A kind of green reprocessing method of polymer hydrogel
A polymer hydrogel and hydrogel technology, applied in the field of polymers, can solve the problems of unfavorable environment, high energy consumption, heating, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0046] 1) Preparation of borax-crosslinked PVA hydrogel: PVA and borax were mixed in an aqueous solution, and the final concentrations of PVA and borax were 50 mg / mL and 13 mg / mL respectively; the hydrogel was formed in less than 10 minutes;
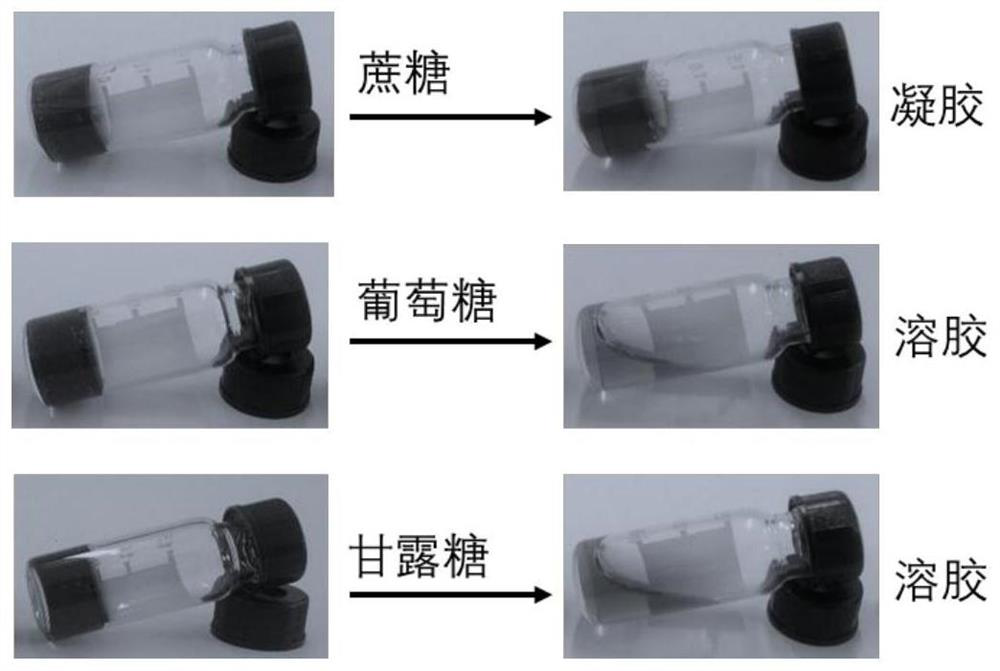
[0047] 2) Glucose, mannose and sucrose were added to the above-mentioned borax cross-linked PVA hydrogel respectively, and when the final concentration of the added glucose, mannose and sucrose increased to 1.2M, such as: figure 1 As shown, glucose and mannose appear as a sol, while sucrose is still in a gel state, indicating that cis-1,2-diol can break boron ester bonds at high concentrations. Therefore, the preferred substrate sugar of the present invention is sucrose.
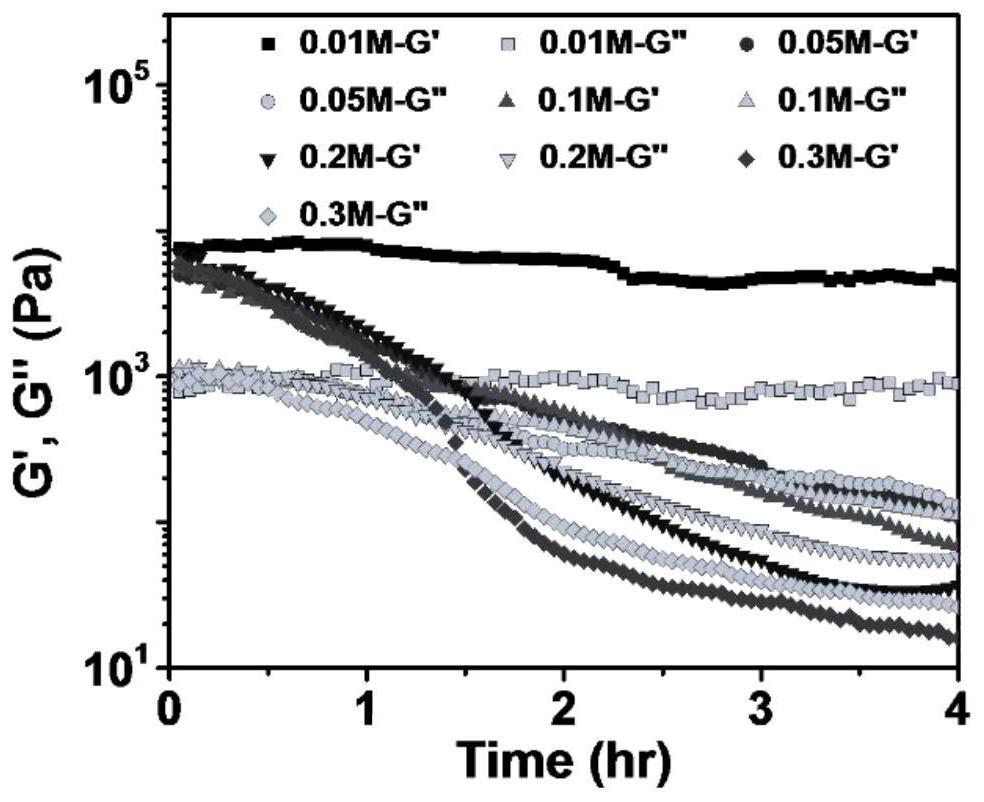
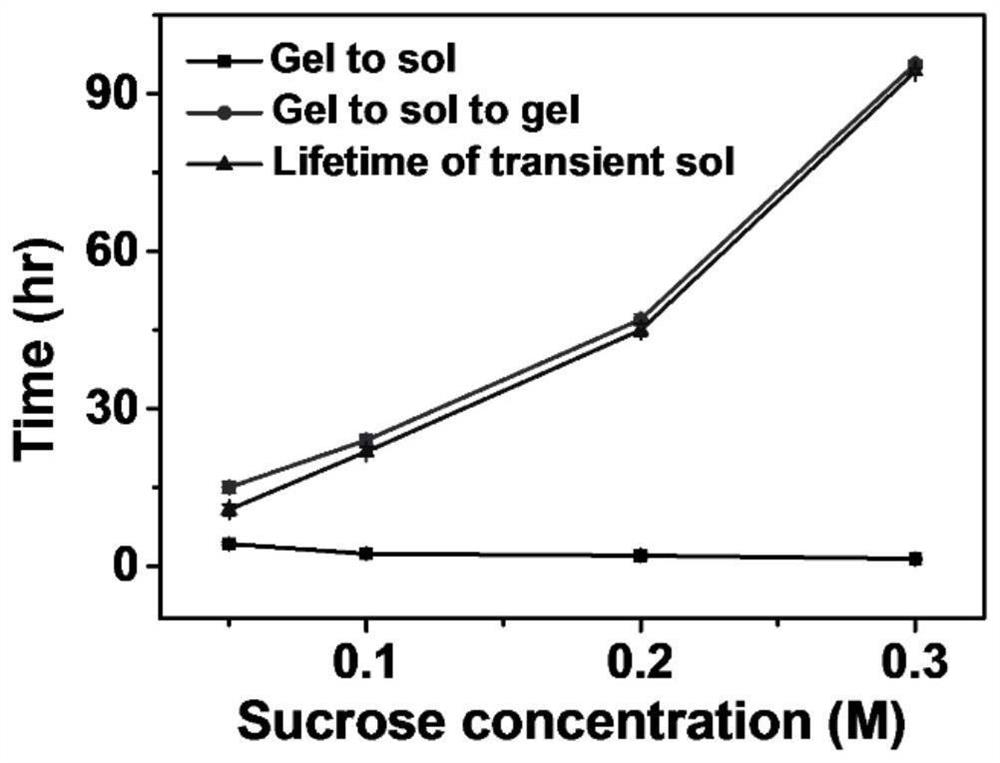
[0048] The effect of sugar concentration on hydrogel reprocessing was tested experimentally. By controlling the sugar concentration, the amount of carbon dioxide produced was regulated, thereby controlling the time from gel to sol and subsequent release of carbon dioxi...
Embodiment 1
[0053] A method for green reprocessing of polymer hydrogel, the steps are as follows:
[0054] (1) Preparation of yeast-containing borax-crosslinked PVA hydrogel: PVA, yeast, borax and pH indicator xylenol orange were mixed in an aqueous solution, and the final concentrations of PVA, yeast, borax and xylenol orange were 50 mg respectively / mL, 13mg / mL, 13mg / mL and 0.18mg / mL; hydrogels formed in less than 10 minutes;
