A kind of collagen-based bioink for 3D bioprinting and its preparation method and application
A bio-ink, bio-printing technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, 3D culture, etc., can solve the problems of poor mechanical properties of pure collagen hydrogels, long collagen gelation time, and low structural resolution, etc. Achieve no cytotoxicity, prevent and treat cardiovascular diseases, and good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Embodiment 1: Preparation of collagen-based bioink
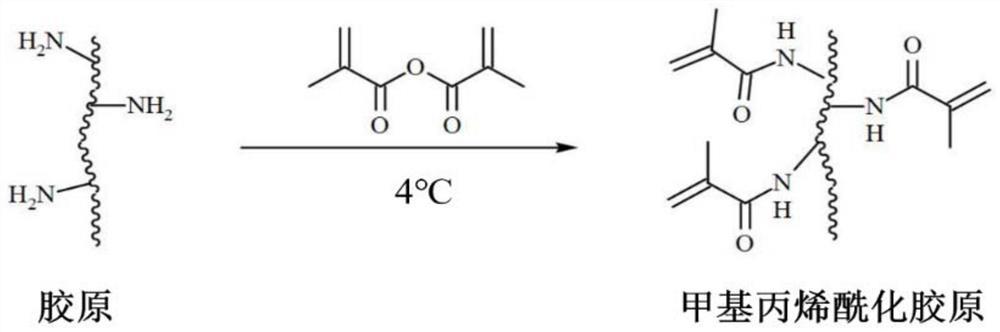
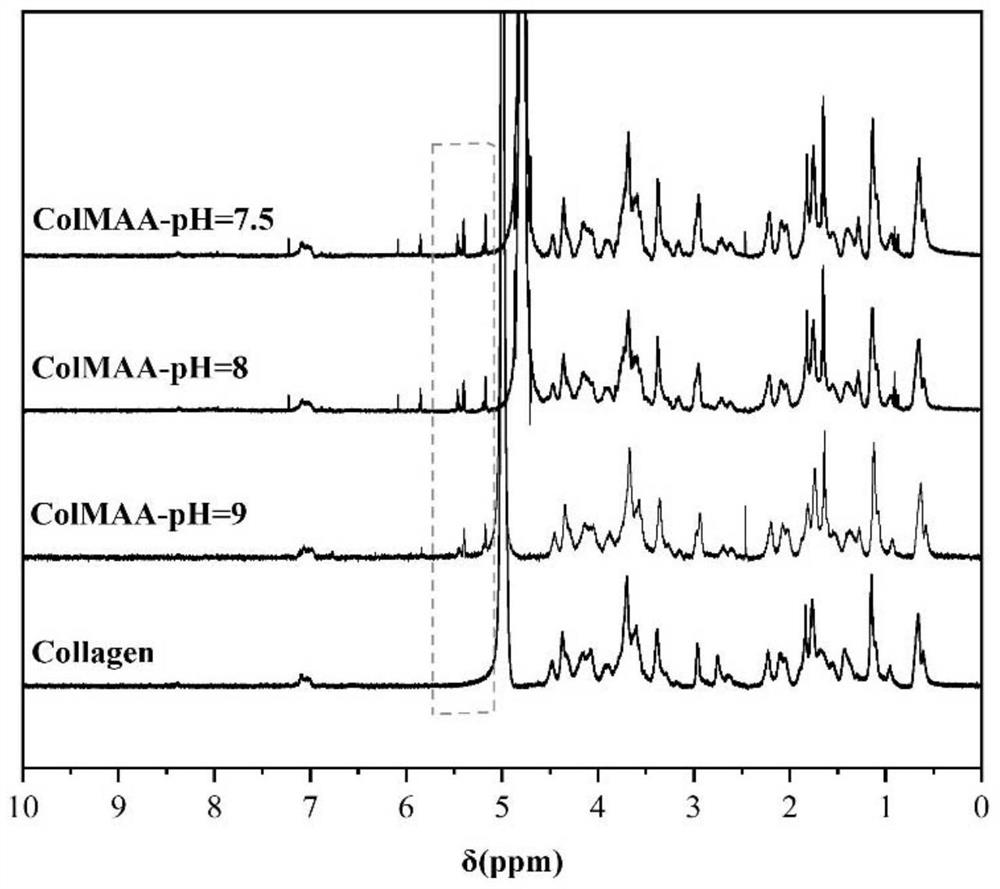
[0049] Dissolve 1 g of collagen in 400 mL of 10 mM hydrochloric acid solution, stir at 4°C for 8 h to dissolve completely, and prepare dilute hydrochloric acid solution of collagen. Use a molar concentration of 1M sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH of the collagen dilute hydrochloric acid solution to 9, add 2.3mL of methacrylic anhydride dropwise to the collagen dilute hydrochloric acid solution while stirring, and simultaneously add a molar concentration of 1M sodium hydroxide solution , the pH was stabilized at 9, and then stirred at 4°C and reacted in the dark for 8h. The reacted solution was poured into a dialysis bag with a cut-off flow rate of 8000-14000 Da, and dialyzed in 10 mM hydrochloric acid at 4° C. for 7 days, and the dialysate was changed twice a day. After the dialysis, the solution was frozen at -20°C, and then placed in a vacuum freeze dryer to freeze-dry to obtain a methacrylylated collagen...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Embodiment 2: the preparation of collagen-based bioink
