Patents
Literature
99 results about "Soft Robotic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Soft conformal laparoscopic instrument
ActiveUS20150257839A1Relieve pressureEasy to operateDiagnosticsElectric circuit arrangementsLess invasive surgerySurgical operation
A soft robotic instrument that is capable of changing its form factor (e.g., expanding and contracting) during use to facilitate minimally invasive surgery. The instrument may be formed wholly or partly of an elastomeric, electrically insulating material for mitigating the risk of injuring tissue and for mitigating the risk of electrical arcing during electrosurgery.
Owner:SOFT ROBOTICS
Sensors for soft robots and soft actuators
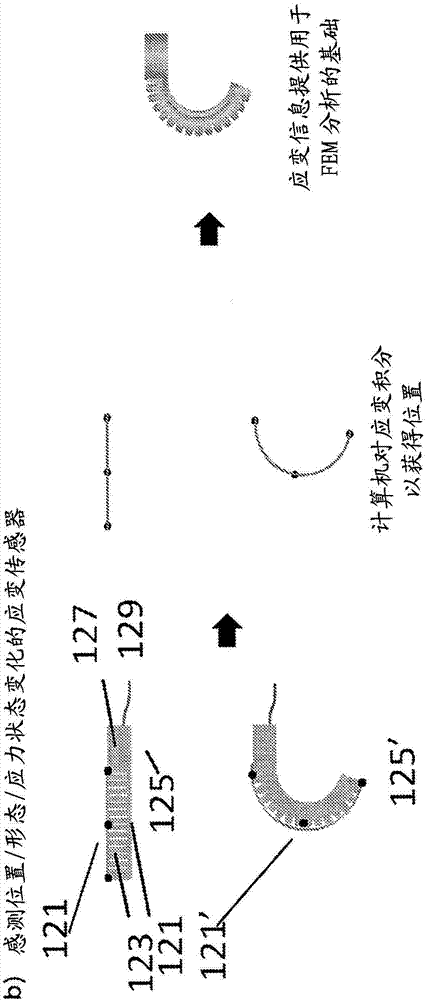
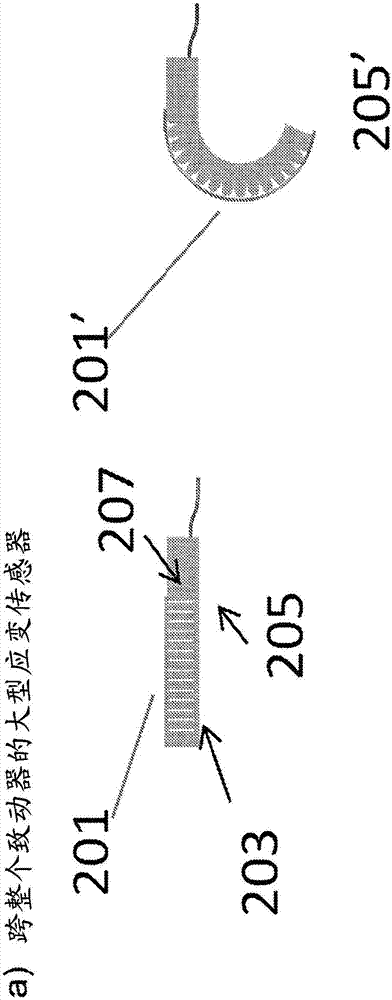
A soft robotic device with one or more sensors is described. The sensor may be embedded in the soft body of the soft robotic device, attached to the soft body of the soft robotic device, or otherwise linked to the soft body of the soft robotic device.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Climbing soft robotics
The present invention relates to a new pneumatic-actuated multifunctional doming actuator. The doming actuator can be used as a doming actuator, which can maintain machine / robotic operation on vertical surfaces without falling. The doming actuators exhibit rapid switchable adhesion / deadhesion on target surfaces upon pressurizing / depressurizing the embedded spiral pneumatic channels. The present invention also relates to novel load-carrying and climbing soft robots using the doming actuators. The soft robots are operable on a wide range of horizontal and vertical surfaces including dry, wet, slippery, smooth, and semi-smooth surfaces. In addition, the doming actuators can be used as a driving actuator for swimming soft robotics and as an actuator for soft grippers.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
Soft robotic assistive gripping device
ActiveUS20180361596A1Easy to controlEasy to removeProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsDiseaseEngineering
This invention is directed to offer a customizable, cost effective, and comfortable soft gripping solution for patients with chronic disabilities, such as diabetic neuropathy, allowing the patients to function independently and perform routine daily tasks. A soft robotic gripper has been developed with one or more inflatable systems actuated by aft to assist a user to grip an object. The main body of the gripper bends with air actuation while the fingertip actuation helps functionality in the extremities. The gripper is further enhanced by adding sensors that integrate feedback for sensitivity to touch, conformability, and grip ability. The modular design modifications allow for gripper adjustments as the disease progresses or rescinds. The gripper also works as a training aid for routine physical therapy exercises. Data collected by a microprocessor can also help learn more about these chronic diseases and use artificial intelligence to customize treatment regimens for individual patients.
Owner:BERI ALEKH RAJESH
3D printing aramid aerogel, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110982111AAdjustable Hierarchical Porous StructurePorosity adjustableAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structures3d printNanofiber
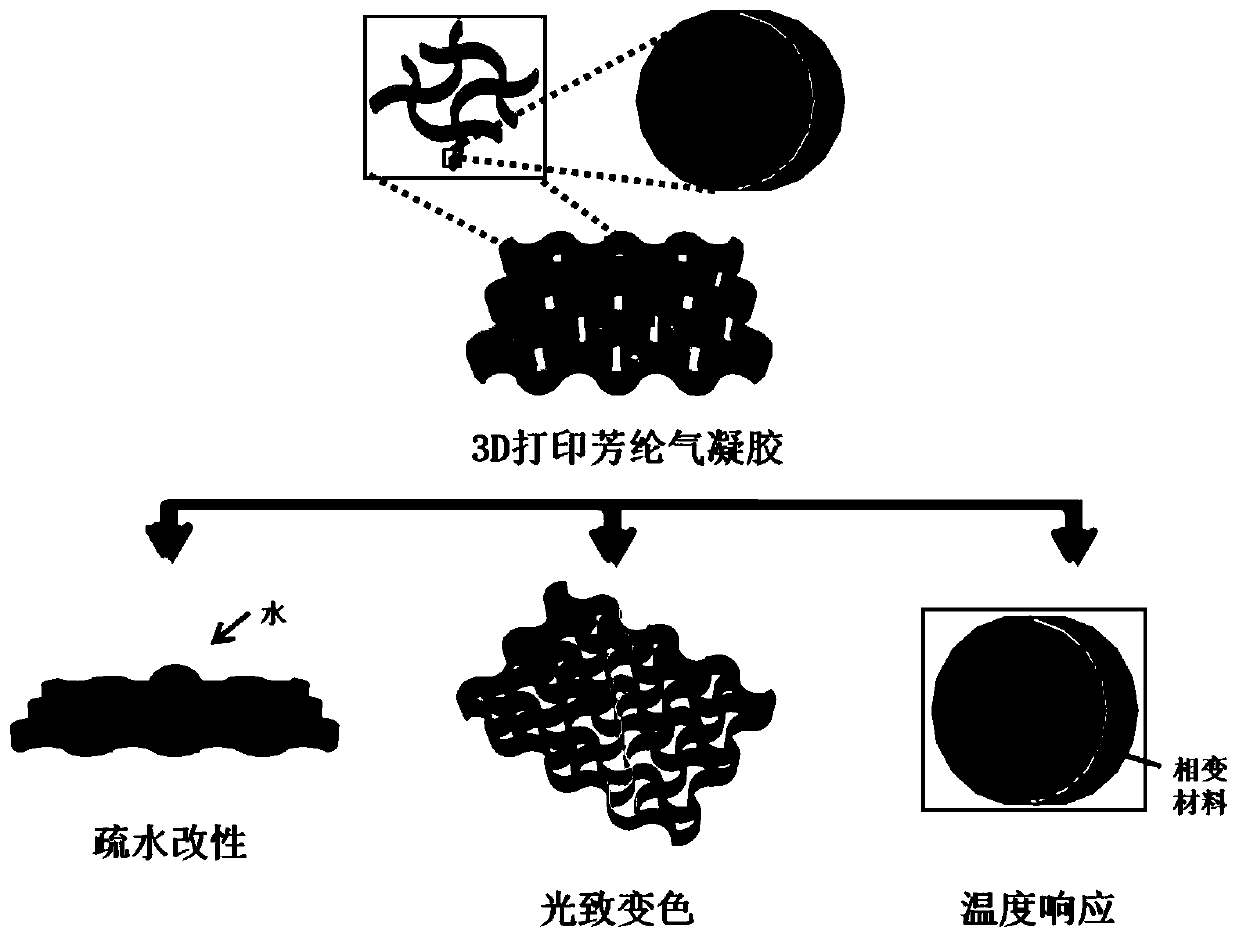
The invention discloses a 3D printing aramid fiber aerogel, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing aramid nanofibers and a solvent to form an aramid nanofiber dispersion; and carrying out sol-gel conversion and drying treatment through a freezing-direct writing forming technology to obtain the 3D printing aramid fiber aerogel. Surface hydrophobic modification and filling modification are respectively carried out on the 3D printing aramid aerogel to respectively obtain a hydrophobic material, a photochromic material and a temperature response material. The preparation method of the 3D printing aramid fiber aerogel has the advantages of wide dispersity, low energy consumption, quick low-temperature response,high printing precision, simple process and short flow, and the obtained 3D aramid aerogel has the advantages of ultralow density, good mechanical properties and structural designability, can be applied to the fields of heat preservation and insulation, catalysis, separation / adsorption, sensing, soft robots and the like, and greatly expands the application range of 3D printing and aramid aerogel.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
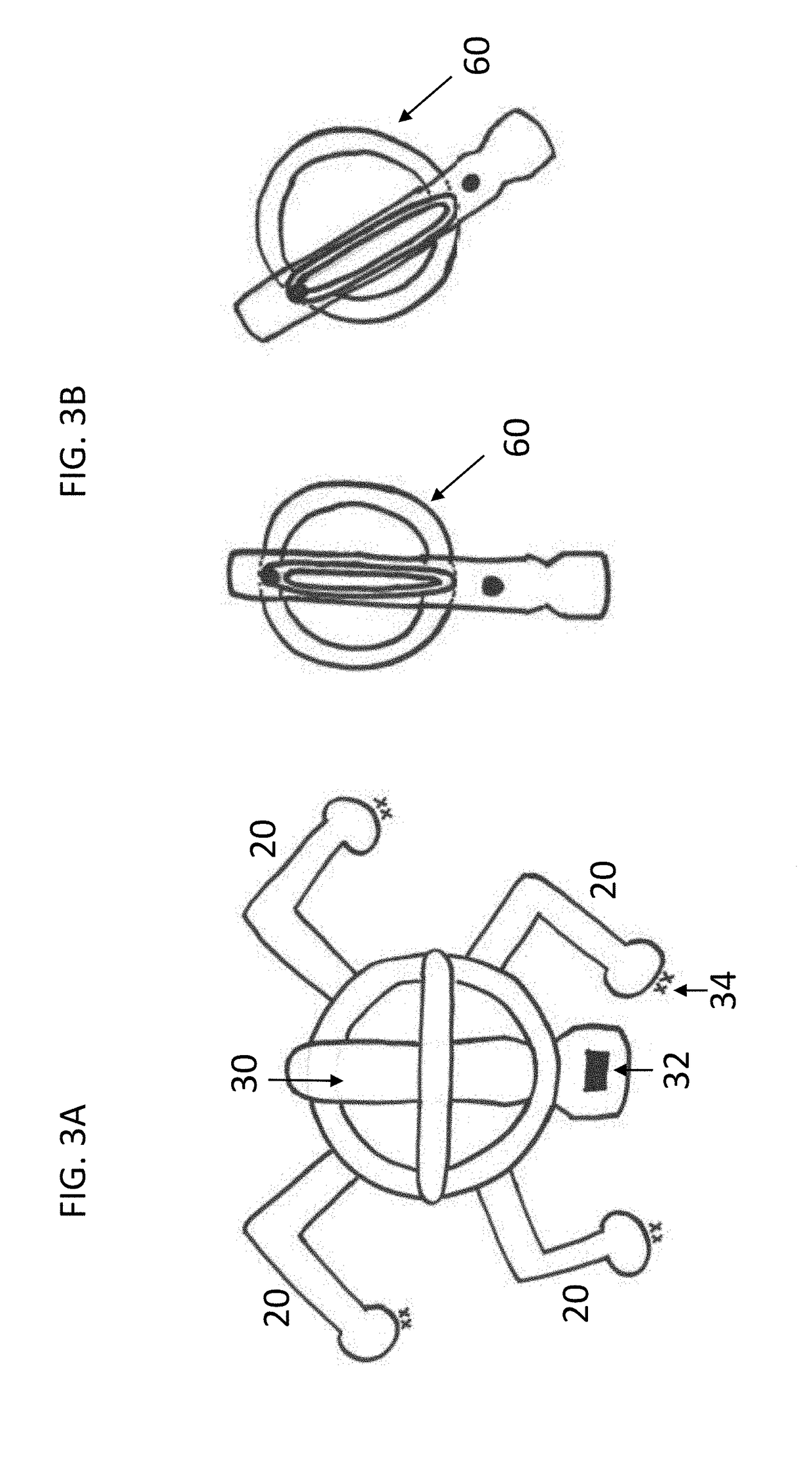
Soft robotic actuator attachment hub and grasper assembly, reinforced actuators, and electroadhesive actuators
A hub assembly for coupling different grasper assemblies including a soft actuator in various configurations to a mechanical robotic components are described. Further described are soft actuators having various reinforcement. Further described are and soft actuators having electroadhesive pads for improved grip, and / or embedded electromagnets for interacting with complementary surfaces on the object being gripped. Still further described are soft actuators having reinforcement mechanisms for reducing or eliminating bowing in a strain limiting layer, or for reinforcing accordion troughs in the soft actuator body.