[0055] (2) Add sucrose with a final concentration of 0.1M to the above-mentioned borax-crosslinked PVA hydrogel containing yeast, and use yeast to metabolize sucrose to generate carbonic acid, thereby reducing the pH of the gel system and breaking the dynamic covalent boron ester bond to initiate the instantaneous liquefaction of the polymer hydrogel, the gel becomes a sol, and then carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), the pH of the gel system increases, so that the sol becomes a gel.
Embodiment 2
[0057] A method for green reprocessing of polymer hydrogel, the steps are as follows:
[0058] (1) Preparation of borax-crosslinked PVA hydrogel containing yeast: PVA, yeast, borax and pH indicator xylenol orange were mixed in an aqueous solution, and the final concentrations of PVA, yeast, borax and xylenol orange were 50 mg respectively / mL, 13mg / mL, 13mg / mL and 0.18mg / mL; hydrogels formed in less than 10 minutes;
[0059] (2) Add sucrose with a final concentration of 0.1M to the above-mentioned borax-crosslinked PVA hydrogel containing yeast, and use yeast to metabolize sucrose to generate carbonic acid, thereby reducing the pH of the gel system and breaking the dynamic covalent boron ester bond to initiate the instantaneous liquefaction of the polymer hydrogel, and the gel becomes a sol. Under stirring conditions, AM, HHM, and MBA were added to the transient sol, and the final concentrations of AM were 50 mg / mL and 100 mg / mL, respectively. , 200mg / mL, the mass ratio of AM...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com