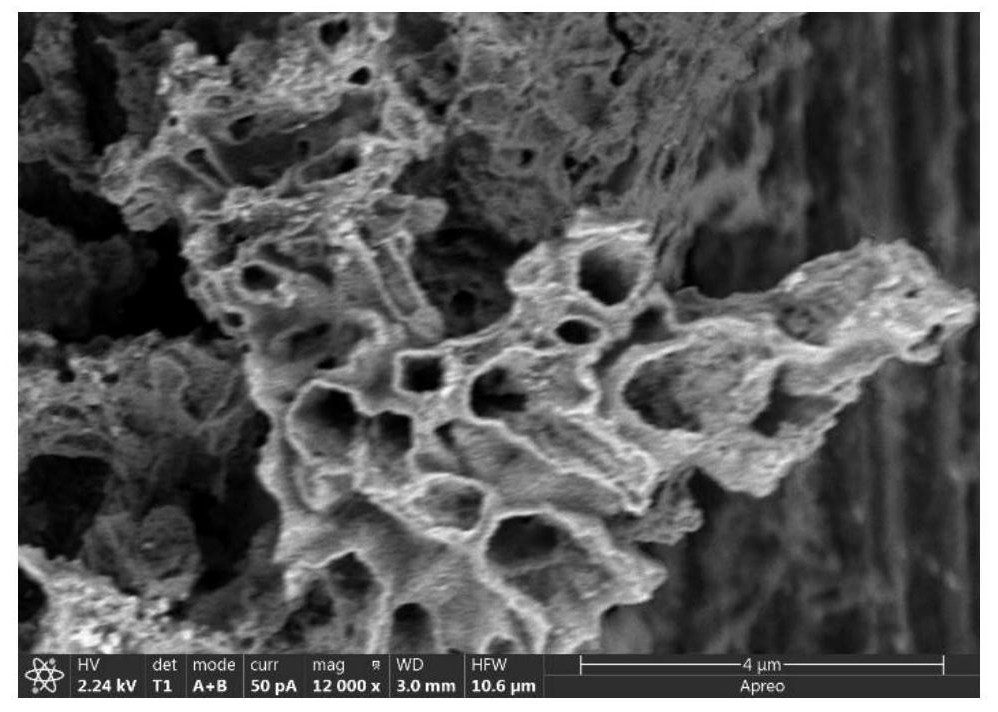
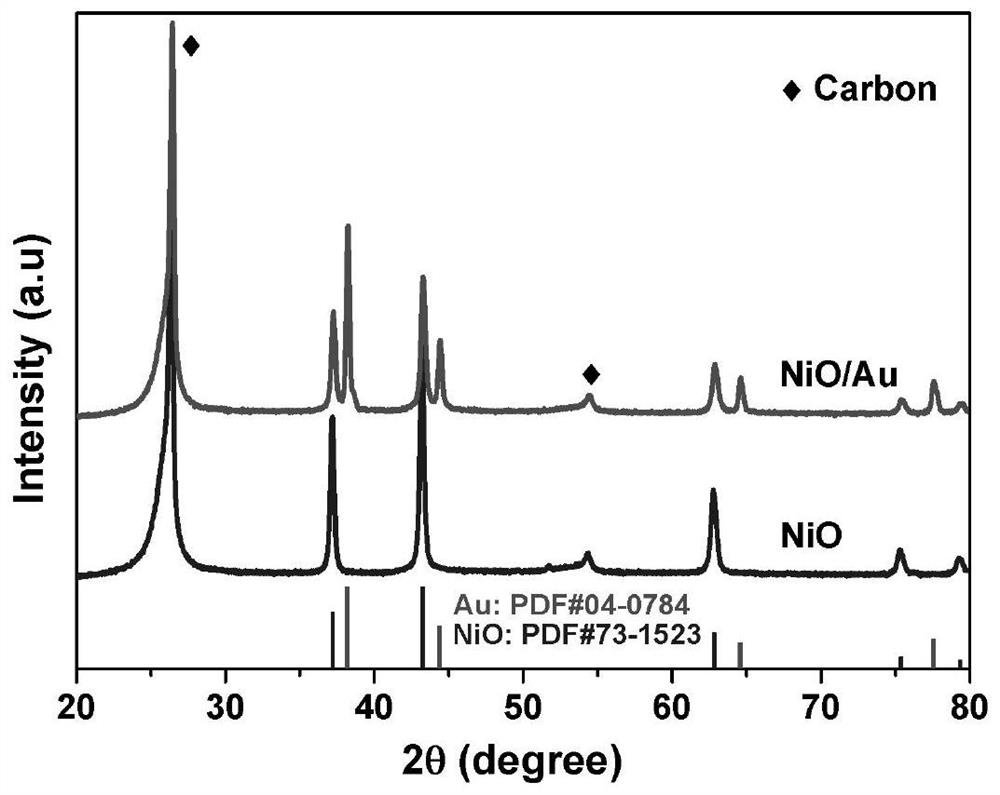
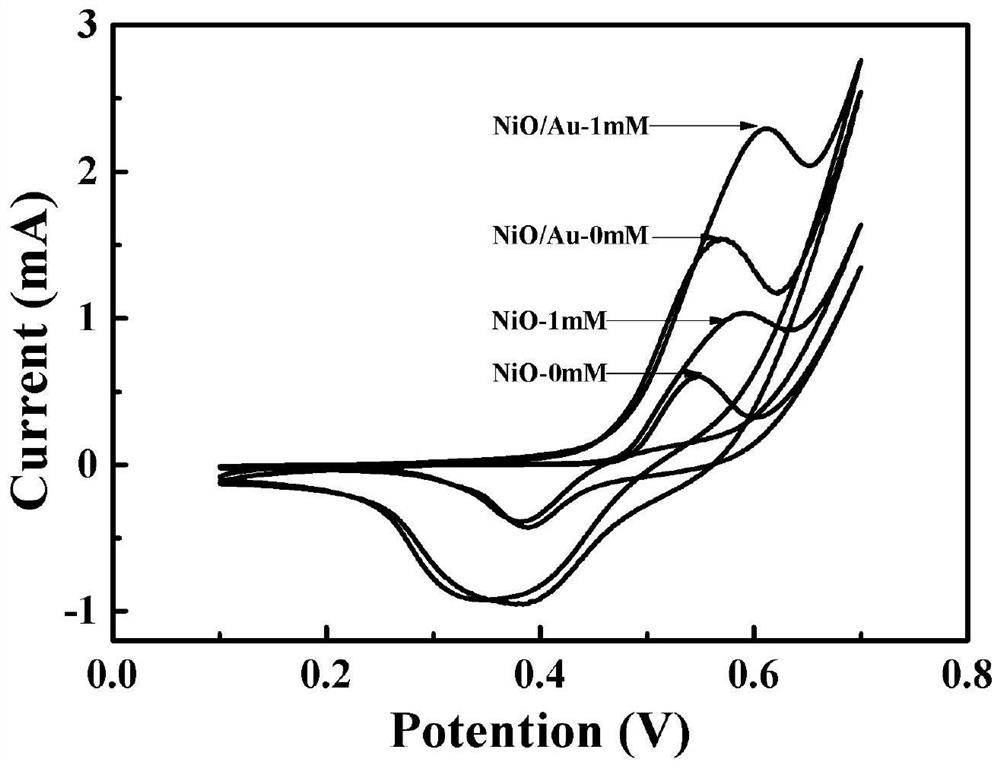
NiO/Au nanotube array flexible electrode with core-shell structure and application of NiO/Au nanotube array flexible electrode
A nanotube array, core-shell structure technology, applied in the field of enzyme-free glucose detection, can solve the problems of difficulty in meeting daily application requirements, poor stability, and high price, and achieve the effects of improving glucose sensing performance, controllable size, and low price.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] (1) First use cyclic voltammetry to test the carbon cloth in H 2 SO 4 Processing in solution, voltage scanning range -1.2V-1.2V, scanning rate 0.1V / S. The treated carbon cloth was then treated with 1mM ZnCl 2 The ZnO nanorod array template was prepared by a two-step constant voltage electrodeposition method in the electrolyte, the deposition temperature was 80°C, the first step deposition potential was -1.3V, and the time was 0.5S, and the second step potential was -1.0V, and the time was 3600S.
[0035] (2) The above-mentioned carbon cloth deposited with ZnO nanorod array template was mixed with 10mM HAuCl 4 H 3 BO 3 A voltage of -0.2V was applied to the solution, and electrodeposition was carried out at room temperature for 30s.
[0036] (3) The above carbon paper containing 0.5M Ni(NO 3 ) 2 H 3 BO 3 The solution was deposited under a voltage of -0.9V for 60s.
[0037](4) Calcining the above materials at 350°C for 2h. Finally, the material was soaked in 6M ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] (1) First use cyclic voltammetry to test the carbon cloth in H 2 SO 4 Processing in solution, voltage scanning range -1.2V-1.2V, scanning rate 0.1V / S. The treated carbon cloth was then