Owner:SOFT ROBOTICS
Waveguides for use in sensors or displays
Waveguides, such as light guides, made entirely of elastomeric material or with indents on an outer surface are disclosed. These improved waveguides can be used in sensors, soft robotics, or displays. For example, the waveguides can be used in a strain sensor, a curvature sensor, or a force sensor. In an instance, the waveguide can be used in a hand prosthetic. Sensors that use the disclosed waveguides and methods of manufacturing waveguides also are disclosed.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Soft robotic actuators utilizing asymmetric surfaces
InactiveCN107002721ASimplify the modeling processSimplify the design processProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsInternal pressureControl theory
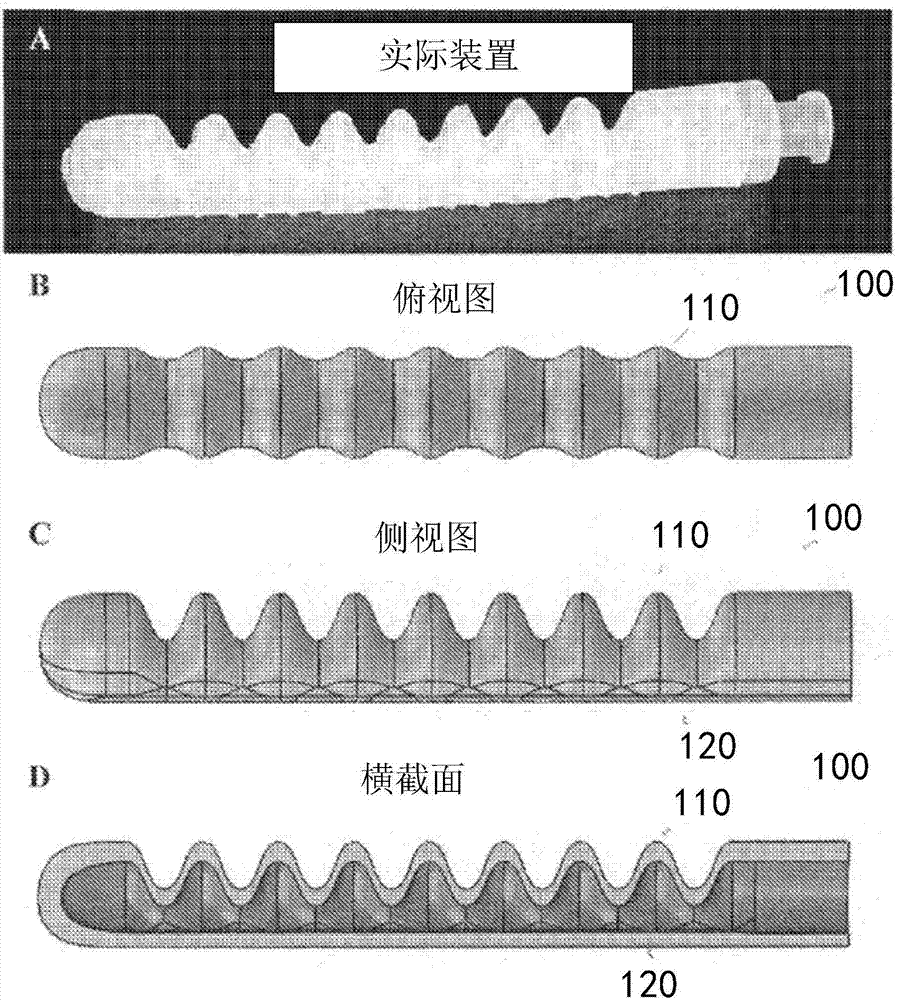
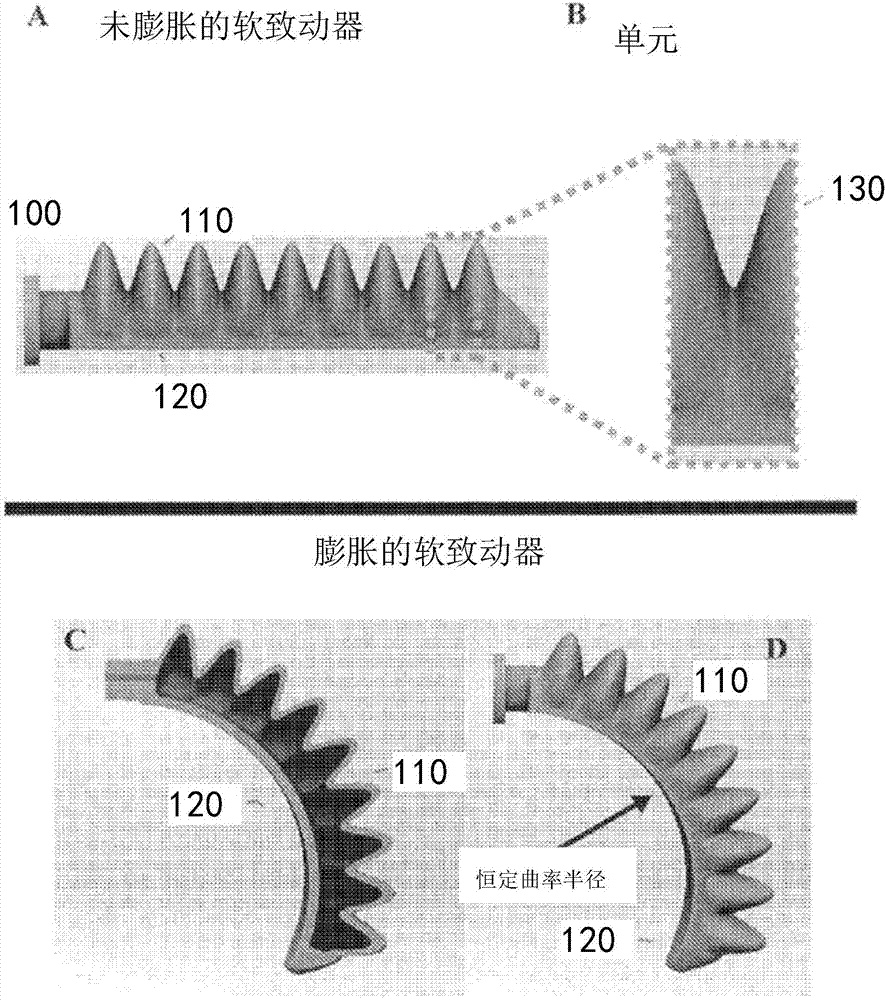
A soft robotic actuator is disclosed. The actuator includes a first portion with a substantially constant profile and a second portion with a regularly varying profile, and bends in a pressure-dependent fashion as the internal pressure within the actuator is increased or decreased. The present invention addresses the needs described above by providing actuators that are configured to perform new fundamental motions through the inclusion of design elements which can be configured, through the manipulation of a relatively short list of parameters, to undergo specific pressure-actuated changes which can be designed using quantitative modeling techniques.
Owner:SOFT ROBOTICS
Soft robotic actuator enhancements
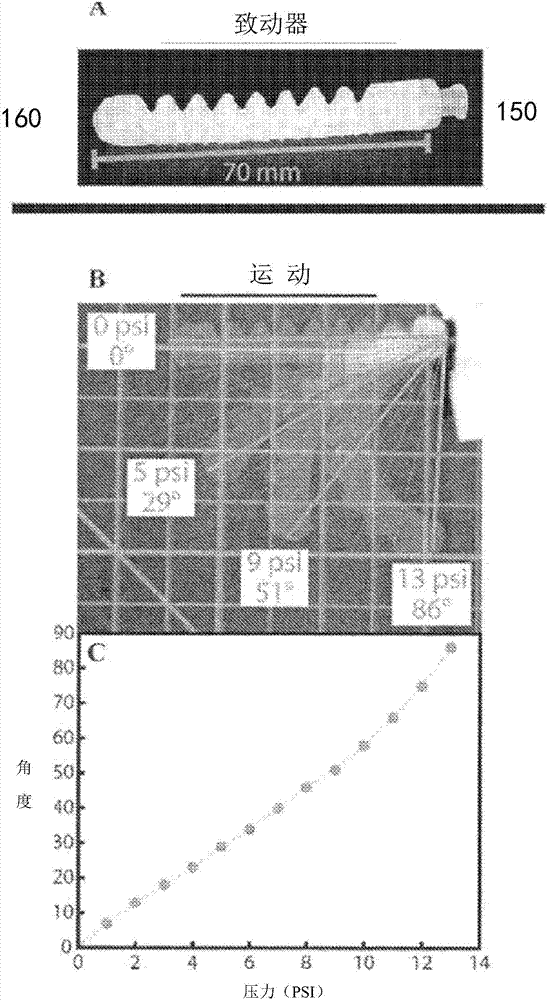
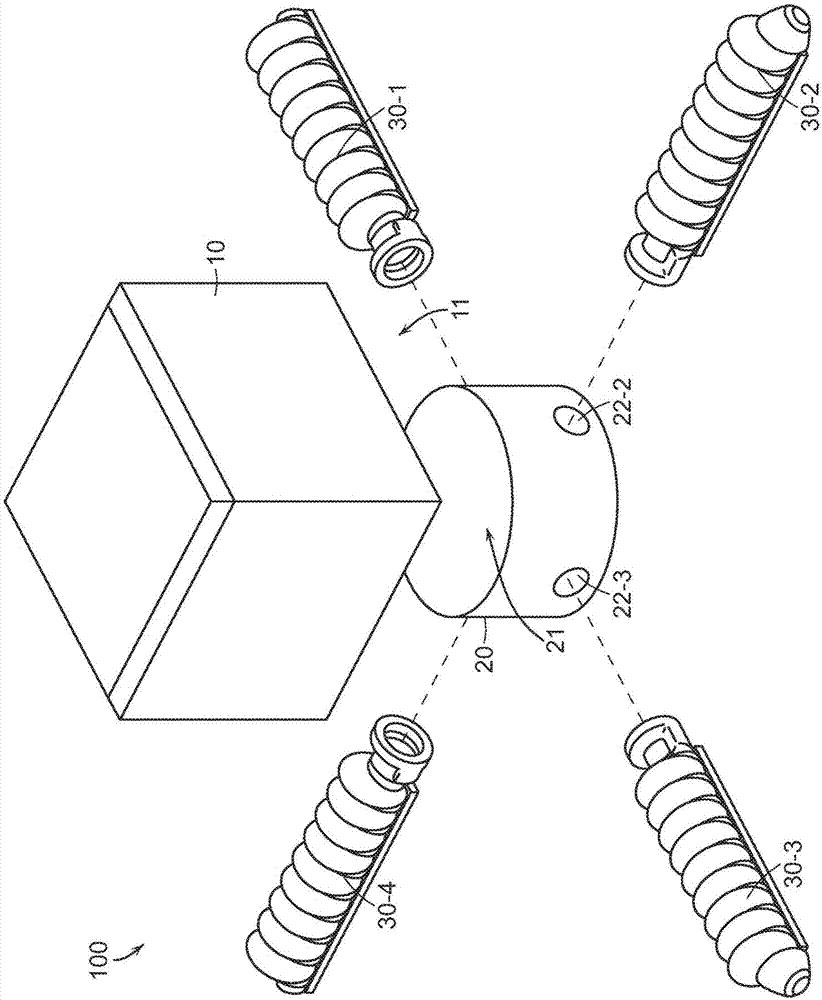
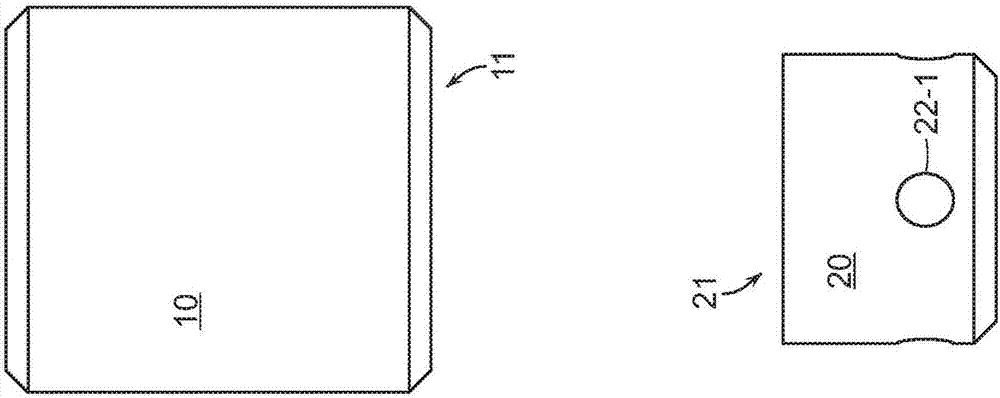
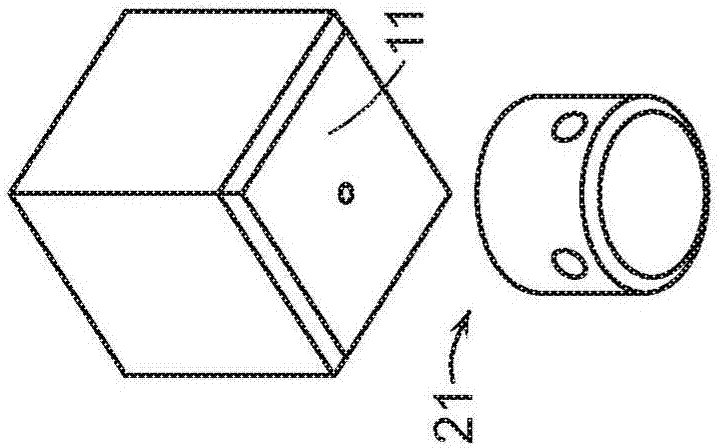
Exemplary embodiments provide enhancements for soft robotic actuators. In some embodiments, angular adjustment systems are provided for varying an angle between an actuator and the hub, or between two actuators. The angular adjustment system may also be used to vary a relative distance or spacing between actuators. According to further embodiments, rigidizing layers are provided for reinforcing one or more portions of an actuator at one or more locations of relatively high strain. According to further embodiments, force amplification structures are provided for increasing an amount of force applied by an actuator to a target. The force amplification structures may serve to shorten the length of the actuator that is subject to bending upon inflation. According to still further embodiments, gripping pads are provided for customizing an actuator's gripping profile to better conform to the surfaces of items to be gripped.
