Method for preparing superfine high-purity high-solid-solubility tungsten-based alloy powder
A tungsten-based alloy, high-solid technology, applied in metal processing equipment, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of uneven particle size, low solid solubility, high impurity introduction, etc., to solve the problem of low solid solubility, promote Homogenize and improve the effect of comprehensive mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Take 60 g of auxiliary material tantalum powder with an average particle size of 27 μm and a purity of ≥99.95%, and put it in a cemented carbide 1L ball mill jar filled with 0.4L of absolute ethanol. Add 2 kg of cemented carbide ball milling beads with a diameter of 6 mm and 1 kg of cemented carbide balls with a diameter of 10 mm, the cemented carbide grade is YG8, and the composition is WC-8Co. After sealing the ball mill jar, evacuate it to 133Pa through a vacuum valve, and then fill it with high-purity argon, repeating 4 times. Install the ball mill tank on the omnidirectional planetary ball mill, add the counterweight at the corresponding position to balance the ball mill, set the rotation speed at 150rpm, stop for 5min every 1h and change the forward and reverse directions once, and start the omnidirectional reverse for 4 cycles at the same time Second-rate. The ball milling time is 8 hours, so that a layer of ductile auxiliary material coating layer is formed on ...
Embodiment 2
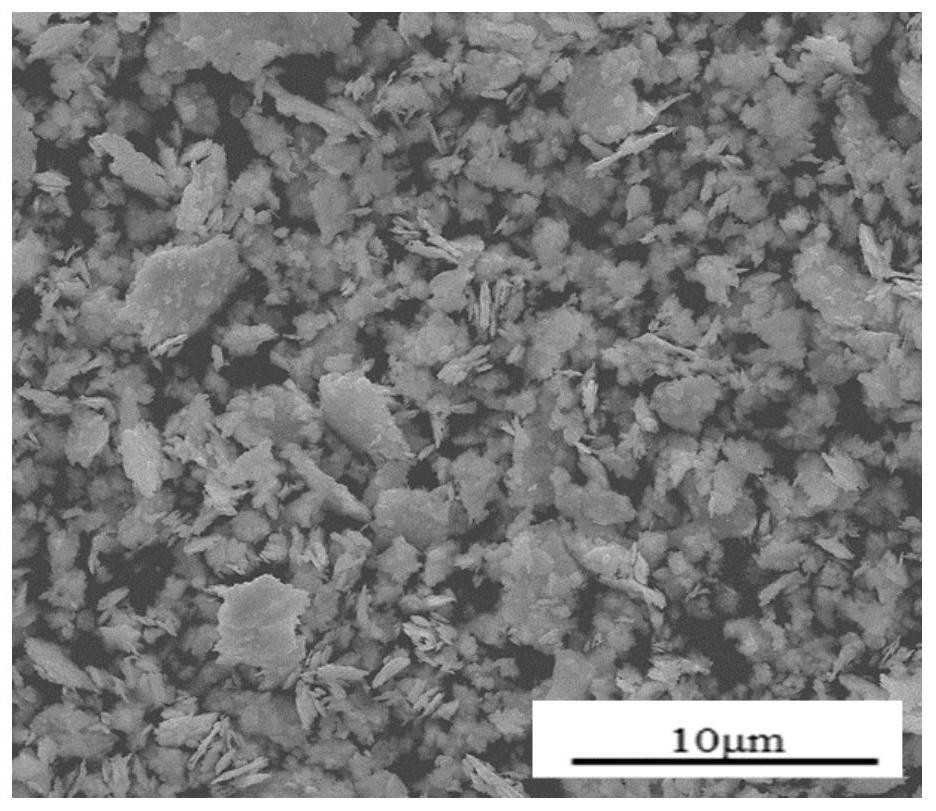
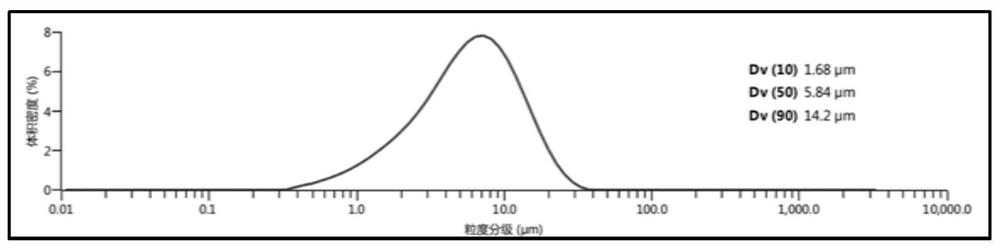
[0048] Get auxiliary material niobium powder 60g (average particle diameter 40 μ m, purity ≥ 99.9%), raw material tungsten powder 240g (average particle diameter 4 μ m, purity ≥ 99.95%), carry out two-step ball milling in the same manner with embodiment 1, second step ball milling time for 35h. Heat treatment temperature 800 ℃, other conditions are with embodiment 1, make tungsten-niobium alloy powder such as image 3 , the particle size distribution see Figure 4 . The average particle diameter of the obtained powder was 3.37 μm. (The span of powder particle size is less than or equal to 8 microns). The impurity content of powder analyzed by ICP-OES and carbon hydrogen oxygen tester is shown in Table 4.
