4-glucinol, and stir for 3 minutes with magnetic force to obtain a 1,2,4-glucinol solution.
[0042] 2. Put the 1,2,4-glucinol solution obtained in step 1 into a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined autoclave, react at 170°C for 6 hours, centrifuge at 8000r / min after the reaction is completed, and take The supernatant was used for later use.
[0043] 3. The supernatant obtained in step 2 was subjected to rotary evaporation and vacuum freeze-drying to obtain a black solid powder.
[0044] 4. Dissolve 0.3 mg of the solid powder obtained in step 3 in 1 mL of ultrapure water to obtain a mother liquor for use.
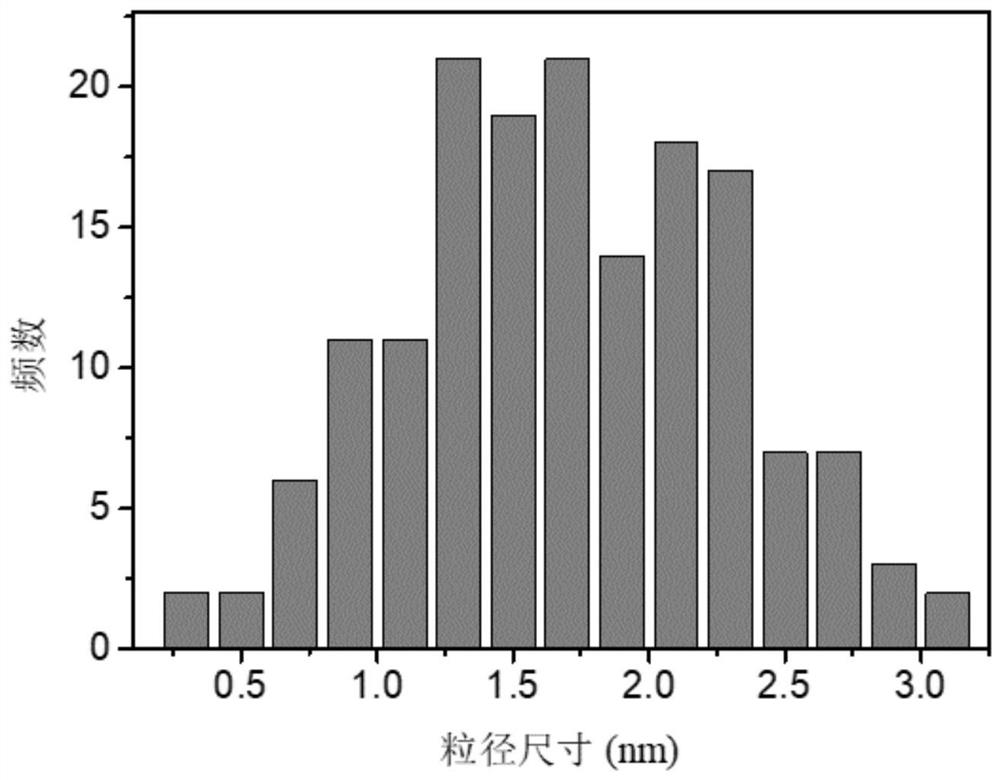
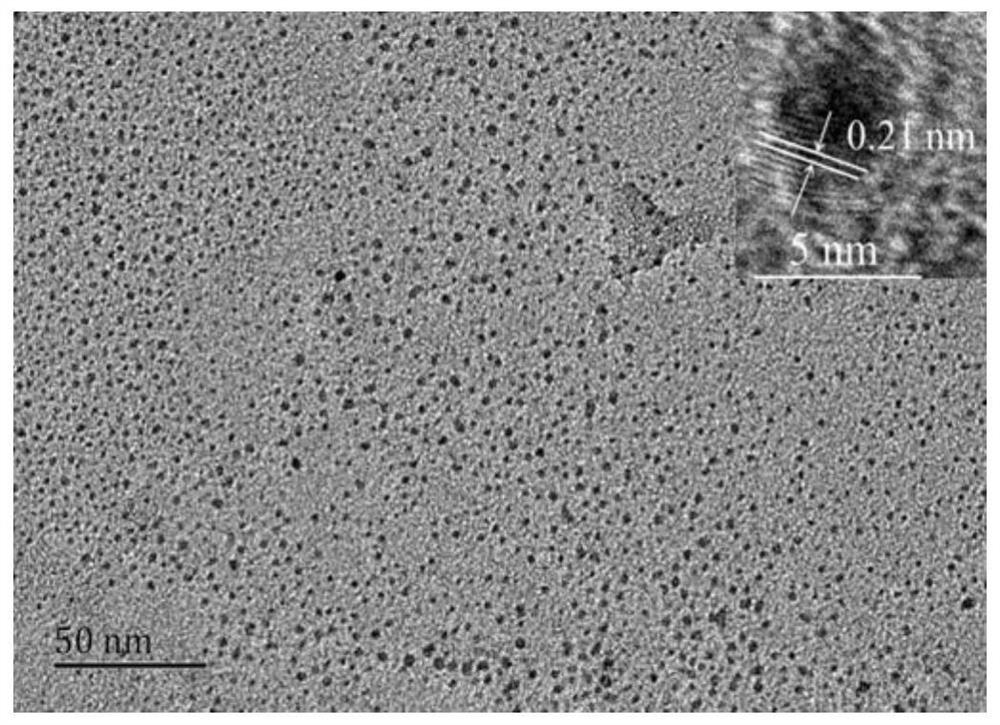
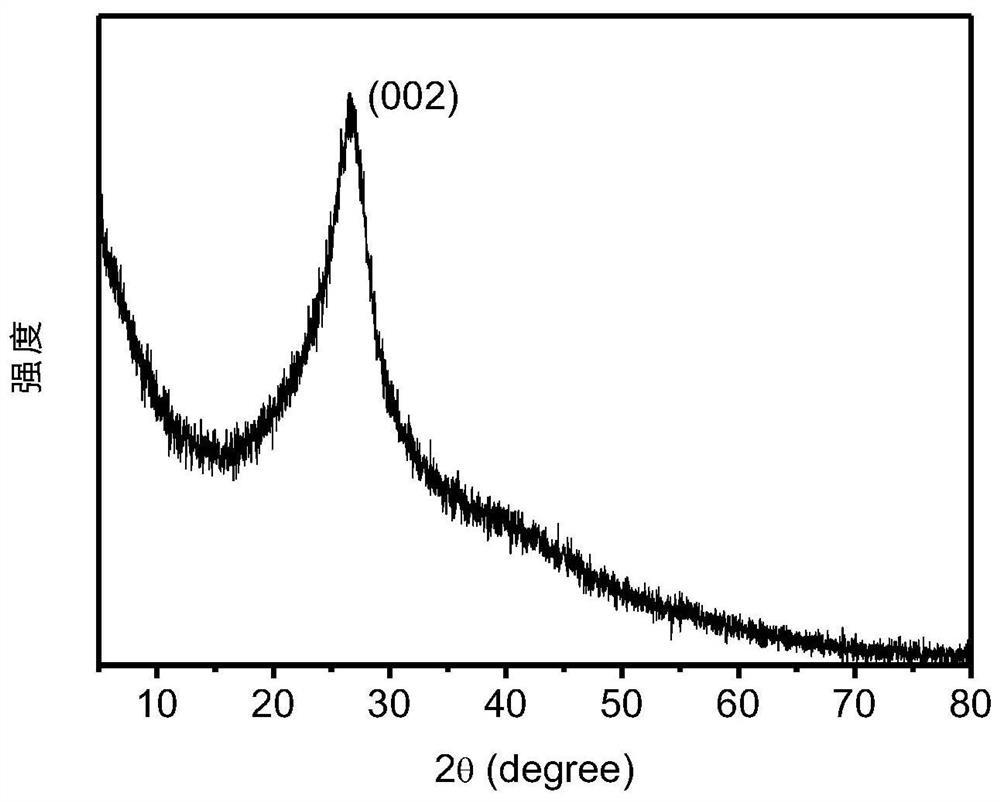
[0045] 5. Observing the mother liquor under a field emission transmission electron microscope, the size of the carbon quantum dots is 0.31 to 3.19 nm, and the average particle diameter is about 1.7 ± 0.38 nm (see attached figure 1 ). The obtained solid powder is tested by high-resolution transmiss...
Embodiment 2
[0049] 1. Add 50mL of ultrapure water to a 100mL beaker, then add 0.074mmol of 1,2,4-glucinol, and stir for 3 minutes with magnetic force to obtain a 1,2,4-glucinol solution.
