Patents
Literature
66 results about "Soft robotics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Soft Robotics is the specific subfield of robotics dealing with constructing robots from highly compliant materials, similar to those found in living organisms. Soft robotics draws heavily from the way in which living organisms move and adapt to their surroundings. In contrast to robots built from rigid materials, soft robots allow for increased flexibility and adaptability for accomplishing tasks, as well as improved safety when working around humans. These characteristics allow for its potential use in the fields of medicine and manufacturing.
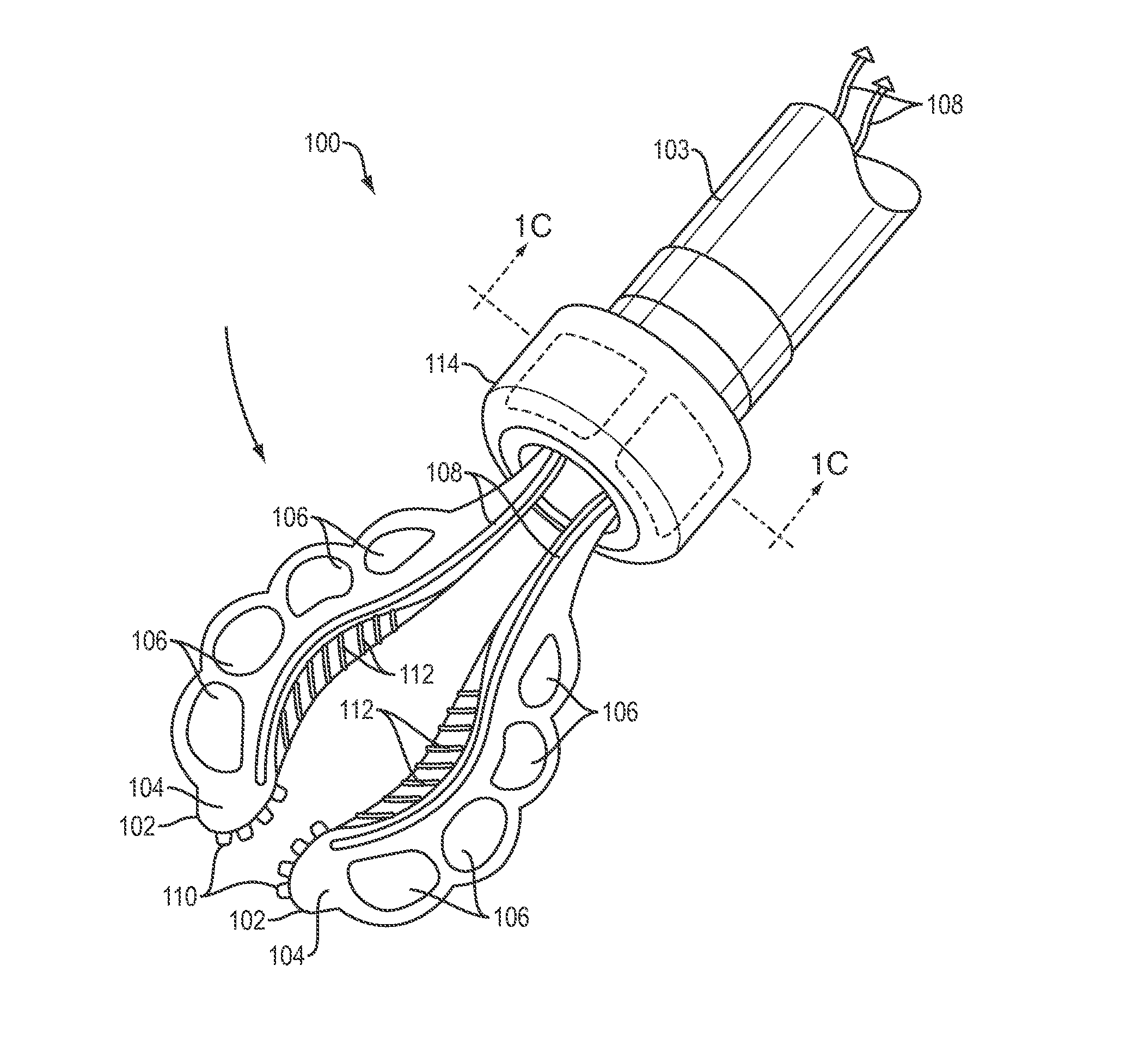
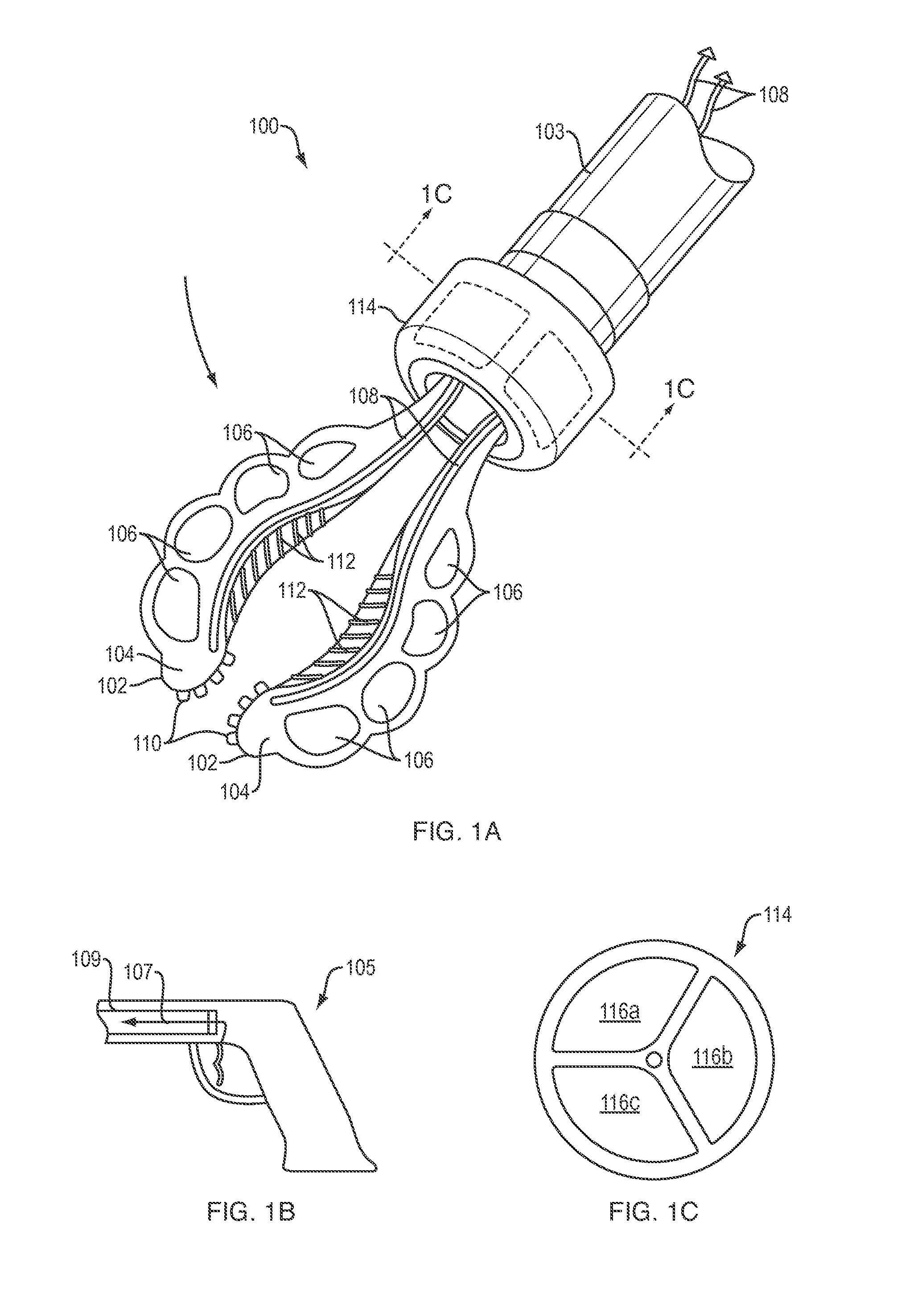
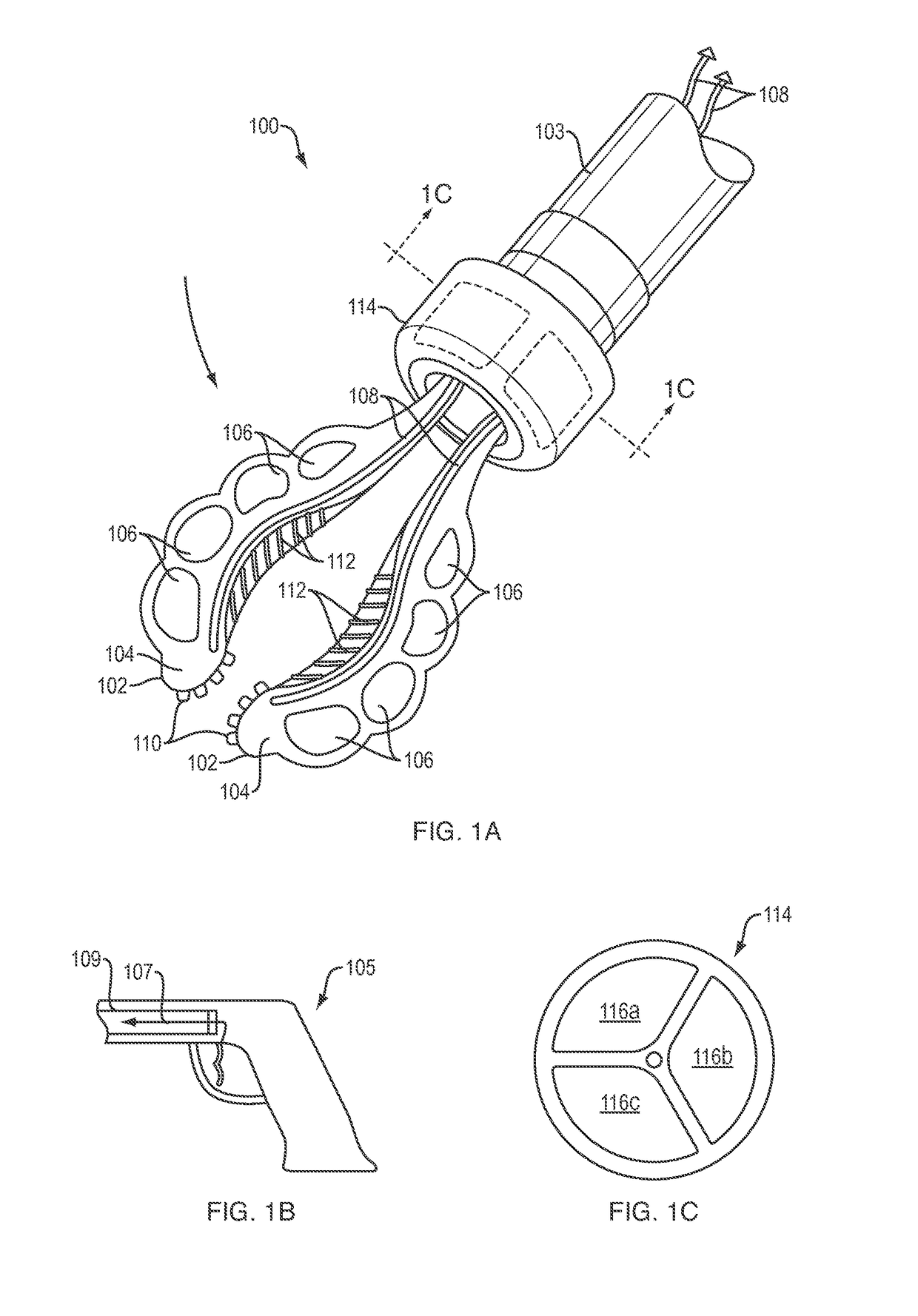
Soft conformal laparoscopic instrument
ActiveUS20150257839A1Relieve pressureEasy to operateDiagnosticsElectric circuit arrangementsLess invasive surgerySurgical operation
A soft robotic instrument that is capable of changing its form factor (e.g., expanding and contracting) during use to facilitate minimally invasive surgery. The instrument may be formed wholly or partly of an elastomeric, electrically insulating material for mitigating the risk of injuring tissue and for mitigating the risk of electrical arcing during electrosurgery.
Owner:SOFT ROBOTICS
Sensors for soft robots and soft actuators
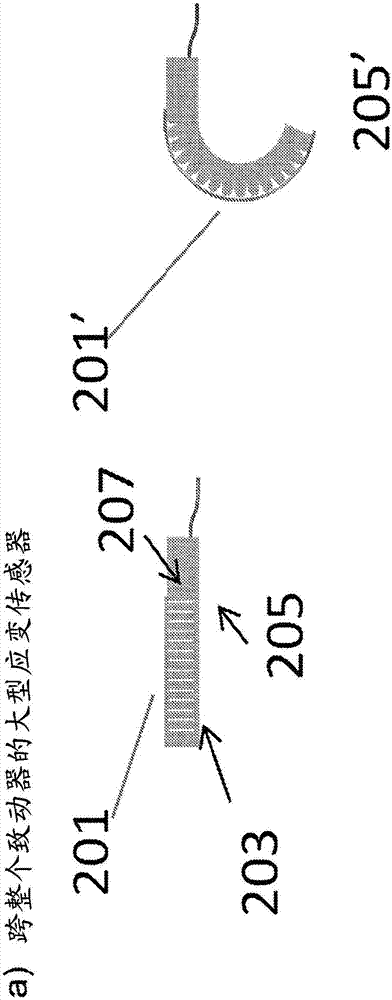
A soft robotic device with one or more sensors is described. The sensor may be embedded in the soft body of the soft robotic device, attached to the soft body of the soft robotic device, or otherwise linked to the soft body of the soft robotic device.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Climbing soft robotics
The present invention relates to a new pneumatic-actuated multifunctional doming actuator. The doming actuator can be used as a doming actuator, which can maintain machine / robotic operation on vertical surfaces without falling. The doming actuators exhibit rapid switchable adhesion / deadhesion on target surfaces upon pressurizing / depressurizing the embedded spiral pneumatic channels. The present invention also relates to novel load-carrying and climbing soft robots using the doming actuators. The soft robots are operable on a wide range of horizontal and vertical surfaces including dry, wet, slippery, smooth, and semi-smooth surfaces. In addition, the doming actuators can be used as a driving actuator for swimming soft robotics and as an actuator for soft grippers.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
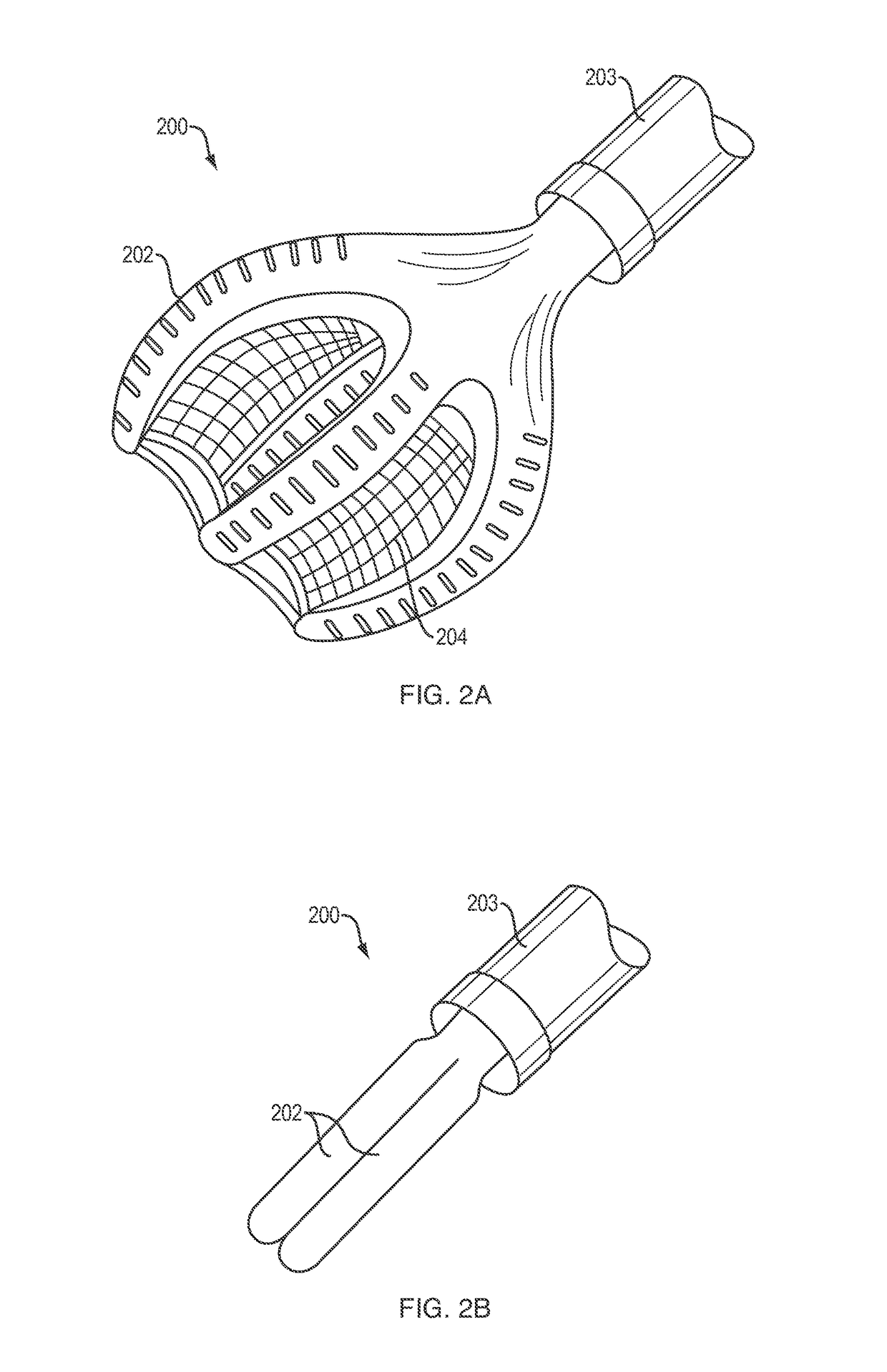
Soft robotic assistive gripping device
ActiveUS20180361596A1Easy to controlEasy to removeProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsDiseaseEngineering
This invention is directed to offer a customizable, cost effective, and comfortable soft gripping solution for patients with chronic disabilities, such as diabetic neuropathy, allowing the patients to function independently and perform routine daily tasks. A soft robotic gripper has been developed with one or more inflatable systems actuated by aft to assist a user to grip an object. The main body of the gripper bends with air actuation while the fingertip actuation helps functionality in the extremities. The gripper is further enhanced by adding sensors that integrate feedback for sensitivity to touch, conformability, and grip ability. The modular design modifications allow for gripper adjustments as the disease progresses or rescinds. The gripper also works as a training aid for routine physical therapy exercises. Data collected by a microprocessor can also help learn more about these chronic diseases and use artificial intelligence to customize treatment regimens for individual patients.
