Preparation and application of iron-sulfur co-doped biochar material for simultaneously removing lead-arsenic combined pollution
A compound pollution and co-doping technology, applied in water pollutants, water/sewage treatment, adsorbed water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of harsh preparation conditions, high cost, anaerobic storage, etc., and achieve good anti-interference ability , low cost, simple operation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Preparation of iron-sulfur co-doped biochar: 10 g of rice straw powder was added to 100 mL of a suspension containing ferrous sulfate and sodium thiosulfate at a molar ratio of 1:1, magnetically stirred for 10 hours, and then freeze-dried. The dried solid was placed in a nitrogen atmosphere, pyrolyzed at 300 °C for 2 h at a heating rate of 5 °C / min, and washed with deionized water three times after cooling to prepare iron-sulfur co-doped biochar (Fe / S-BC) . The unmodified biochar was used for comparison.
[0022] Preparation of unmodified biochar: rice straw powder was placed in a nitrogen atmosphere, pyrolyzed at 300°C for 2 h at a heating rate of 5°C / min, and washed three times with deionized water after cooling to prepare unmodified biochar (BC ).
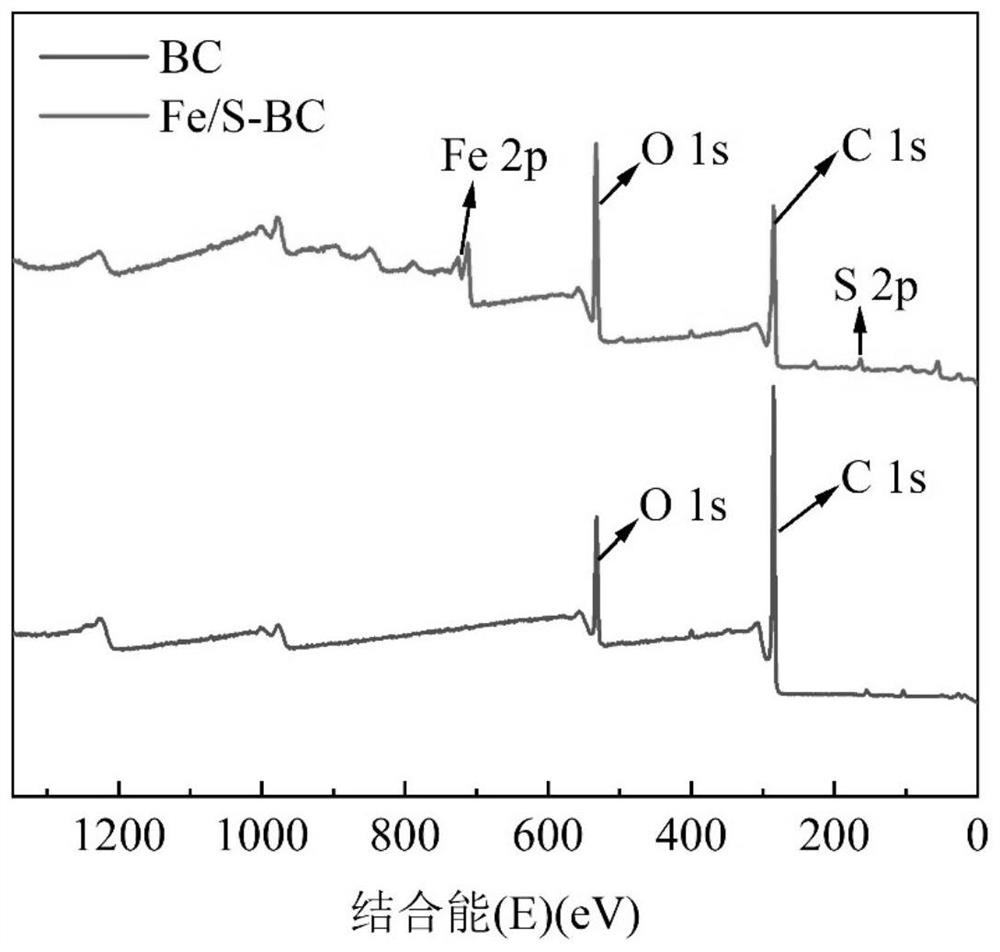
[0023] The BET test results are shown in Table 1, and the XPS results are shown in Table 1. figure 1 shown.