Owner:SOFT ROBOTICS
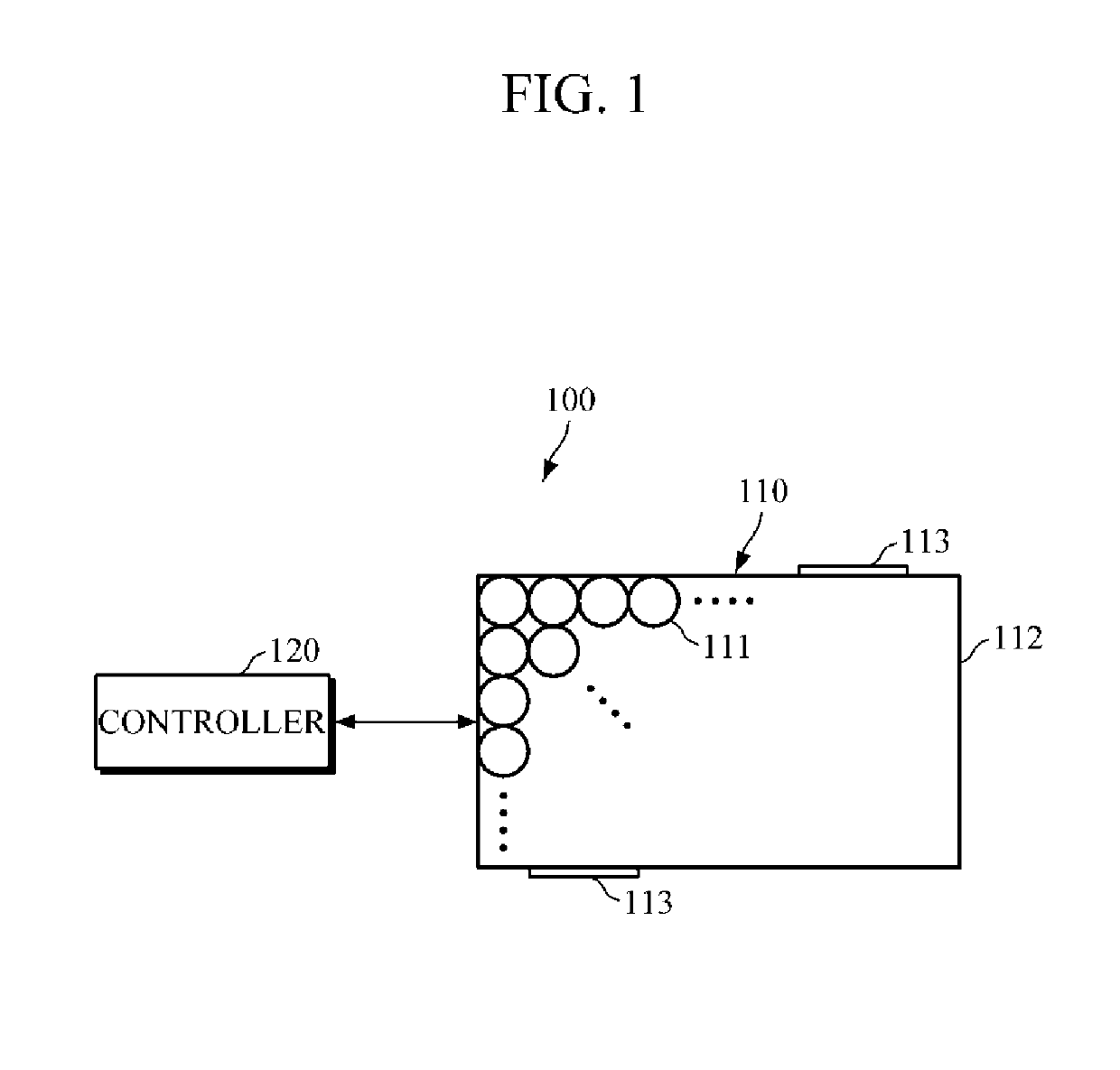
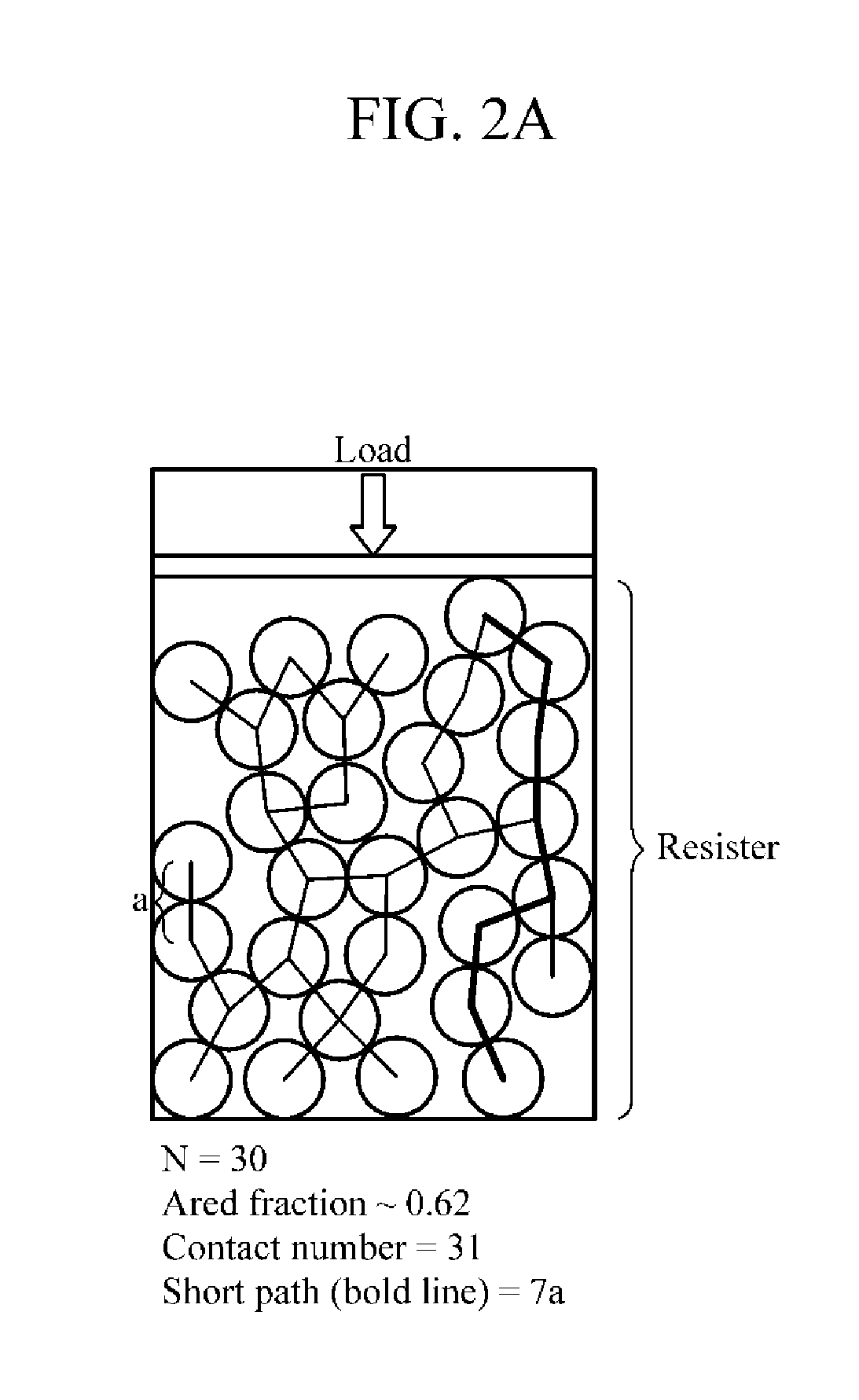
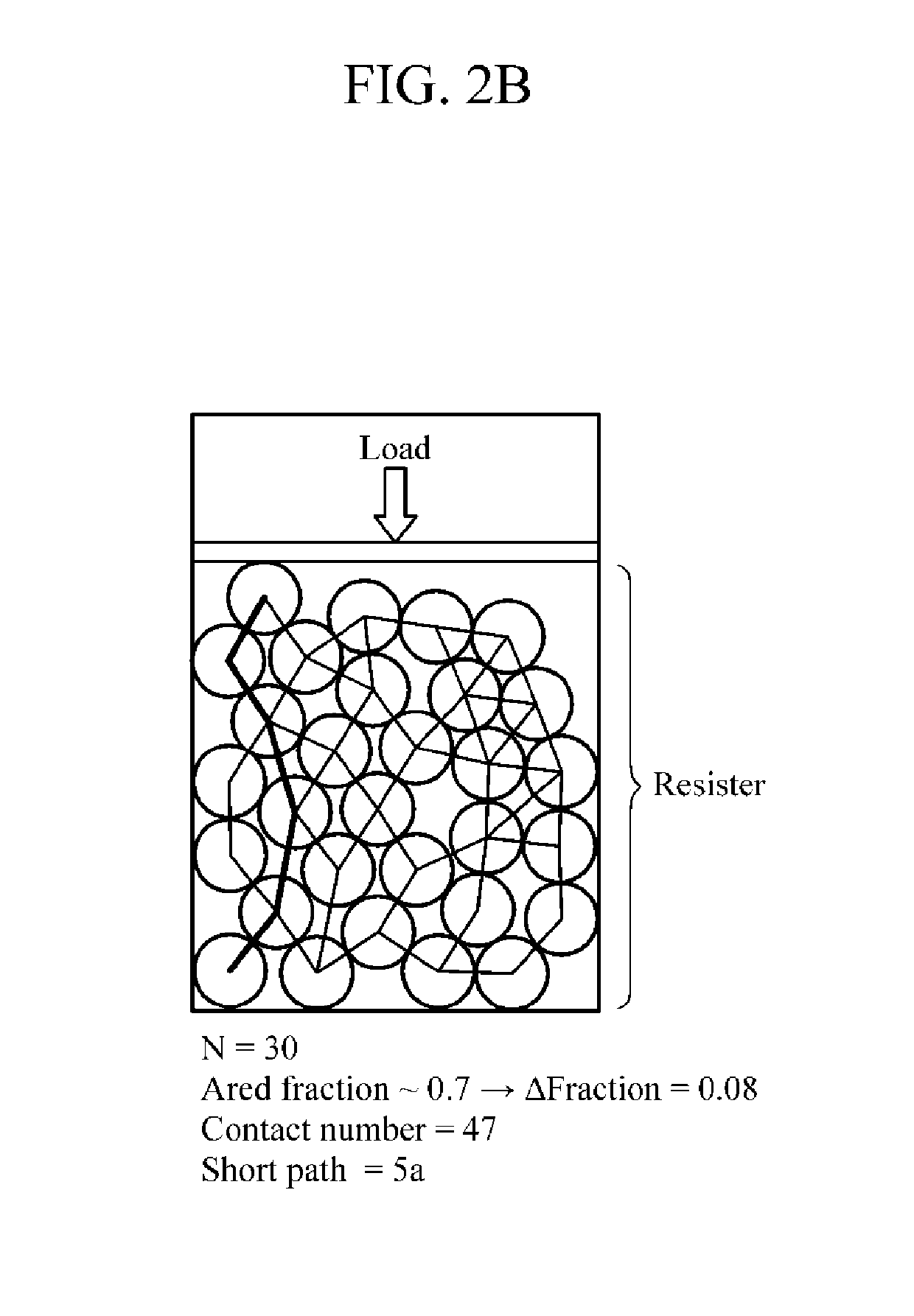
Actuator and soft robot
ActiveUS20190296217A1Different flexibilityDifferent shapesProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsControl theorySoft Robotic
An actuator according to an aspect of the present invention includes: a driving body including a plurality of conductive grains, a chamber configured to confine the plurality of conductive grains, and two or more electrodes disposed on a surface of the chamber, and a controller configured to obtain, through the two or more electrodes, a change in an electric signal, in response to a load applied to the chamber, and to adjust the load applied to the chamber based on the change in the electric signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Soft biomimetic legged robot
ActiveUS20200391814A1Improve rigidityProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsSimulationLegged robot
A soft biomimetic legged robot is provided in the present invention, including a plurality of soft robotic arms. The soft robotic arms include a plurality of motion units, and each of the motion units includes one or more of a twist module, an extension module, a contraction, and a bending module. The plurality of motion units is combined to achieve a full-posture motion of the soft robotic arms. By using soft robotic arms composed of different motion units, the soft biomimetic legged robot of the present invention can not only realize the underwater swimming and crawling, but the crawling on land or slopes, thereby adapting to more complicated environments and achieving richer functions. The motion posture is not limited to a single bending, twisting, extension, and shortening. The soft robotic arm can achieve full-posture movements, and its motion type is more complete.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
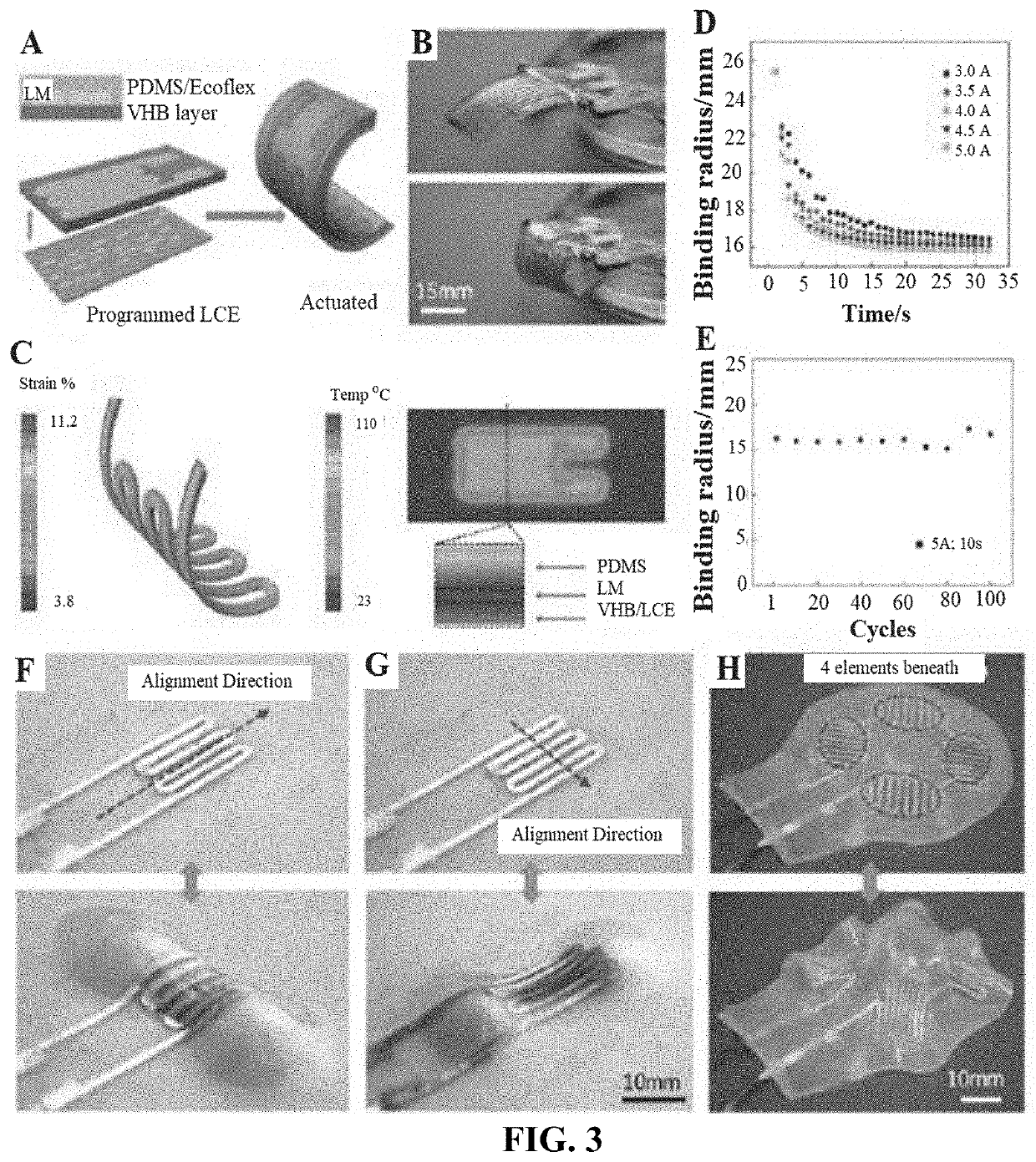
Systems and methods of soft robotic actuation with a liquid metal actuator
ActiveUS20210205103A1Increase temperatureLiquid crystal compositionsProgramme-controlled manipulatorLiquid stateEngineering
Methods, systems, and methods of manufacture for soft robotic actuators are described herein. In one aspect, a soft robotic actuator can include an elastomeric material defining a cavity; a volume of liquid metal (LM) positioned within the cavity; and an energy source coupled to the LM, where the energy source is adapted or configured to alter a temperature of the volume of LM, whereby altering the temperature of the volume of LM initiates an actuation of the elastomeric material.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
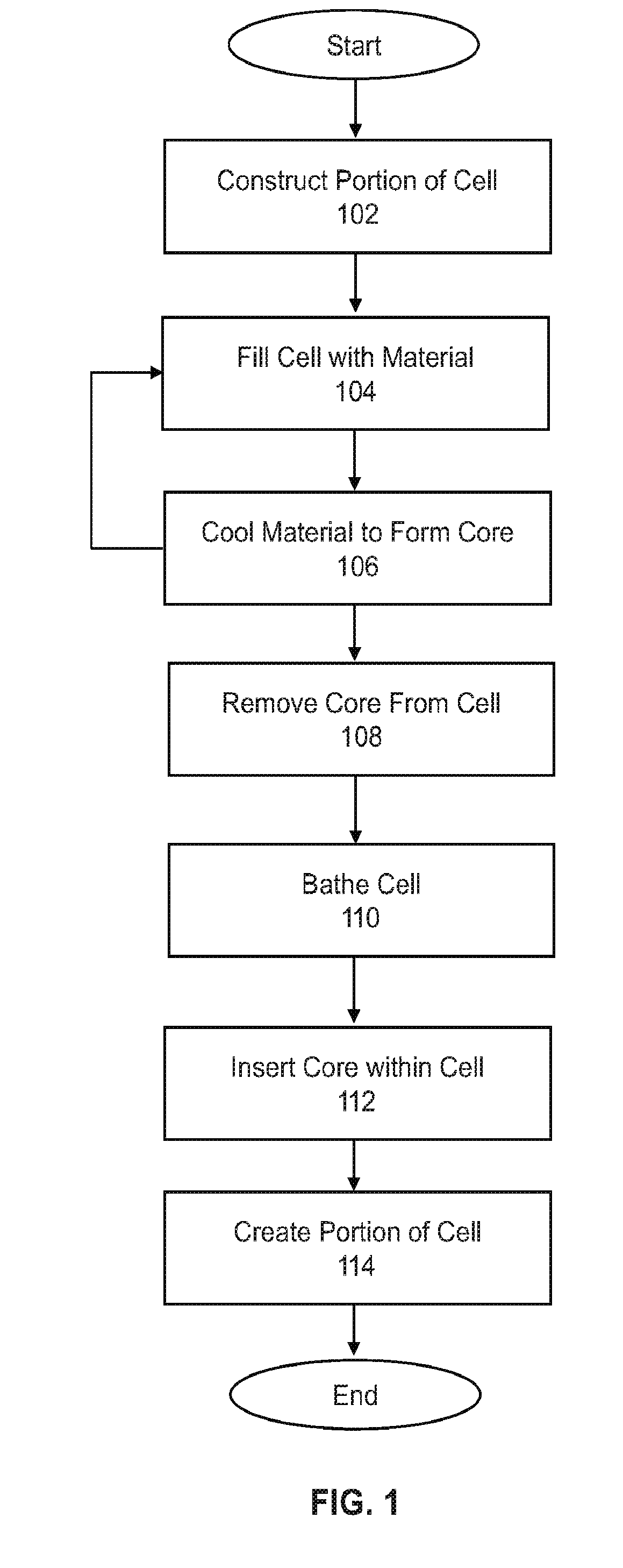
System and methods for fabricating actuators and electrically actuated hydraulic solid materials
InactiveUS20180156204A1Fast formingRapid designSynthetic resin layered productsMachines/enginesElectricityShell molding