Owner:BERI ALEKH RAJESH
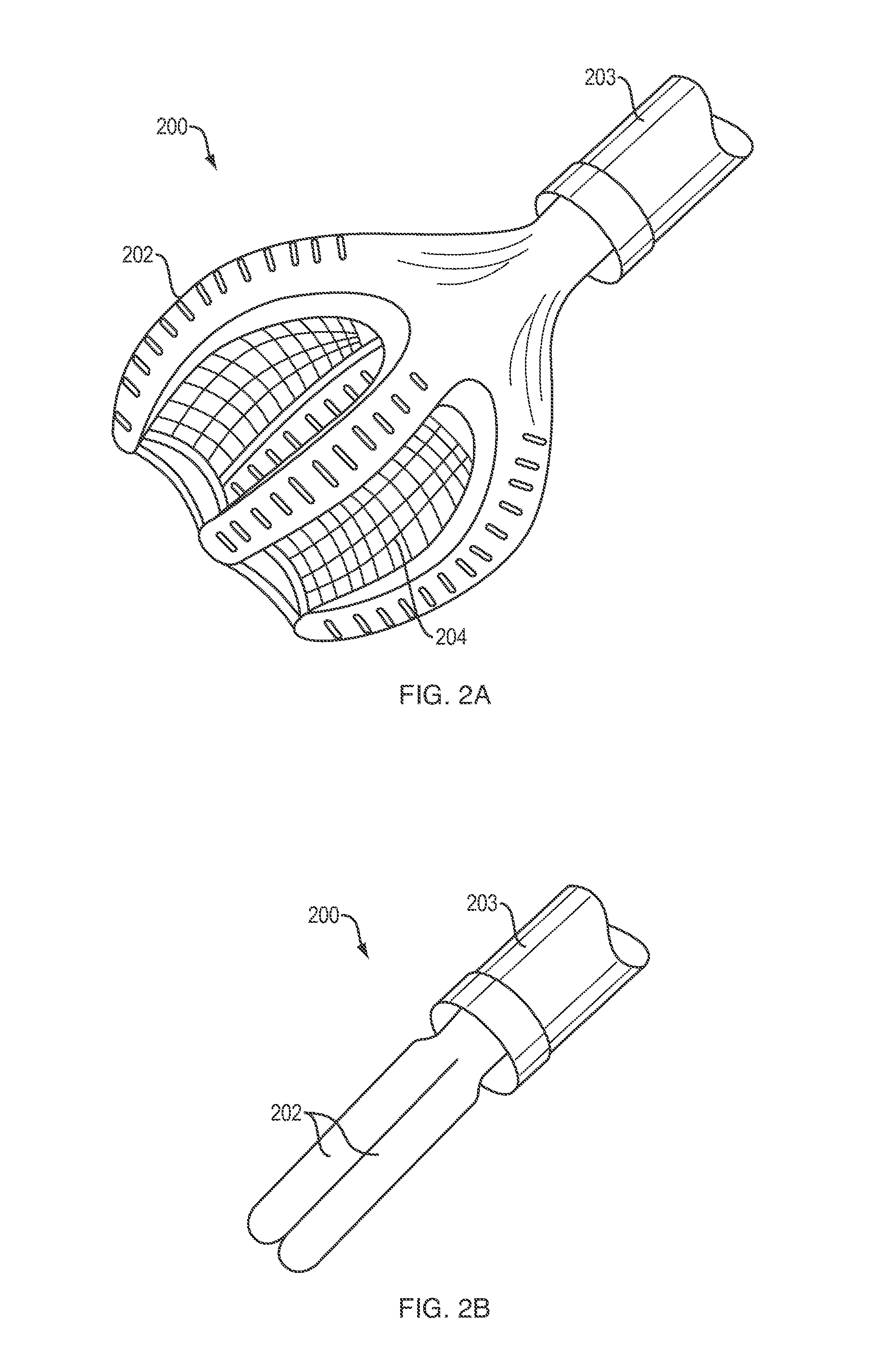
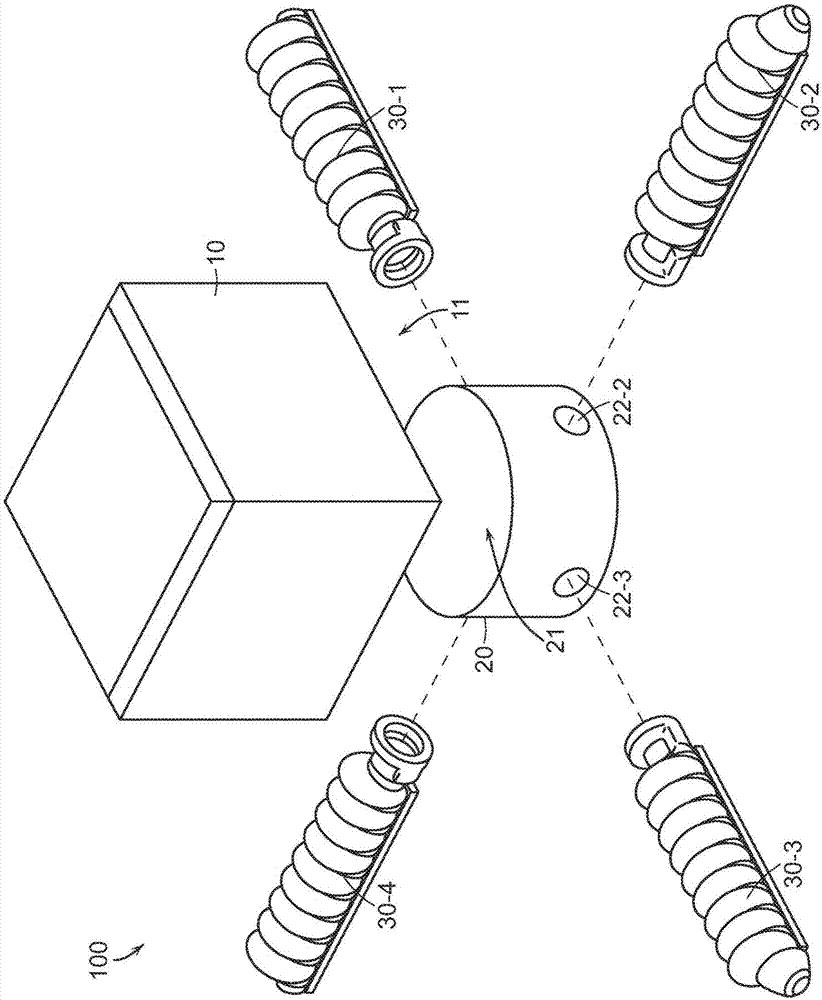
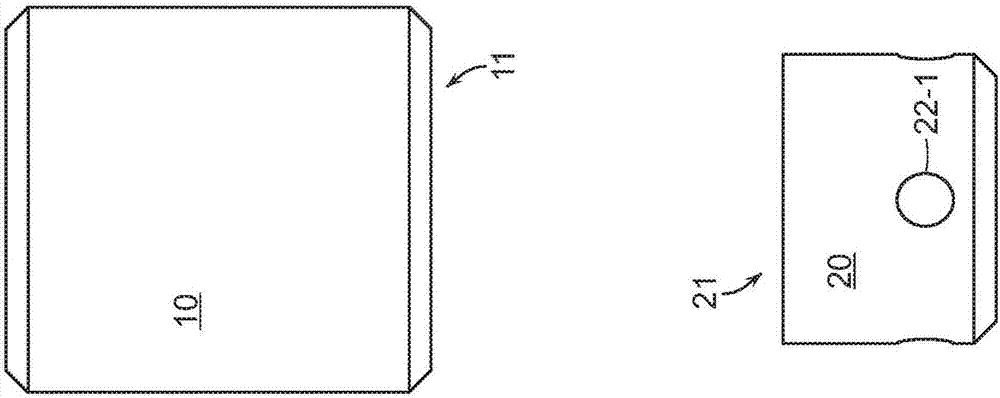
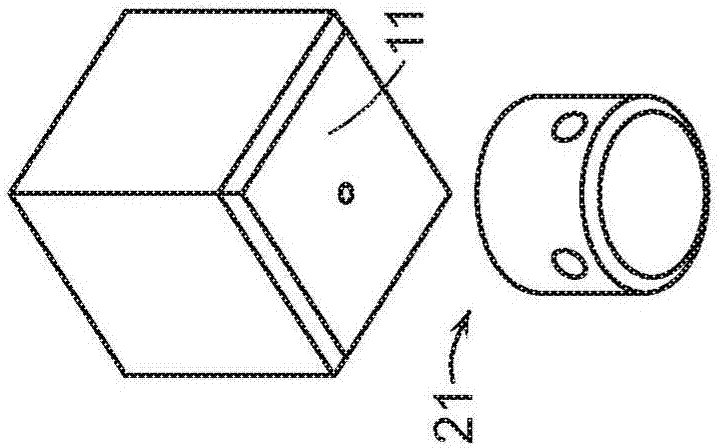
Soft robotic actuator attachment hub and grasper assembly, reinforced actuators, and electroadhesive actuators
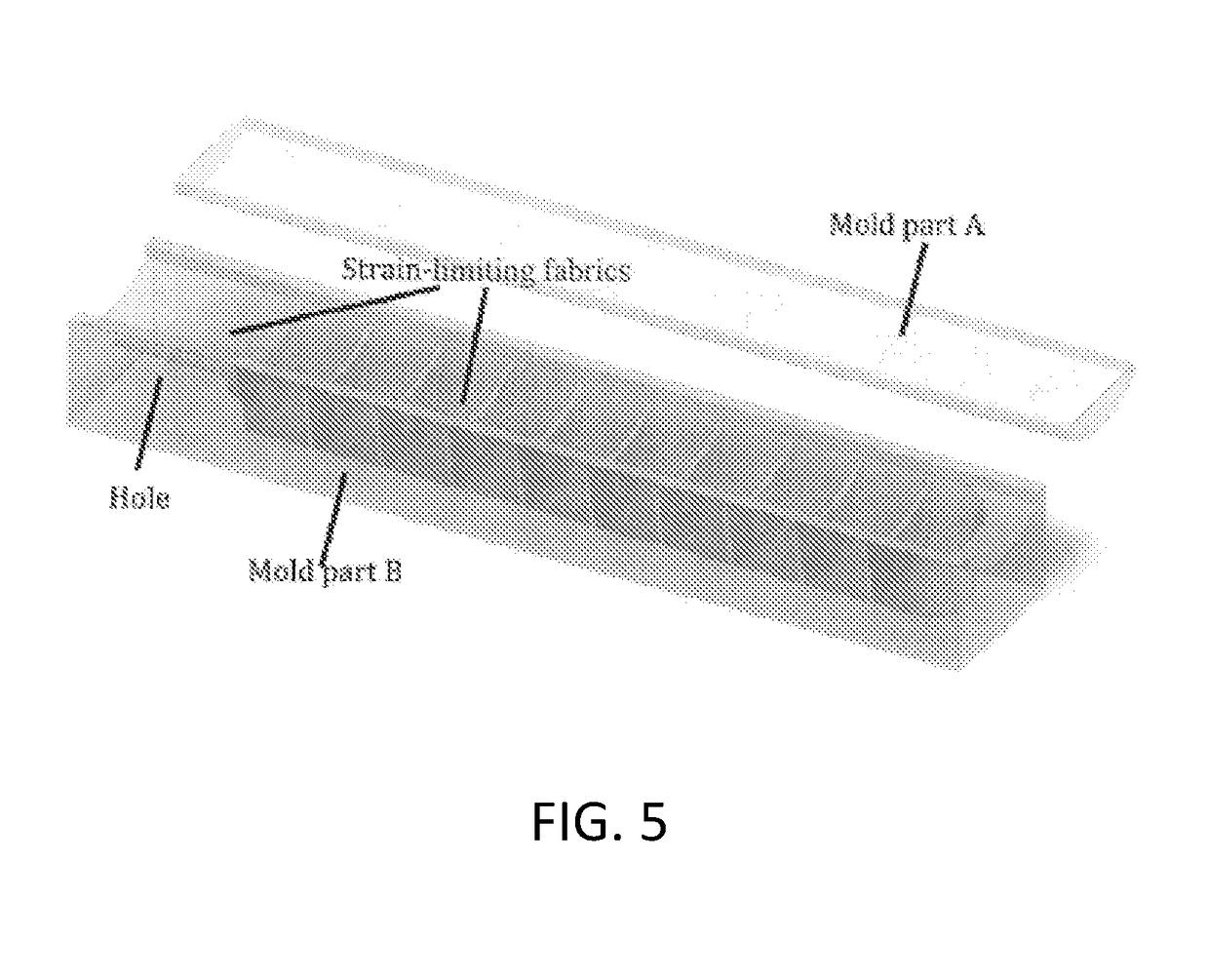
A hub assembly for coupling different grasper assemblies including a soft actuator in various configurations to a mechanical robotic components are described. Further described are soft actuators having various reinforcement. Further described are and soft actuators having electroadhesive pads for improved grip, and / or embedded electromagnets for interacting with complementary surfaces on the object being gripped. Still further described are soft actuators having reinforcement mechanisms for reducing or eliminating bowing in a strain limiting layer, or for reinforcing accordion troughs in the soft actuator body.