Embodiment 3
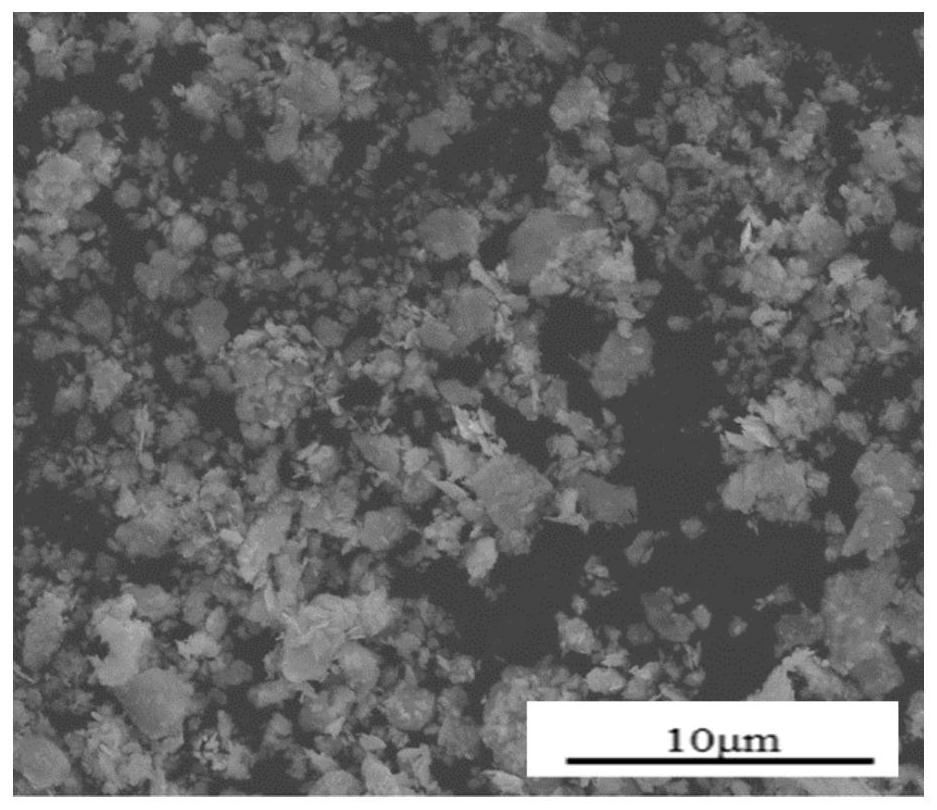
[0050] Get auxiliary material niobium powder 60g (average particle diameter 40 μm, purity ≥ 99.9%), auxiliary material tantalum powder 60g (average particle diameter 27 μm, purity ≥ 99.95%), raw material tungsten powder 180g (average particle diameter 4 μ m, purity ≥ 99.95%), with In the same manner as in Example 1, first add auxiliary materials tantalum powder and niobium powder for the first step of ball milling, then add tungsten powder for the second step of ball milling, the second step of ball milling time is 50h, the heat treatment temperature is 820°C, and other conditions are the same as in Example 1 , to obtain tungsten-tantalum-niobium alloy powder. The solid solution effect was analyzed by XRD as Figure 5 It can be seen from the figure that only the main peak of tungsten exists in the alloy powder, indicating that niobium and tantalum have been dissolved into the crystal lattice of tungsten to achieve alloying. The average particle diameter of the obtained powder...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com