With applications such as soft robotics being severely hindered by the lack of strong soft actuators, the invention provides a new soft-actuator material—Electrically Actuated Hydraulic Solid (EAHS) material—with a stress-density that outperforms any known electrically-actuatable material. One type of actuator is fabricated by making a closed cell that acts as highly paralyzed version of a standard paraffin actuator. Each cell exhibits microscopic expansion, which is summed to produce macroscopic motion. The closed cellular nature of the material allows the system to be cut and punctured and still operate. It can be produced in a lab or industrial scale, and can be formed using molding, 3D printing or cutting.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Sensors for soft robots and soft actuators
A soft robotic device with a variety of sensors and / or imaging areas is described. The sensor and / or imaging area may be embedded in the soft body or the strain limiting layer of the soft robotic device, attached to the soft body or the strain limiting layer of the soft robotic device, or otherwise linked to the soft body or the strain limiting layer of the soft robotic device.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
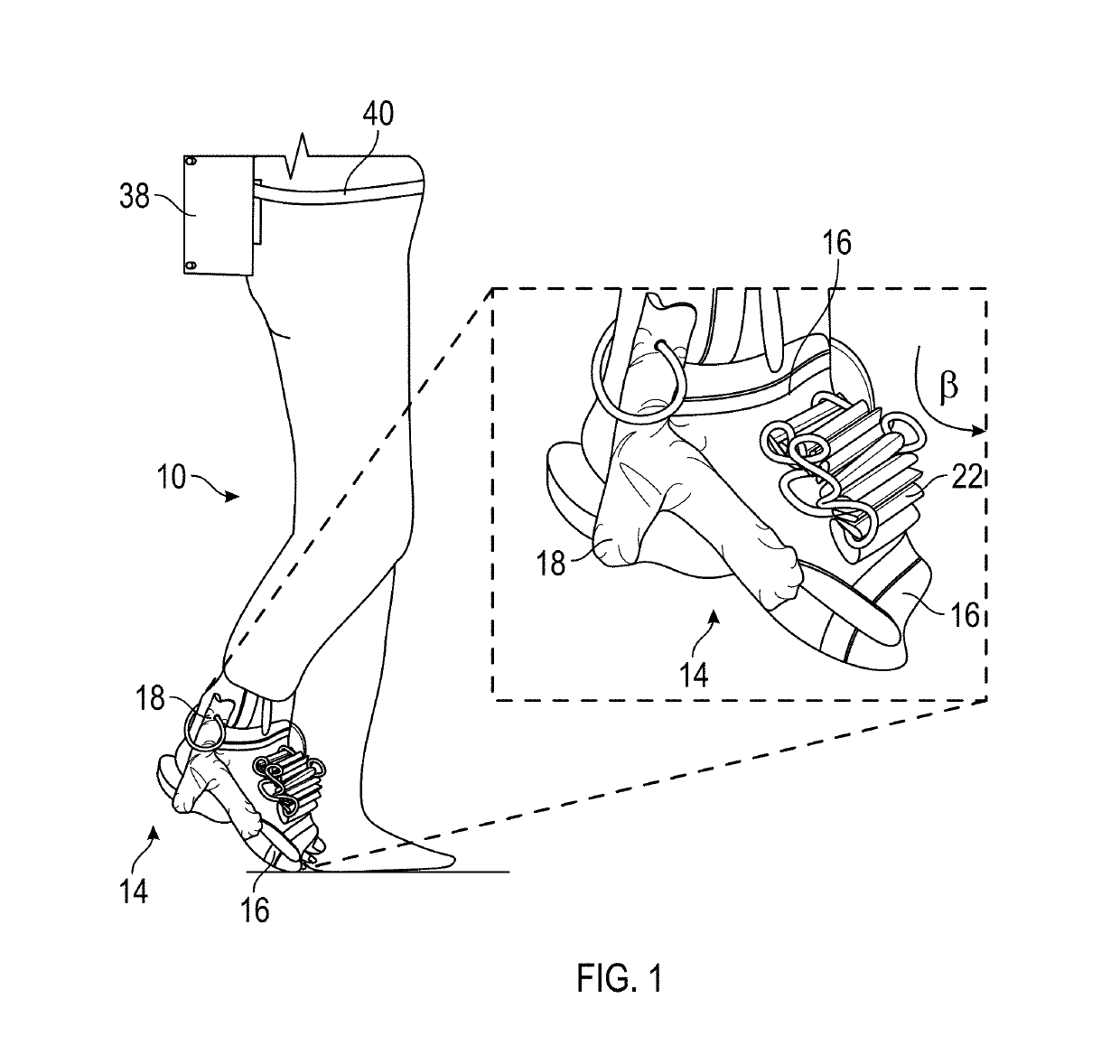
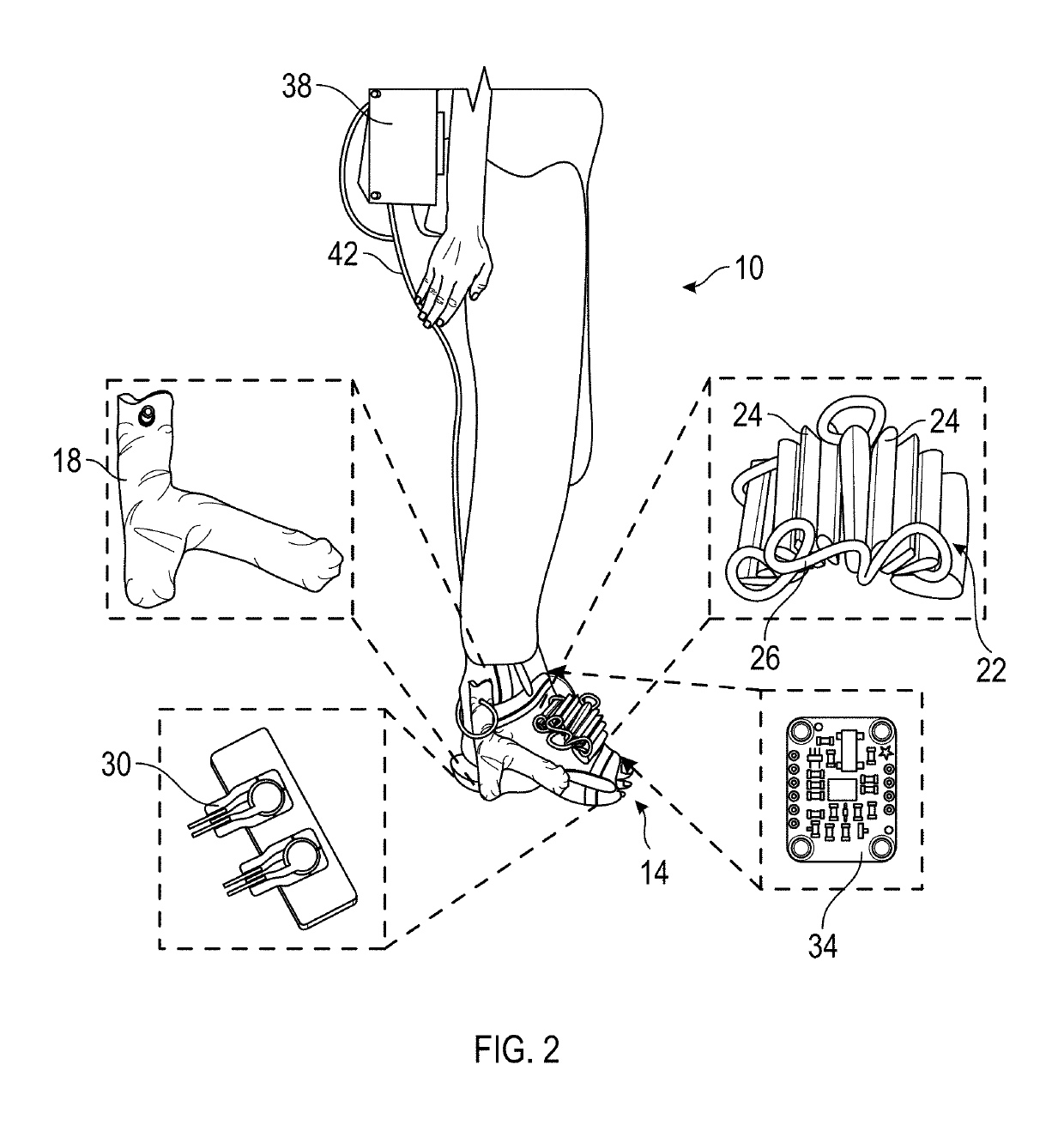
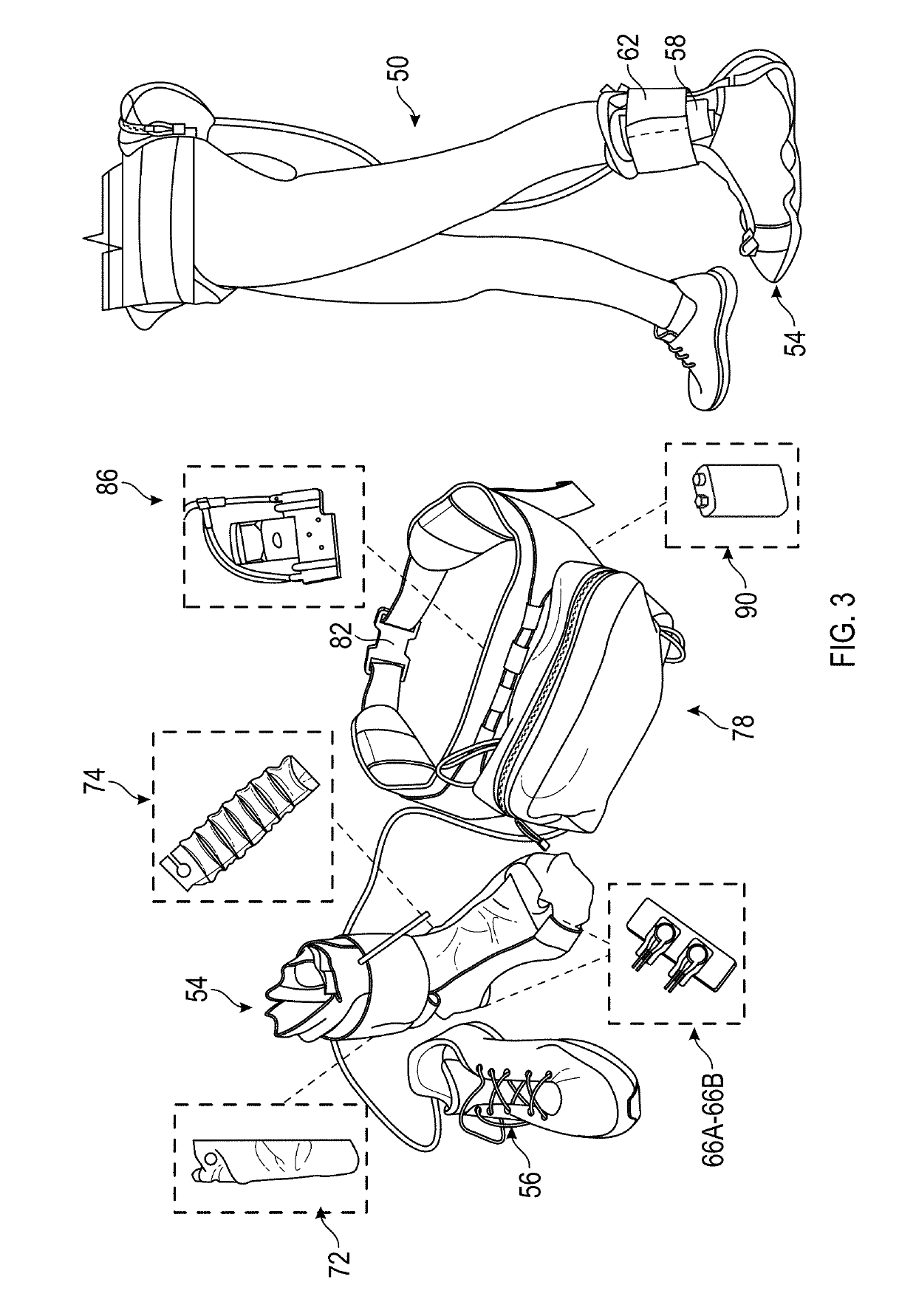
Soft dynamic ankle-foot orthosis exosuit for gait assistance with foot drop
InactiveUS20190336315A1Improve abilitiesPromote recoveryChiropractic devicesWalking aidsInternal pressureKnee orthosis
A soft robotic ankle-foot orthosis exosuit includes a brace configured to be worn on a user's foot, a first soft actuator, a second soft actuator, and a pneumatic system. The first soft actuator is coupled to the brace so that it is configured to be positioned proximate a top of the user's foot. The second soft actuator is also coupled to the brace and is configured to be positioned proximate a side of the user's foot. The pneumatic system is configured to change an internal pressure of the first soft actuator and the second soft actuator.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Photothermal stimulation intelligent response actuator film, preparation method of film and application of film
ActiveCN111396273AReversibleWide variety of sourcesMachines/enginesMechanical power devicesThermal stimulationCarbon nanocomposite
The invention discloses a photothermal stimulation intelligent response actuator film, a preparation method of the film and application of the film, and belongs to the technical field of polymer compounding. The photothermal stimulation intelligent response actuator film is composed of three layers of films which are sequentially arranged in a stacked mode from top to bottom, wherein the first layer is a carbon nanocomposite film layer of poly N-isopropylacrylamide, the second layer is a carbon nanomaterial film layer, and the third layer is a carbon nanocomposite film layer of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylamide). The invention further discloses the preparation method and application of the photothermal stimulation intelligent response actuator film. The photothermal stimulation intelligent response actuator film can generate large deformation in stages within a wider temperature range, such temperature stimulation response has reversibility, and therefore the photothermal stimulation intelligent response actuator film is particularly suitable for photo-thermal response actuators such as soft robots, drug conveyor, motors and artificial muscles.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