treated with 2mM ZnSO 4 The ZnO nanorod array template was prepared by a two-step constant voltage electrodeposition method in the electrolyte, the deposition temperature was 70°C, the first step deposition potential was -1.4V, and the time was 3S, and the second step potential was -0.6V, and the time was 4000S.
[0040] (2) The above-mentioned carbon cloth deposited with ZnO nanorod array template was mixed with 5mM HAuCl 4 H 3 BO 3 A voltage of -0.1V was applied to the solution, and electrodeposition was carried out at room temperature for 50s.
[0041] (3) The above carbon paper containing 0.3M NiCl 2 H 3 BO 3 The solution was deposited under the voltage of -1.1V for 20s.
[0042] (4) The above materials were calcined at 300°C for 4h. Finally, the material was soaked in 5M Na...
Embodiment 3
[0044] (1) First use cyclic voltammetry to test the carbon cloth in H 2 SO 4 Processing in solution, voltage scanning range -1.2V-1.2V, scanning rate 0.1V / S. Then the treated carbon cloth was mixed with 3mM Zn(NO 3 ) 2 The ZnO nanorod array template was prepared by a two-step constant voltage electrodeposition method in the electrolyte, the deposition temperature was 100°C, the deposition potential of the first step was -1.2V, and the time was 0.3S, and the potential of the second step was -1.1V, and the time was 1000S.
[0045] (2) The above-mentioned carbon cloth deposited with ZnO nanorod array template was mixed with 20mM HAuCl 4 H 3 BO 3 A voltage of -0.4V was applied to the solution, and electrodeposition was performed at room temperature for 10s.
[0046] (3) The above carbon paper containing 0.8M NiSO 4 H 3 BO 3 The solution was deposited under a voltage of -0.8V for 120s.
[0047] (4) Calcining the above materials at 500°C for 0.5h. Finally, the material wa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com