Vanadium-doped iron-based low-temperature denitration catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
A low-temperature denitrification and catalyst technology, which is applied in the direction of catalyst activation/preparation, chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of reduced catalyst activity, reduced catalytic performance, and unsuitable for practical applications.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
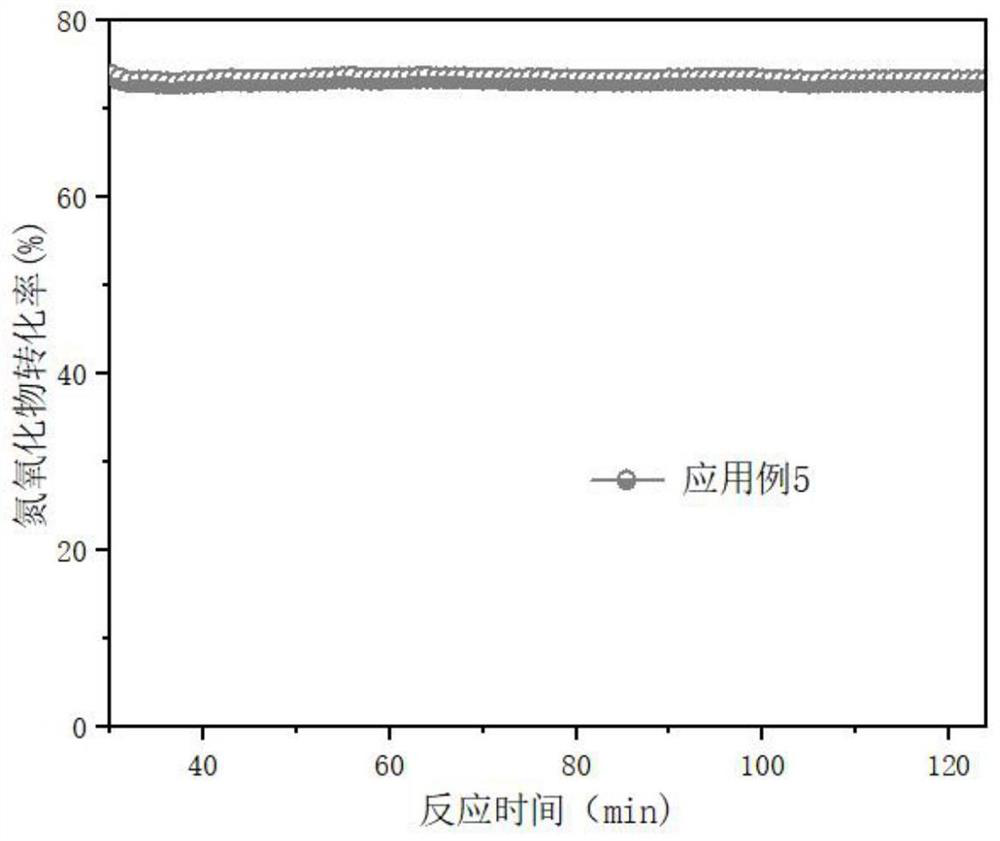
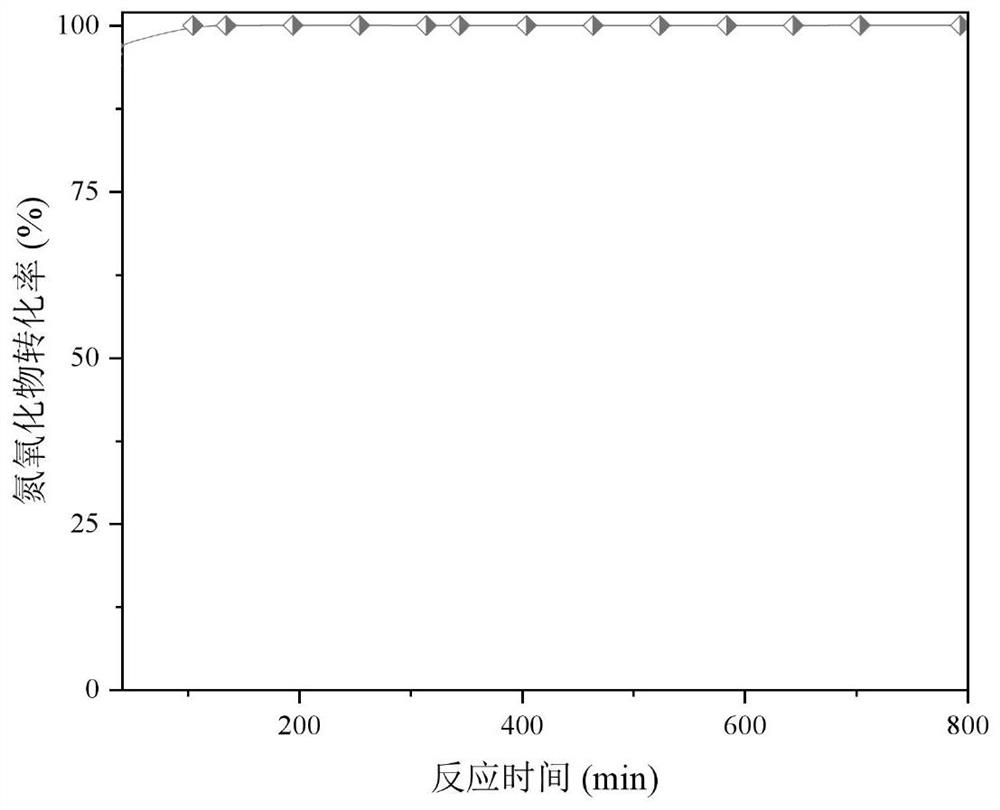
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0021] The invention provides a method for preparing a vanadium-doped iron-based low-temperature denitration catalyst, comprising the following steps:
[0022] Dissolving ferric salt, ferrous salt and pentavalent vanadium salt in water to obtain a mixed solution;
[0023] The mixed solution is mixed with the precipitant solution to undergo co-precipitation, and the obtained precipitate is dried and calcined in sequence to obtain a vanadium-doped iron-based low-temperature denitrification catalyst.