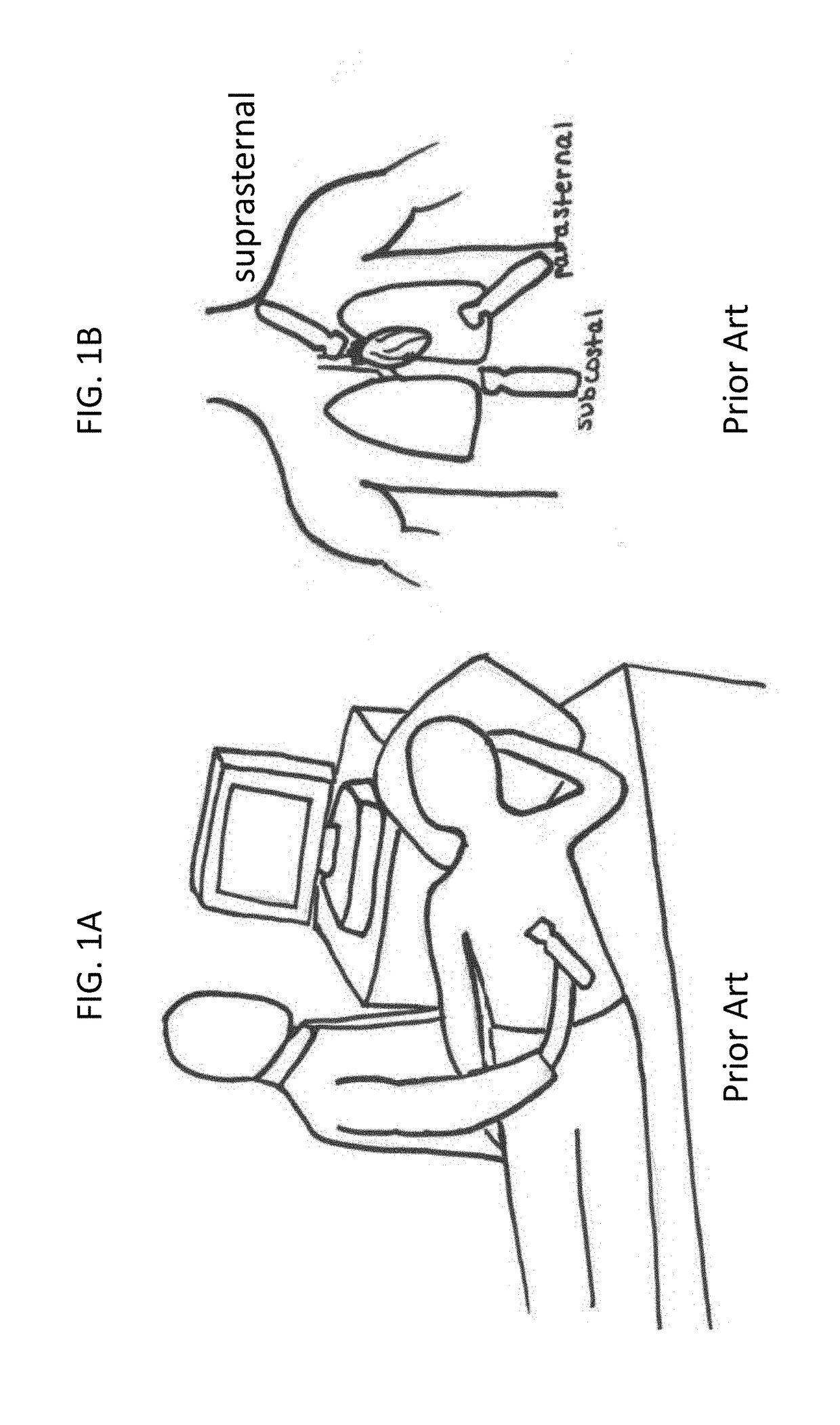
Ultrasound transducer holder
ActiveUS20190053784A1Programme-controlled manipulatorOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingCost effectiveness
Described herein are devices and methods useful in automating ultrasound imaging. The device include a base coupled with soft robotics, which may be attached to an ultrasound transducer probe in order to robotically manipulate the probe to perform an ultrasound scan. The device has an adjustable structure configured to hold the probe on a walking soft robot. The device can be configured to be attached to, or worn by, the patient. With soft robotic actuation and locomotion, the holder can move and position the probe during a real time ultrasound scanning procedure. Furthermore, the holder may be equipped with sensors to sense and map pressure and location. The position of the holder can be robotically monitored and controlled so as to achieve consistency and reproducibility between ultrasound scans. Due to the wearable nature of the holder, the scans may be conducted while the patient is in motion, thereby providing a portable solution for ultrasonic imaging. The holder is cost effective and may be used in conjunction with various ultrasound probes.
Owner:BERI SERENA
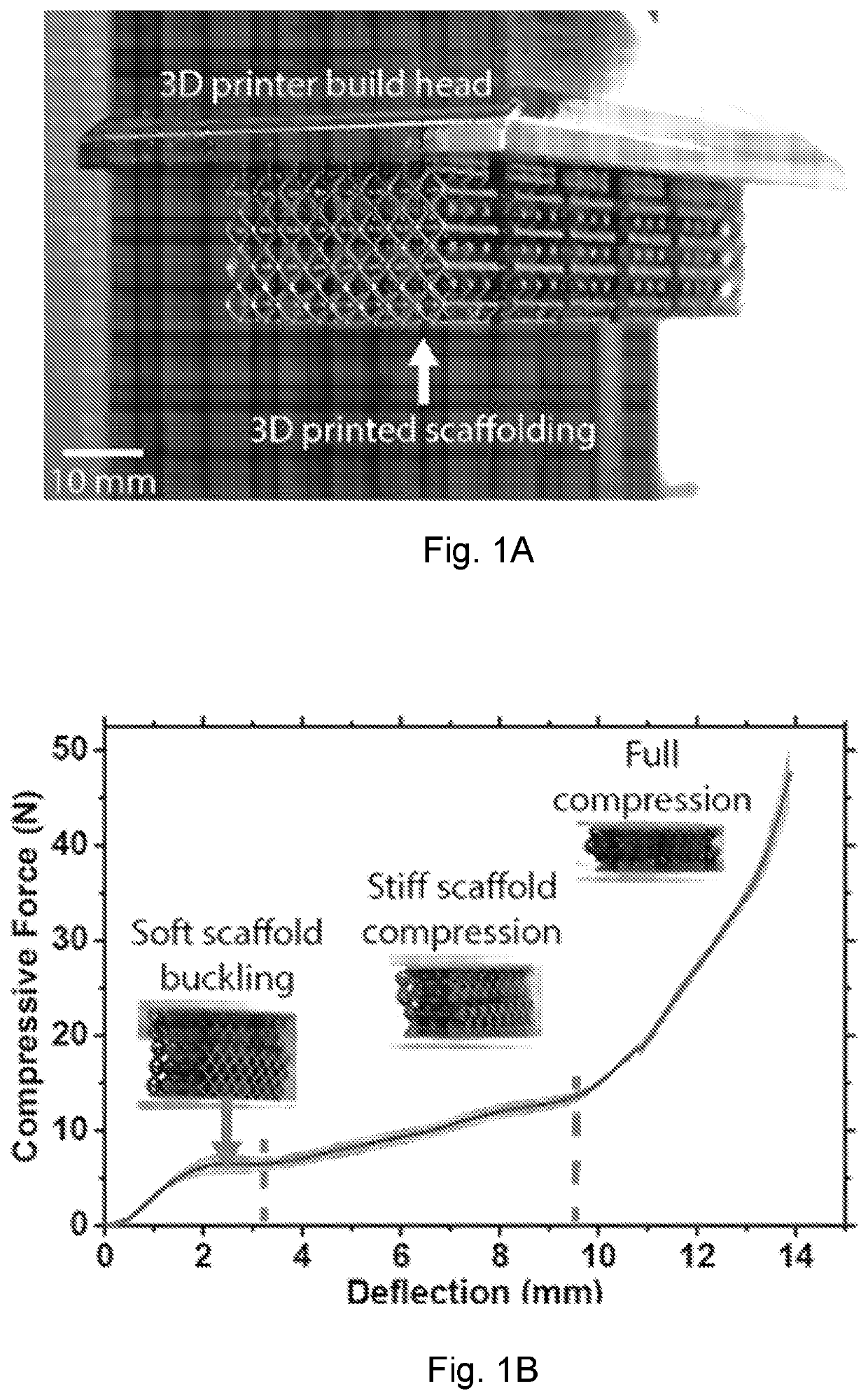
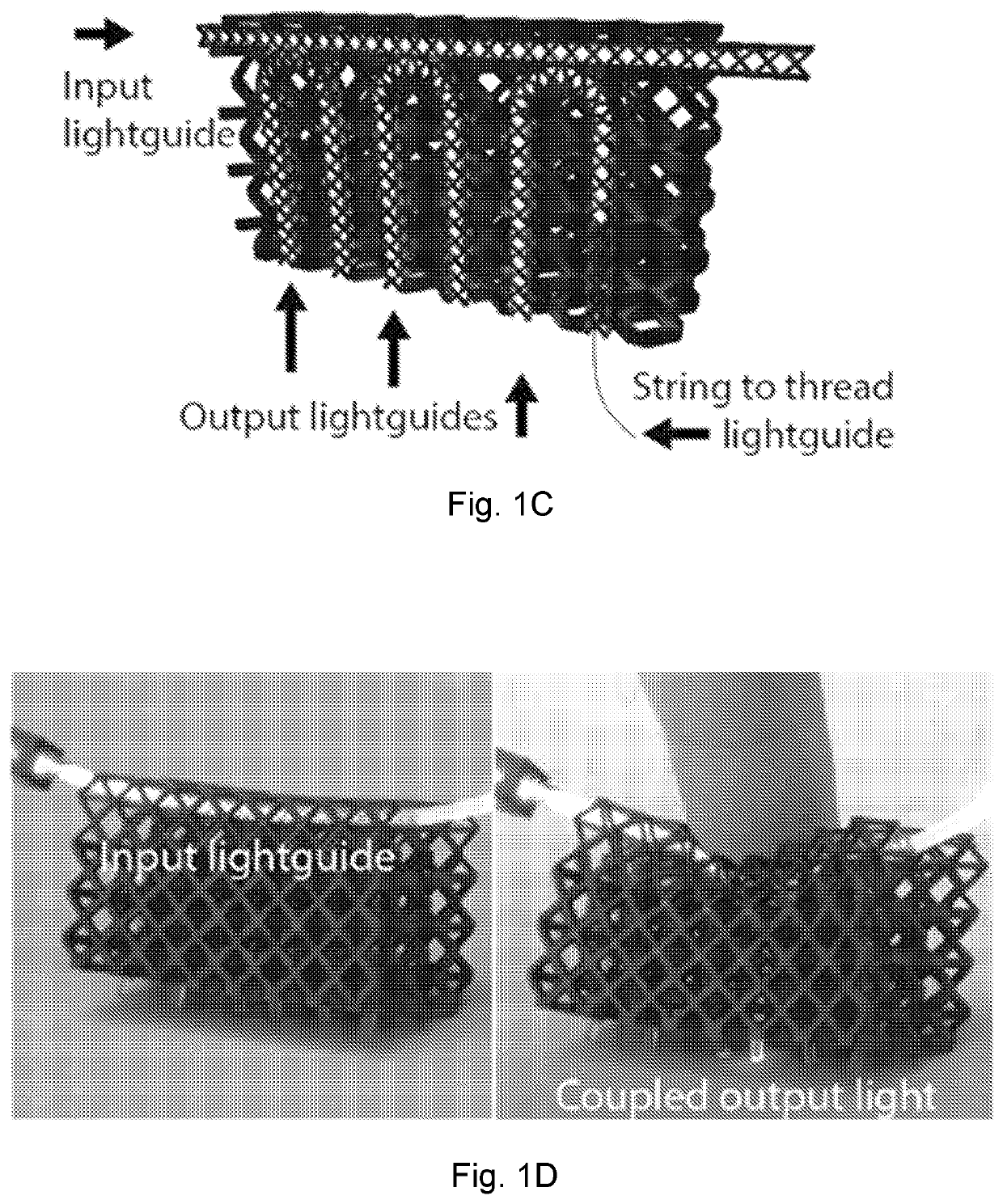
Elastomeric lightguide coupling for continuous position localization in 1,2, and 3D
ActiveUS20200400886A1Force measurement by measuring optical property variationUsing optical meansTotal internal reflectionEngineering
Provided are three dimensional, stretchable, optical sensor networks that can localize deformations. The devices described herein are suitable for uses in soft robots to determine the position of external contact, such as touching, and possibly internal deformations that may be caused by actuation. Sensor networks of the present disclosure contain a substrate, such as a 3D lattice, and cores having a cladding, such as air. Light passes through the cores and upon deformation of the substrate, cores may come into contact, allowing light to couple between cores due to frustrated total internal reflection. The resulting changes in intensity in the cores can be used to determine the placement and magnitude of deformation.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Edible Pneumatic Soft Robotic Actuators
The present invention relates to a biocompatible, digestible and edible material for use in soft edible robots. The present invention provides a pneumatic actuator for edible robotics, and a toy set including at least one pneumatic actuator and an inflating device. Further, the biocompatible, digestible and edible material can be used for making bubble gum products.