[0054] Dissolve 1 g of collagen in 400 mL of 10 mM hydrochloric acid solution, stir at 4°C for 8 h to dissolve completely, and prepare dilute hydrochloric acid solution of collagen. Use a molar concentration of 1M sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH of the collagen dilute hydrochloric acid solution to 9, add 2.3mL of methacrylic anhydride dropwise to the collagen dilute hydrochloric acid solution while stirring, and simultaneously add a molar concentration of 1M sodium hydroxide solution , the pH was stabilized at 9, and then stirred at 4°C and reacted in the dark for 8h. The reacted solution was poured into a dialysis bag with a cut-off flow rate of 8000-14000 Da, and dialyzed in 10 mM hydrochloric acid at 4° C. for 7 days, and the dialysate was changed twice a day. After the dialysis, the solution was frozen at -20°C, and then placed in a vacuum freeze dryer to freeze-dry to obtain a methacrylylated coll...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment 3: the preparation of collagen-based bioink
[0058] The preparation method of the methacrylylated collagen freeze-dried sponge is the same as that in Example 2.
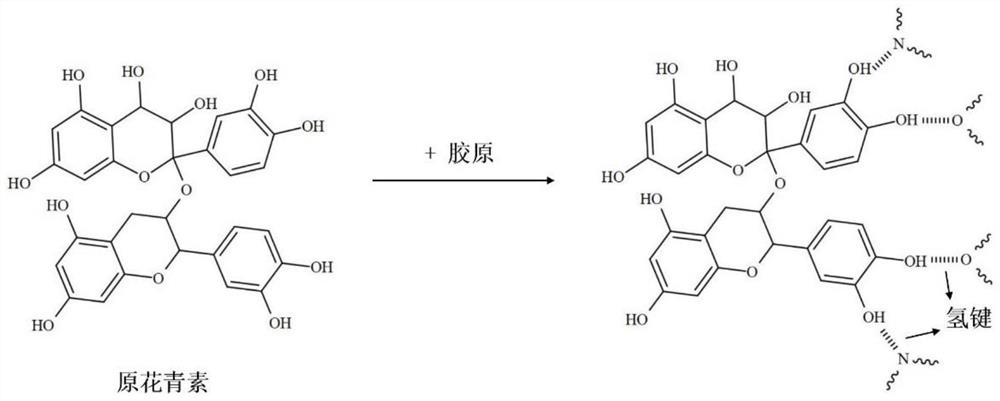
[0059] Dissolve 100 mg of methacrylylated collagen freeze-dried sponge in 5 mL of 0.2% acetic acid solution. After fully dissolving, adjust the pH to 7 with molar concentration of 1 M sodium hydroxide, add photoinitiator LAP aqueous solution and proanthocyanidin aqueous solution to the solution, The concentration of LAP in the solution is 0.5% (w / v), and the concentration of proanthocyanidin is 0.008% (w / v). After mixing evenly, centrifuge to remove air bubbles to obtain collagen-based bioink, and place it in a refrigerator at 4°C for 24 hours.
[0060] Take an appropriate amount of collagen-based bio-ink in the mold, irradiate it with ultraviolet light with a power of 10W and a wavelength of 365nm, and it can be cured for 30-50s to form a hydrogel.
[0061] Collagen-based bioink of example 1-3 i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of grafting | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com