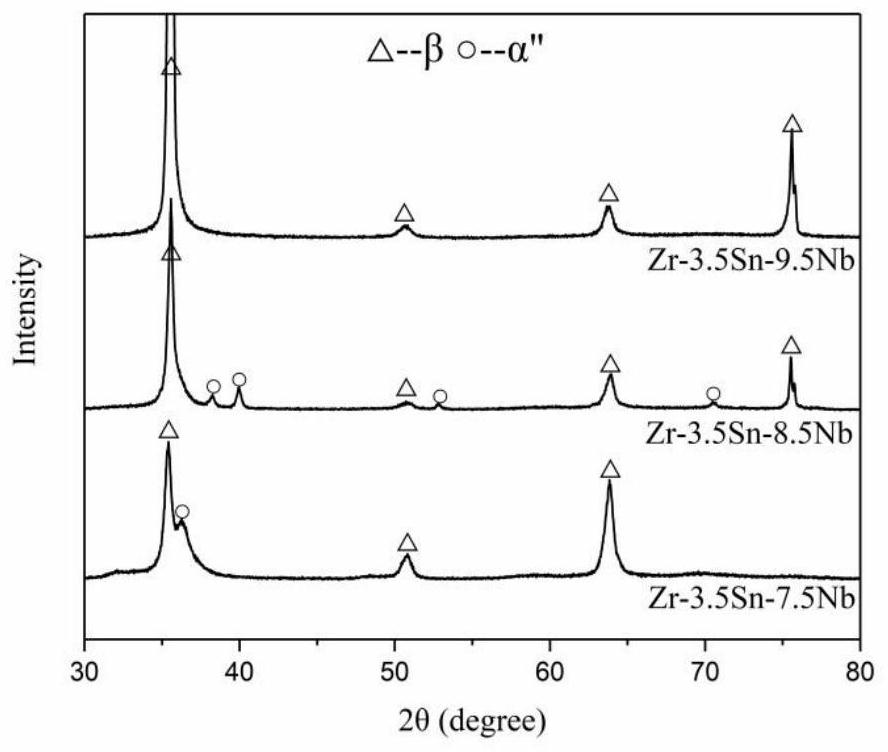
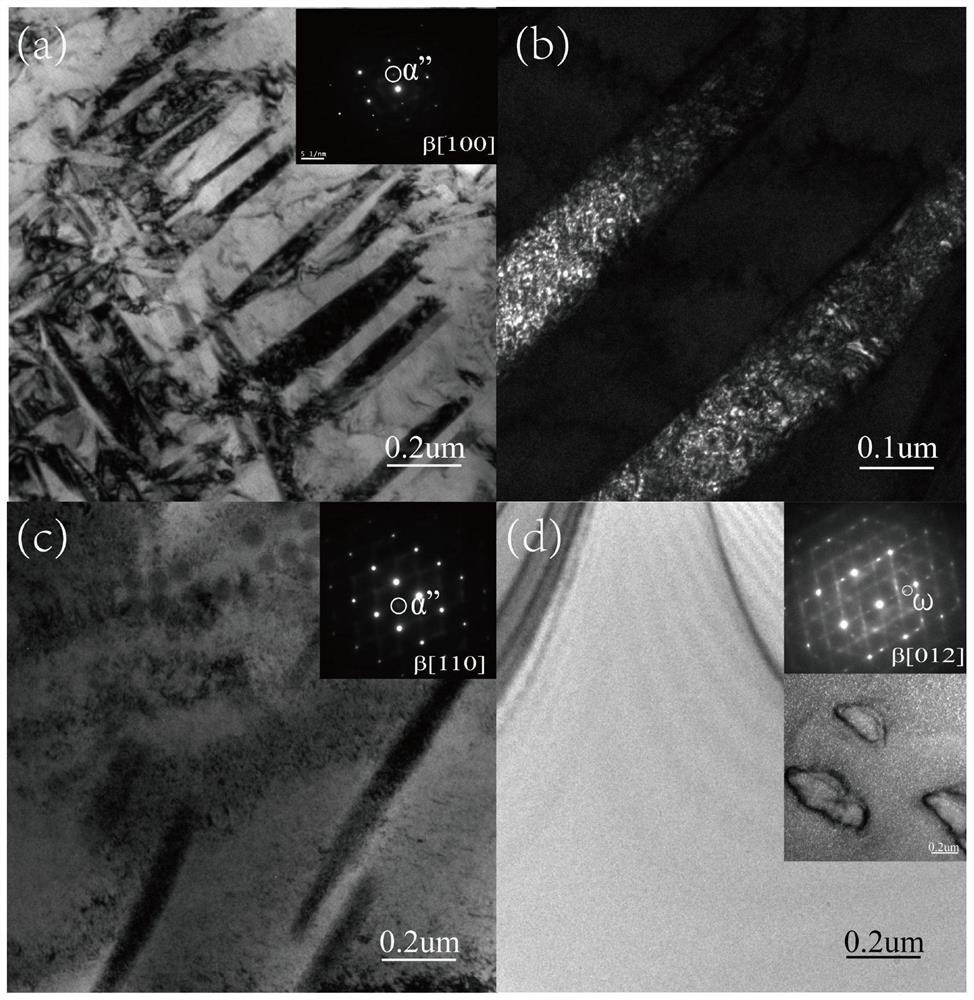
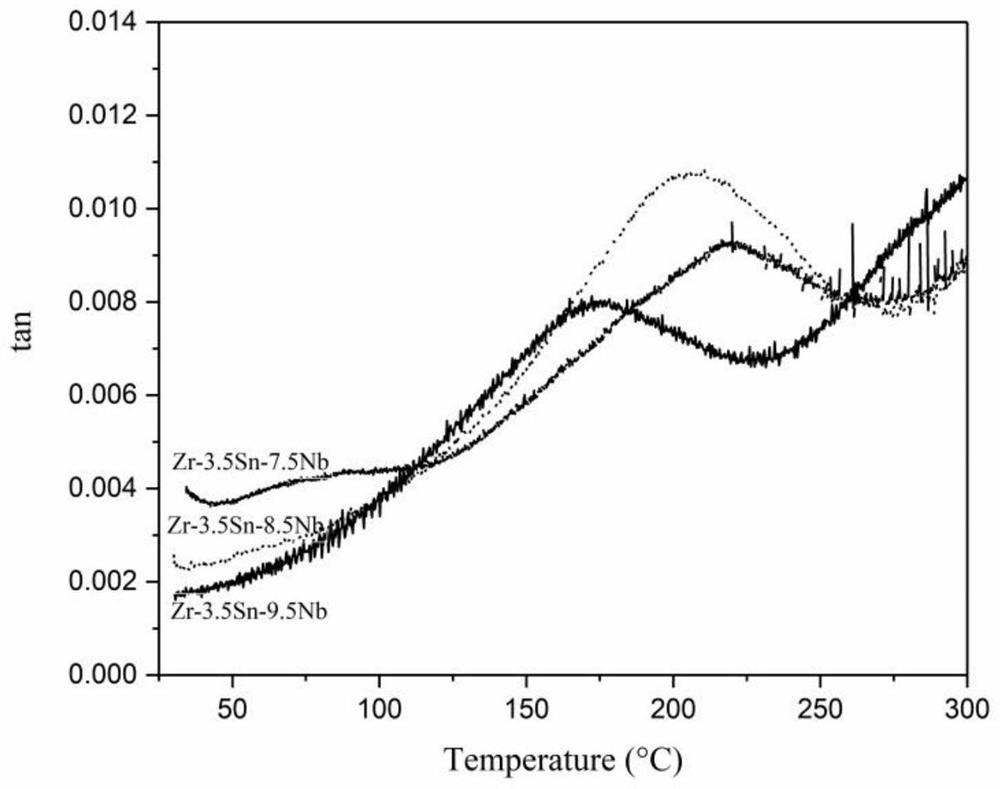
Biomedical zirconium-based nickel-free low-susceptibility shape memory alloy, preparation method thereof and biomedical material
A biomedical and memory alloy technology, applied in the field of alloy materials, can solve problems such as unfavorable diagnosis, imaging artifacts, etc., and achieve the effects of good superelasticity, shape memory effect, high elongation, and wide application range.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0040] The present invention provides a preparation method of a biomedical zirconium-based nickel-free low magnetic susceptibility shape memory alloy described in the above technical solution, comprising the following steps:
[0041] According to the elemental composition of the biomedical zirconium-based nickel-free low magnetic susceptibility shape memory alloy described in the above technical scheme, the raw materials are blended and smelted, and cooled to obtain an ingot;
[0042] performing annealing treatment and first ice-water quenching on the ingot in sequence to obtain a quenched ingot;
[0043] Forging the quenched ingot to obtain a forging billet;
[0044] The forged billet is sequentially subjected to solid solution treatment and second ice-water quenching to obtain a biomedical zirconium-based nickel-free low magnetic susceptibility shape memory alloy.
[0045] According to the elemental composition of the biomedical zirconium-based nickel-free low magnetic suscep...