Owner:THE HAVERFORD SCHOOL
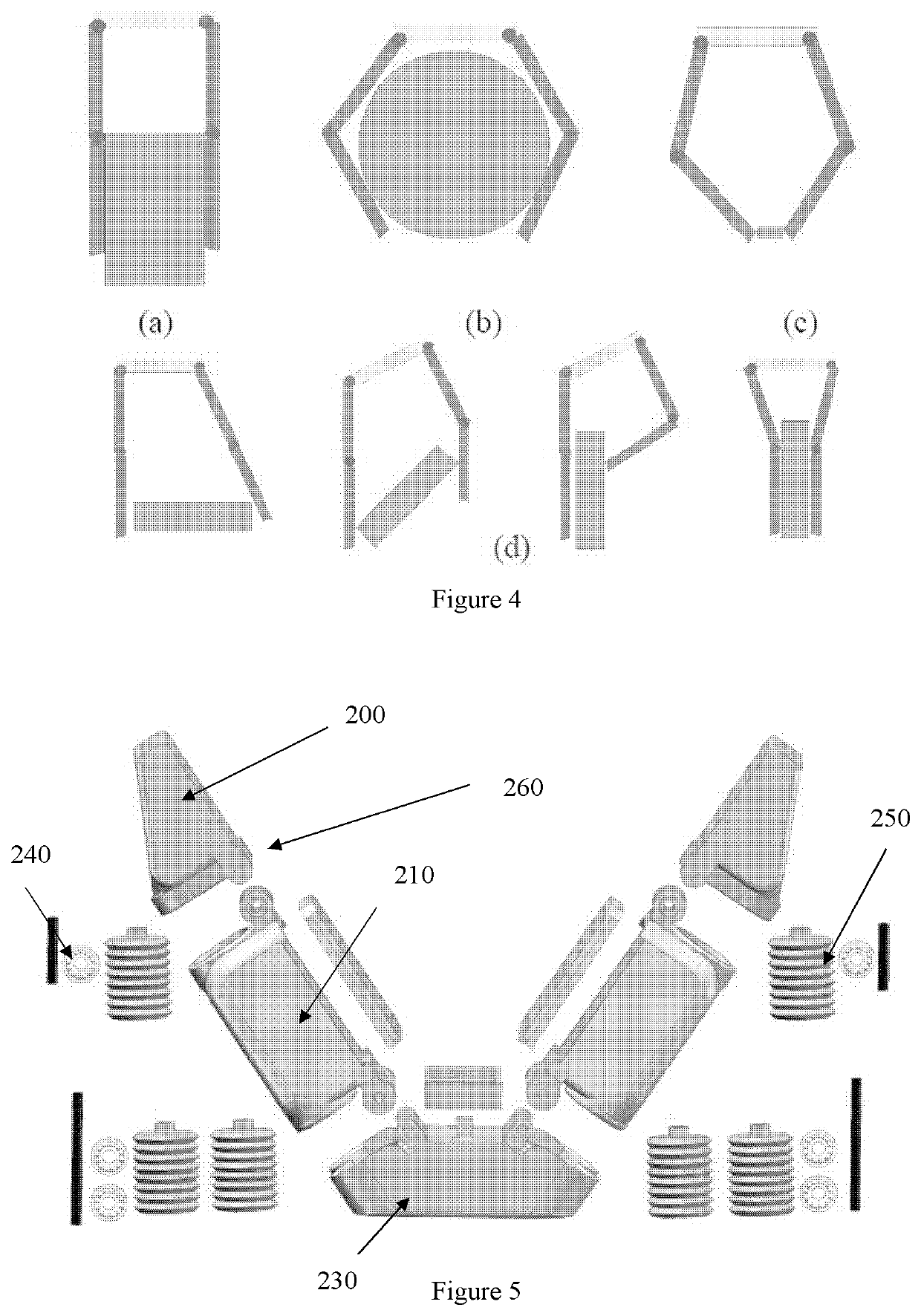
Soft robotic gripper with hybrid structure and grasping reliability
ActiveUS20200298420A1Robust structureMaintaining inherent complianceProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsAnatomySilicon rubber
A robotic end effector and method for use thereof are provided. The robotic end effector can include a rigid base structure (230), a plurality of rigid proximal phalanges (210) connected to the rigid base structure (230), a plurality of rigid distal phalanges (200) connected to the proximal phalanges (210) respectively, and a plurality of bellows (250), wherein one end of a proximal phalange (210) is connected to one end of the base structure (230) by a bellows (250), wherein one end of a distal phalange (200) is connected to a proximal phalange (210) by a bellows (250), and wherein a portion of the base structure (230), each proximal phalange (210), and each distal phalange (200) are covered in silicone rubber. It can achieve a high output force to input pressure ratio, and cost efficiently.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
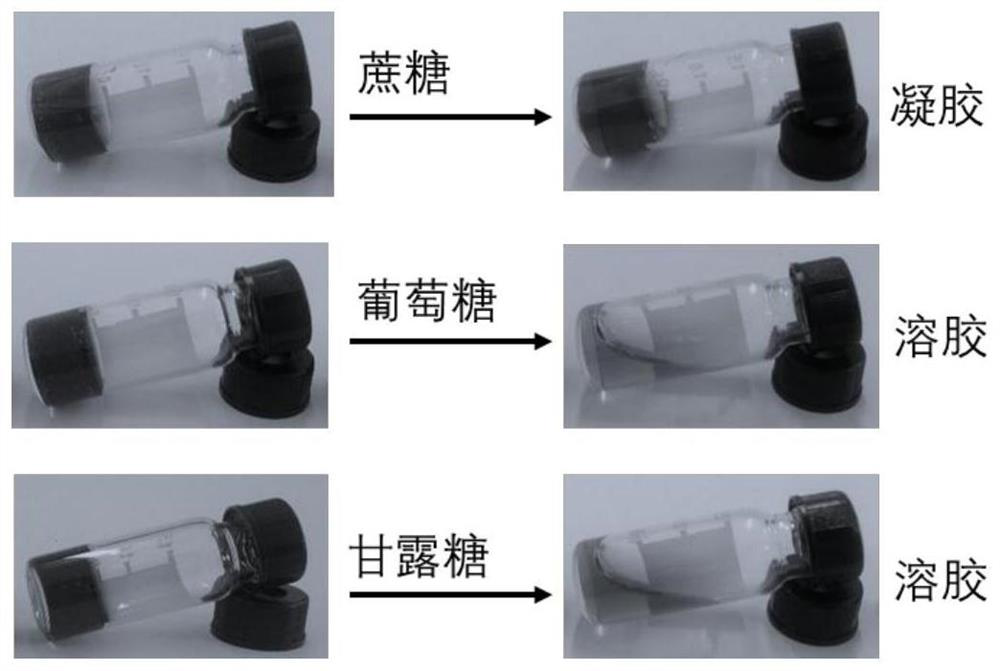
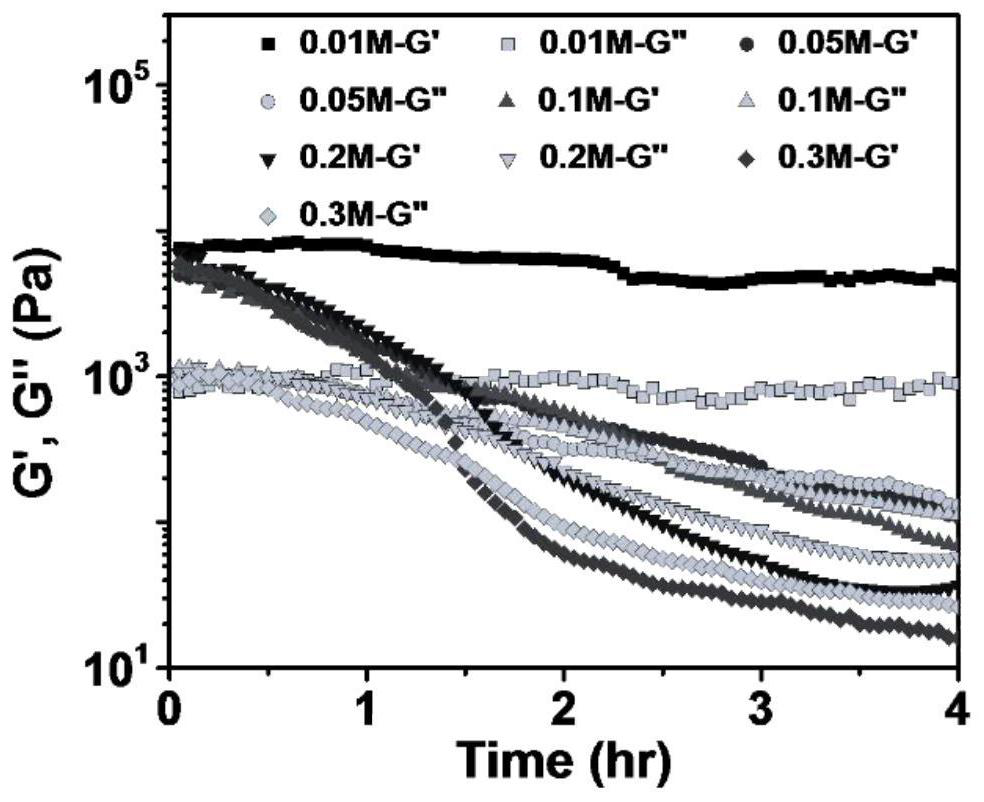
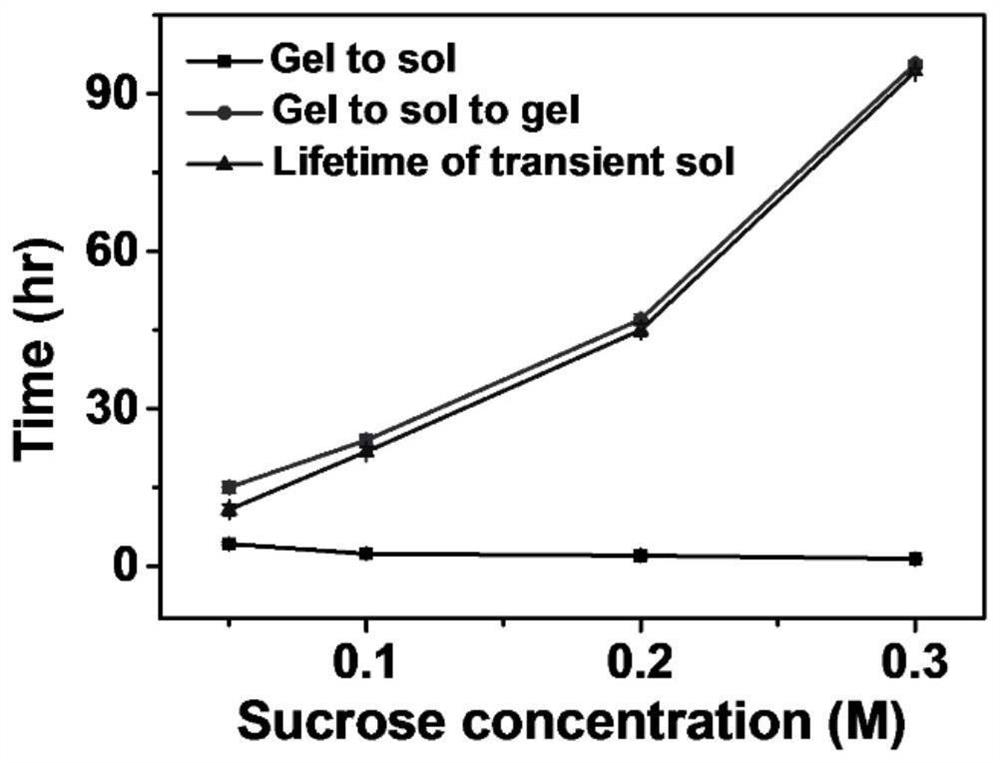
Green reprocessing method of polymer hydrogel
ActiveCN112694631ARealize reprocessingRich functionalityPlastic recyclingPolymer scienceFlexible electronics
The invention relates to a green reprocessing method of polymer hydrogel. According to the invention, the polymer material gel is driven by a chemical fuel to be converted into sol and then into gel, so that the gel is reprocessed, and a functional material is added in the reprocessing process, so that the gel is endowed with more functional effects. Switching between the sol state and the gel state enables the polymer hydrogel to be functionalized again, so that multi-functional polymer materials are generated, and the materials can be applied to the fields of flexible electronics, low-temperature-resistant strain sensors, magnetic actuators and soft robots. According to the reprocessing method of the present invention, covalently adaptive and supramolecular polymer networks are reconstructed repeatedly in a green manner.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
MXene-based composite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113968992AImprove bindingImprove mechanical propertiesCoatingsConductive polymerMoisture absorption
The invention discloses an MXene-based composite material and an actuator thereof disclosed by the invention. An emerging two-dimensional material MXene composite material is combined with a traditional conductive polymer, and excellent photo-thermal conversion performance and moisture absorption performance are shown, so that multiple responsiveness of photo-thermal and humidity is realized. The double-layer actuator with photo-thermal and humidity response is prepared by utilizing a simple synthesis method, illumination bending can be realized, and humidity response can be realized by simulating a dynamic process of plant flowering. According to the experimental method, a relatively good experimental effect can be achieved by avoiding complex synthesis steps, and a method is provided for a soft robot to realize multi-factor response.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Reconfigurable driver based on self-healing elastomer and preparation method of reconfigurable driver
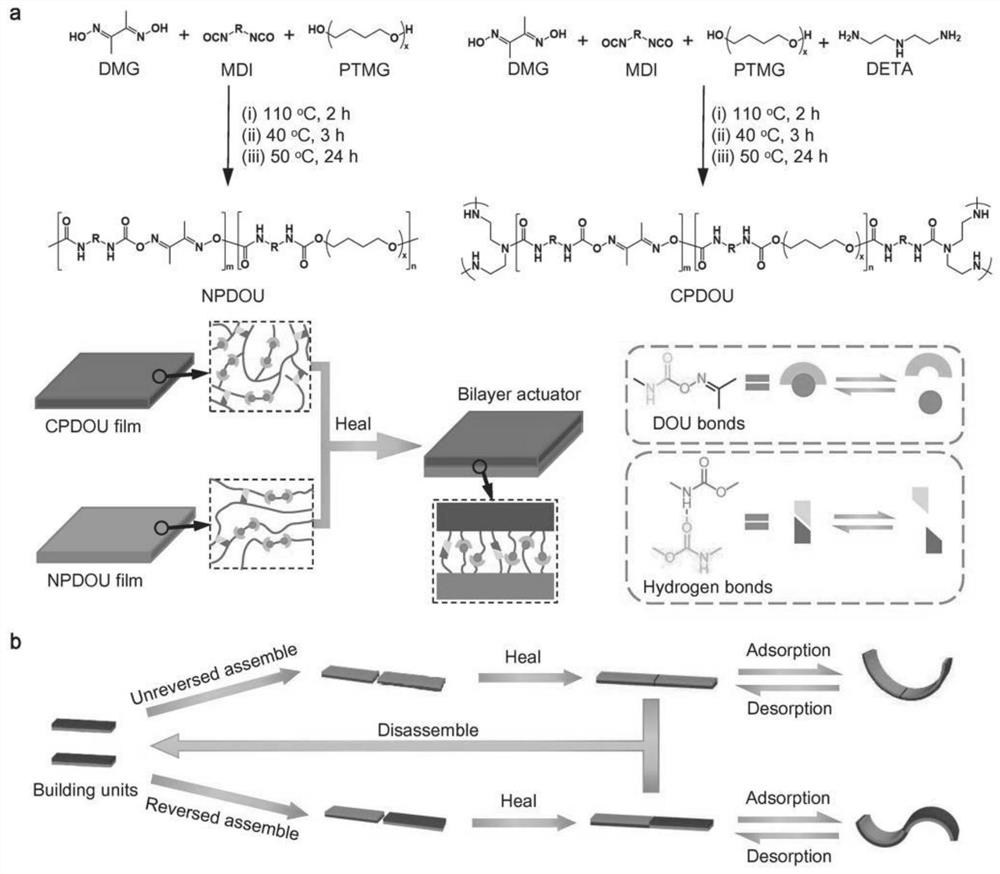
ActiveCN112778489AEasy to assemble and healSimple pathProgramme-controlled manipulatorSynthetic resin layered productsPolyurethane elastomerEngineering
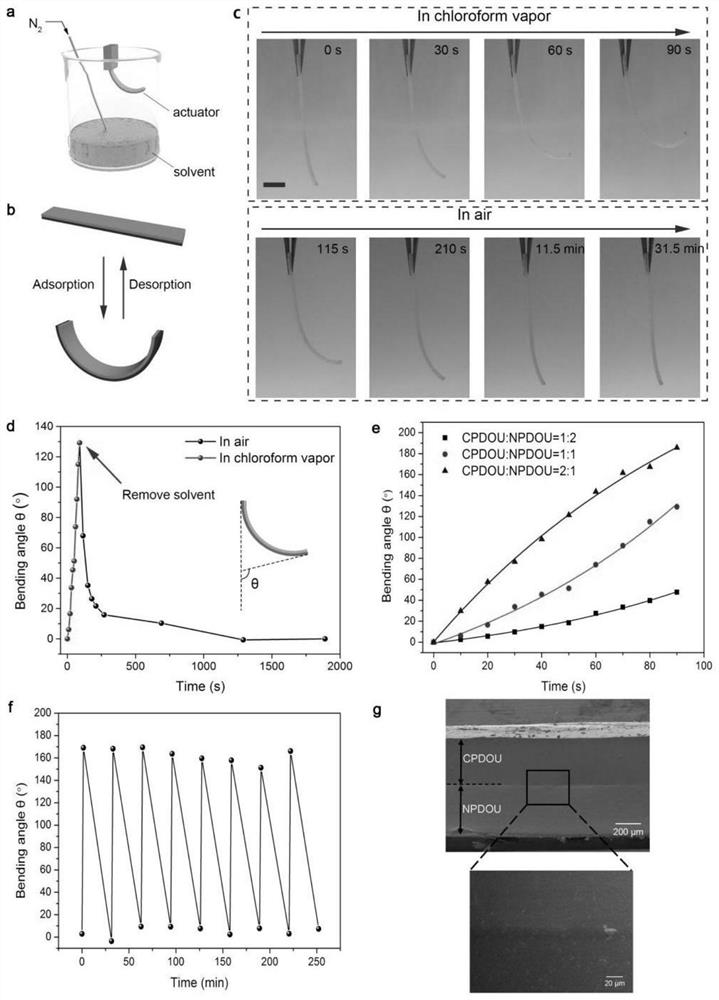
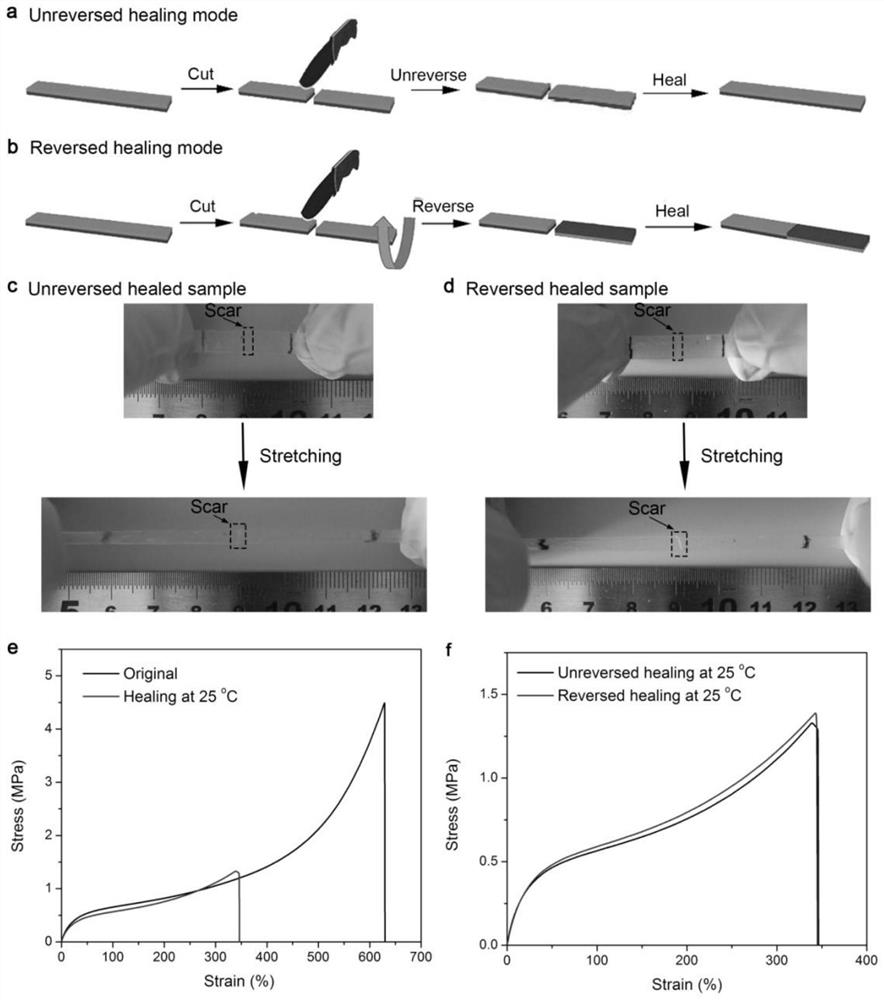
The invention relates to a reconfigurable driver based on a self-healing elastomer and a preparation method of the reconfigurable driver. The reconfigurable driver is composed of a self-healing non-crosslinked PDOU film NPDOU and a crosslinked PDOU film CPDOU. According to the reconfigurable soft driver based on the intrinsic type self-healing polyurethane elastomer, the PDOU elastomers with different crosslinking degrees show different responsiveness to a solvent, and seamless healing can be achieved; and the assembled driver / robot can be reprogrammed through simple cutting and reassembling without any external stimulation so as to display various driving modes, and a simple, powerful and universal path is laid for constructing a soft robot with a complex structure.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Soft robotic assistive gripping device