Owner:SOFT ROBOTICS
Waveguides for use in sensors or displays
Waveguides, such as light guides, made entirely of elastomeric material or with indents on an outer surface are disclosed. These improved waveguides can be used in sensors, soft robotics, or displays. For example, the waveguides can be used in a strain sensor, a curvature sensor, or a force sensor. In an instance, the waveguide can be used in a hand prosthetic. Sensors that use the disclosed waveguides and methods of manufacturing waveguides also are disclosed.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Soft robotic actuators utilizing asymmetric surfaces
InactiveCN107002721ASimplify the modeling processSimplify the design processProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsInternal pressureControl theory
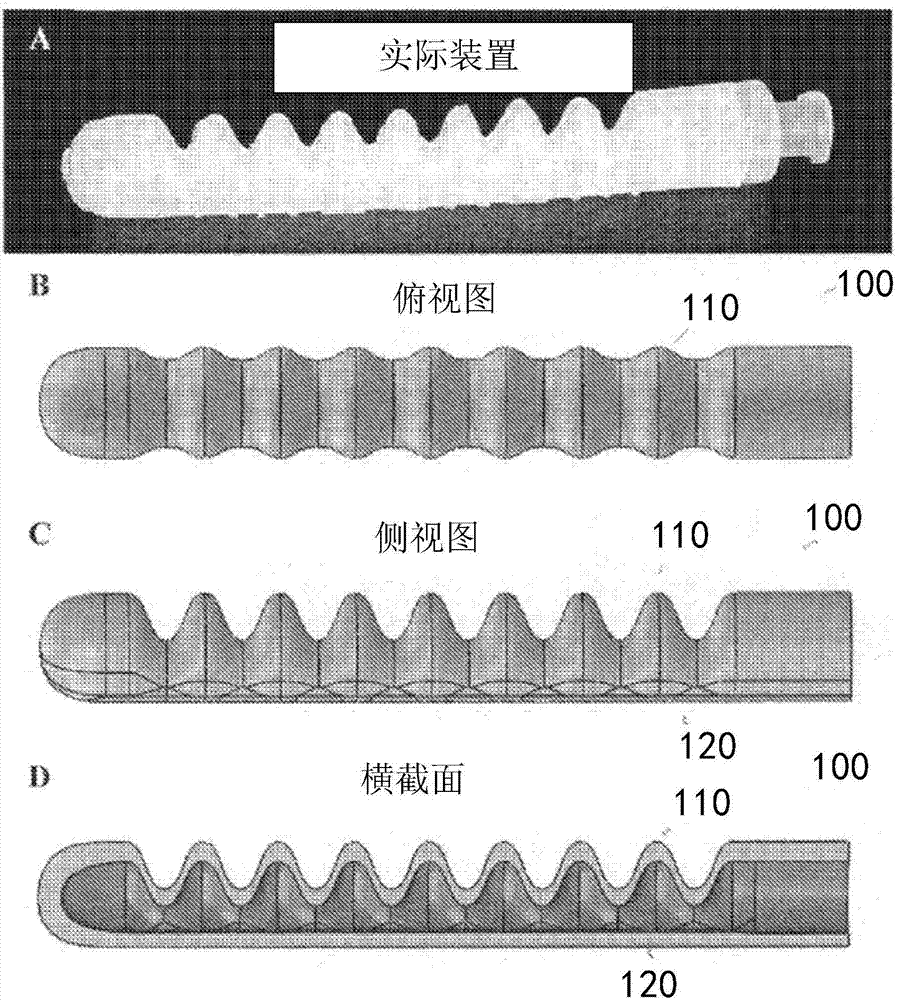
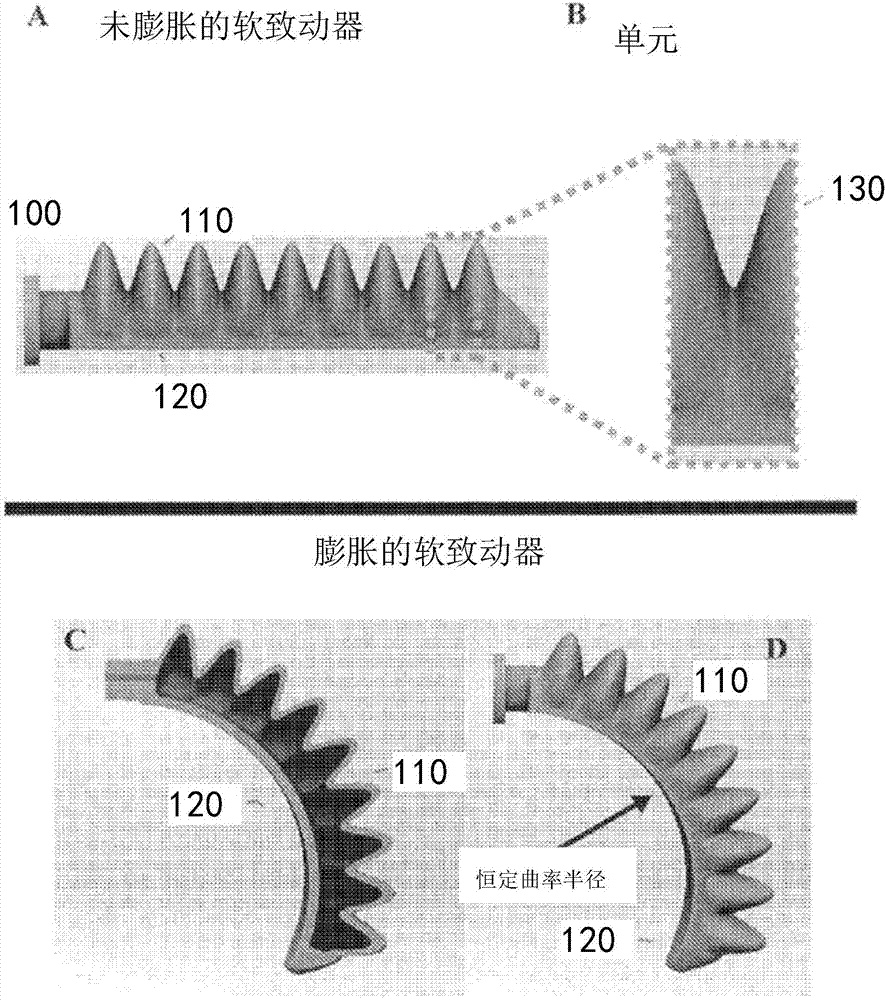
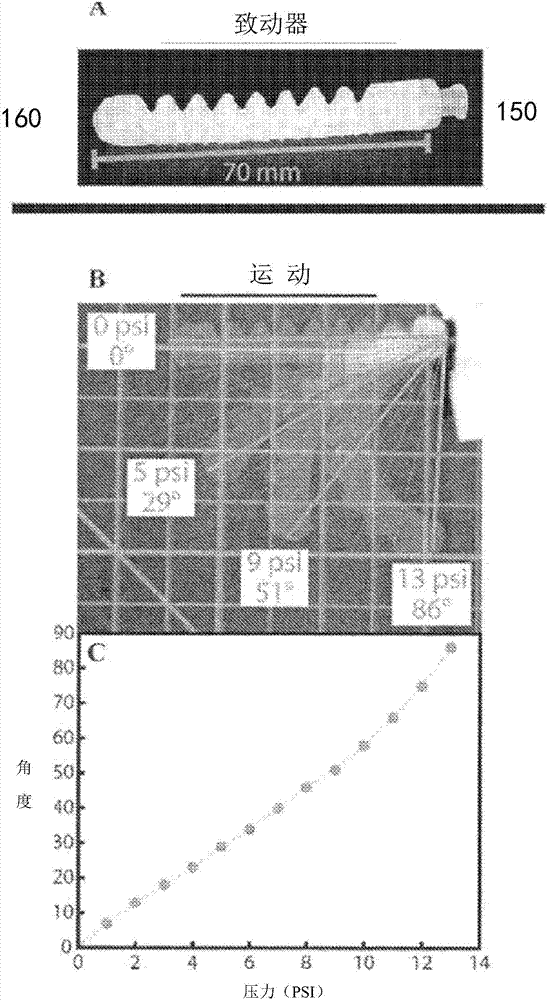
A soft robotic actuator is disclosed. The actuator includes a first portion with a substantially constant profile and a second portion with a regularly varying profile, and bends in a pressure-dependent fashion as the internal pressure within the actuator is increased or decreased. The present invention addresses the needs described above by providing actuators that are configured to perform new fundamental motions through the inclusion of design elements which can be configured, through the manipulation of a relatively short list of parameters, to undergo specific pressure-actuated changes which can be designed using quantitative modeling techniques.
Owner:SOFT ROBOTICS
Soft robotic actuator enhancements
Exemplary embodiments provide enhancements for soft robotic actuators. In some embodiments, angular adjustment systems are provided for varying an angle between an actuator and the hub, or between two actuators. The angular adjustment system may also be used to vary a relative distance or spacing between actuators. According to further embodiments, rigidizing layers are provided for reinforcing one or more portions of an actuator at one or more locations of relatively high strain. According to further embodiments, force amplification structures are provided for increasing an amount of force applied by an actuator to a target. The force amplification structures may serve to shorten the length of the actuator that is subject to bending upon inflation. According to still further embodiments, gripping pads are provided for customizing an actuator's gripping profile to better conform to the surfaces of items to be gripped.
Owner:SOFT ROBOTICS
Soft biomimetic legged robot
ActiveUS20200391814A1Improve rigidityProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsSimulationLegged robot
A soft biomimetic legged robot is provided in the present invention, including a plurality of soft robotic arms. The soft robotic arms include a plurality of motion units, and each of the motion units includes one or more of a twist module, an extension module, a contraction, and a bending module. The plurality of motion units is combined to achieve a full-posture motion of the soft robotic arms. By using soft robotic arms composed of different motion units, the soft biomimetic legged robot of the present invention can not only realize the underwater swimming and crawling, but the crawling on land or slopes, thereby adapting to more complicated environments and achieving richer functions. The motion posture is not limited to a single bending, twisting, extension, and shortening. The soft robotic arm can achieve full-posture movements, and its motion type is more complete.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
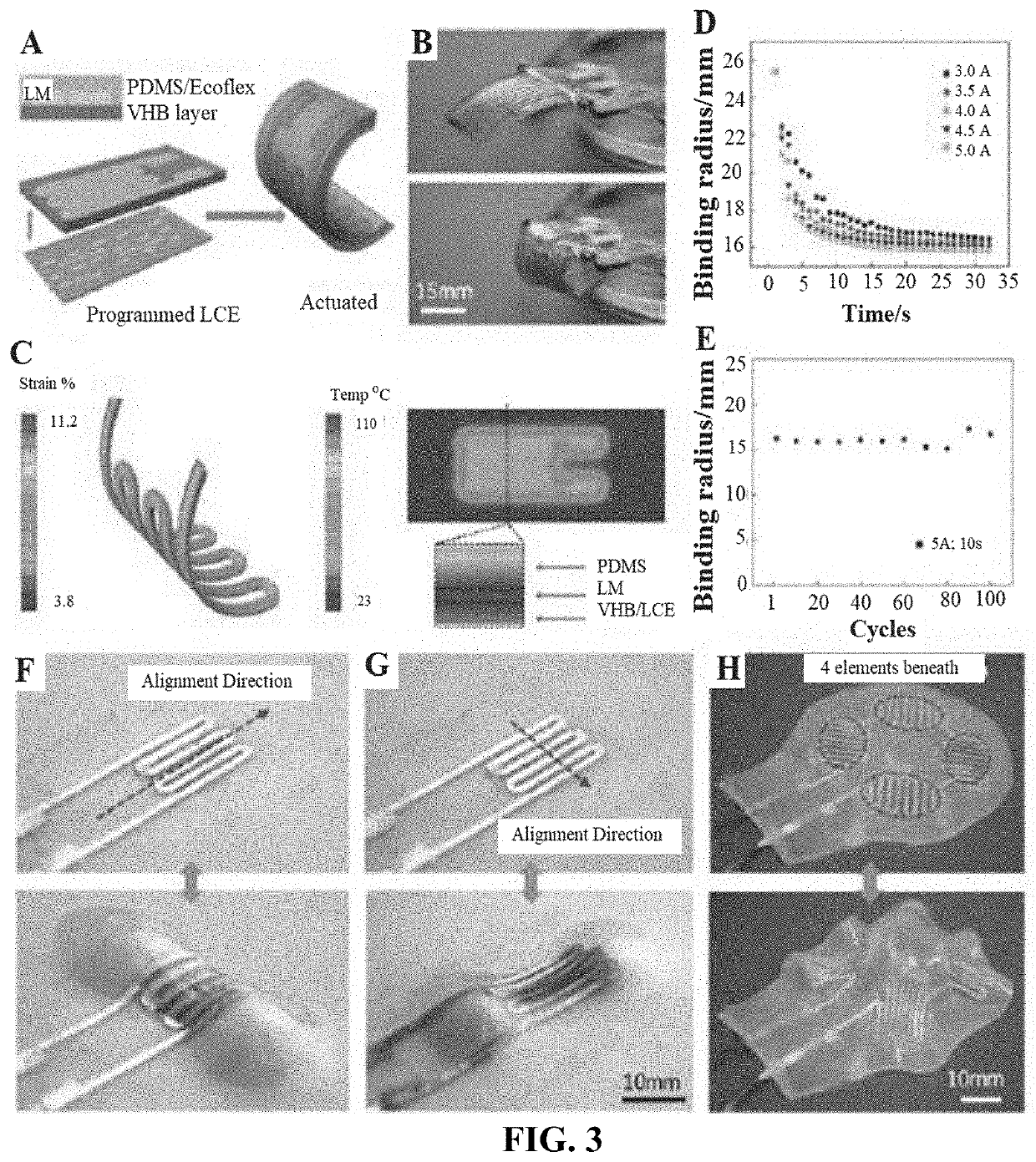
Systems and methods of soft robotic actuation with a liquid metal actuator
ActiveUS20210205103A1Increase temperatureLiquid crystal compositionsProgramme-controlled manipulatorLiquid stateEngineering
