Probiotic agent PAPCH for preventing and treating helicobacter pylori infection and preparation method of probiotic agent PAPCH
A technology of Helicobacter pylori and probiotics, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, methods based on microorganisms, medical preparations with non-active ingredients, etc., can solve the problem of fewer probiotics and their bacterial agents, and improve human immunity High strength, high strain survival rate, and the effect of improving the micro-ecological environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1 PAPCH performance detection
[0050] 1. PAPCH acid resistance test
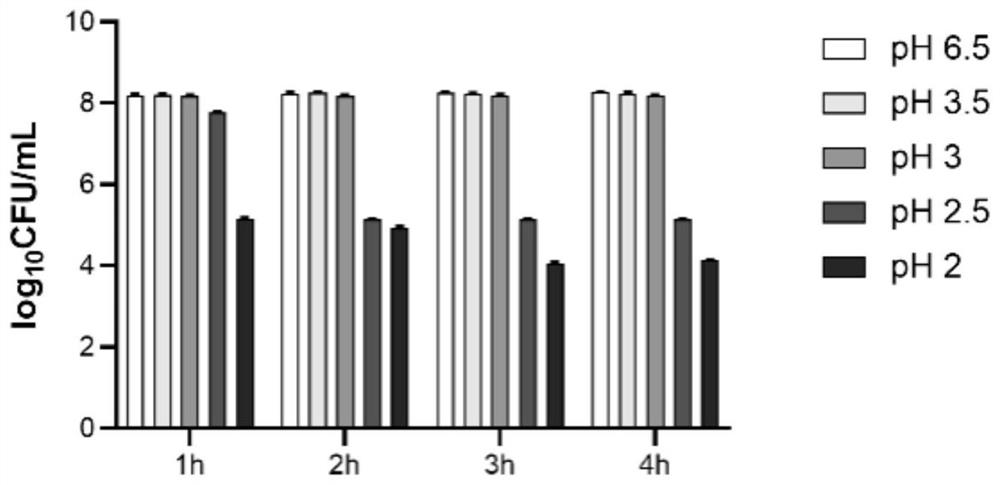
[0051] PAPCH acid resistant such as figure 1 as shown, figure 1 The histograms in each set of data represent the detection results of pH6.5, pH3.5, pH3, pH2.5, and pH2 from left to right; The number of PAPCH viable bacteria at 3.5 and 6.5. When PAPCH was at pH 3.5 and 3.0, the survival amount of PAPCH was almost the same as that of the blank group (pH 6.5). After 2 hours under the condition of pH 2.5, the number of viable bacteria in PAPCH was significantly reduced, and then the number of viable bacteria was stable at 10 5 On the order of magnitude; after 1 hour under the condition of pH2.0, the number of viable bacteria in PAPCH has been significantly reduced, and the number of viable bacteria in PAPCH has stabilized at 10 after 2 hours. 4 order of magnitude.
[0052] Probiotics are defined as live microorganisms that, when ingested in appropriate amounts, confer a benefit on the host. ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2 Establishment of PAPCH Prevention Model of Hp Infection
[0062] 1. Preparation of bacterial suspension
[0063] (1) Preparation of PAPCH bacterial suspension
[0064] Take the subcultured PAPCH, centrifuge at 6000rpm for 10min in a centrifuge, take it out, discard the supernatant, wash with normal saline, and adjust the concentration of the bacterial suspension to 2×10 9 CFU / mL, prepared before each gavage to ensure the viability of bacteria.
[0065] (2) Preparation of Helicobacter pylori suspension
[0066] Take the subcultured Helicobacter pylori blood plate, add 1mL / dish of normal saline, scrape off the colony with a coating stick, suck it into a centrifuge tube with a pipette gun, and adjust the concentration of the bacterial suspension to 2×10 9 CFU / mL, prepared before each gavage to ensure the viability of bacteria.
[0067] 2. Mouse experiment
[0068] (1) The first period of gavage: establish a prevention model
[0069] After 7 days of adaptive...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Embodiment 3 fast urease reaction
[0086] Put the gastric tissue in the quick urease test paper, and observe the result within 5 minutes. The result is as Figure 5 as shown, Figure 5 NC is the blank group; PAPCH is the PAPCH treatment group; HP is the H.pylori treatment group; pre-P / post-H is the pre-PAPCH / post-H.pylori treatment group.
[0087] Put the gastric tissue of the mice in the blank group and the PAPCH treatment group on the test paper, and the color of the test paper did not change significantly. Put the Helicobacter pylori treatment group and the pre-P / post-H group on the test paper, and the test paper quickly turned red. And the color of the Helicobacter pylori treatment group was more purple than that of the pre-P / post-H group.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com