Ultra-sensitive electrochemical LCR sensor for detecting methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus in synovial fluid
A methicillin and staphylococcus-resistant technology, applied in the field of electrochemical LCR sensors, can solve the problems of difficulty in distinguishing single bases, false positives and false negatives, etc., and achieves low detection cost, simple detection operation process, and high sequence sensitivity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
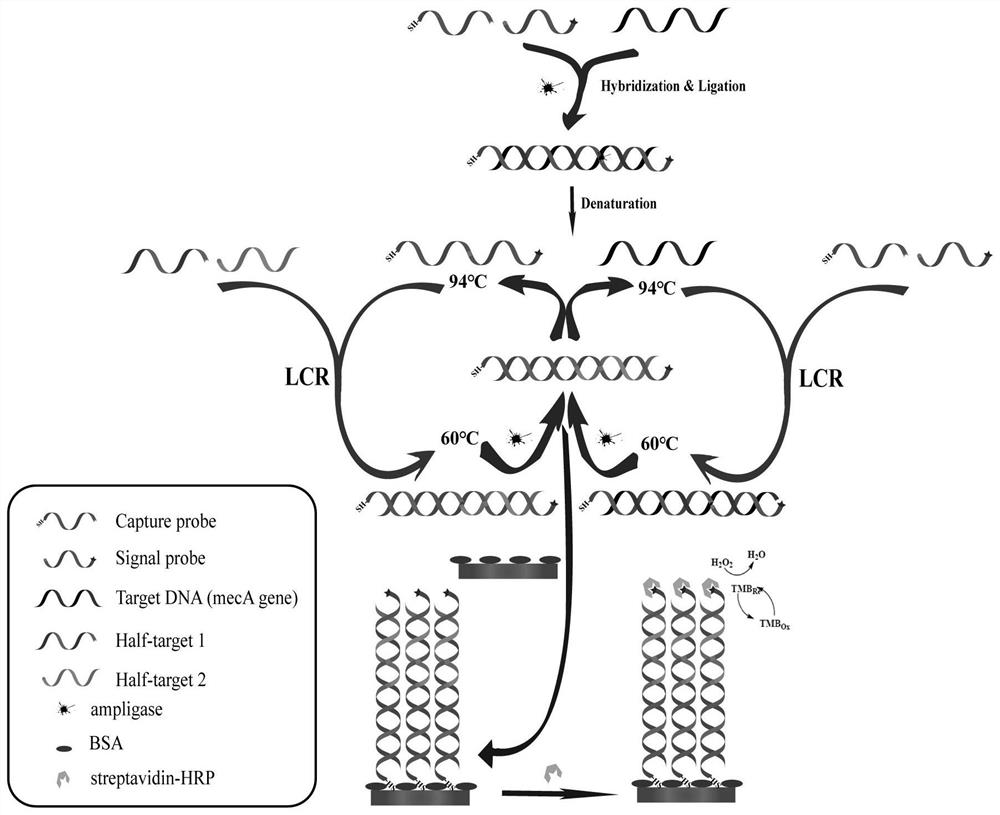
[0035] An LCR-based electrochemical sensing technique for the detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in the synovial fluid of patients with periprosthetic joint infections (eg figure 1 shown), including the following steps:
[0036] (1) Find out various homolog series of MecA gene through NCBI, and select the common conservative series to design probes. The designed probe series are: MecA gene (completely matching DNA target strand, T-full DNA target) : 5'-CCTCTGCTCAACAAGTTCCAGATTACAACTTCACCAGGTT CAACTC-3'; capture probe (end modified SH-C6, CP): 5'-SH-TTTTTTTTTT GAGTTGAACCTGGTGA AGTTGTAA-3'; signal probe (5' end modified PO4 - , 3' end modified biotin biotin, SP): 5'-PO4-TCTGGA ACTTGTTGAGCAGAGG-Biotin-3'; Partial target probe 1 (Half-target 1, hT-1): 5'-CCTCTGCTCA ACAAGTTCCAGA-3'; Partial target probe 2 (Half-target 2, hT-2): 5'-CCTCTGCTCAACAAGTTC CAGA-3'.
[0037] (2) Add the specimens, reagents and ligase required for the amplification reaction to...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A method for detecting methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in the joint fluid of patients with periprosthetic infection based on sensing technology, the steps are as follows:
[0045](1) The three-electrode system was used for the measurement, the dsDNA-BSA-AuE modified electrode prepared in Example 1 was used as the working electrode, the Ag / AgCl was used as the reference electrode, and the platinum wire electrode was used as the counter electrode, and the electrochemical workstation was used for detection. The three-electrode system was immersed in 500 μL of TMB substrate solution, and the current-time curve (i-t, initial potential 100 mV, t=100 s) and cyclic voltammetry curve (CV, scan speed 0.1 V / s) were recorded.