Methods, systems, and methods of manufacture for soft robotic actuators are described herein. In one aspect, a soft robotic actuator can include an elastomeric material defining a cavity; a volume of liquid metal (LM) positioned within the cavity; and an energy source coupled to the LM, where the energy source is adapted or configured to alter a temperature of the volume of LM, whereby altering the temperature of the volume of LM initiates an actuation of the elastomeric material.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
System and methods for fabricating actuators and electrically actuated hydraulic solid materials
InactiveUS20180156204A1Fast formingRapid designSynthetic resin layered productsMachines/enginesElectricityShell molding
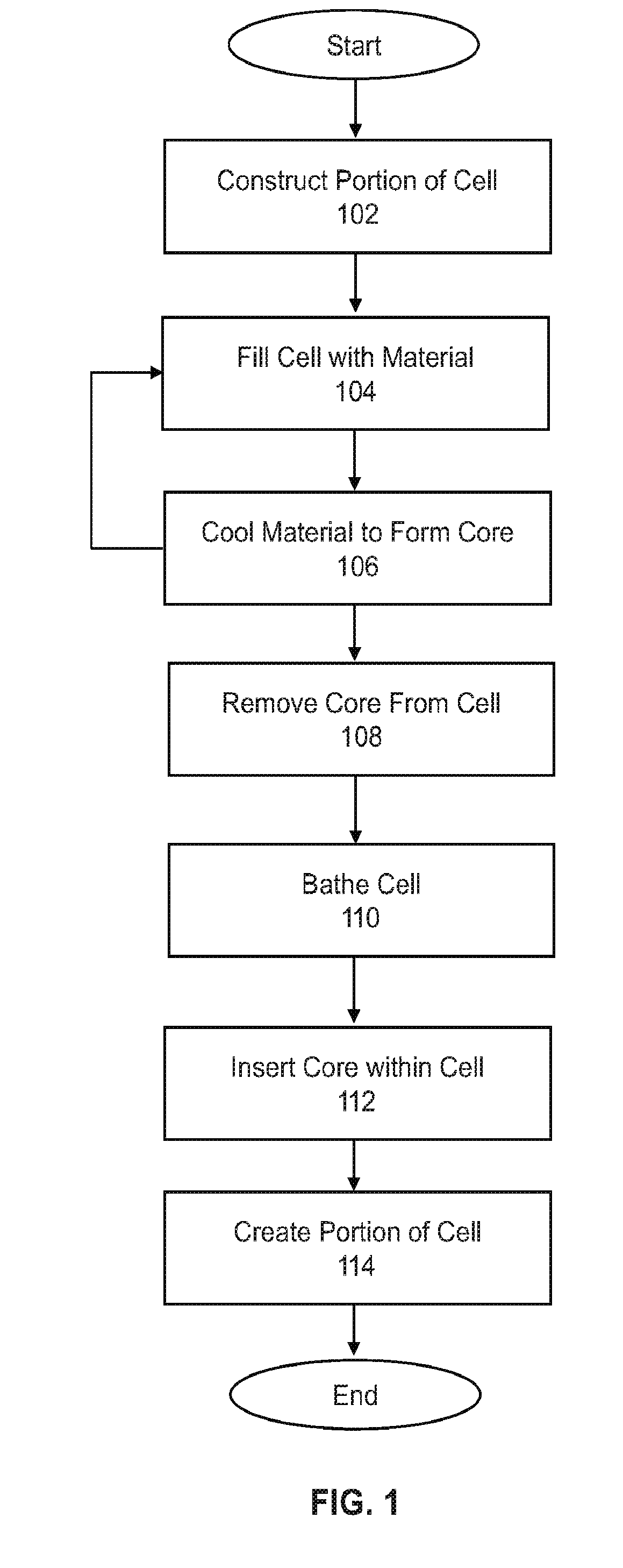
With applications such as soft robotics being severely hindered by the lack of strong soft actuators, the invention provides a new soft-actuator material—Electrically Actuated Hydraulic Solid (EAHS) material—with a stress-density that outperforms any known electrically-actuatable material. One type of actuator is fabricated by making a closed cell that acts as highly paralyzed version of a standard paraffin actuator. Each cell exhibits microscopic expansion, which is summed to produce macroscopic motion. The closed cellular nature of the material allows the system to be cut and punctured and still operate. It can be produced in a lab or industrial scale, and can be formed using molding, 3D printing or cutting.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Sensors for soft robots and soft actuators
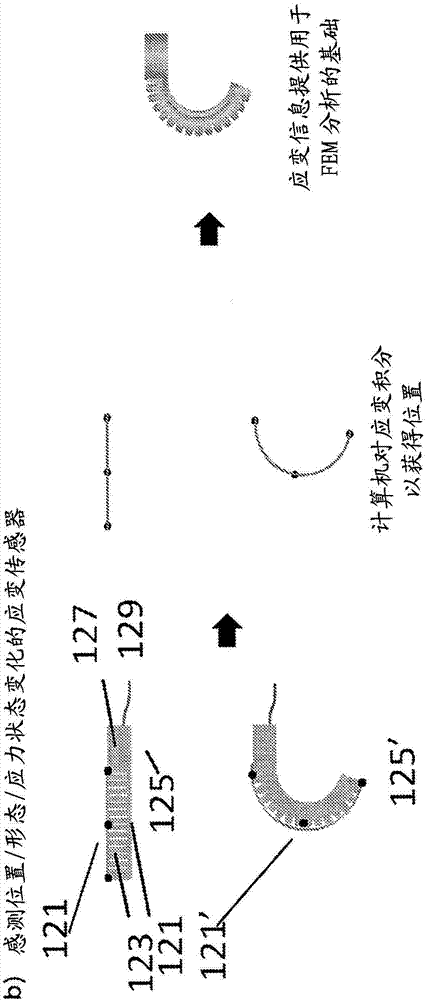
A soft robotic device with a variety of sensors and / or imaging areas is described. The sensor and / or imaging area may be embedded in the soft body or the strain limiting layer of the soft robotic device, attached to the soft body or the strain limiting layer of the soft robotic device, or otherwise linked to the soft body or the strain limiting layer of the soft robotic device.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
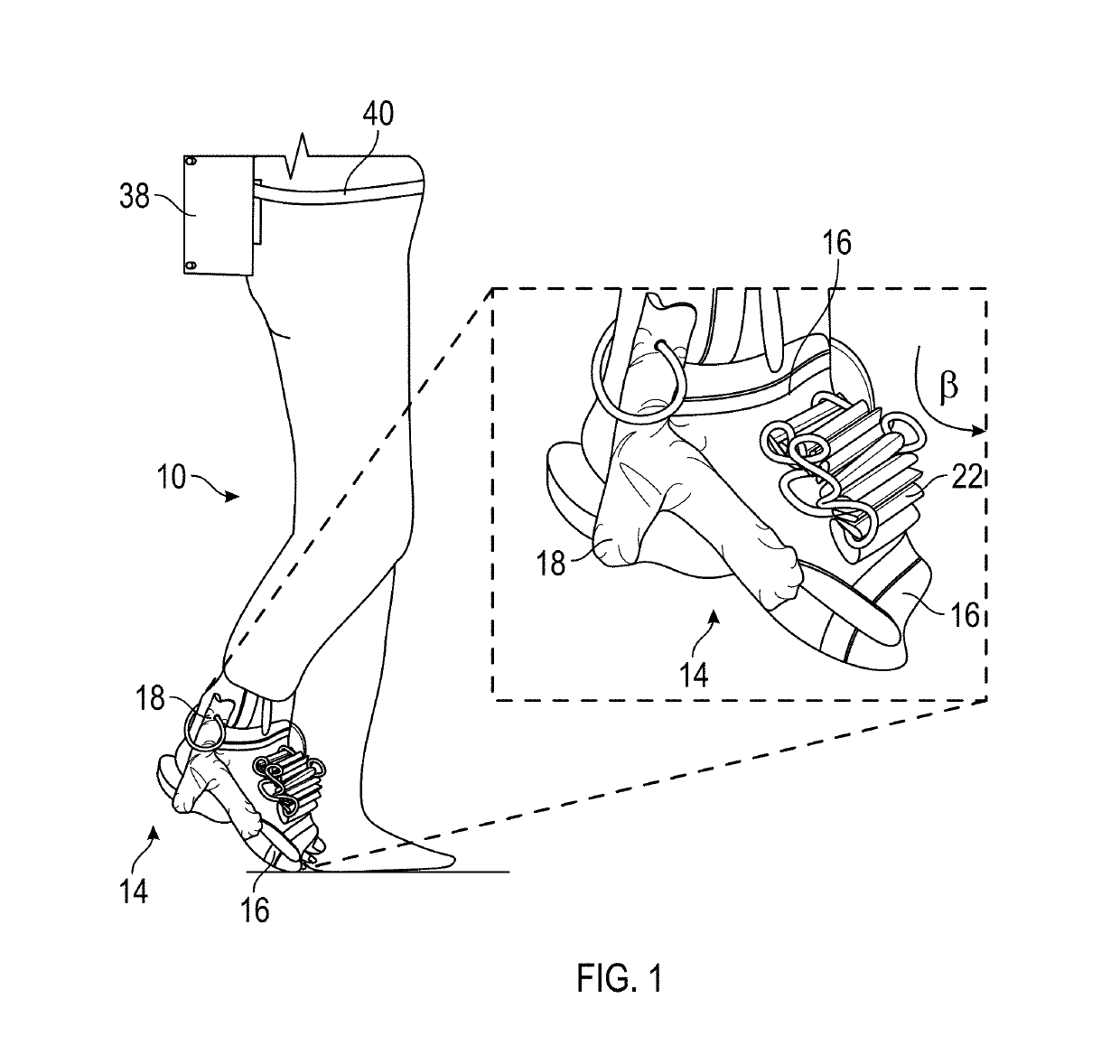
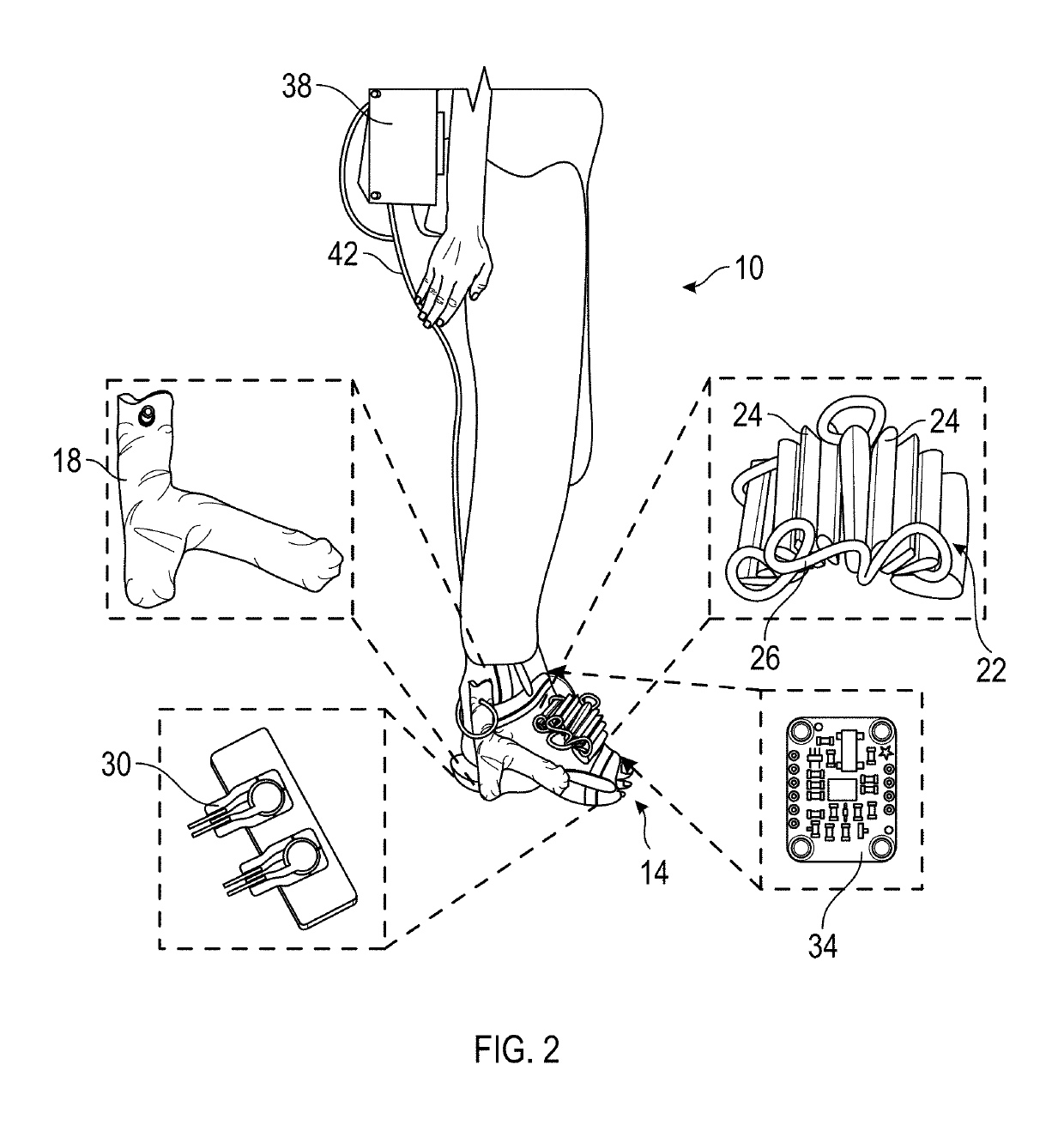
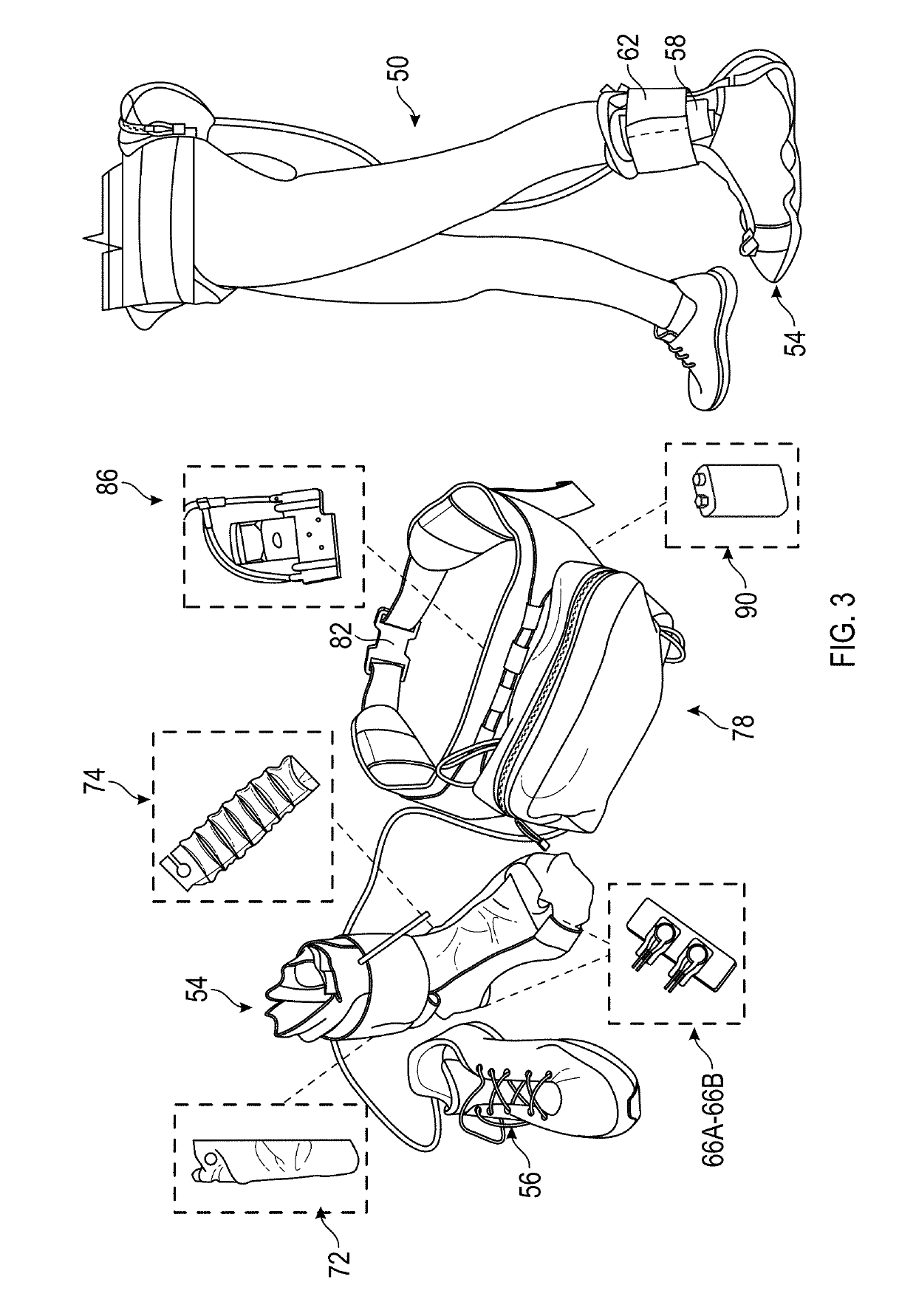
Soft dynamic ankle-foot orthosis exosuit for gait assistance with foot drop
InactiveUS20190336315A1Improve abilitiesPromote recoveryChiropractic devicesWalking aidsInternal pressureKnee orthosis
A soft robotic ankle-foot orthosis exosuit includes a brace configured to be worn on a user's foot, a first soft actuator, a second soft actuator, and a pneumatic system. The first soft actuator is coupled to the brace so that it is configured to be positioned proximate a top of the user's foot. The second soft actuator is also coupled to the brace and is configured to be positioned proximate a side of the user's foot. The pneumatic system is configured to change an internal pressure of the first soft actuator and the second soft actuator.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Ultrasound transducer holder
ActiveUS20190053784A1Programme-controlled manipulatorOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingCost effectiveness
Described herein are devices and methods useful in automating ultrasound imaging. The device include a base coupled with soft robotics, which may be attached to an ultrasound transducer probe in order to robotically manipulate the probe to perform an ultrasound scan. The device has an adjustable structure configured to hold the probe on a walking soft robot. The device can be configured to be attached to, or worn by, the patient. With soft robotic actuation and locomotion, the holder can move and position the probe during a real time ultrasound scanning procedure. Furthermore, the holder may be equipped with sensors to sense and map pressure and location. The position of the holder can be robotically monitored and controlled so as to achieve consistency and reproducibility between ultrasound scans. Due to the wearable nature of the holder, the scans may be conducted while the patient is in motion, thereby providing a portable solution for ultrasonic imaging. The holder is cost effective and may be used in conjunction with various ultrasound probes.
Owner:BERI SERENA
Edible Pneumatic Soft Robotic Actuators