Embodiment 1
[0056] (1) Use an electronic balance to accurately weigh the raw materials Zr particles (99.9%), Nb particles (99.9%) and Sn particles (99.99%) for batching. In order to prevent volatilization during the Sn smelting process, first place some Zr particles in the crucible , then the Sn particles are evenly placed on the Zr particles, and finally the Nb particles and the remaining Zr particles are evenly placed on the Sn particles, wherein the part of the Zr particles accounts for 25% of the total mass of the Zr particles; Put it in a high-vacuum non-consumable arc melting furnace, under the protection of argon, carry out melting at 1900°C for 2.5 hours to obtain a melting solution; after cooling the melting solution, a button-shaped ingot with a mass of 400g is obtained;
[0057] (2) Heating the vacuum tube furnace to 1000°C, then placing the ingot in the vacuum tube furnace, annealing at 1000°C for 24 hours, and then quenching the annealed ingot with a mixture of ice and water t...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Prepare biomedical zirconium-based nickel-free low magnetic susceptibility shape memory alloy according to the method of Example 1, the difference is that the composition of the obtained alloy is specifically Nb 8.46at.%, Sn 3.58at.%, and the balance Zr; the alloy is recorded as Zr-3.5Sn-8.5Nb alloy.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| magnetic susceptibility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| magnetic susceptibility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com