ActiveUS11027436B2Easy to controlEasy to removeProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationChronic disability
This invention is directed to offer a customizable, cost effective, and comfortable soft gripping solution for patients with chronic disabilities, such as diabetic neuropathy, allowing the patients to function independently and perform routine daily tasks. A soft robotic gripper has been developed with one or more inflatable systems actuated by aft to assist a user to grip an object. The main body of the gripper bends with air actuation while the fingertip actuation helps functionality in the extremities. The gripper is further enhanced by adding sensors that integrate feedback for sensitivity to touch, conformability, and grip ability. The modular design modifications allow for gripper adjustments as the disease progresses or rescinds. The gripper also works as a training aid for routine physical therapy exercises. Data collected by a microprocessor can also help learn more about these chronic diseases and use artificial intelligence to customize treatment regimens for individual patients.
Owner:BERI ALEKH RAJESH
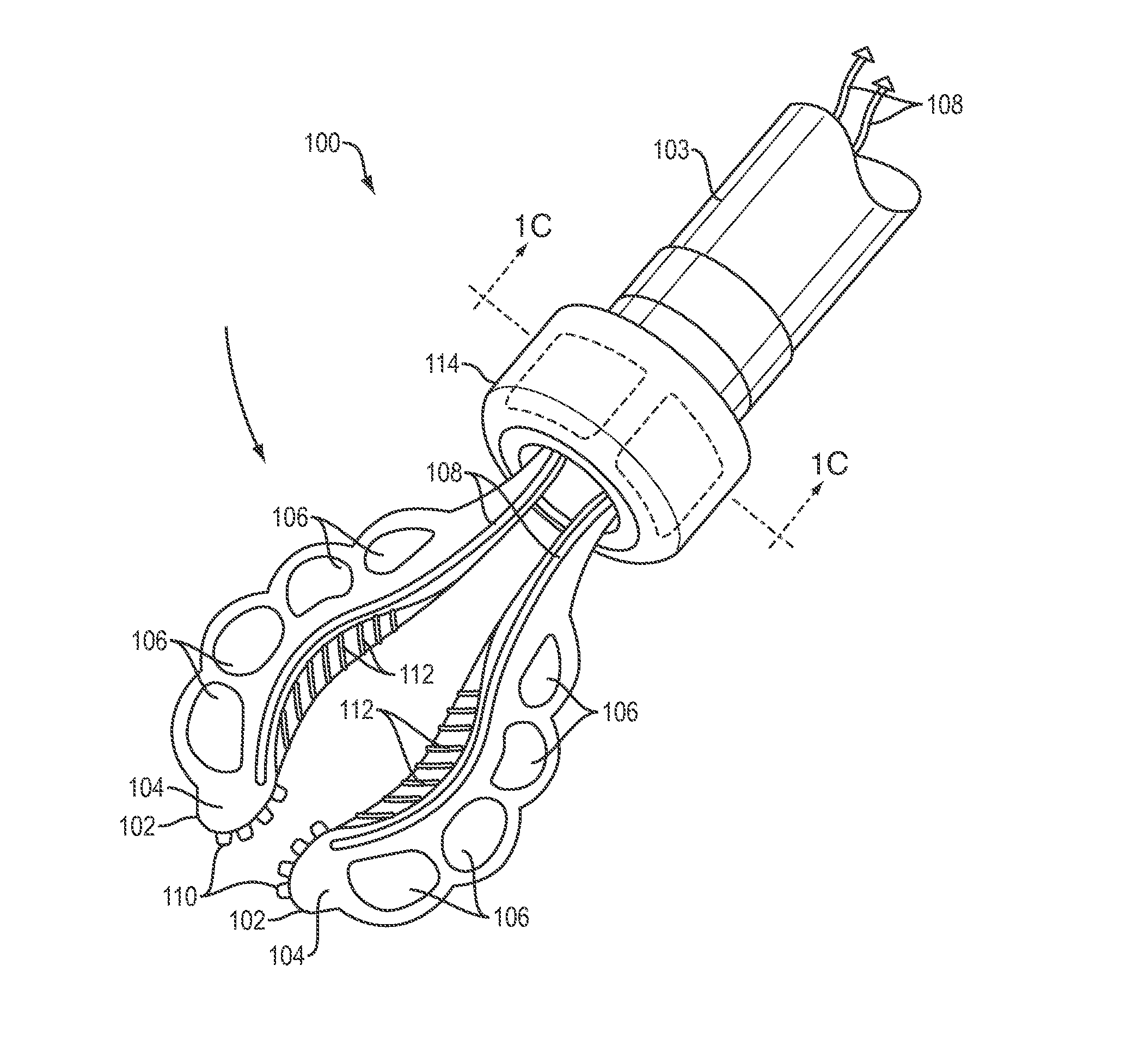
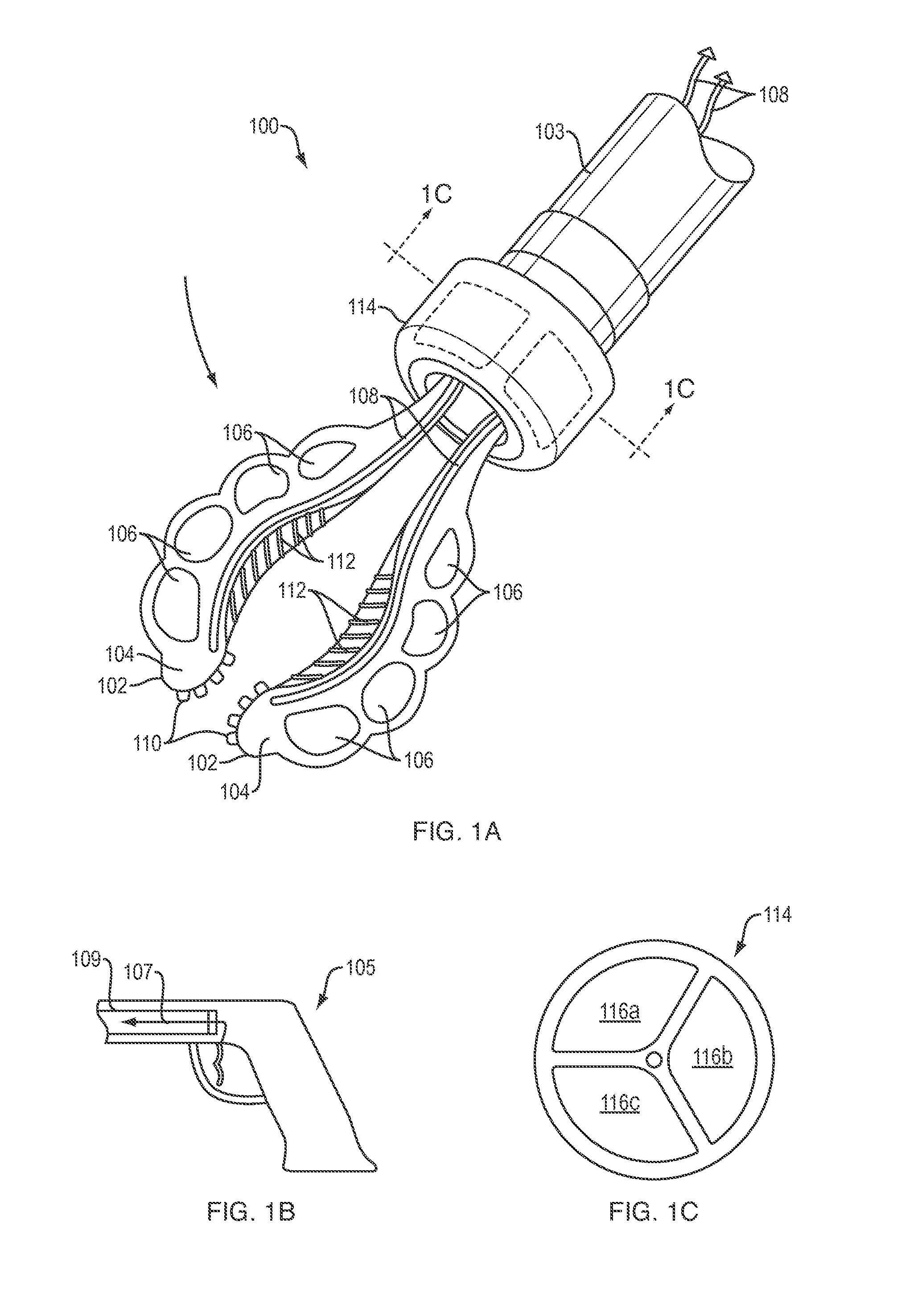
Positioning device
PendingUS20200191172A1Precise positioningEasy to operateProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsSoftware engineeringSoft Robotic
A positioning device for positioning and using a tool within a cavity having a cavity wall. The device comprises a flexible deployment device / arm carrying the tool. The deployment device / arm further comprises a soft robotics fixturing element adjustable between a contracted deployment configuration during positioning of the tool to an expanded bracing configuration for abutment with the cavity wall during use of the tool.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Soft biomimetic legged robot
ActiveUS11377162B2Improve rigidityProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsSimulationLegged robot
A soft biomimetic legged robot is provided in the present invention, including a plurality of soft robotic arms. The soft robotic arms include a plurality of motion units, and each of the motion units includes one or more of a twist module, an extension module, a contraction, and a bending module. The plurality of motion units is combined to achieve a full-posture motion of the soft robotic arms. By using soft robotic arms composed of different motion units, the soft biomimetic legged robot of the present invention can not only realize the underwater swimming and crawling, but the crawling on land or slopes, thereby adapting to more complicated environments and achieving richer functions. The motion posture is not limited to a single bending, twisting, extension, and shortening. The soft robotic arm can achieve full-posture movements, and its motion type is more complete.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
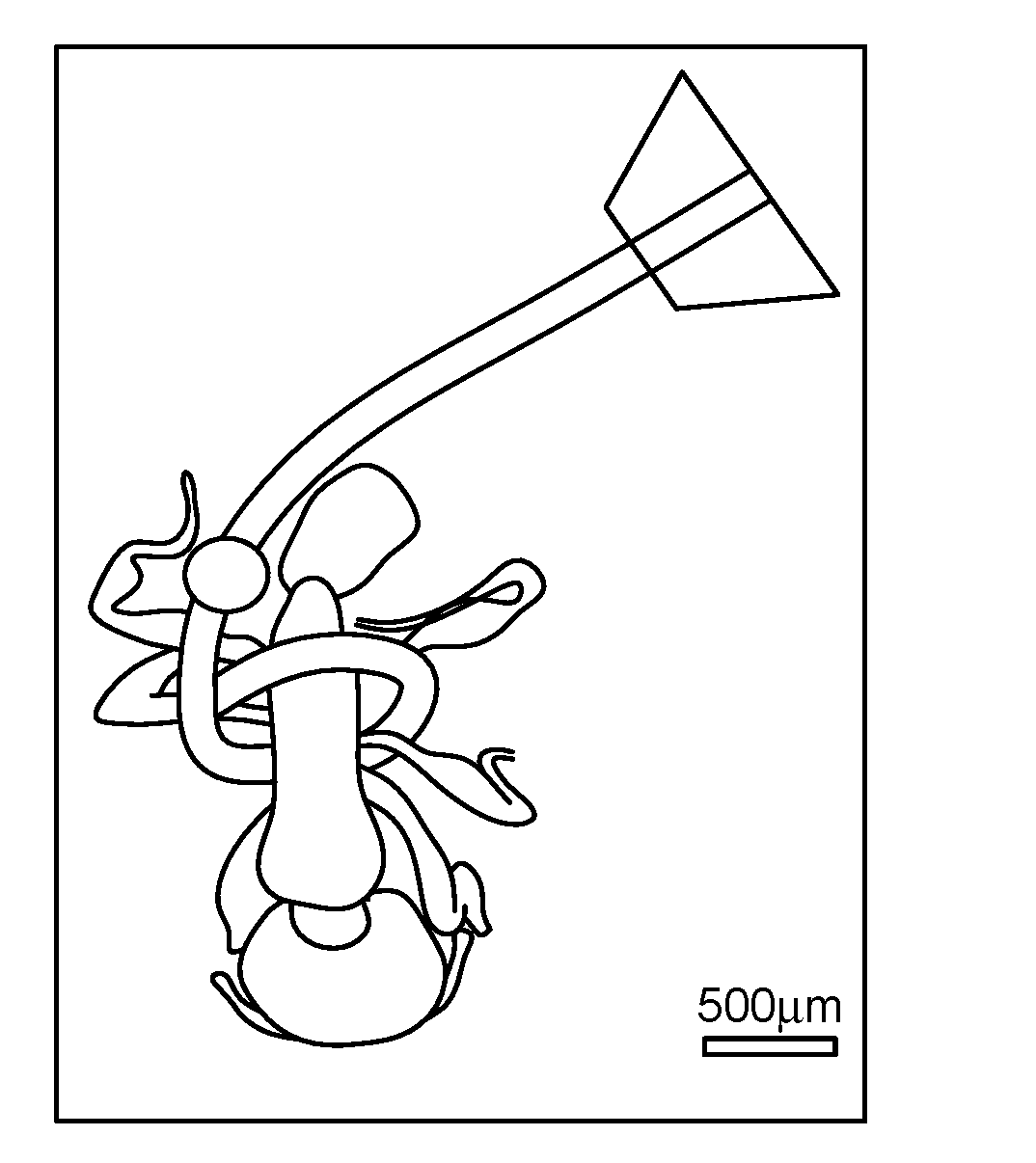
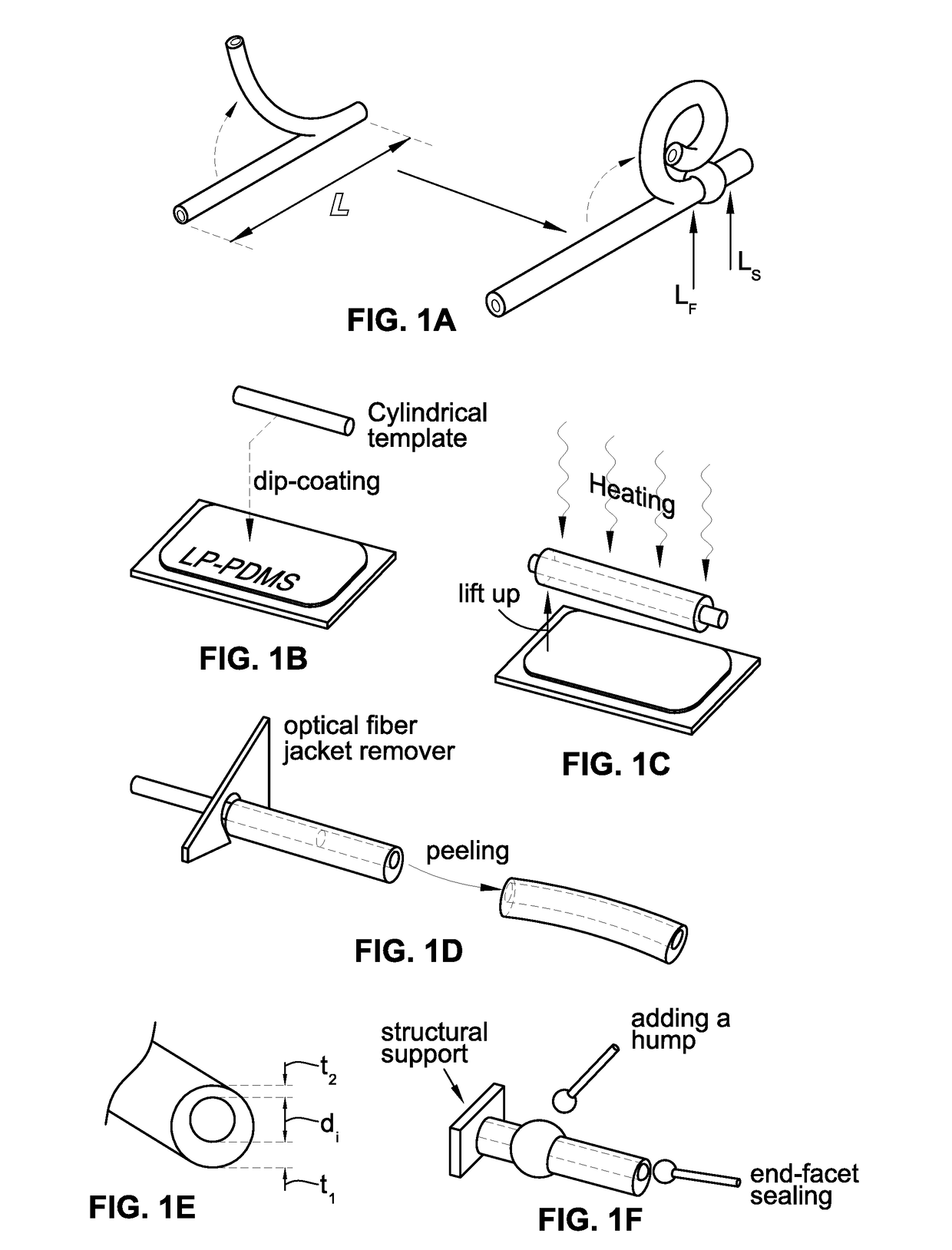
Microrobotic tentacles with spiral bending capability based on shape-engineered elastomeric microtubes and methods of manufacturing same
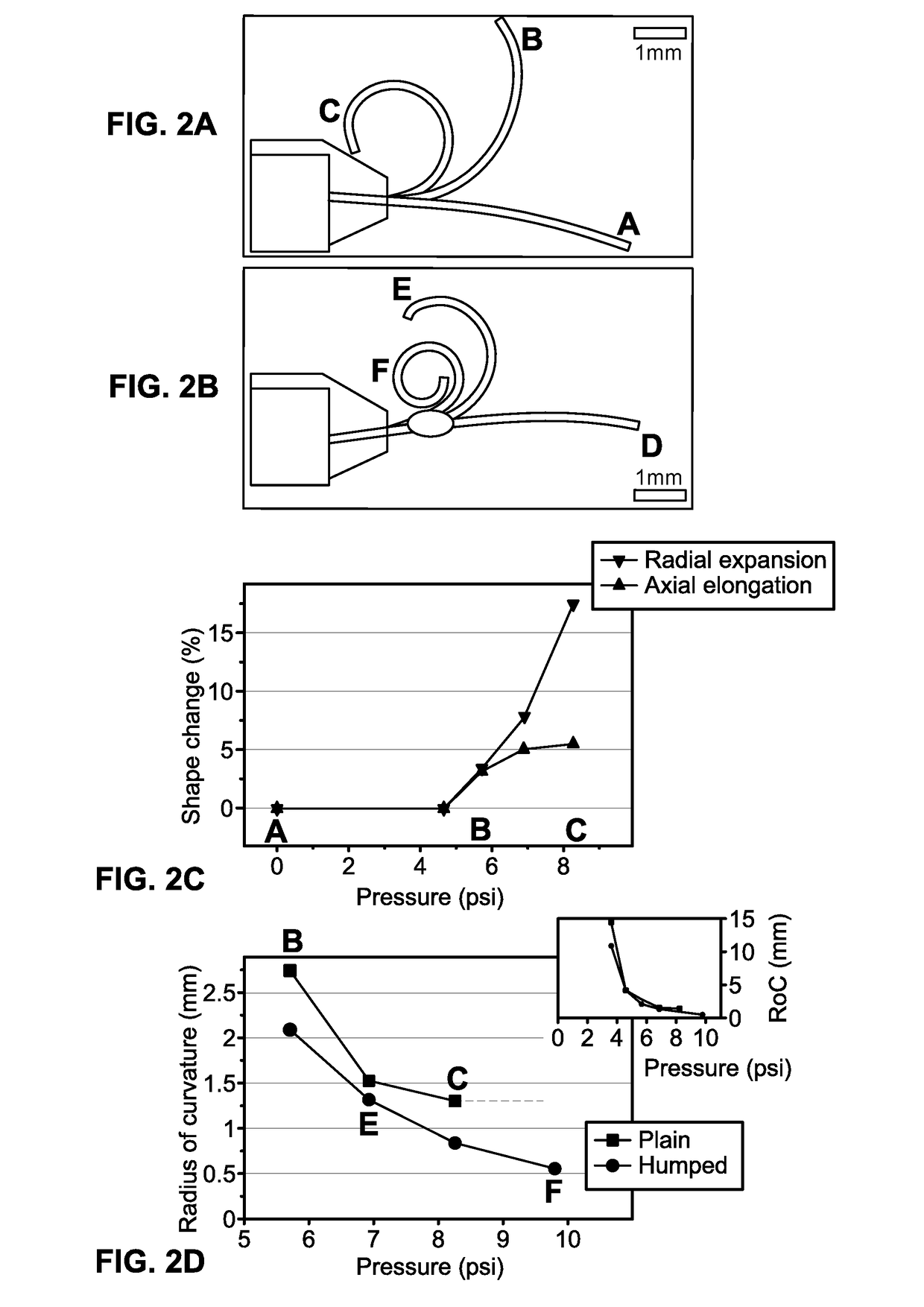
Elastomer-based soft-robotic micro-tentacles capable of winding around and holding microscale objects and methods of fabricating same are provided. To realize the thin, highly deformable microtubes, a fabrication technique based on in situ thermal solidification of PDMS dip-coated around a cylindrical template and direct peeling of the cured structure is presented. This process is capable to asymmetrize the microtube's cross-sectional shape and enable the microtube to bend up to a single turn. To amplify the bending into a life-like, multi-turn spiraling motion, a semi-analytical model to shape-engineer the microtube and turn it into a micro-tentacle was produced. As a result, a hump is added to the microtube to enable the multi-turn spiraling motion.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Full-flexible fin driven by magnetic field and production method thereof