[0024] Table 1 BET test results of iron-sulfur co-doped biochar and unmodified biochar
[0025] ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Preparation of iron-sulfur co-doped biochar:
[0038] Referring to Example 1, the difference is that the solid-to-liquid ratio of rice straw powder and suspension is 7g:100mL, the protective atmosphere is argon, and the heating rate is 10°C / min.
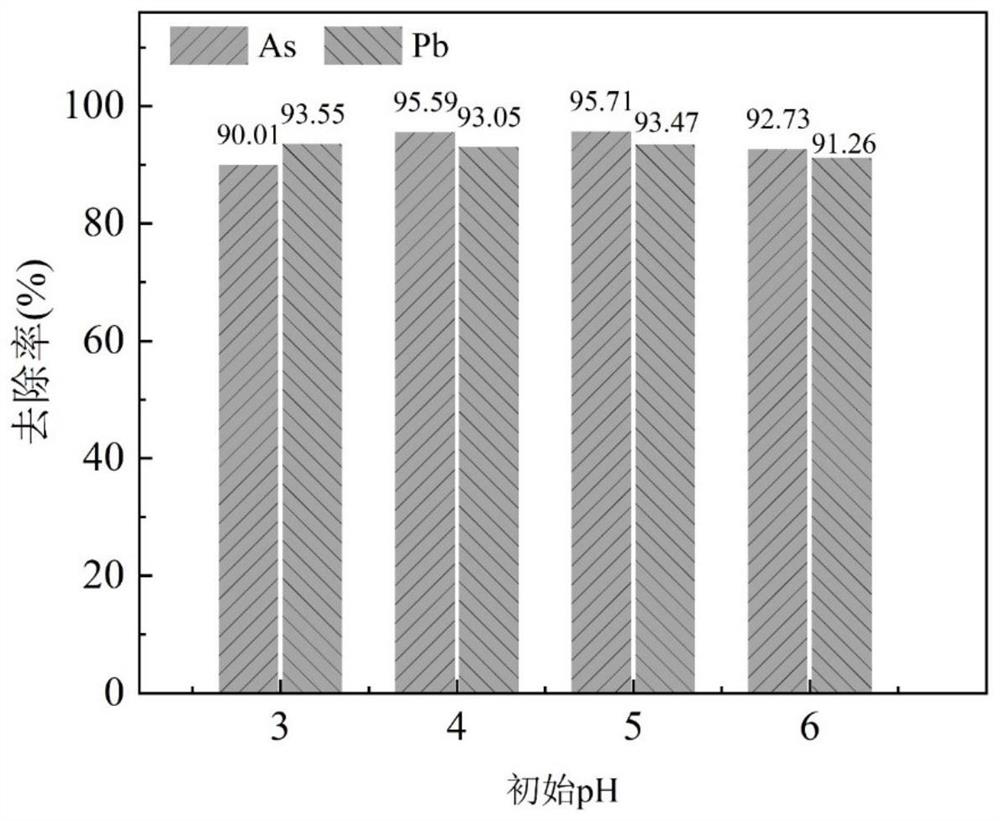
[0039] Removal of arsenic and lead experiment: carried out according to the method of Example 1, wherein the iron-sulfur co-doped biochar was 1g / L, and the pH value of the composite solution of As(III) and Pb(II) was 5. After the experiment, the percentage of arsenic and lead removal was measured. The results showed that the removal rate of As(Ⅲ) was 93.66%, and the removal rate of Pb(Ⅱ) was 91.93% when the reaction was balanced.
Embodiment 3
[0041]Preparation of iron-sulfur co-doped biochar: Referring to Example 1, the difference is that the molar ratio of ferrous sulfate and sodium thiosulfate in the suspension is 2:1, and the pyrolysis time is 3h , all the other are with embodiment 1.
[0042] Removal of arsenic and lead experiment: carried out according to the method of Example 1, wherein the iron-sulfur co-doped biochar was 1g / L, and the pH value of the composite solution of As(III) and Pb(II) was 5. After the experiment, the percentage of arsenic and lead removal was measured. The results showed that the removal rate of As(Ⅲ) was 94.21% and that of Pb(Ⅱ) was 95.68% when the reaction was balanced.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com