[0050] 2. Put the 1,2,4-glucinol solution obtained in step 1 into a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined autoclave, react at 150°C for 4 hours, centrifuge at 8000r / min after the reaction is completed, and take The supernatant was used for later use.
[0051] 3. The supernatant obtained in step 2 was subjected to rotary evaporation and vacuum freeze-drying to obtain a black solid powder.
[0052] 4. Dissolve 0.3 mg of the solid powder obtained in step 3 in 1 mL of ultrapure water to obtain a mother liquor for use.
Embodiment 3
[0054] 1. Add 50mL of ultrapure water to a 100mL beaker, then add 0.3mmol of 1,2,4-glucinol, and stir for 3 minutes with magnetic force to obtain a 1,2,4-glucinol solution.
[0055] 2. Put the 1,2,4-glucinol solution obtained in step 1 into a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined autoclave, react at 180°C for 8 hours, centrifuge at 12000r / min after the reaction is completed, and take The supernatant was used for later use.
[0056] 3. The supernatant obtained in step 2 was subjected to rotary evaporation and vacuum freeze-drying to obtain a black solid powder.
[0057] 4. Dissolve 0.3 mg of the solid powder obtained in step 3 in 1 mL of ultrapure water to obtain a mother liquor for use.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| lattice spacing | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com