ActiveCN113232812ASimple structureImprove stabilityPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeUnderwater equipmentEngineeringBiocompatibility
The invention discloses a full-flexible fin driven by a magnetic field and a production method thereof. The full-flexible fin comprises a strip-shaped elastic polymer matrix and a plurality of magnetized magnetic active polymer matrixes embedded in the strip-shaped elastic polymer matrix. The plurality of magnetized magnetic active polymer matrixes are arranged on the strip-shaped elastic polymer matrix in parallel, and the distribution directions of adjacent magnetic domains are completely opposite; and the magnetic active polymer matrixes and the strip-shaped elastic polymer matrix are attached together through the intermolecular force of a material to form the full-flexible fin, and the full-flexible fin is put into an alternating excitation magnetic field to realize periodic flapping motion. The invention discloses a production method of the full-flexible fin. The full-flexible fin is simple, good in stability, high in movement efficiency, excellent in deformation performance, good in movement continuity due to full flexibility, capable of adapting to different complex environments, good in biocompatibility, capable of being applied to a power driving part of an underwater navigation robot and wide in application in the field of soft robots.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Ultrasound transducer holder
ActiveUS10987083B2Programme-controlled manipulatorOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic imagingComputer vision
Described herein are devices and methods useful in automating ultrasound imaging. The device include a base coupled with soft robotics, which may be attached to an ultrasound transducer probe in order to robotically manipulate the probe to perform an ultrasound scan. The device has an adjustable structure configured to hold the probe on a walking soft robot. The device can be configured to be attached to, or worn by, the patient. With soft robotic actuation and locomotion, the holder can move and position the probe during a real time ultrasound scanning procedure. Furthermore, the holder may be equipped with sensors to sense and map pressure and location. The position of the holder can be robotically monitored and controlled so as to achieve consistency and reproducibility between ultrasound scans. Due to the wearable nature of the holder, the scans may be conducted while the patient is in motion, thereby providing a portable solution for ultrasonic imaging. The holder is cost effective and may be used in conjunction with various ultrasound probes.
Owner:BERI SERENA
Inchworm type magnetic control soft robot for small pipeline detection and use method
ActiveCN113236905ALarge bending deformationVariety of movementPigs/molesClassical mechanicsEngineering
The invention discloses an inchworm type magnetic control soft robot for small pipeline detection and a use method. According to the inchworm type magnetic control soft robot for small pipeline detection, the structure and the motion principle of inchworms in the nature are imitated, structural optimization is conducted in a finite element simulation mode, transverse and longitudinal zigzag structures are determined, large bending deformation can be achieved, and the inchworm-type magnetic control soft robot is used in cooperation with a controllable magnetic field operation table. Various movement modes such as straight movement and bending movement around the x-axis and the z-axis can be achieved. A miniature camera and a miniature illuminating lamp are further arranged on the soft robot, and free movement and detection in a small dark space can be achieved. Meanwhile, a multi-material 3D printing technology is adopted, the whole robot is manufactured in a one-time printing mode, precision is accurate, and due to the full-soft structure, the inchworm type magnetic control soft robot can pass through narrow spaces such as narrow slits through flexible deformation.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com