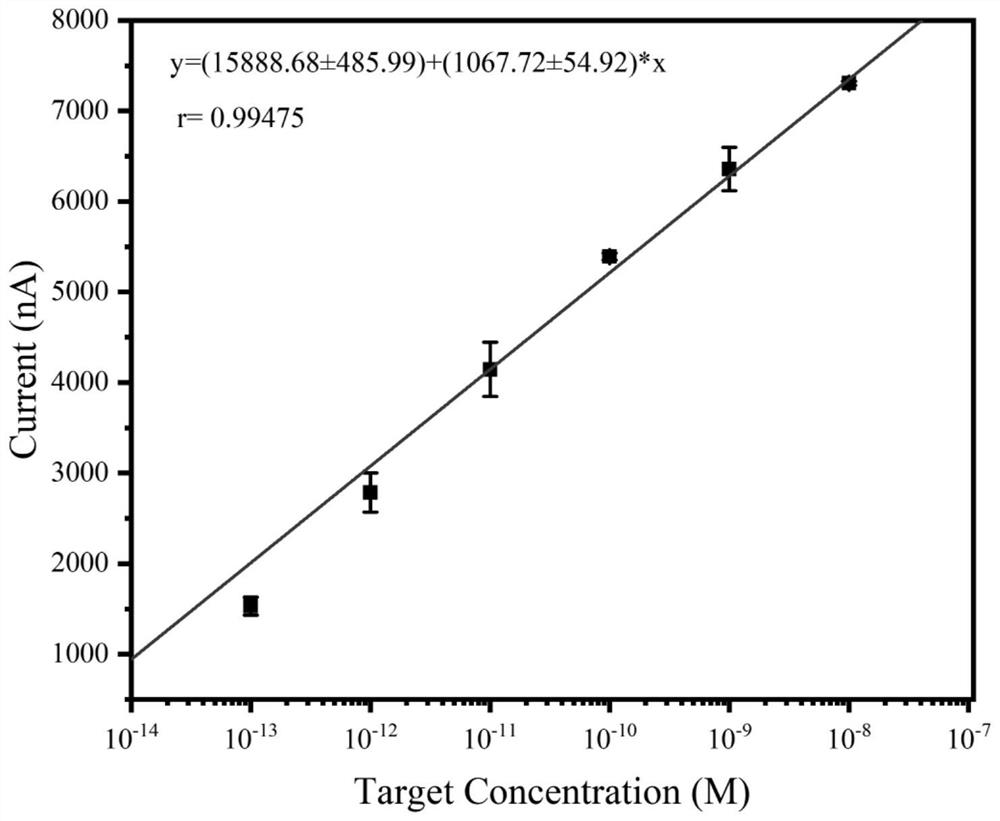
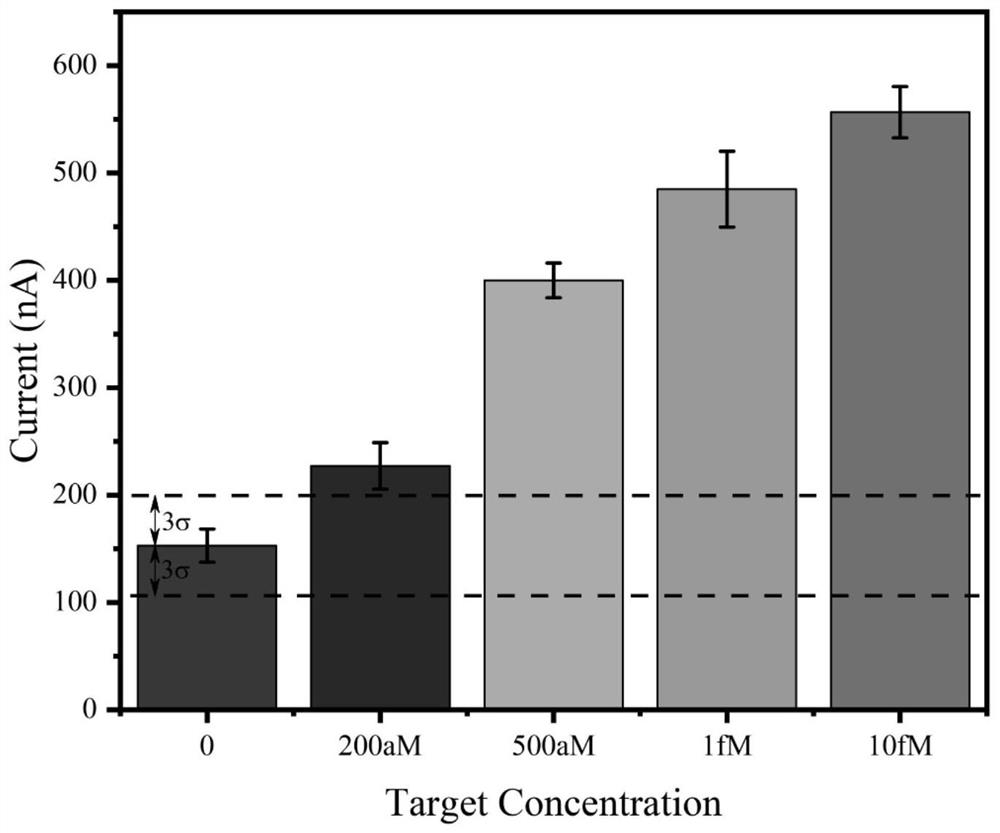
[0046] (2) In the LCR reaction system, add 1.0 × 10 -13 - 1.0×10 -8 M a series of DNA target strands with different concentrations, and the obtained products are electrochemically detected by the method of step (1), and different curren...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com