Method for preparing copolymer/HKUST-1 composite material by emulsion polymerization method
A HKUST-1, emulsion polymerization technology, applied in separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, dispersed particle separation, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the performance of polymer/MOFs composites, uneven particle dispersion, poor compatibility, etc. , to achieve the effects of good emulsion stability, improved compatibility, and enhanced synergistic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
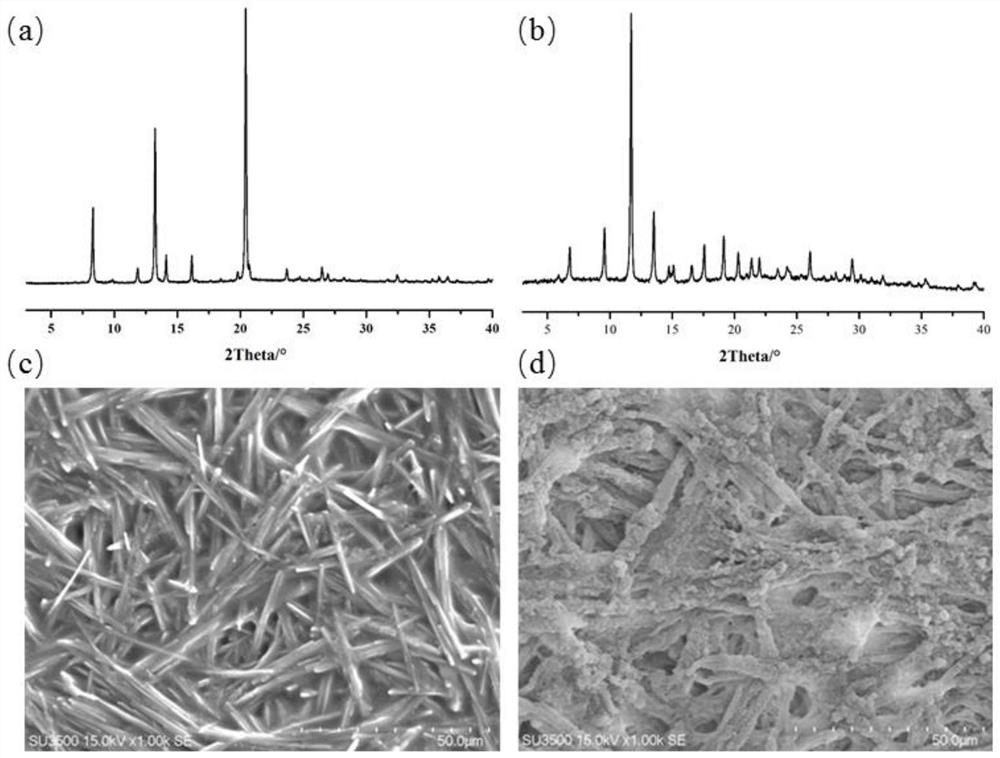
[0027] Weigh 0.28g of copper nitrate, 0.14g of copper methacrylate, and 0.42g of trimesic acid, place them in a beaker, add 15mL of deionized water, and transfer them to a three-necked flask with mechanical stirring after being fully dissolved by ultrasonic waves , placed in a water bath. An additional 0.12 g of sodium lauryl sulfate was then added. In addition, weigh 0.8g of butyl acrylate, 0.2g of styrene, 0.6g of methyl methacrylate, and 0.06g of methacrylic acid into a beaker, transfer them to a three-necked flask after mixing, and raise the temperature of the water bath to 40 -50°C, pre-emulsify at this temperature for 30-60min. Then raise the temperature to 75-85°C, and add fully dissolved potassium persulfate aqueous solution (0.12g dissolved in 5mL deionized water), react for 6-8h, and obtain a light blue emulsion after the reaction is completed. After the reaction stopped, part of the emulsion was taken out, centrifuged, and the supernatant was removed. The resulti...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Weigh 0.14g of copper nitrate, 0.07g of copper methacrylate, and 0.21g of trimesic acid, place them in a beaker, add 15mL of deionized water, and transfer them to a three-necked flask with mechanical stirring after being fully dissolved by ultrasound. , placed in a water bath. An additional 0.12 g of sodium lauryl sulfate was then added. In addition, weigh 0.8g of butyl acrylate, 0.2g of styrene, 0.6g of methyl methacrylate, and 0.06g of methacrylic acid into a beaker, transfer them to a three-necked flask after mixing, and raise the temperature of the water bath to 40 -50°C, pre-emulsify at this temperature for 30-60min. Then the temperature was raised to 75-85° C., and a fully dissolved potassium persulfate aqueous solution (0.12 g dissolved in 5 mL deionized water) was added to react for 6-8 hours, and a light blue emulsion was obtained after the reaction was completed. After the reaction stopped, part of the emulsion was taken out, centrifuged, and the supernatant...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Weigh 0.14g of copper nitrate, 0.07g of copper methacrylate, and 0.21g of trimesic acid, place them in a beaker, add 15mL of deionized water, and transfer them to a three-necked flask with mechanical stirring after being fully dissolved by ultrasound. , placed in a water bath. An additional 0.12 g of sodium lauryl sulfate was then added. In addition, weigh 1.6g of butyl acrylate, 0.4g of styrene, 1.2g of methyl methacrylate, and 0.12g of methacrylic acid into a beaker, transfer them to a three-necked flask after mixing, and heat the water bath to 40 -50°C, pre-emulsify at this temperature for 30-60min. Then raise the temperature to 75-85°C, and add fully dissolved potassium persulfate aqueous solution (0.12g dissolved in 5mL deionized water), react for 6-8h, and obtain a light blue emulsion after the reaction is completed. After the reaction stopped, part of the emulsion was taken out, centrifuged, and the supernatant was removed. The resulting solid was washed five ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com