The present invention relates to a biocompatible, digestible and edible material for use in soft edible robots. The present invention provides a pneumatic actuator for edible robotics, and a toy set including at least one pneumatic actuator and an inflating device. Further, the biocompatible, digestible and edible material can be used for making bubble gum products.
Owner:THE HAVERFORD SCHOOL
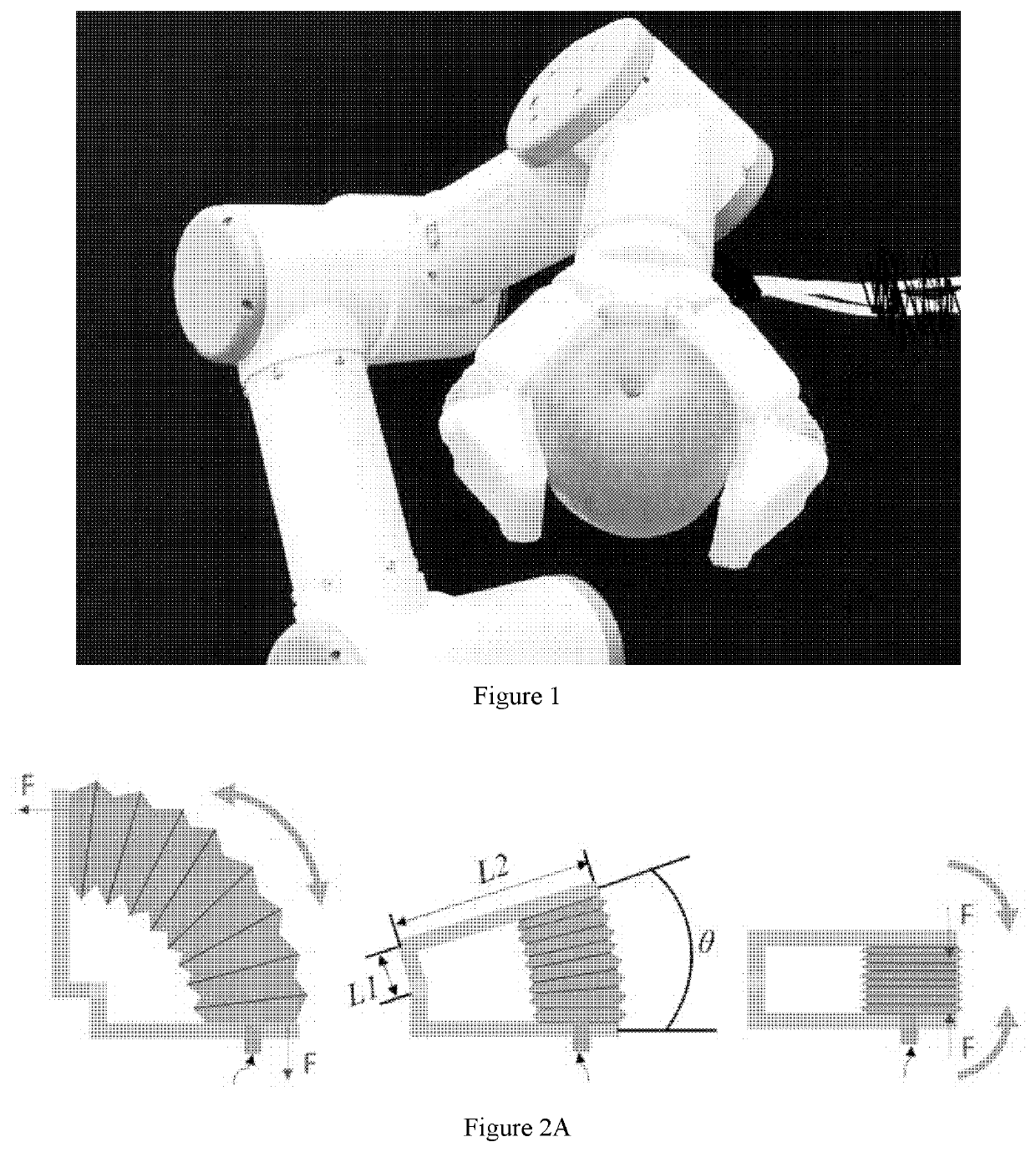
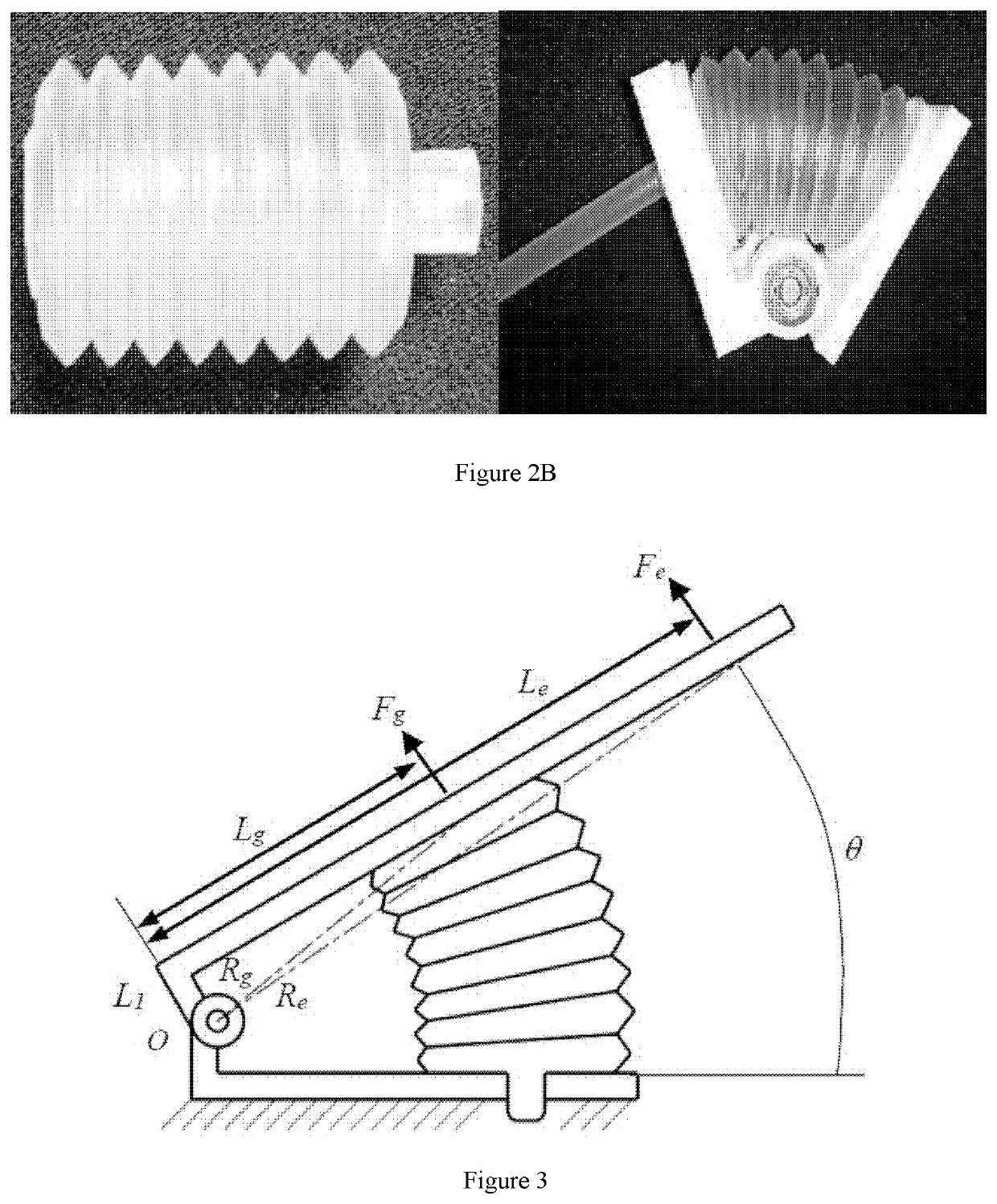
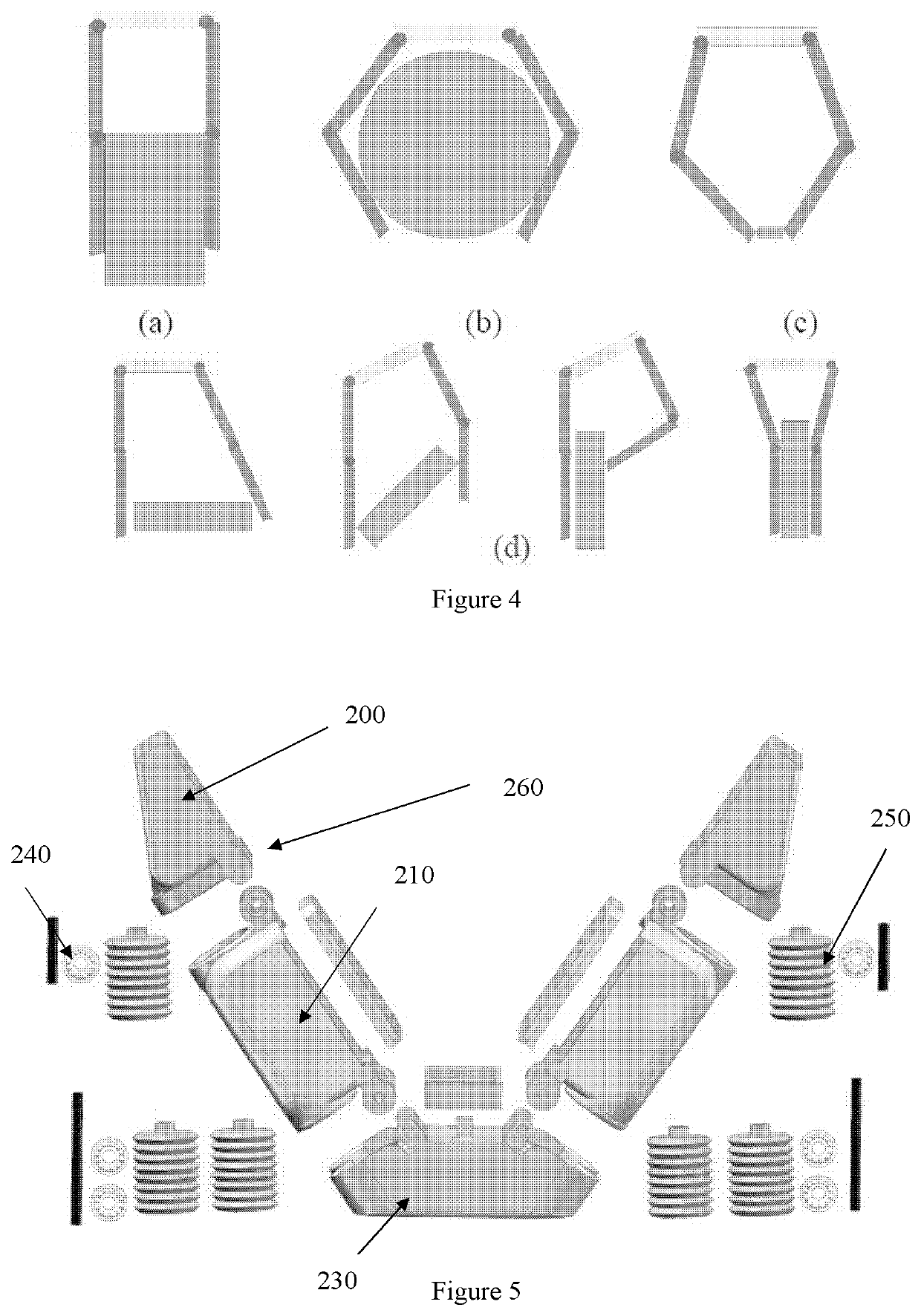
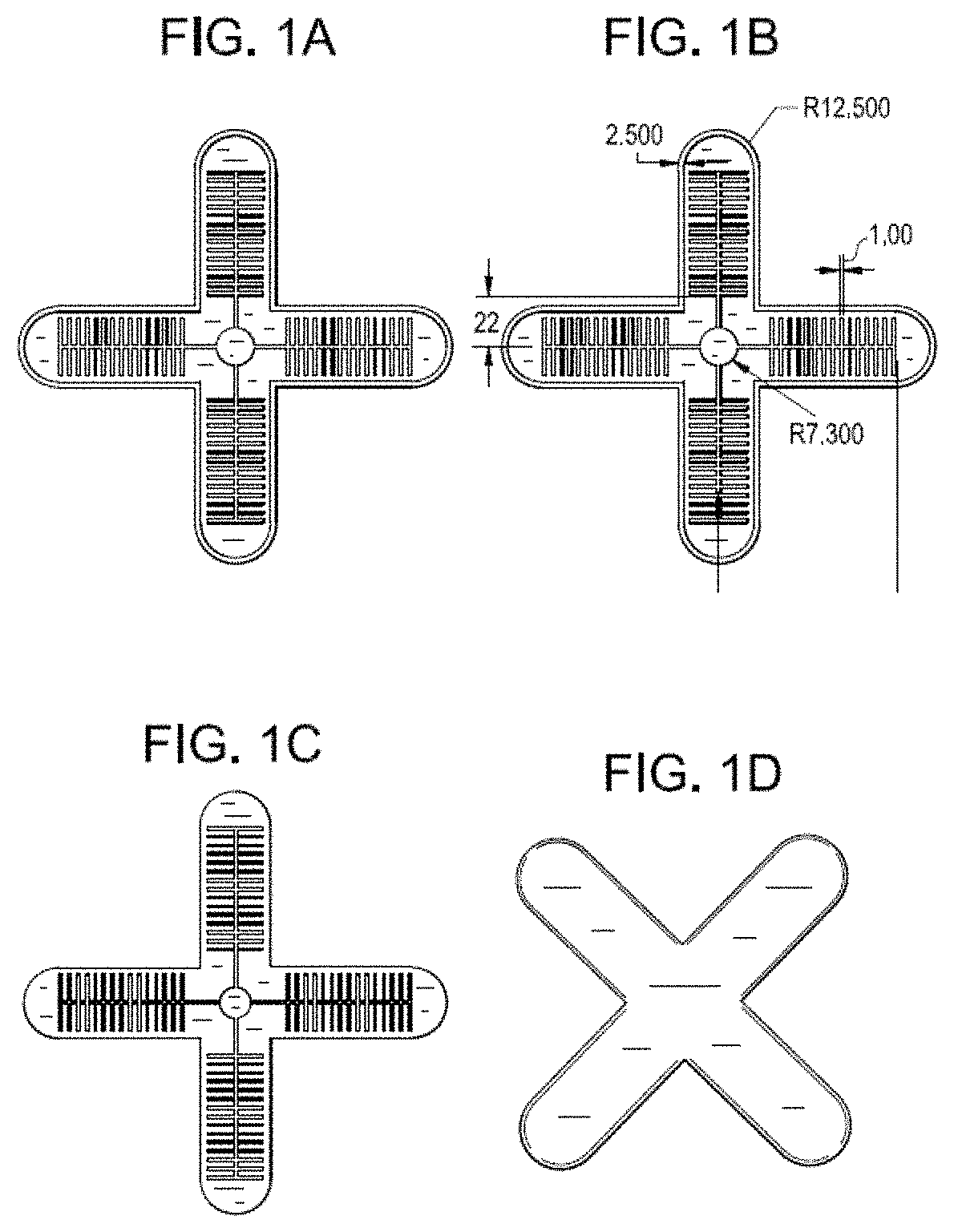
Soft robotic gripper with hybrid structure and grasping reliability
ActiveUS20200298420A1Robust structureMaintaining inherent complianceProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsAnatomySilicon rubber
A robotic end effector and method for use thereof are provided. The robotic end effector can include a rigid base structure (230), a plurality of rigid proximal phalanges (210) connected to the rigid base structure (230), a plurality of rigid distal phalanges (200) connected to the proximal phalanges (210) respectively, and a plurality of bellows (250), wherein one end of a proximal phalange (210) is connected to one end of the base structure (230) by a bellows (250), wherein one end of a distal phalange (200) is connected to a proximal phalange (210) by a bellows (250), and wherein a portion of the base structure (230), each proximal phalange (210), and each distal phalange (200) are covered in silicone rubber. It can achieve a high output force to input pressure ratio, and cost efficiently.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Soft robotic assistive gripping device
ActiveUS11027436B2Easy to controlEasy to removeProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationChronic disability
This invention is directed to offer a customizable, cost effective, and comfortable soft gripping solution for patients with chronic disabilities, such as diabetic neuropathy, allowing the patients to function independently and perform routine daily tasks. A soft robotic gripper has been developed with one or more inflatable systems actuated by aft to assist a user to grip an object. The main body of the gripper bends with air actuation while the fingertip actuation helps functionality in the extremities. The gripper is further enhanced by adding sensors that integrate feedback for sensitivity to touch, conformability, and grip ability. The modular design modifications allow for gripper adjustments as the disease progresses or rescinds. The gripper also works as a training aid for routine physical therapy exercises. Data collected by a microprocessor can also help learn more about these chronic diseases and use artificial intelligence to customize treatment regimens for individual patients.
Owner:BERI ALEKH RAJESH
Positioning device
PendingUS20200191172A1Precise positioningEasy to operateProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsSoftware engineeringSoft Robotic
A positioning device for positioning and using a tool within a cavity having a cavity wall. The device comprises a flexible deployment device / arm carrying the tool. The deployment device / arm further comprises a soft robotics fixturing element adjustable between a contracted deployment configuration during positioning of the tool to an expanded bracing configuration for abutment with the cavity wall during use of the tool.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Soft biomimetic legged robot
ActiveUS11377162B2Improve rigidityProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsSimulationLegged robot
A soft biomimetic legged robot is provided in the present invention, including a plurality of soft robotic arms. The soft robotic arms include a plurality of motion units, and each of the motion units includes one or more of a twist module, an extension module, a contraction, and a bending module. The plurality of motion units is combined to achieve a full-posture motion of the soft robotic arms. By using soft robotic arms composed of different motion units, the soft biomimetic legged robot of the present invention can not only realize the underwater swimming and crawling, but the crawling on land or slopes, thereby adapting to more complicated environments and achieving richer functions. The motion posture is not limited to a single bending, twisting, extension, and shortening. The soft robotic arm can achieve full-posture movements, and its motion type is more complete.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
