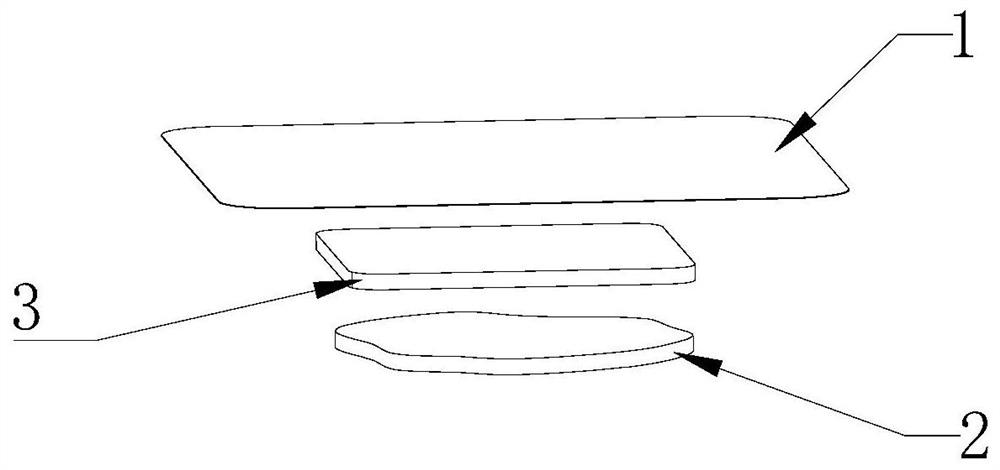
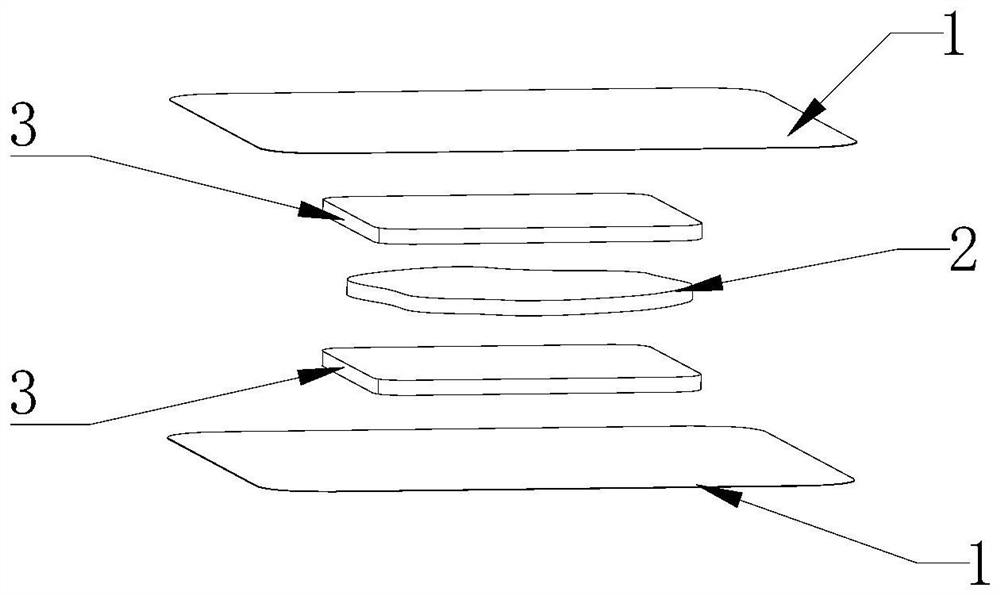
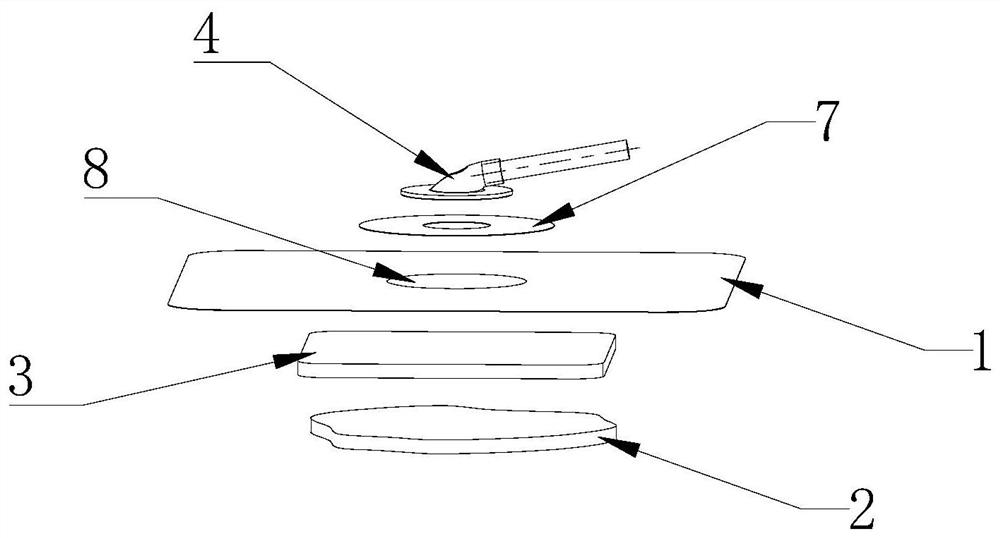
Multilayer dressing for assisting wound healing
A protective layer and filling layer technology, applied in the chemical field, can solve problems such as inconvenient use, unbalanced force, and unfit dressings
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1: A kind of moist dressing and preparation method thereof
[0047] This embodiment provides a wet dressing, the preparation method of which is as follows:
[0048] Mix 0.5mol PPG6000 triol (weight-average molecular weight of 6000) with 2.5mol HDI, react at 80°C for 1 hour to obtain the reaction product; add 0.85mol PEG1000 (weight-average molecular weight of 1000), 0.85mol PEG2000 ( The weight average molecular weight is 2000) and 0.1mol hyaluronic acid (the weight average component is 1,000,000), cross-linking reaction at 80°C for 6 hours to obtain star-shaped hydrophilic polyurethane; 0.1mol sodium bicarbonate (foaming agent), 0.4 mol water, 0.5mol polydimethylsiloxane-polyoxyalkylene copolymer (surfactant), 0.1mol ethylenediamine and 0.1mol zinc isooctanoate (catalyst) are mixed to obtain a foaming component; the star-shaped hydrophilic After the permanent polyurethane and the foaming component were mixed uniformly according to the mass ratio of 1:2.5, t...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: a kind of moist dressing and preparation method thereof
