Universal plasmid, construction method of universal plasmid and novel method for expressing exogenous genes by synechocystis
A Synechocystis and plasmid technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of weakened start-up ability and dependence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
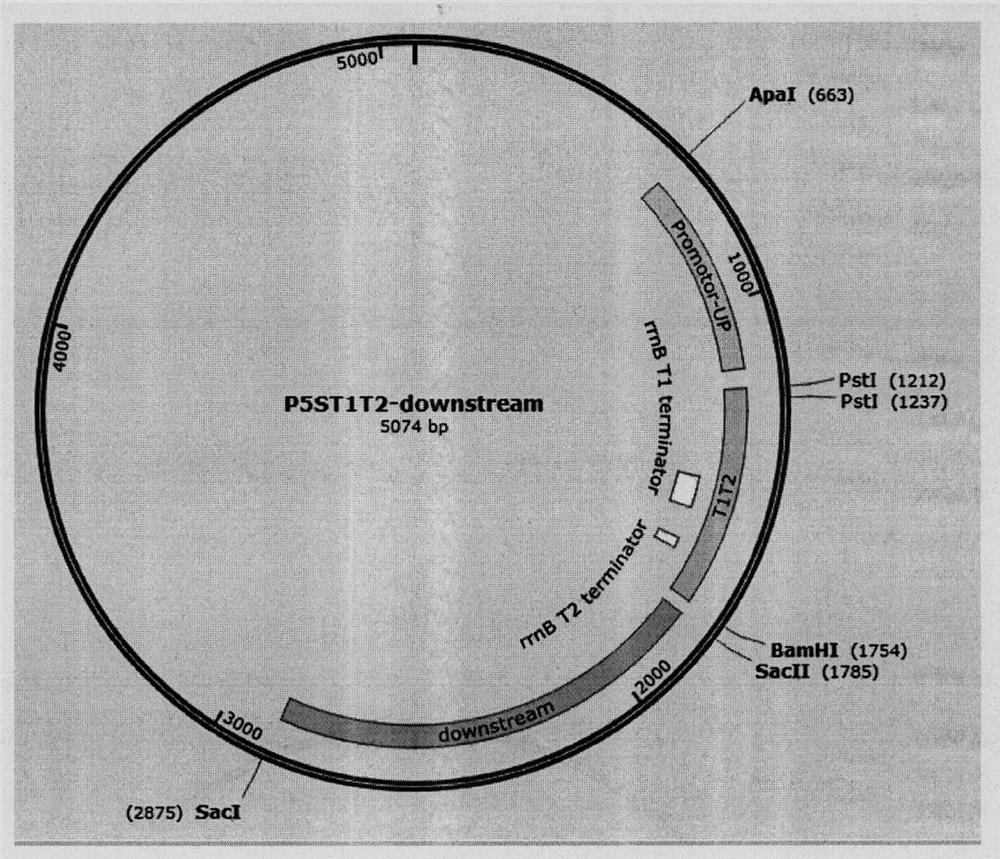
[0052] Construction of plasmid P5ST1T2-downstream:
[0053] (1) Use SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2 in the sequence listing as upstream and downstream primers, use the wild Synechocystis PCC6803 genome as a template; use SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO: 4 in the sequence listing as upper For downstream primers, the Genbank accession number is U02439.1 Escherichia coli as a template; with SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 6 in the sequence listing as upstream and downstream primers, using wild Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 as a template, amplified by PCR The technology obtains the photosensitive promoter and the upstream arm gene sequence Promoter-up, the terminator T1T2 gene fragment and the downstream arm sequence downstream. The obtained sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 11, SEQ ID NO: 12, and SEQ ID NO: 13 in the sequence listing; (2) Promoter-up of the light-sensitive promoter and upstream arm gene sequence obtained in step (1) Carry out ApaI enzyme digestion treatment, perform PSt I and Ba...