[0024] In the present invention, unless otherwise specified, the raw materials used are commercially available products well known in the art.
[0025] The present invention dissolves trivalent iron salt, divalent iron salt and pentavalent vanadium salt in water to obtain a mixed solution.
[0026] The present invention has no special requirements on the specific type of the ferric salt, as long as it can be dissolved in water. In the present invention, the ferric salt preferably...
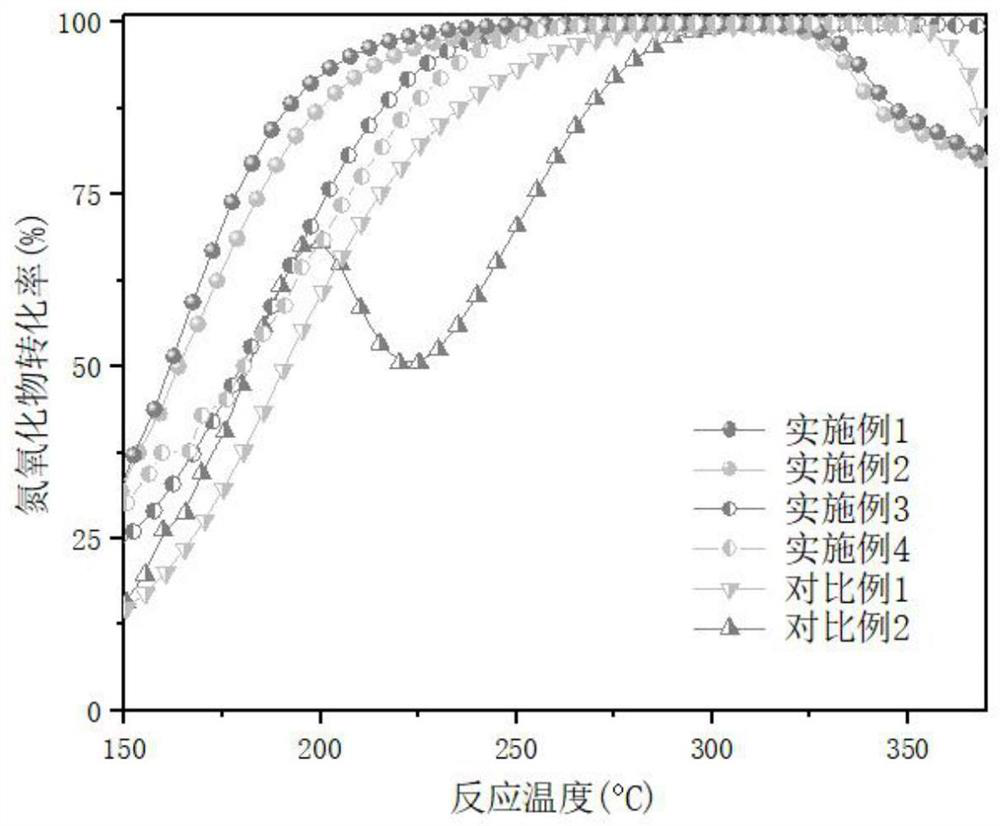
Embodiment 1
[0055] (1) Take 9.0g (0.0333mol) FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O and 4.63g (0.0166mol) FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O powder was added into deionized water, and stirred to dissolve it to obtain an iron salt solution.
[0056] (2) Take 0.065g (0.0006mol) NH 4 VO 3 Dissolve in deionized water to obtain a vanadium salt solution.
[0057] (3) Slowly drop the vanadium salt solution into the iron salt solution under stirring to obtain a mixed solution (wherein the molar ratio of V:Fe is 0.01:1).
[0058] (4) Under stirring, add NH dropwise to the mixed solution in step (3) 3 ·H 2 O, adjust the pH to 9.0, wash the obtained precipitate with deionized water three times, dry at 90°C for 9h, and calcinate the obtained solid in an air atmosphere at 300°C for 2h to obtain a vanadium-doped iron-based low-temperature denitrification catalyst.
Embodiment 2
[0060] The difference with Example 1 is that the NH added in step (2) 4 VO 3 The mass is 0.132g (0.001mol), and the molar ratio of V:Fe in the mixed solution obtained in the corresponding step (3) is 0.02:1, and the rest are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com