Method for creating high-anthocyanin horticultural ornamental poplar by utilizing miR156
A kind of anthocyanin and poplar technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve the problem of single color of poplar, achieve the effects of increasing branches, small leaves, and improving stress resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The poplar transgenic plant with up-regulated expression of embodiment 1 miR156 was obtained
[0039] 1. Pre-MtmiR156b overexpression vector construction
[0040] (1) Use the DNA of alfalfa R108 as a template (the partial sequence of the template is shown in SEQ ID NO.3), and use HiFi high-fidelity amplification enzyme and primers pre-MtmiR156b-F, pre-MtmiR156b-R to clone the precursor of alfalfa miR156 miR156b.
[0041] pre-MtmiR156b-F: CACCCTTCCTCAGACAACAACAAG, SEQ ID NO.4;
[0042] pre-MtmiR156b-R: CTGGTGGTAGGATTTTTGTCA, SEQ ID NO.5.
[0043] (2) Digest the pCXSN plasmid with XcmI.
[0044] (3) Ligate the amplified fragment in step (1) with the digested pCXSN in step (2) with T4 ligase to obtain the overexpression vector pCXSN-pre- MtmiR156b.
[0045] 2. Obtaining of transgenic plants
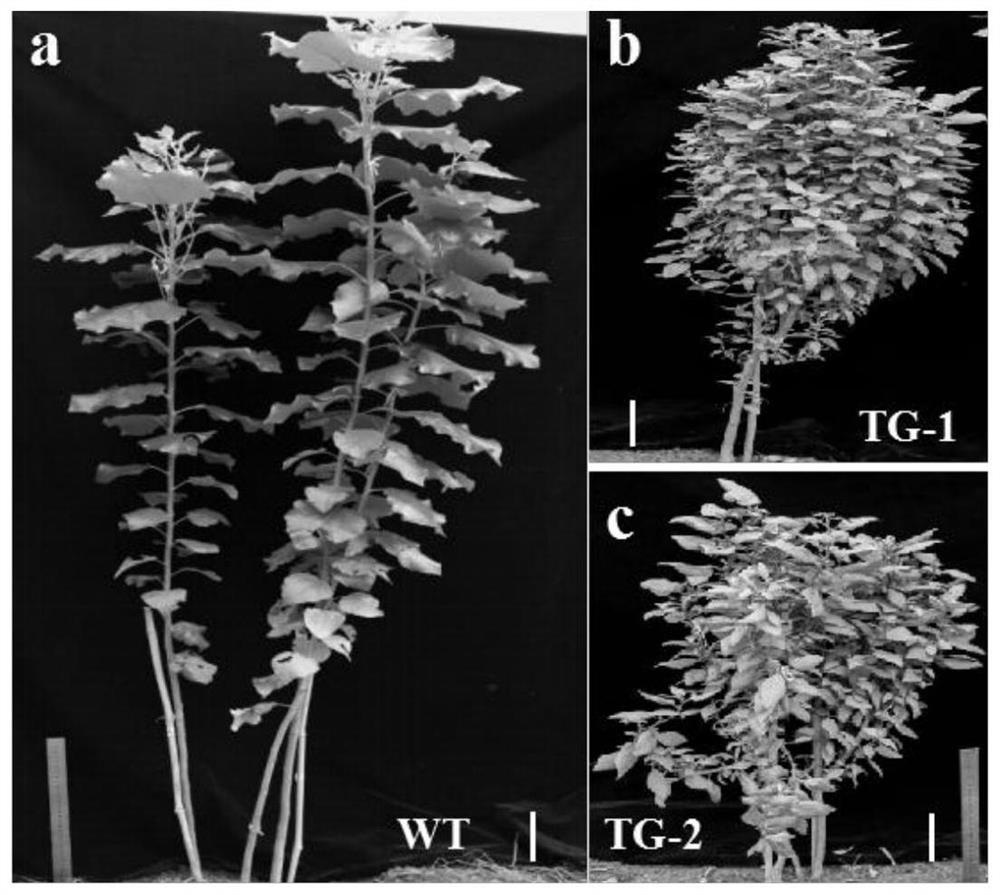
[0046] The overexpression vector pCXSN-pre-MtmiR156b was genetically transformed into the hybrid poplar variety 84K through the mediation of Agrobacterium EHA105, so as to up-re...
