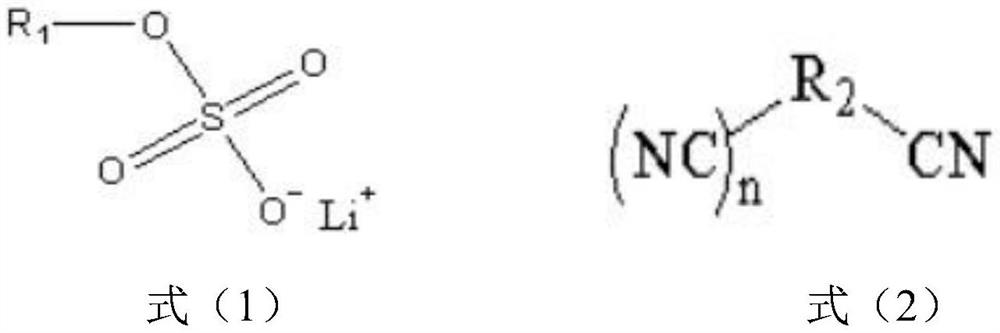Non-aqueous electrolyte for lithium ion battery and lithium ion battery using same
A technology of lithium ion battery and non-aqueous electrolyte, which is applied in the field of lithium ion battery, can solve the problems that nitrile additives can not improve the high temperature performance of the battery, reduce the low temperature discharge performance of the battery, and increase the impedance of the lithium cobalt oxide battery. Achieve the effect of ensuring room temperature and high temperature performance, low impedance, and reducing restrictions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
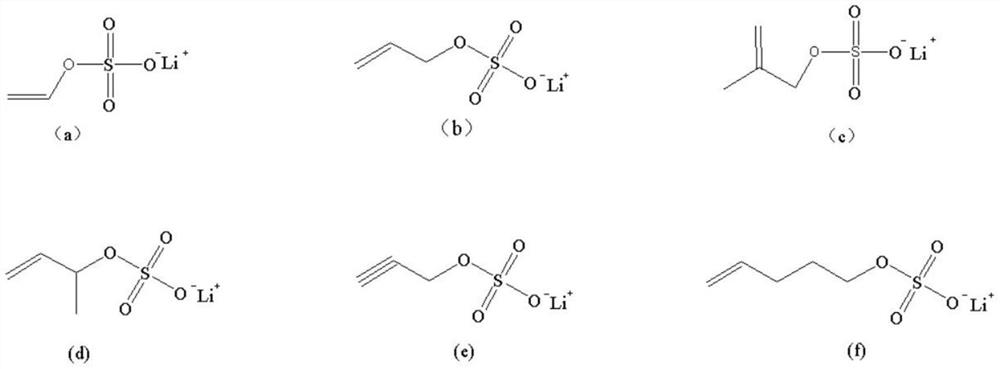
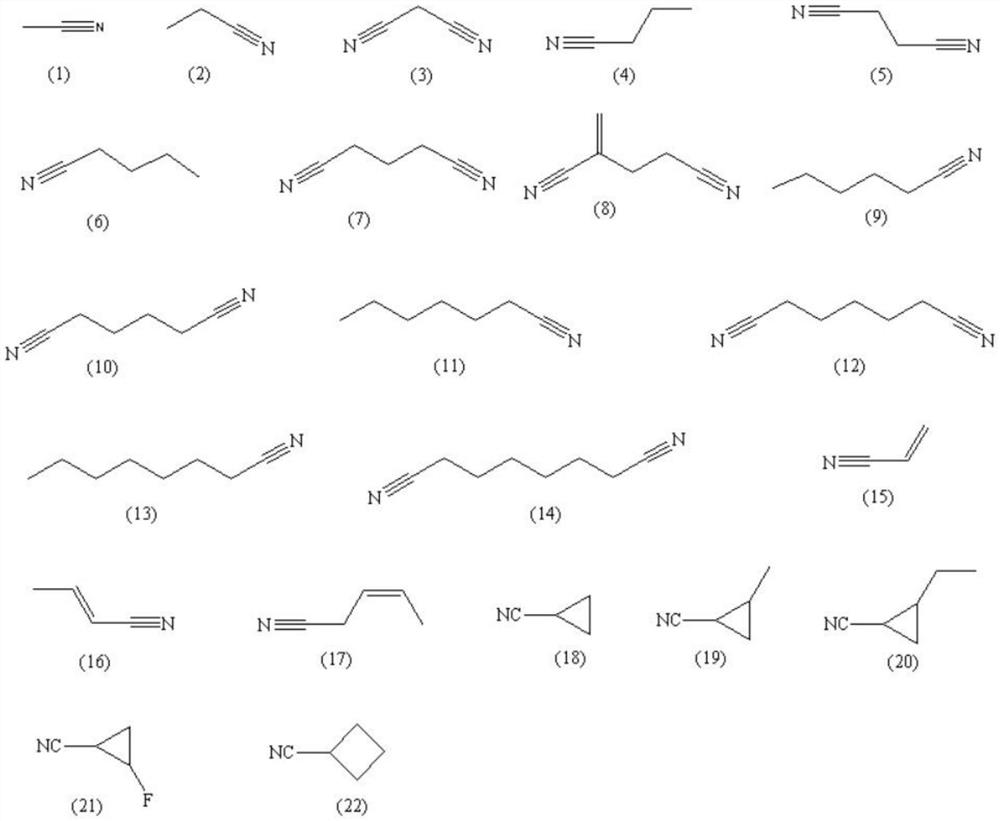
[0029] The non-aqueous electrolyte is prepared as follows: in the glove box, ethylene carbonate (EC), diethyl carbonate (DEC) and ethyl methyl carbonate (EMC) are carried out according to the ratio of 1:1:1 by weight Mix and then add lithium hexafluorophosphate for dissolution to prepare an electrolyte solution with a lithium hexafluorophosphate concentration of 1.1M. After that, add 0.5% vinylene carbonate (VC), 5% fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) and 4% 1,3-propane to the electrolyte. sultone (PS), compound (a) accounting for 0.5% of the mass of the electrolyte and compound (4) accounting for 1% of the mass of the electrolyte.
[0030] Inject the prepared non-aqueous electrolyte solution for lithium-ion batteries into fully dried, 4.4V lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO 2 ) / graphite soft pack battery, after shelving at 45°C, high-temperature fixture formation and secondary sealing process, the battery performance test was carried out to obtain the battery of Example 1.
Embodiment 2
[0032] The preparation method of the positive electrode and the negative electrode in Example 2 is the same as in Example 1; the difference is that 0.5% of the compound (b) is added to the electrolyte solution in Example 2.
Embodiment 3
[0034] The preparation method of the positive electrode and the negative electrode of Example 3 is the same as that of Example 1; the difference is that the compound (c) accounting for 0.5% of the mass of the electrolyte is added to the electrolyte of Example 3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com