[0050] This embodiment provides a wet dressing, the preparation method of which is as follows:
[0051] On the basis of Example 1, by 0.1mol sodium bicarbonate (foaming agent), 0.4mol water, 0.5mol polydimethylsiloxane-polyoxyalkylene copolymer (surfactant), 0.1mol ethylenediamine and 0.1mol zinc isooctanoate (catalyst) is mixed and the foaming component is replaced by 0.1mol sodium bicarbonate (foaming agent), 0.4mol water, 0.5mol polydimethylsiloxane-polyoxyalkylene copolymer (interface active agent), 0.1mol ethylenediamine and 0.4mol dimethylethanolamine (catalyst) were mixed to obtain a foaming component, and wet dressing 2 was obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0052] Embodiment 3: a kind of moist dressing and preparation method thereof
[0053] This embodiment provides a wet dressing, the preparation method of which is as follows:
[0054] On the basis of Example 1, by 0.1mol sodium bicarbonate (foaming agent), 0.4mol water, 0.5mol polydimethylsiloxane-polyoxyalkylene copolymer (surfactant), 0.1mol ethylenediamine and 0.1mol of zinc isooctanoate (catalyst) is mixed and the foaming component is replaced by 0.1mol of sodium bicarbonate (foaming agent), 0.4mol of water, 0.5mol of polyoxyalkylene (surfactant), 0.2mol of butanediamine and 0.4 mol dimethylethanolamine (catalyst) was mixed to obtain a foaming component, and wet dressing 3 was obtained.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com