Embodiment 2
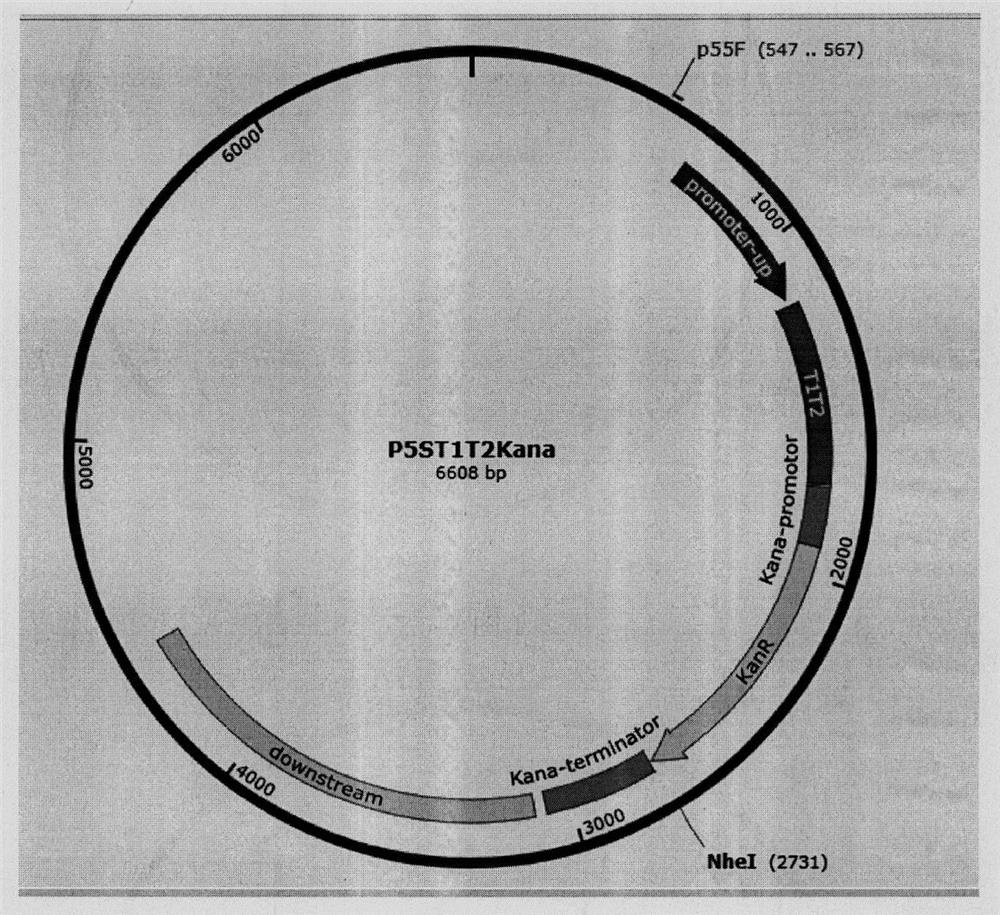
[0056] Construction of Universal Plasmid P5ST1T2Kana
[0057] (1) Treat the puc4K plasmid with the restriction endonuclease BamHI to recover the Kana resistance sequence, the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 14 in the sequence listing; (2) use SEQ ID NO: 7 and SEQ ID NO in the sequence listing: 8 is the upstream and downstream primers, use the sequence recovered in step (1) as a template, and obtain the promoter and Kana resistance gene sequence by PCR amplification technology: Promote-Kana, add enzymes at the upstream and downstream ends of Promote-Kana respectively through primers Cutting sites BamHI and NheI, the obtained sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 15 in the sequence listing; using SEQ ID NO: 9 and SEQ ID NO: 10 in the sequence listing as upstream and downstream primers, and the sequence recovered in step 2 is Template, obtain the terminator gene sequence by PCR amplification technology: terminator, respectively add enzyme cutting sites Nhe I and BamHI at the upstream a...
