Degradable polypropylene wood-plastic composite modified material
A wood-plastic composite and modified material technology, applied in the field of wood-plastic materials and degradable polypropylene wood-plastic composite modified materials, can solve the problems of low water absorption, decreased impact strength, affecting the impact resistance of materials, etc. Effects of fluidity, improved impact resistance and toughness, improved compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
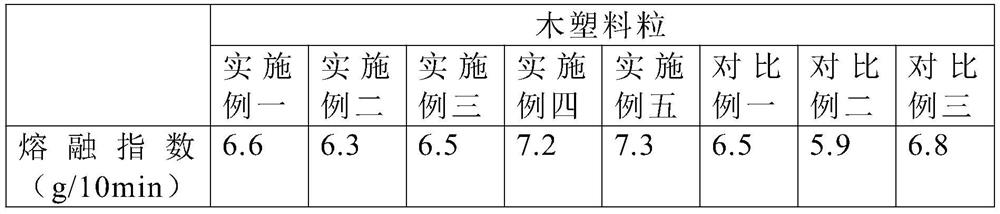
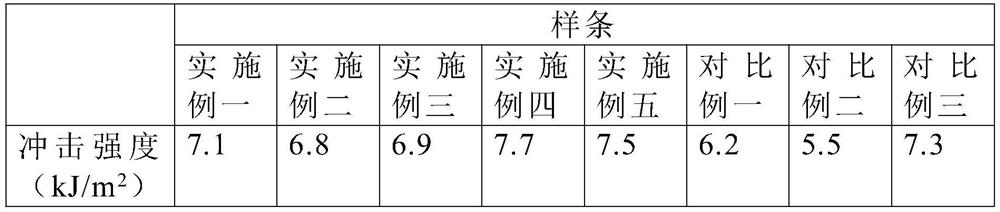
[0027] A kind of degradable polypropylene wood-plastic composite modified material, by weight, by 30 parts of wood flour, 45.5 parts of polypropylene, 19.5 parts of glass fiber, 2 parts of zinc stearate, 1 part of vinyl bis stearamide, Consists of 1 part compatibilizer and 1 part polyethylene wax.
[0028] Wherein, the wood powder is obtained by drying birch sawdust at 60-80° C. until the water content is less than 5 wt %, ball milling for 2.5 hours and passing through a 100-mesh sieve. The glass fiber is short glass fiber with a length of 0.2-0.6mm, and the compatibilizer is maleic anhydride grafted compatibilizer.
Embodiment 2
[0030] A degradable polypropylene wood-plastic composite modified material, in parts by weight, consists of 25 parts of wood powder, 50 parts of polypropylene, 20 parts of glass fiber, 1 part of zinc stearate, 2 parts of vinyl bis stearamide, Consists of 1 part compatibilizer and 1 part polyethylene wax.
[0031] Wherein, the wood powder is obtained by drying oak sawdust at 60-80° C. until the water content is less than 5 wt %, ball milling for 1.5 hours, and passing through a 100-mesh sieve. The glass fiber is short glass fiber with a length of 0.2-0.6mm, and the compatibilizer is acrylic graft compatibilizer.
Embodiment 3
[0033] A degradable polypropylene wood-plastic composite modified material, consisting of 40 parts of wood flour, 40 parts of polypropylene, 18 parts of glass fiber, 1 part of zinc stearate, 0.2 parts of vinyl bis stearamide, and 0.5 parts of compatibilizer and 0.3 parts of polyethylene wax.
[0034] Wherein, the wood flour is obtained by drying bamboo fiber at 60-80° C. until the moisture content is less than 5 wt %, ball milling for 3 hours, and passing through a 100-mesh sieve. The glass fiber is short glass fiber with a length of 0.2-0.6mm, and the compatibilizer is maleic anhydride grafted compatibilizer.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com