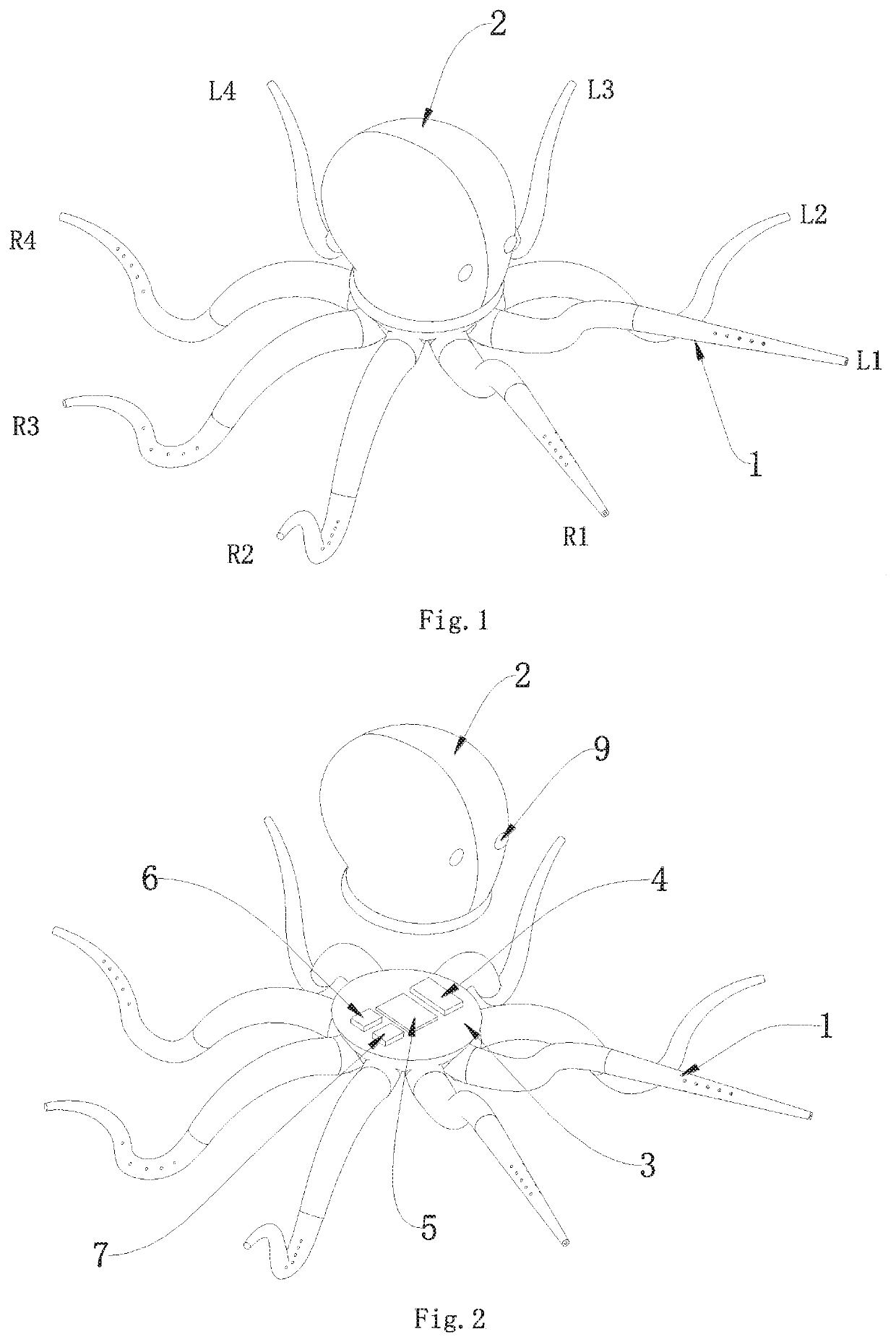
Microrobotic tentacles with spiral bending capability based on shape-engineered elastomeric microtubes and methods of manufacturing same
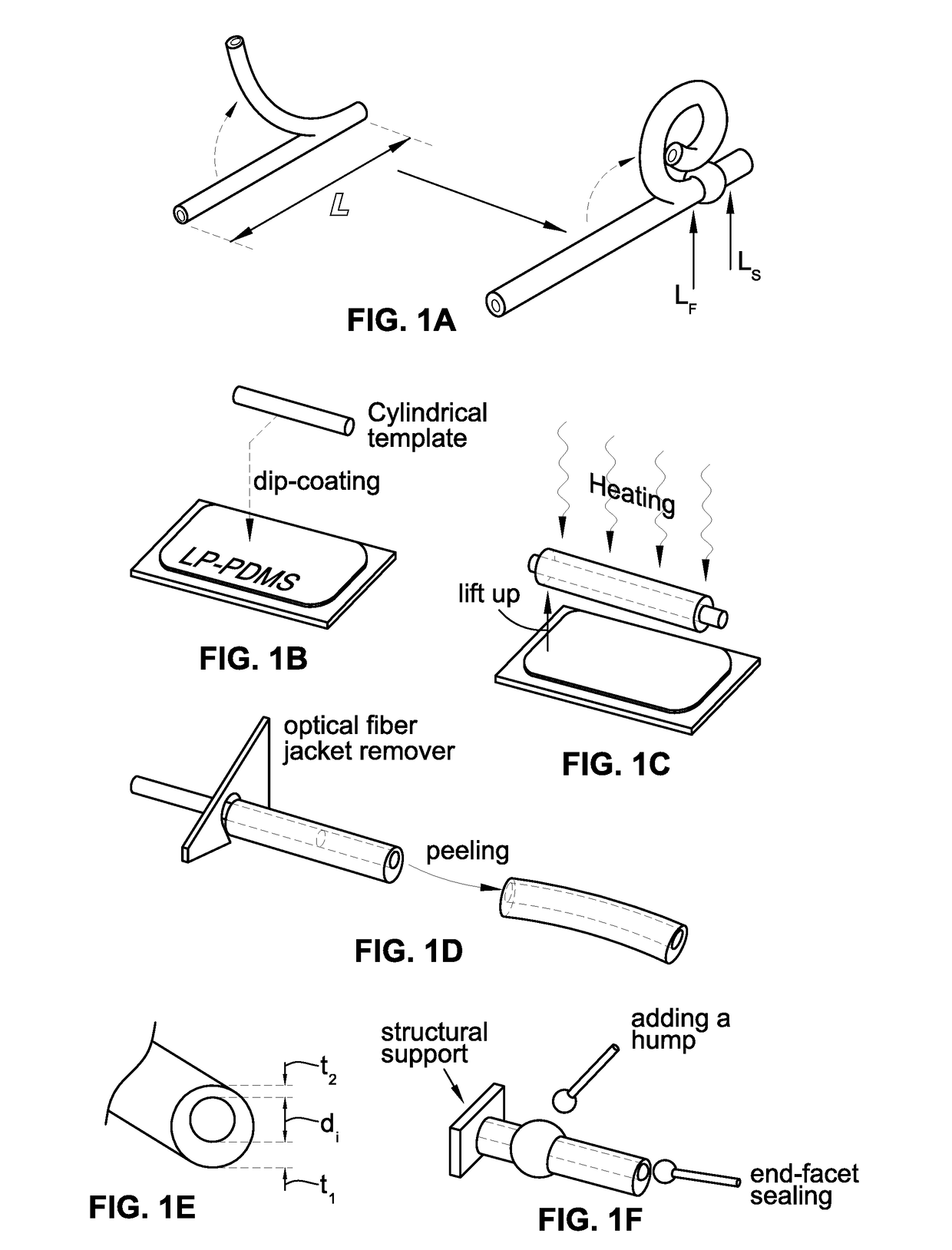
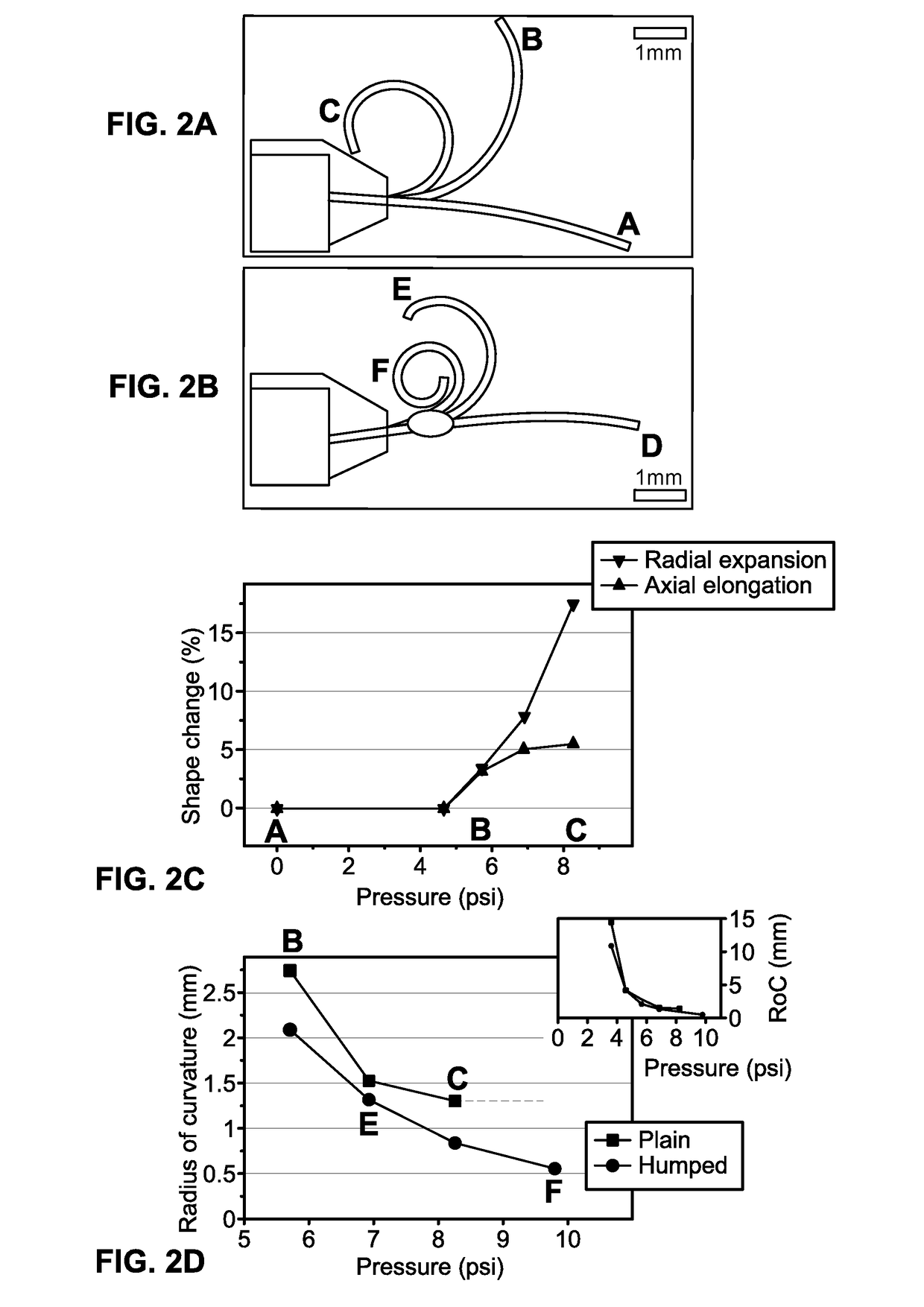
Elastomer-based soft-robotic micro-tentacles capable of winding around and holding microscale objects and methods of fabricating same are provided. To realize the thin, highly deformable microtubes, a fabrication technique based on in situ thermal solidification of PDMS dip-coated around a cylindrical template and direct peeling of the cured structure is presented. This process is capable to asymmetrize the microtube's cross-sectional shape and enable the microtube to bend up to a single turn. To amplify the bending into a life-like, multi-turn spiraling motion, a semi-analytical model to shape-engineer the microtube and turn it into a micro-tentacle was produced. As a result, a hump is added to the microtube to enable the multi-turn spiraling motion.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Ultrasound transducer holder
ActiveUS10987083B2Programme-controlled manipulatorOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic imagingComputer vision
Described herein are devices and methods useful in automating ultrasound imaging. The device include a base coupled with soft robotics, which may be attached to an ultrasound transducer probe in order to robotically manipulate the probe to perform an ultrasound scan. The device has an adjustable structure configured to hold the probe on a walking soft robot. The device can be configured to be attached to, or worn by, the patient. With soft robotic actuation and locomotion, the holder can move and position the probe during a real time ultrasound scanning procedure. Furthermore, the holder may be equipped with sensors to sense and map pressure and location. The position of the holder can be robotically monitored and controlled so as to achieve consistency and reproducibility between ultrasound scans. Due to the wearable nature of the holder, the scans may be conducted while the patient is in motion, thereby providing a portable solution for ultrasonic imaging. The holder is cost effective and may be used in conjunction with various ultrasound probes.
Owner:BERI SERENA
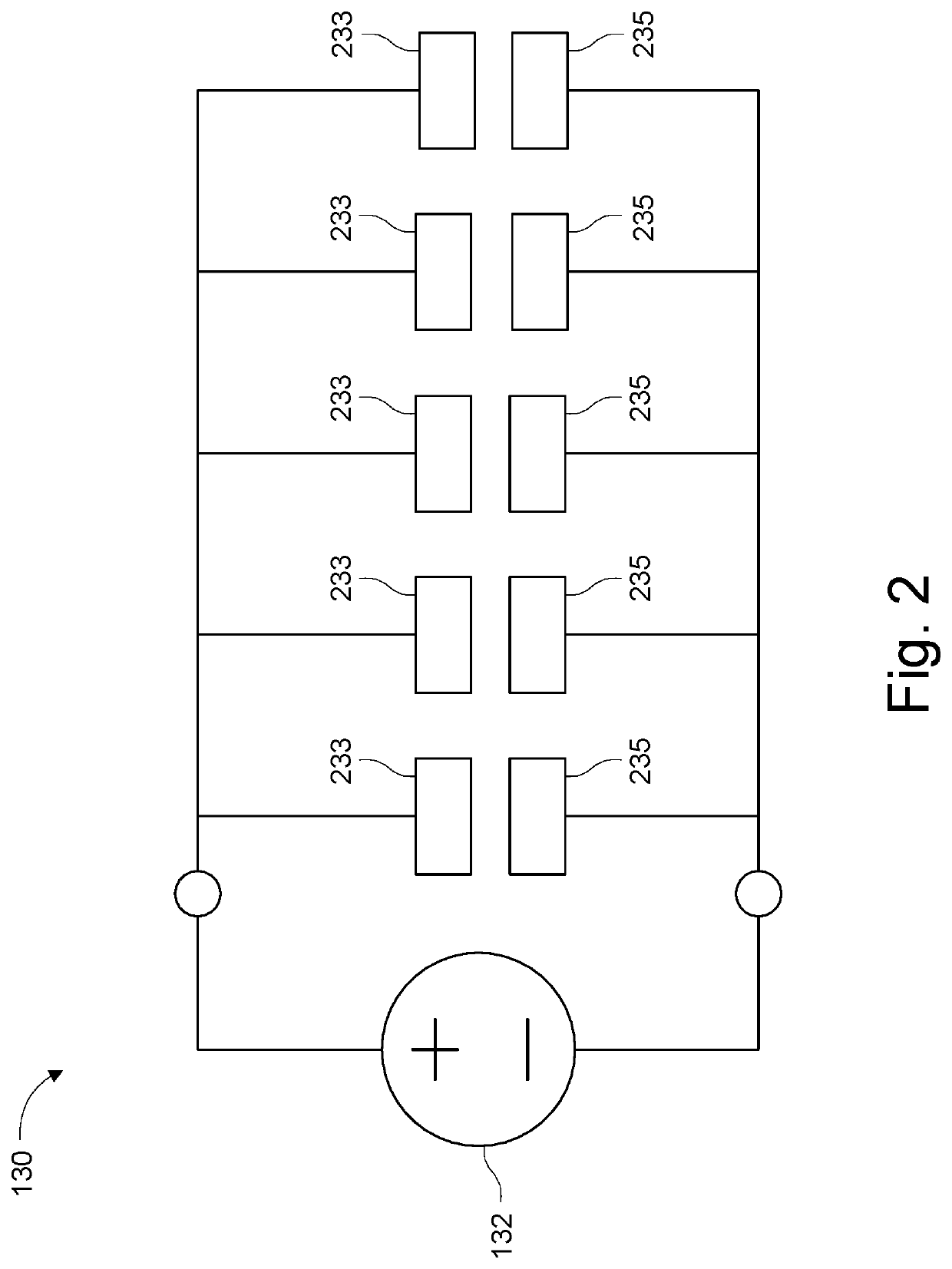
Self-contained robotic gripper system
Exemplary embodiments relate to improvements in soft robotic systems that permit a soft robotic end effector to be a self-contained system, without reliance on a tether to deliver inflation fluid to the actuator(s) of the end effector. According to some embodiments, a robotic system may be provided including a soft actuator and a hub. The body of the hub may include an integrated pressure source configured to supply inflation fluid through the actuator interface to the soft actuator. The pressure source may be, for example, a compressor (such as a twin- head compressor) or a reaction chamber configured to vaporize a fuel to create a high- temperature pressurized gas and deliver the pressurized gas to the actuator One or more accumulators may receive inflation fluid (or a partial vacuum) from the compressor over time, and store the inflation fluid under pressure, thus allowing actuation over a relatively short time period.
Owner:SOFT ROBOTICS
Soft conformal laparoscopic instrument
ActiveUS10208925B2Easy to operateLess traumaticDiagnosticsGripping headsSurgical operationLess invasive surgery
A soft robotic instrument that is capable of changing its form factor (e.g., expanding and contracting) during use to facilitate minimally invasive surgery. The instrument may be formed wholly or partly of an elastomeric, electrically insulating material for mitigating the risk of injuring tissue and for mitigating the risk of electrical arcing during electrosurgery.
