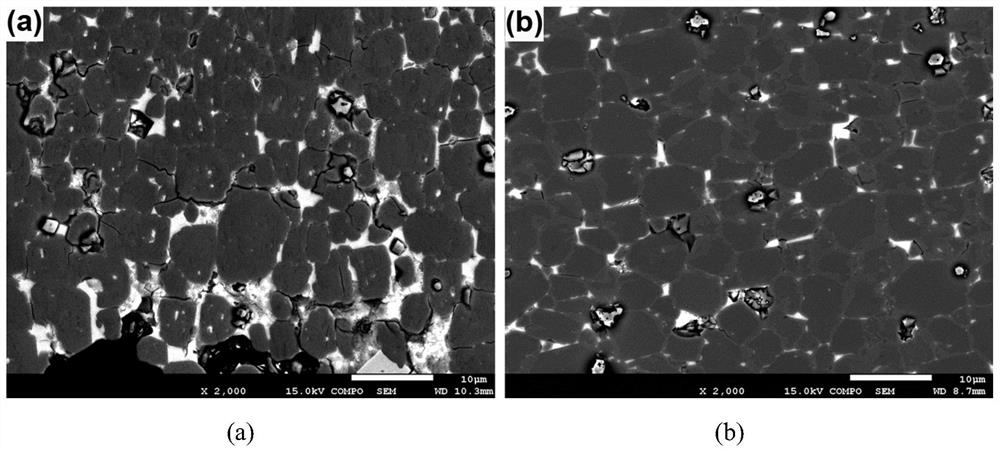
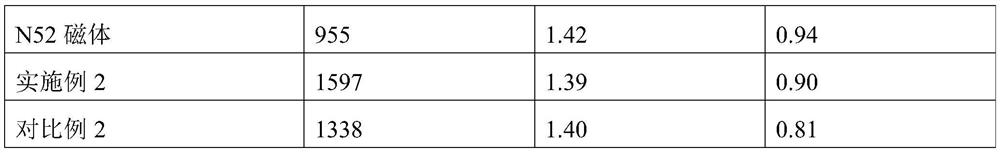
Preparation method of neodymium-iron-boron magnet with large-depth grain boundary diffusion
A technology of grain boundary diffusion and NdFeB, applied in the direction of magnetic objects, inductance/transformer/magnet manufacturing, magnetic materials, etc., can solve the problem of shallow depth of grain boundary diffusion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] A method for preparing a large depth grain boundary diffuse NdFeB magnet, including the following steps:
[0024] Step 1, select the NICE iron magnet of the commercial grade N52, cut N52 magnets into 10 × 10 × 5 (c-axis) mm 3 The surface oxide layer was placed with sandpaper, and clean with acetone.
[0025] Step 2, the magnet produced by steps is immersed in liquid nitrogen in -196 ° C for 20 minutes;
[0026] Step three, the magnet processed by step deeper is taken out from liquid nitrogen to increase the temperature of the magnet to room temperature;
[0027] Step 4, repeat steps 2 and step three 3 times;
[0028] Step 5. The magnet surface after step four is applied to the low melting point alloy DY. 70 Cu 30 Powder, put it in a vacuum furnace to 1 × 10 -2 PA, then elevated temperature to 800 ° C, heat insulation 1H;
[0029] Step 6. The magnet after the diffusion process in step five is lowered at 450 ° C for 2 hours, and the vacuum is set to 1 × 10 -2 PA.
Embodiment 2
[0038] A method for preparing a large depth grain boundary diffuse NdFeB magnet, including the following steps:
[0039] Step 1, select the sintered NdFeB magnet of the commercial grade N52, cut N52 magnets into 10 × 10 × 15 (c-axis) mm 3 The surface oxide layer was placed with sandpaper, and clean with acetone.
[0040] Step 2, the magnet produced by the step is immersed in liquid nitrogen in liquid nitrogen for 40 minutes;
[0041] Step three, the magnet processed by step deeper is taken out from liquid nitrogen to increase the temperature of the magnet to room temperature;
[0042] Step four, repeat steps 2 and steps three 4 times;
[0043] Step 5, the magnet surface is applied to the surface of the magnet surface to apply low melting point alloy TB 70 Cu 30 Powder, put it in a vacuum furnace to 1 × 10 -3 PA, then elevated temperature to 900 ° C, heat insulation 10h;
[0044] Step 6. The magnet after the step five diffusion is lowered at 480 ° C for 1 h, and the vacuum is set t...
Embodiment 3
[0054] A method for preparing a large depth grain boundary diffuse NdFeB magnet, including the following steps:
[0055] Step 1, select the sintered NdFeB magnet of the commercial grade N52, cut N52 magnets into 10 × 10 × 10 (c-axis) mm 3 The surface oxide layer was placed with sandpaper, and clean with acetone.
[0056] Step 2, the magnets formed by the steps were immersed in liquid nitrogen in liquid nitrogen in liquid nitrogen for 30 minutes;
[0057] Step three, the magnet processed by step deeper is taken out from liquid nitrogen to increase the temperature of the magnet to room temperature;
[0058] Step 4, repeat steps 2 and step three 5 times;
[0059] Step 5, the magnet surface after step four is applied to the low melting point alloy DYF 3 Powder, put it in a vacuum furnace to 1 × 10 -3 PA, then elevated temperatures to 950 ° C, heat insulation 5h;
[0060] Step 6, the magnet after the diffusion process in step five is lowered at 520 ° C for 6 hours, and the vacuum is se...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com