Nucleic acid molecule, vector, cell, application of nucleic acid molecule, vector and cell, and screening method of plant apomixis clone seeds based on paternal imprinting gene
A nucleic acid molecule and transgenic plant technology, applied in the field of nucleic acid molecules, vectors and cells and their applications and the screening of plant apomictic cloned seeds based on paternally imprinted genes, can solve the problem of inability to sort seeds, low purity requirements, inability to The realization of the application of hybrid apomixis system, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0038] According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the nucleic acid molecule further comprises an expression cassette E2 carrying an embryo autonomous gene.
[0039] More preferably, the expression cassette E2 includes from upstream to downstream: a second promoter, an embryo autonomous gene and a second terminator, and more preferably, in order to further improve the purity of cloned seeds, the expression cassette E2 includes an egg cell-specific promoter Son, embryo autonomous gene and second terminator.
[0040] According to the present invention, the egg cell-specific promoter can be a variety of conventional promoters capable of specifically promoting the expression of embryo autonomous gene expression, preferably selected from but not limited to AtDD45, Os03g0296600pro, ECA1-like1 pro, DCL2, AT1G74480.1 and ZmEAl promoter; more preferably AtDD45, the sequence of AtDD45 is preferably shown in SEQ ID NO.7.
[0041] According to the present invention, the e...
Embodiment 1
[0094] This example is used to illustrate the acquisition of transgenic plants
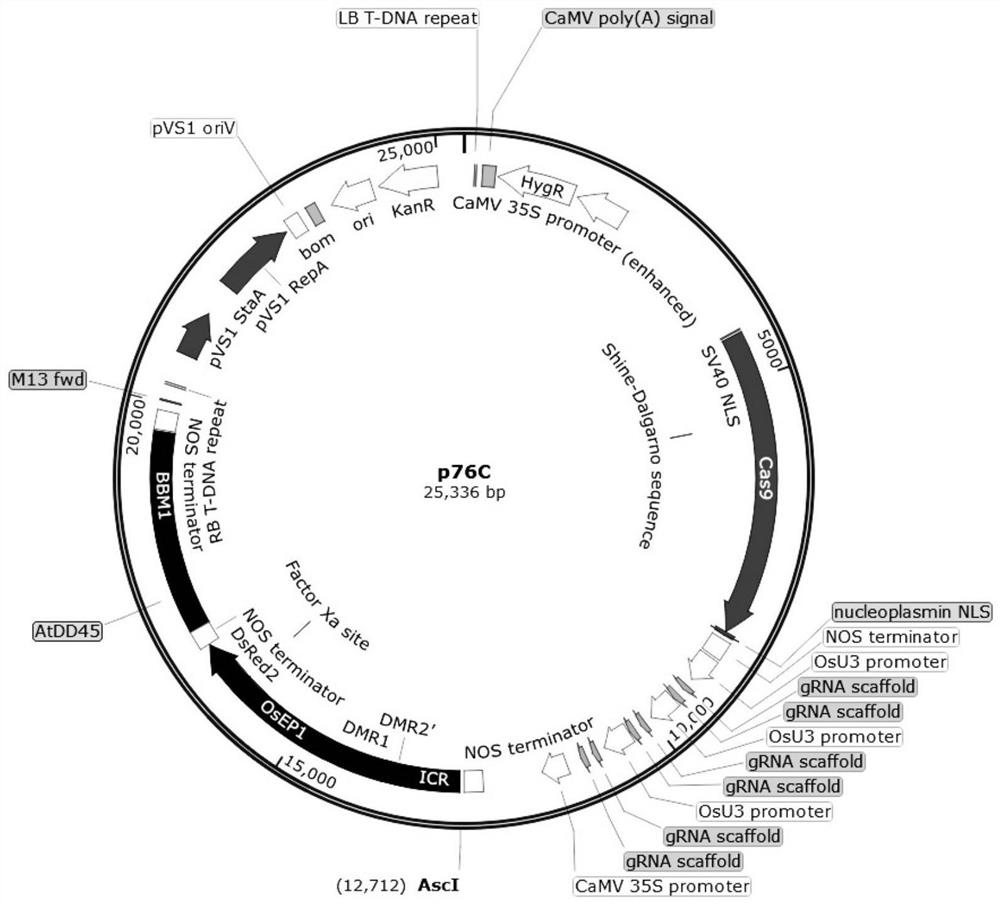
[0095] 1. Vector construction of apomictic vector p76C
[0096] 1. Synthetic expression cassettes E1 and E2
[0097] Synthetic expression cassette E1, the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1: including the fusion sequence of the paternal imprinted gene functional regions ICR, DMR2', DMR1 (SEQ ID NO.2), the embryo-specific expression promoter OsESP1 (SEQ ID NO.3 ), red fluorescent protein gene DsRed2 (SEQ ID NO.4), NOS terminator (SEQ ID NO.5).
[0098] The synthetic expression cassette E2, whose sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.6, includes egg cell-specific promoter AtDD45 (SEQ ID NO.7), embryo autonomous gene selection from BBM1 (SEQ ID NO.8), NOS terminator (SEQ ID NO. .5).
[0099] E1 and E2 were constructed as a linked expression cassette, named 76E.
[0100] 2. Construction of expression vector p76C
[0101] Two targets were designed in the coding regions of PAIR1, REC8, and OSD1 genes (PAI...
Embodiment 2
[0119] This example is used to illustrate the acquisition of transgenic plants
[0120] The transgenic plants were prepared according to the method of Example 1, except that the functional region of the paternally imprinted gene in the expression cassette E1 did not include ICR, DMR2', and DMR1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com