Owner:SOFT ROBOTICS
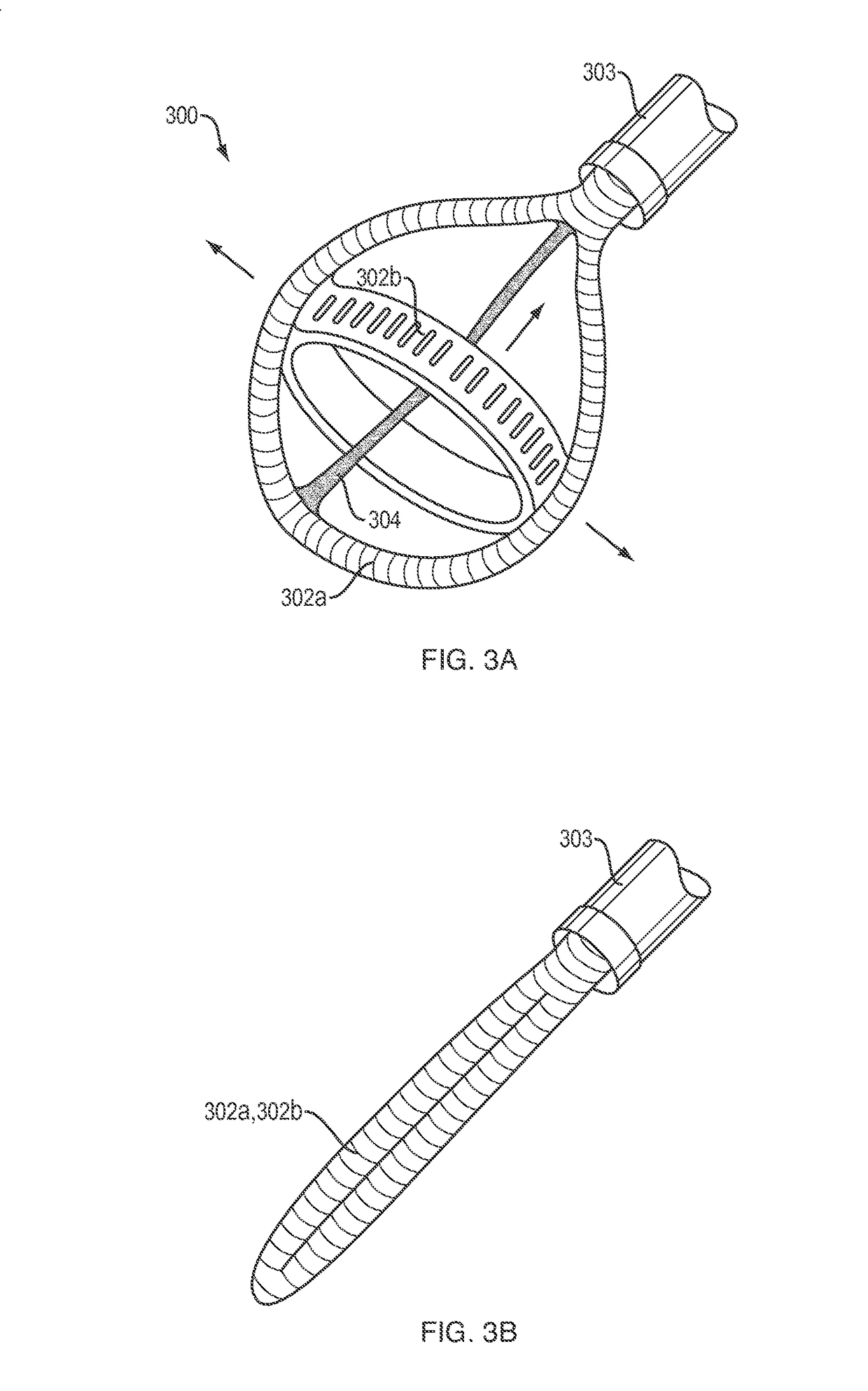
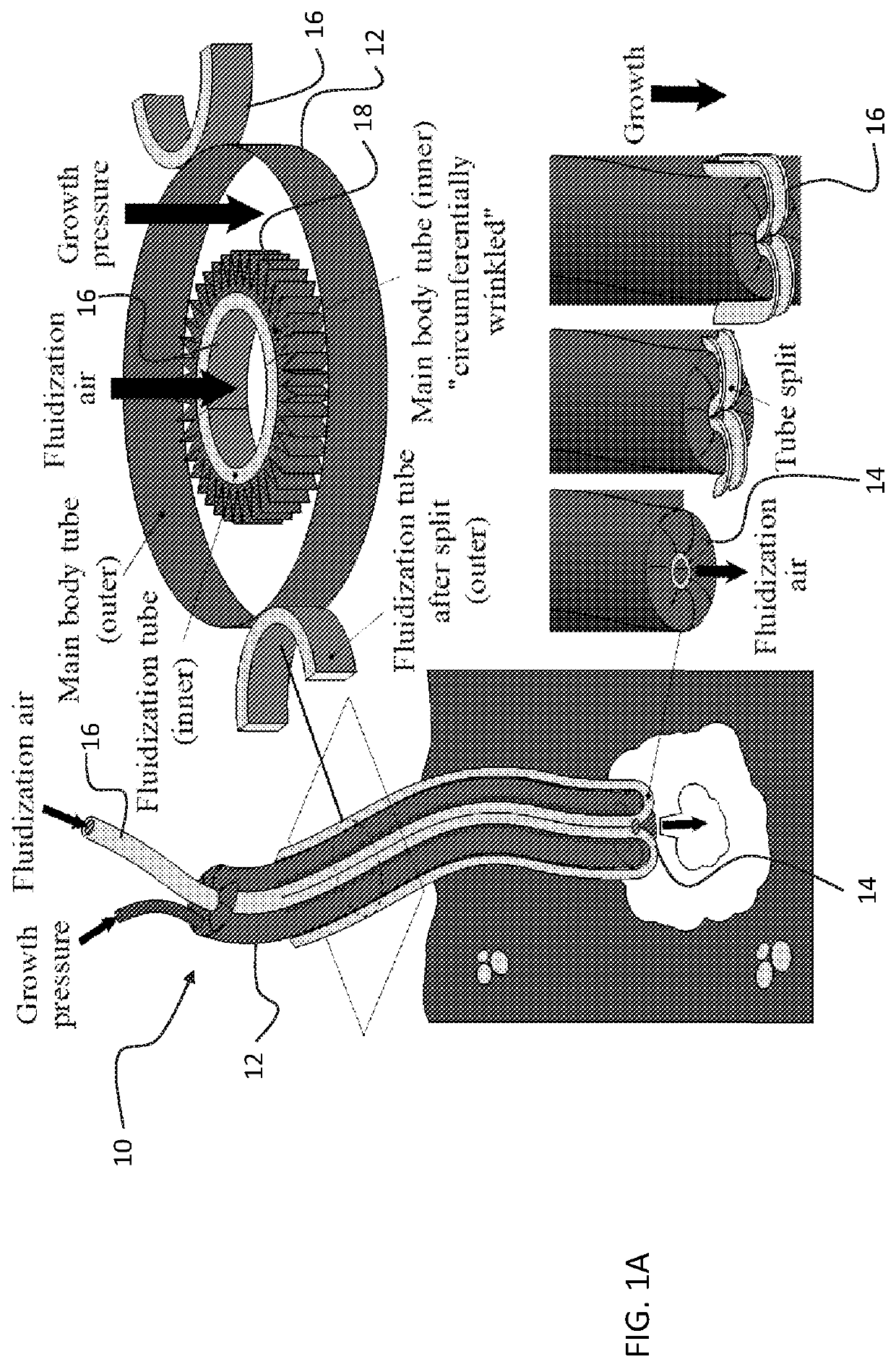
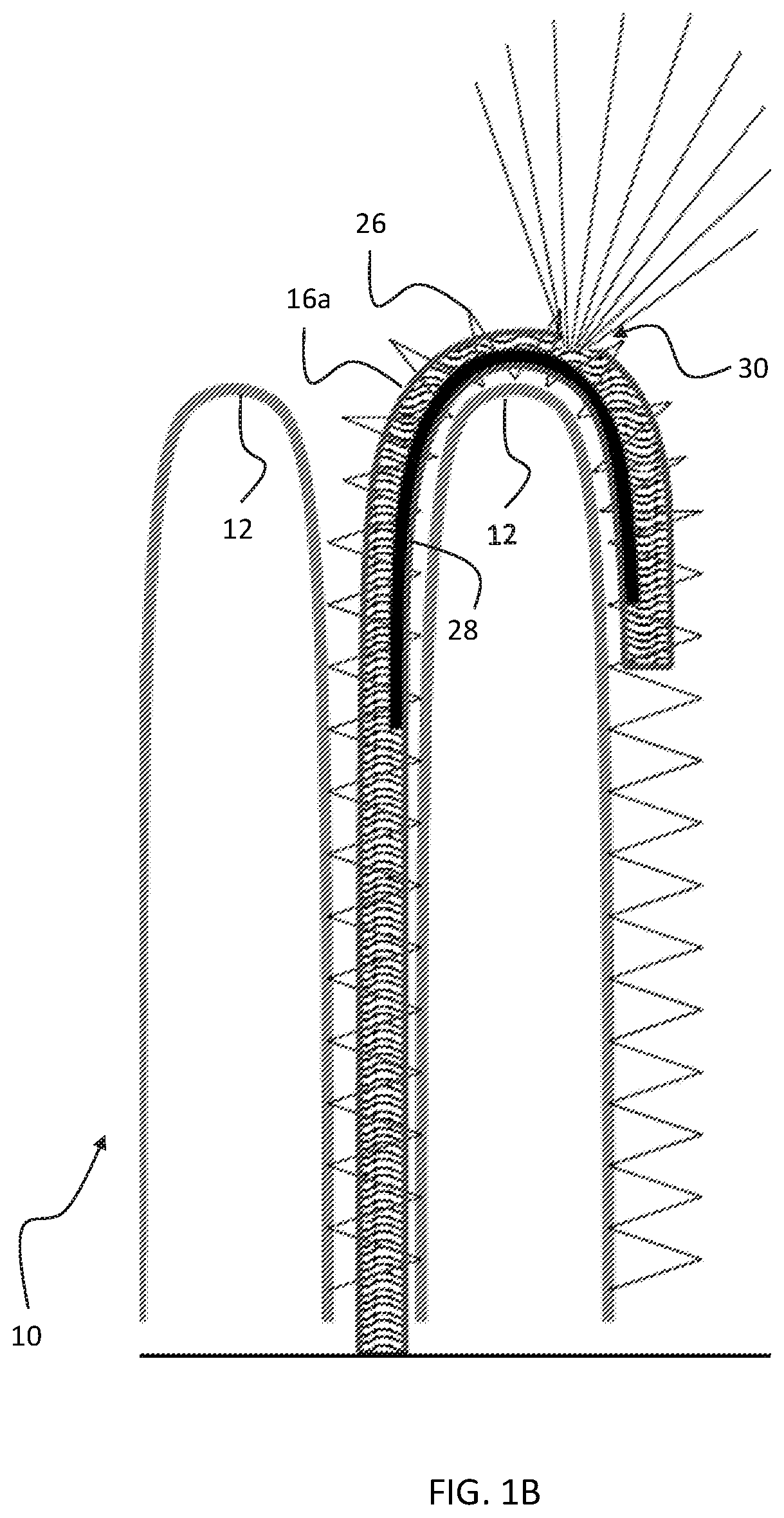
Soft robotic device with fluid emission for burrowing and cleaning
ActiveUS20210354289A1Programme-controlled manipulatorDrilling without earth removalSoft RoboticMechanical engineering
A soft robot includes a main body configured as a tube inverted back inside itself to define a pressure channel, such that when the channel is pressurized, the main body everts, and inverted material everts and passes out of a tip at a distal end of the main body. A fluidization tube for passing air or other fluid through a core of the main body in the fluidization tube, wherein the fluidization tube engages the main body such that the fluidization tube is ejected as the distal end as the main body everts and joins part of the side of the main body as the main body everts and extends its distal tip.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
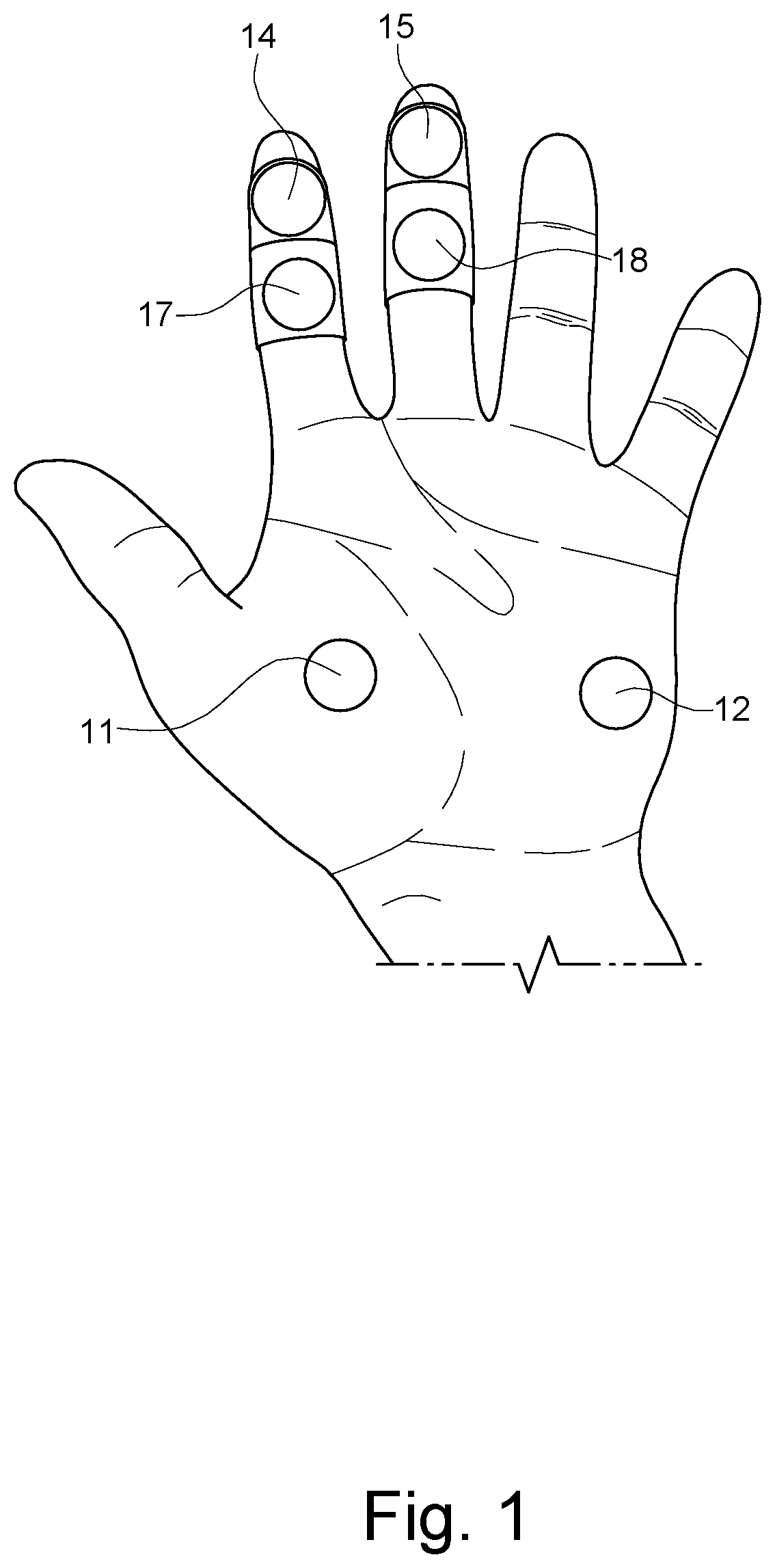
Hybrid interface for simultaneous biosensing and user input
ActiveUS20220121285A1Easy and seamless data collectionEasy data collectionInput/output for user-computer interactionPsychotechnic devicesPattern recognitionEngineering
Dynamically adjustable EDA measurement device may include: a dynamically formable base comprising a soft robotics material, wherein the dynamically formable base comprises a formable surface configured to be dynamically formed in response to input signals; and an EDA sensing layer affixed to the formable surface of the dynamically formable base, the EDA sensing layer comprising a plurality of electrodes arranged on a flexible substrate and configured to be connected to a power supply; wherein, in response to input signals, the formable surface of the dynamically formable base and the EDA sensing layer affixed thereto are reformed into a desired contour.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
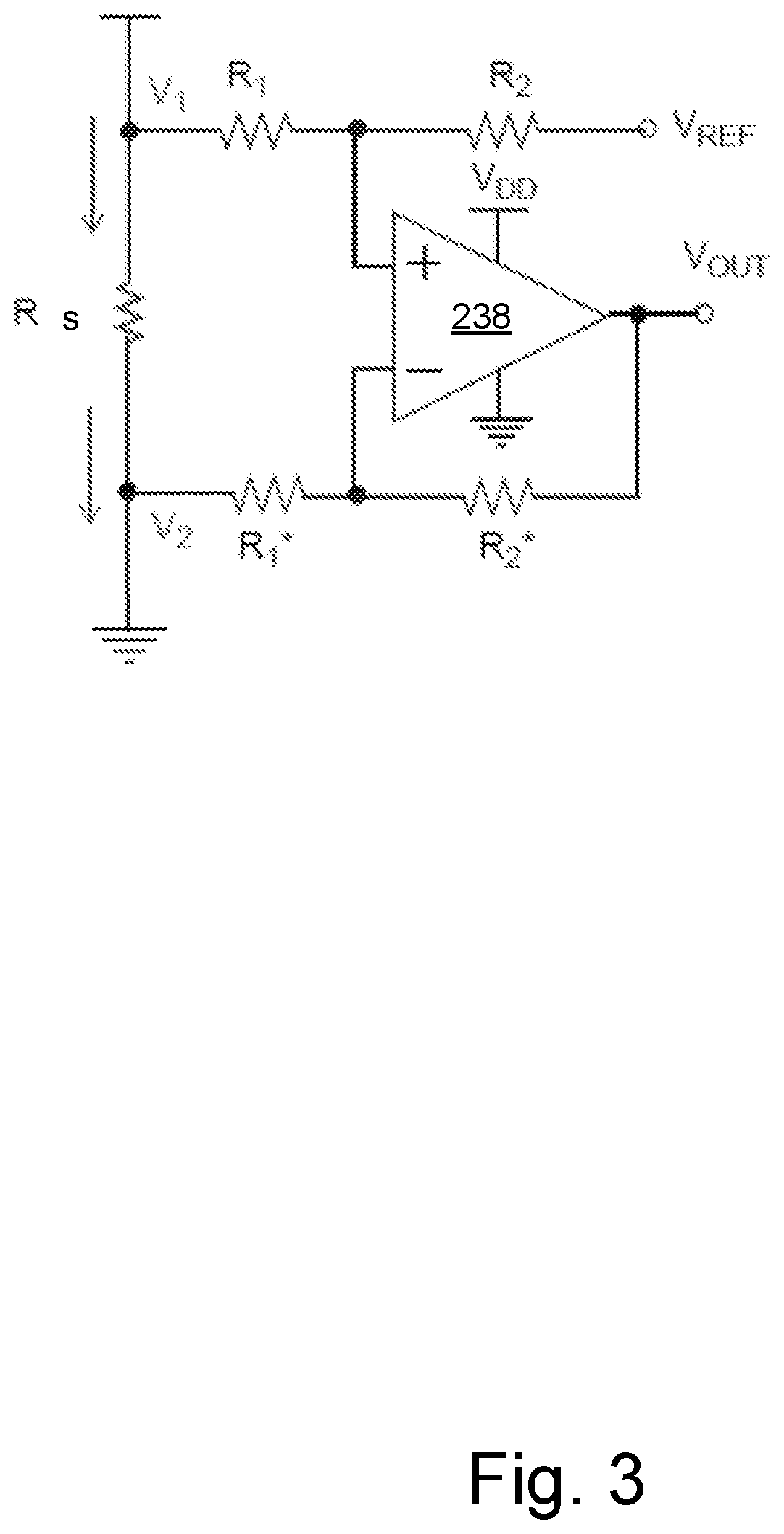
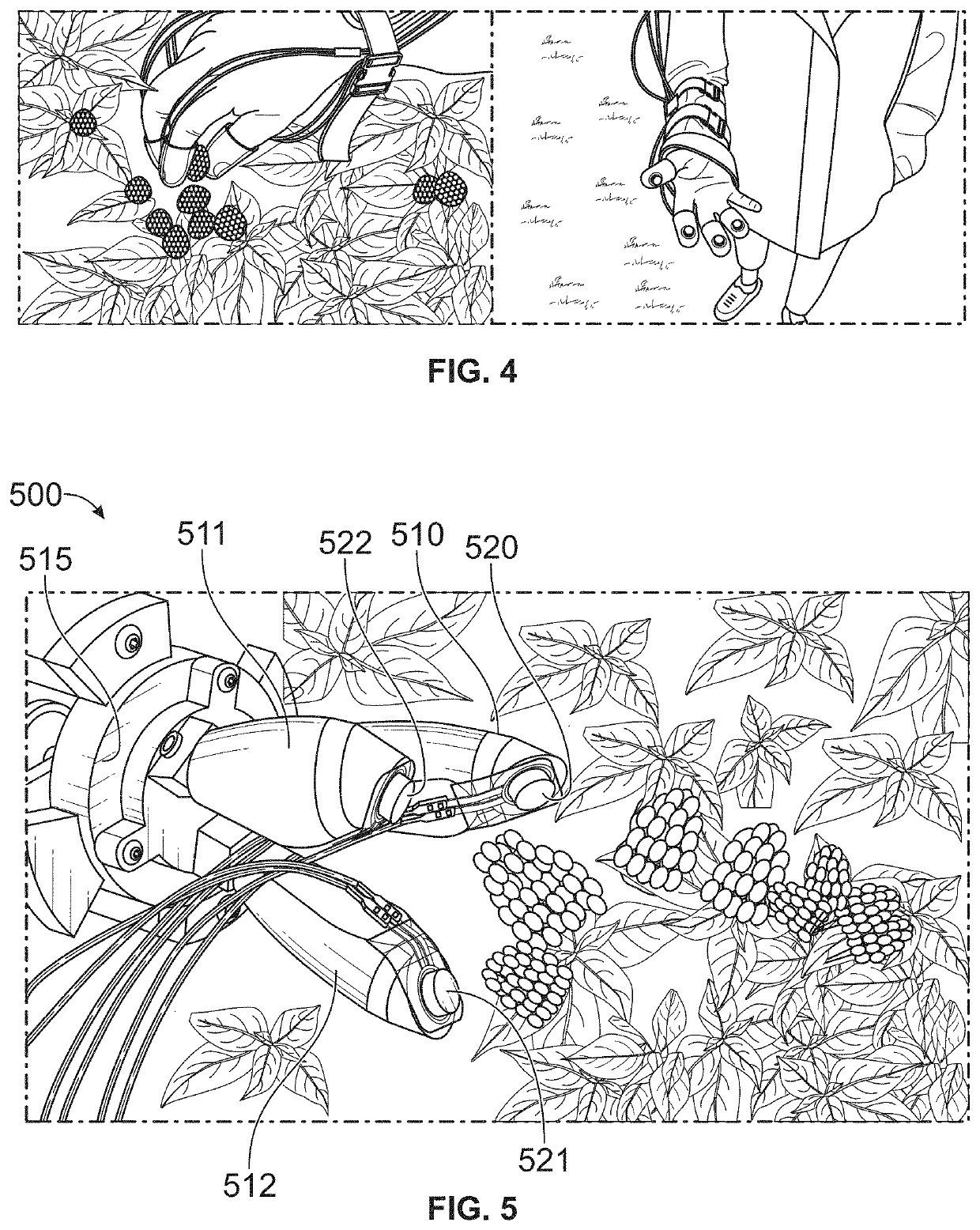
Soft Robotic Gripper for Berry Harvesting
PendingUS20220142050A1Reduce maintenanceAccurate placementProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorStructural engineeringSoft Robotic
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Soft robotic tools with sequentially underactuated magnetorheological fluidic joints
InactiveUS20210086351A1Programme-controlled manipulatorMagnetic materialsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationMagnetorheological fluid
A soft robotic tool may include a plurality of rigid links, a plurality of magnetorheological fluid soft joints, and a plurality of tendons. The rigid links may be disposed in series. Each magnetorheological fluid soft joint may be disposed between a pair of the rigid links. Each magnetorheological fluid soft joint may include a capsule containing a magnetorheological fluid, and an inductive coil disposed around the capsule. The tendons may extend along a length of the soft robotic tool. Each tendon may be attached to each of the rigid links.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
Probe insertion system