Embodiment 3
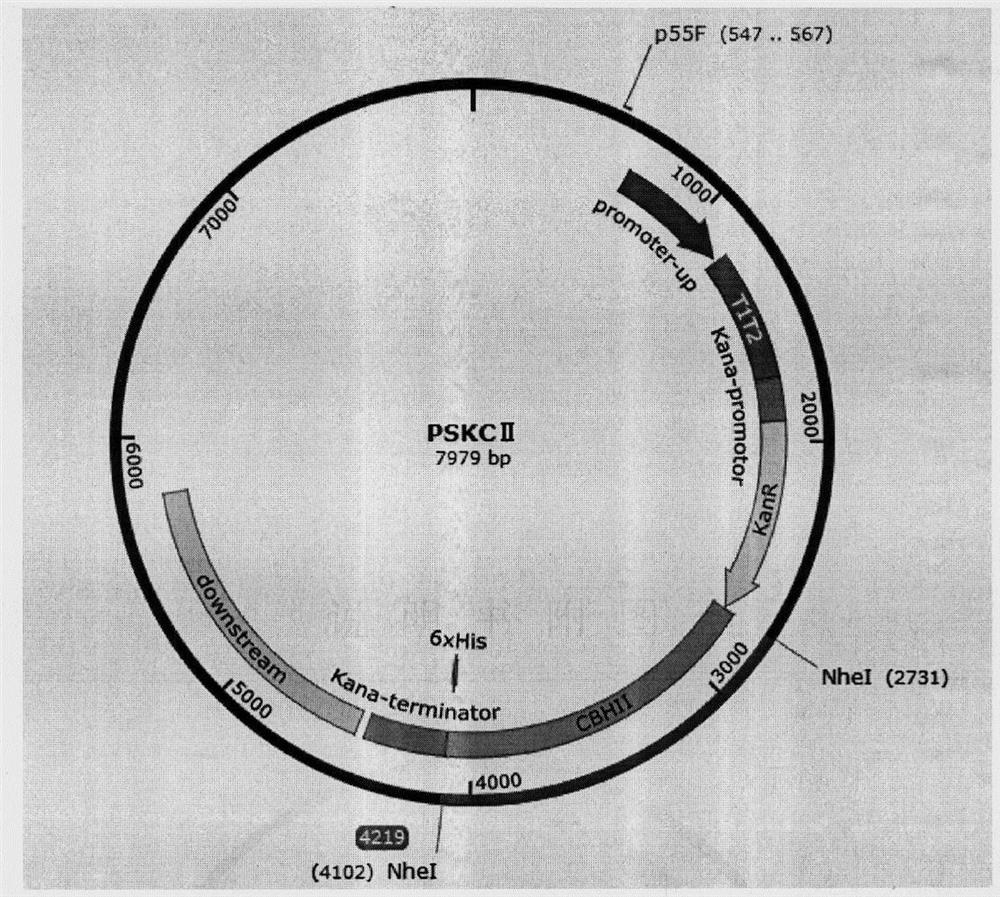
[0060] Construction of Recombinant Plasmid PSKC II Expressing Cellulase in Synechocystis sp.
[0061] Using SEQ ID NO: 17 and SEQ ID NO: 18 in the sequence listing as upstream and downstream primers, using the corresponding gene sequence of Trichoderma reesei (Trichoderma reesei QM9414) in the GenBank database as a template, the cellulase exonuclease CBH was obtained by PCR technology II gene fragment, and add homology arm sequences at both ends of the target gene through primers, the sequence is shown in SEQID NO: 19 in the sequence listing; the shuttle recombinant expression vector P5ST1T2Kana is treated with the restriction endonuclease Nhe I, and the obtained The gene fragment of cellulosic exonuclease CBH II undergoes homologous recombination under the action of recombinase to obtain recombinant expression vector plasmid PSKC II.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com