Embodiment 2
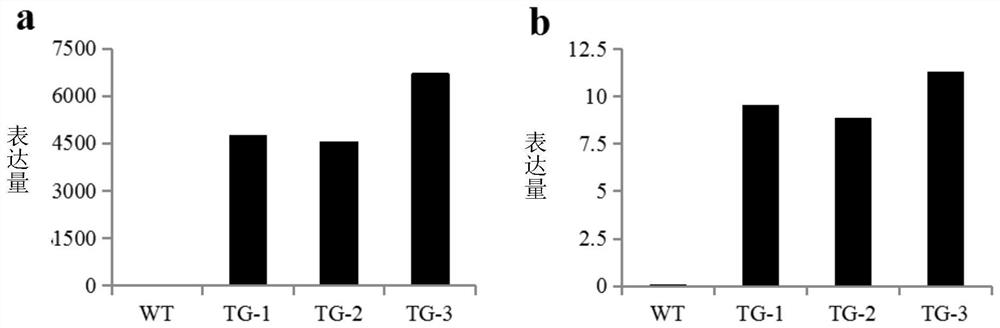
[0078] Example 2: Determination of anthocyanin content in poplar transgenic plants with up-regulated expression of miR156
[0079] 10-month-old wild-type plants and transgenic plants overexpressing miR156 were selected, samples were taken from the tops of poplar trees, and sent to Maiwei Metabolism for metabolomics analysis.
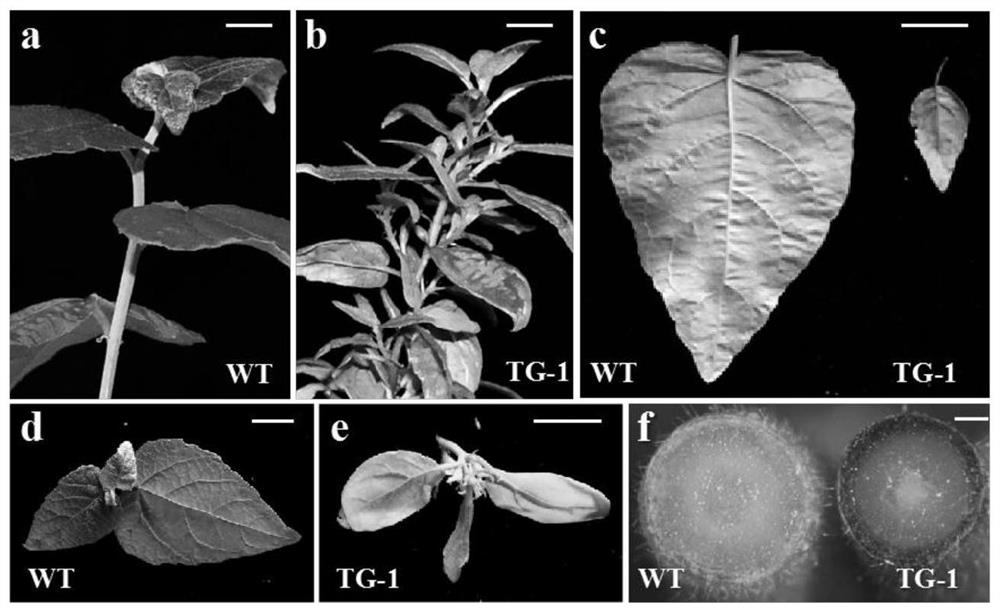
[0080] Such as image 3 As shown, the epidermis of stems, leaf margins and petioles of poplar transgenic plants with up-regulated expression of miR156 are red, while wild-type plants are all green. It can be seen that the content of anthocyanins in the stems, leaf margins and petioles of transgenic plants has increased.
[0081] Further, as Figure 4 As shown, the results of metabolomics analysis showed that the anthocyanin content in the transgenic plants was significantly higher than that in the wild-type plants. At the same time, the content of other flavonoids in the phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway to which anthocyanins belong is also significant...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com