Systems for inserting and orienting a soft robotic probe into an apparatus and capturing images and methods of using the same are generally disclosed. For example, the system includes a cable, an actuation assembly, and a camera at the tip of the probe. The cable includes an adjustable sheath at an exterior of the cable defined around a probe centerline extending the length of the probe. The adjustable sheath extends and contracts the cable between a first length and a second length different from the first length and is defined within the adjustable sheath. The actuation assembly extends or contracts the cable between the first length and the second length and further adjusts an orientation of the cable, an orientation of the tip of the probe, or both along at least one axis. The camera captures images at least partially around a circumferential direction relative to a camera centerline.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
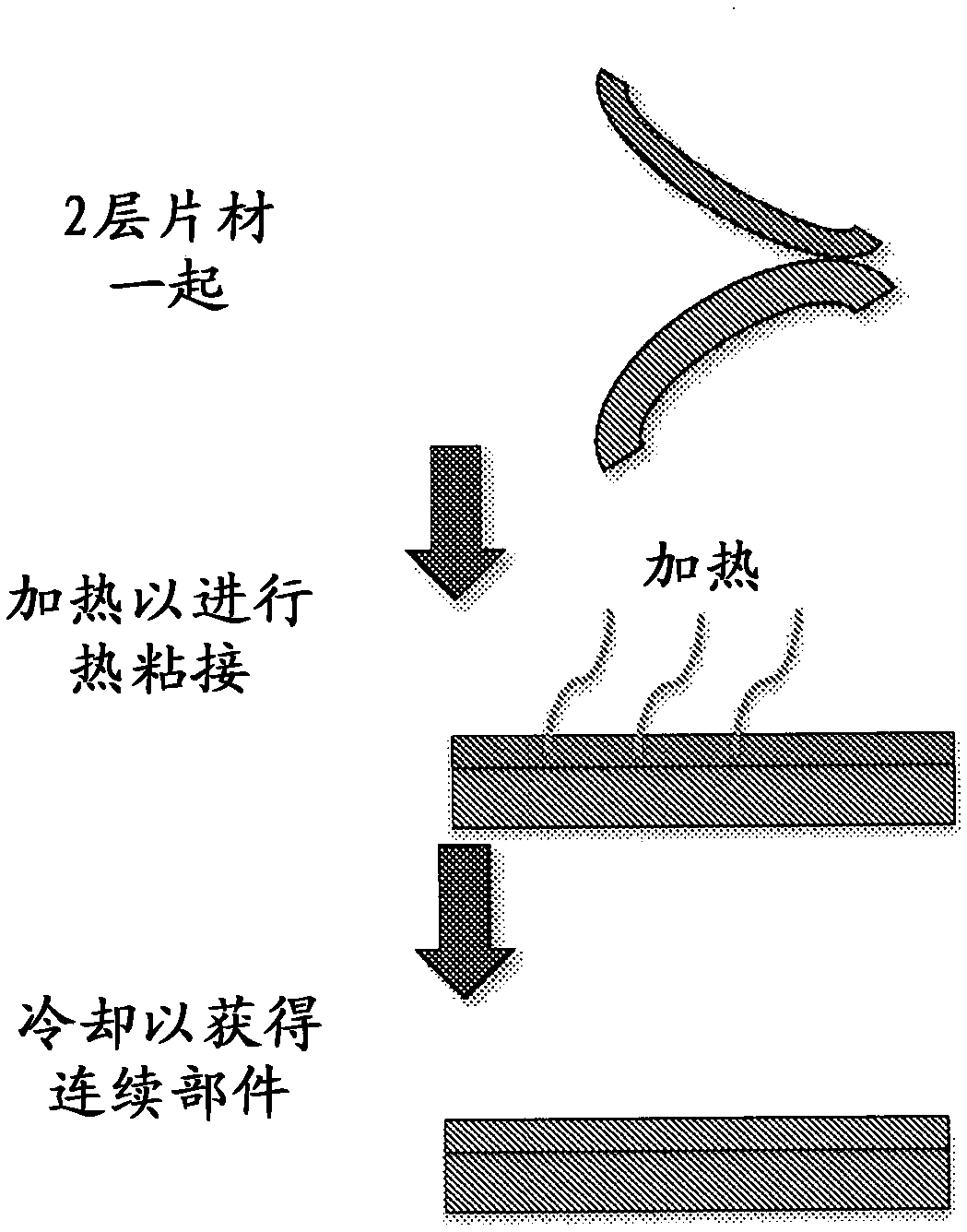
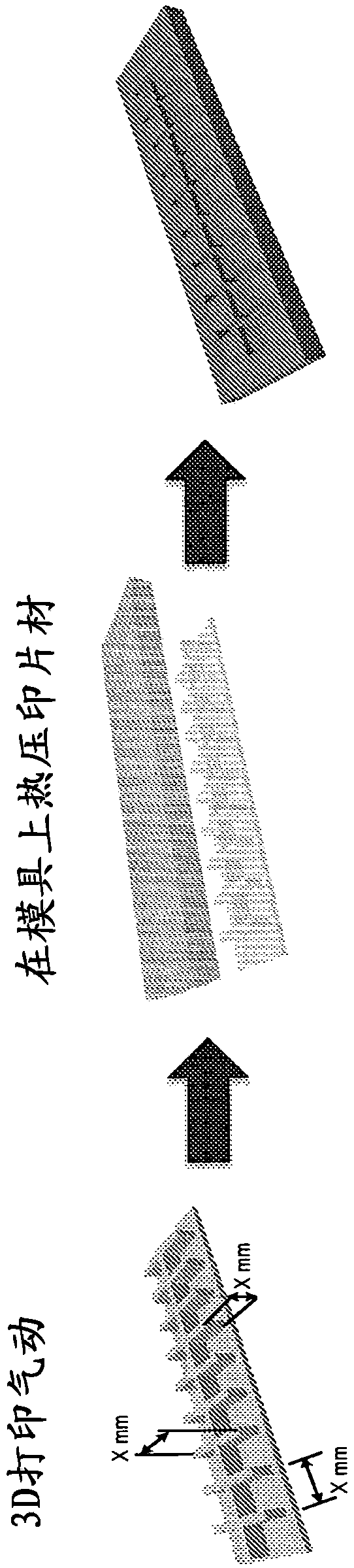
High Productivity Manufacturing of Soft Machines
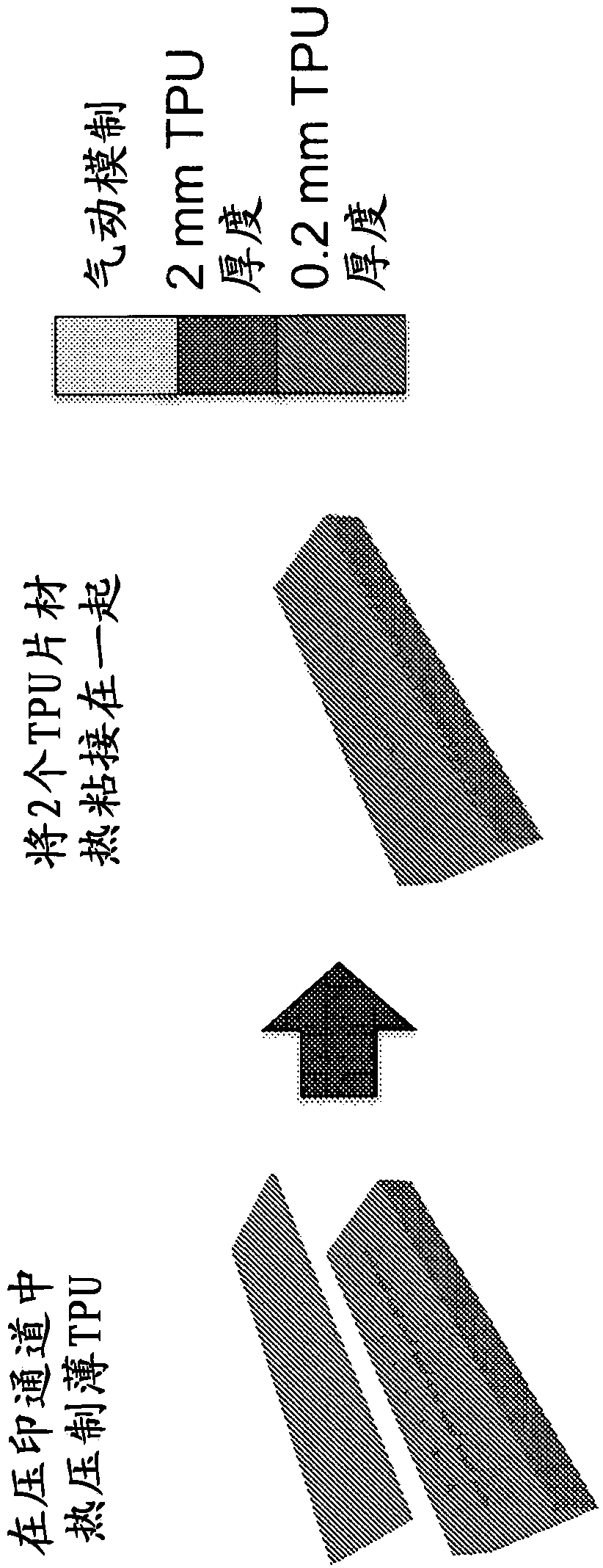
The present invention relates to a soft robotic device comprising at least a first thermoplastic layer and a second thermoplastic layer, wherein at least one layer is composed of an extensible thermoplastic material; at least one layer is a non-extensible layer; and at least one layer comprises an aerodynamic network, Wherein the pneumatic network is configured to be in fluid contact with a pressurized source, wherein the first thermoplastic layer and the second thermoplastic layer are thermally bonded to each other.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Deep-sea soft robotic fish propelled by tail fin
ActiveCN114475986AImprove concealmentExcellent deep sea pressure adaptabilityPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeUnderwater vesselsFisherySilica gel
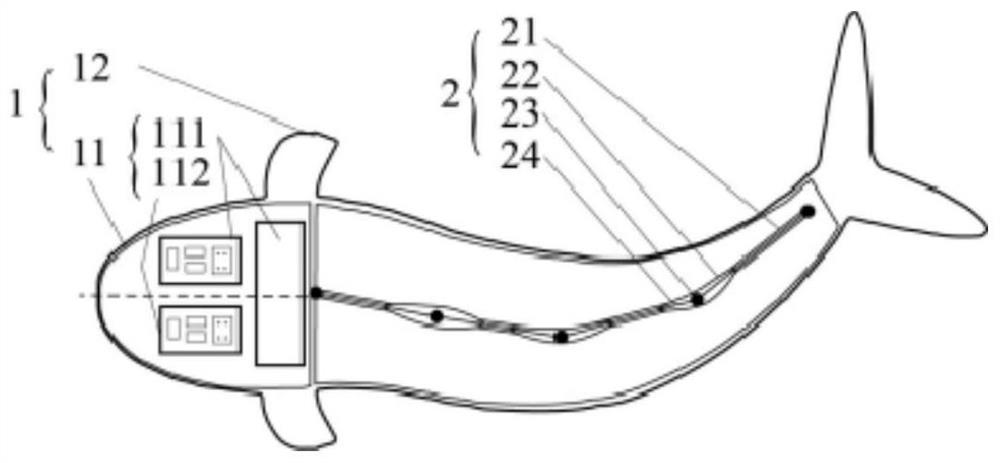
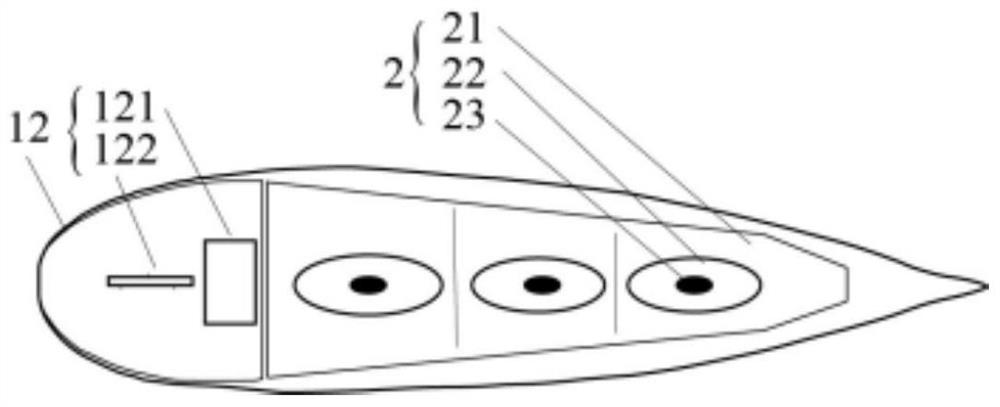
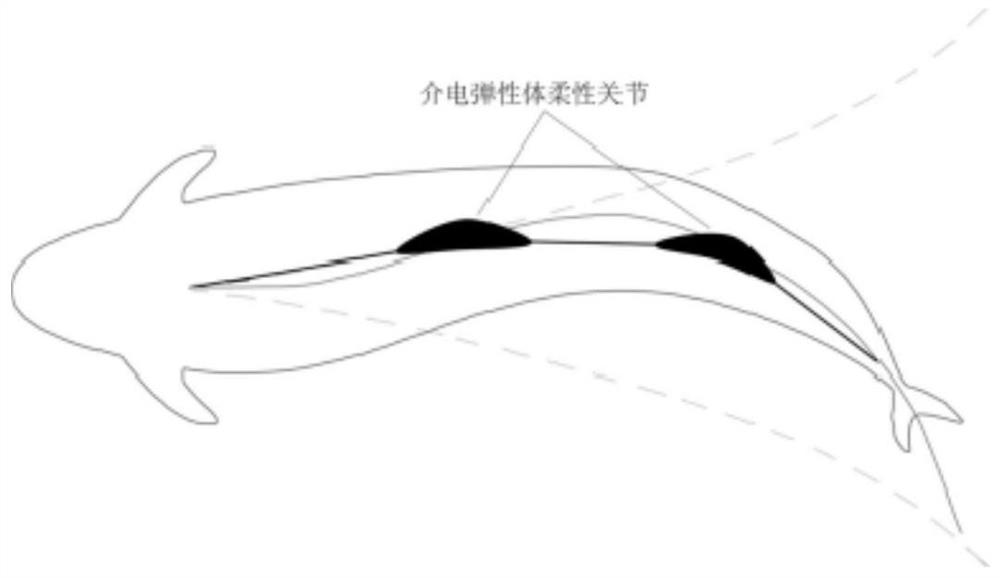
The invention provides a tail fin propelled deep-sea soft robotic fish. The tail fin propelled deep-sea soft robotic fish comprises a bionic fish head and a trunk / tail fin, the bionic fish head is connected with the trunk / tail fin, the bionic fish head comprises a cabin body and side fins, the cabin body is arranged in the bionic fish head and is arranged in the middle, and the cabin body comprises an energy module and a control module; the side fins are symmetrically arranged on the two sides of the bionic fish head, the trunk / tail fin comprises a propelling module, the propelling module is composed of more than two dielectric elastomer flexible joints which are connected in series, and each dielectric elastomer flexible joint comprises a supporting framework, a dielectric elastomer film, a flexible electrode and a wire. The bionic fish head and the trunk / tail fin are connected through silica gel in an integrated pouring mode, so that deep-sea pressure self-adaption of the soft robotic fish is achieved. The deep-sea soft robotic fish propelled by the tail fin has the characteristics of high efficiency, flexibility and high concealment, does not need a hard shell and a pressure compensation device, can realize low-cost deep-sea detection, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com