Zinc/graphene three-dimensional composite structure negative electrode for zinc battery and preparation method thereof
A three-dimensional composite and three-dimensional structure technology, applied in the direction of electrode manufacturing, battery electrodes, negative electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of limited contact interface, unfavorable device magnification, power, etc., achieve strong negative electrode stability, improve the growth of zinc dendrites, Effect of bendable mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0024] The invention provides a preparation method of a zinc / graphene three-dimensional composite structure negative electrode for zinc batteries, comprising the following steps:
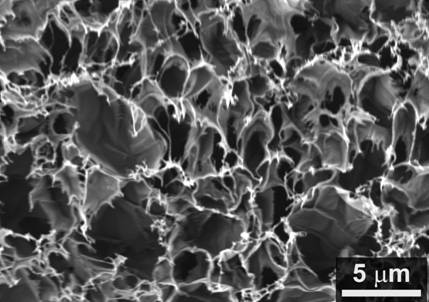
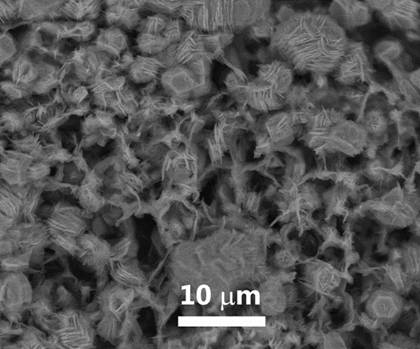
[0025] (1) Using polyimide fiber paper or polyimide film as carbon source, CO 2 The laser is the heat source, and the three-dimensional graphene layer is prepared by laser induction to obtain laser-induced graphene, such as figure 1 and 2 shown.
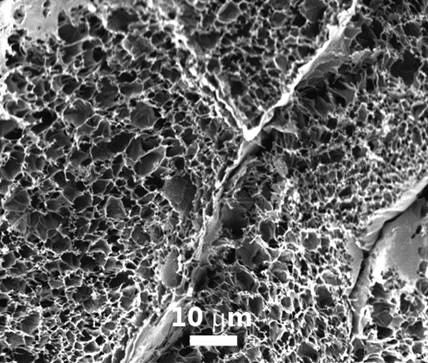
[0026] (2) Using the laser-induced graphene as the working electrode and the zinc sheet as the reference electrode and the counter electrode, immersed in the electrolyte solution, using an electrochemical workstation, electroplating at a constant voltage in the range of -1.0 to -0.8V for 20–60 min, The zinc / graphene three-dimensional composite structure negative electrode is obtained, such as image 3 shown.
[0027] The electrolyte solution used in the electroplating process is a weak acid zinc salt aqueous solution.
[0028] Another embodiment of th...
Embodiment 1
[0030] Using porous polyimide fiber paper as carbon source, CO 2 The laser is the heat source, the power is 15W, the scanning speed of the laser beam is 15 cm / s, and the induction preparation is 1×2 cm 2 Graphene region obtained by laser-induced graphene. figure 1 The SEM morphology of the laser-induced graphene prepared in Example 1.
[0031] The laser-induced graphene was used as the working electrode, and two zinc sheets were used as the reference electrode and the counter electrode, respectively, immersed in a 2M zinc sulfate aqueous solution, and electroplated at a constant voltage of – 0.9 V for 40 min using an electrochemical workstation to obtain three-dimensional zinc / graphene. Composite structure negative electrode. image 3 This is the SEM image of the zinc / graphene three-dimensional composite structure negative electrode prepared in Example 1.
Embodiment 2
[0033] Using porous polyimide membrane as carbon source, CO 2 The laser is the heat source, the power is 20W, the scanning speed of the laser beam is 50 mm / s, and the induction preparation is 2×2 cm 2 Graphene region obtained by laser-induced graphene. figure 2 It is the SEM topography of the laser-induced graphene prepared in Example 2.
[0034] The laser-induced graphene was used as the working electrode, and the two zinc sheets were used as the reference electrode and the counter electrode, respectively, immersed in a 3 M zinc sulfate aqueous solution, and electroplated at a constant voltage of – 0.8 V for 25 min using an electrochemical workstation to obtain zinc / Graphene three-dimensional composite structure anode.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com