Depletion type power semiconductor structure, series structure and processing technology
A power semiconductor and series structure technology, which is applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as secondary breakdown, difficult to achieve withstand voltage, and productivity limitations, so as to improve reliability and reduce processing Difficulty, the effect of improving the yield rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
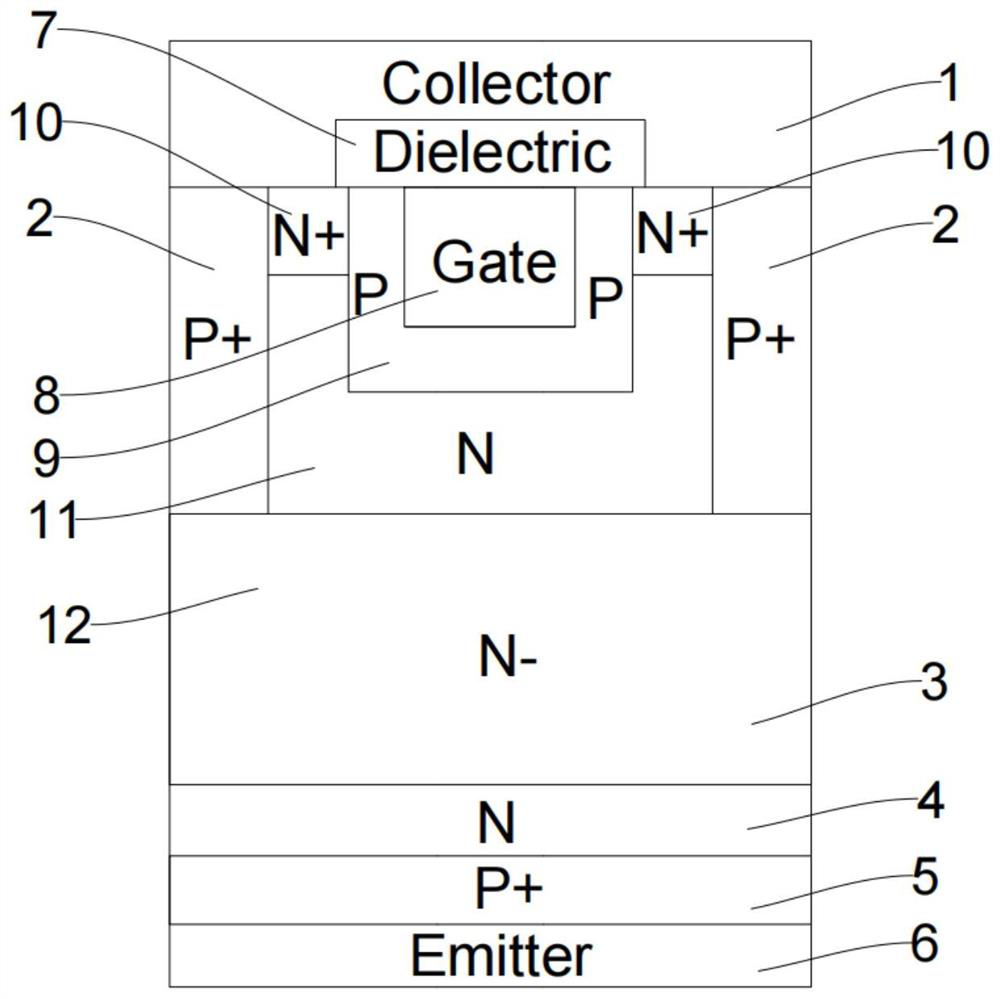
[0070] This embodiment is basically as attached figure 1 Shown: a depletion-type power semiconductor structure, the structure is a semiconductor device, the device is composed of cells arranged in parallel, and its cell structure includes: BJT rear-stage structure and JFET front-stage structure;
[0071] The JFET front-stage structure is set in the BJT post-stage structure, that is, the JFET front-stage structure is used to replace the MOSFET structure of the input stage of the IGBT device. Compared with the MOSFET structure in the IGBT device in the prior art, the gate oxide layer for the silicon carbide planar MOSFET or the gate oxide layer for the trench MOSFET is required, and the JFET front-end structure replaces the MOSFET structure of the input stage of the IGBT device without affecting the original IGBT device. function, and after replacing the MOSFET structure, the JFET front-end structure does not need to set the gate oxide layer for the silicon carbide planar MOSFET...
Embodiment 2
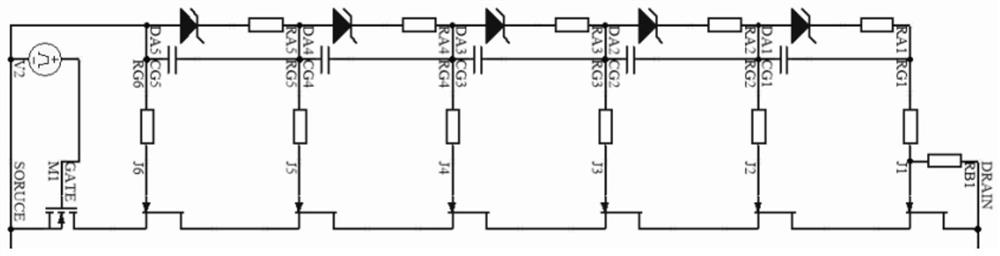
[0086] This embodiment is basically as attached figure 2 Shown: a kind of depletion mode power semiconductor series structure, comprises the depletion mode power device ( figure 2 Medium J1, J2, J3, J4, J5, and J6) and low voltage MOSFETs ( figure 2 M1) in series, the emitter of each depletion power device is connected to the collector of the next depletion power device, and the final depletion power device ( figure 2 The emitter of J6) is connected to the drain of the low-voltage MOSFET, figure 2 Among them, DRAIN represents the positive electrode of the overall device after series connection, GATE represents the control electrode of the entire device after series connection, and SOURCE represents the negative electrode of the entire device after series connection. In this embodiment, six stages are connected in series.
[0087] The gates of each stage of depletion-mode power devices are connected in series with a first resistor ( figure 2 In RG1, RG2, RG3, RG4, RG5...
Embodiment 3
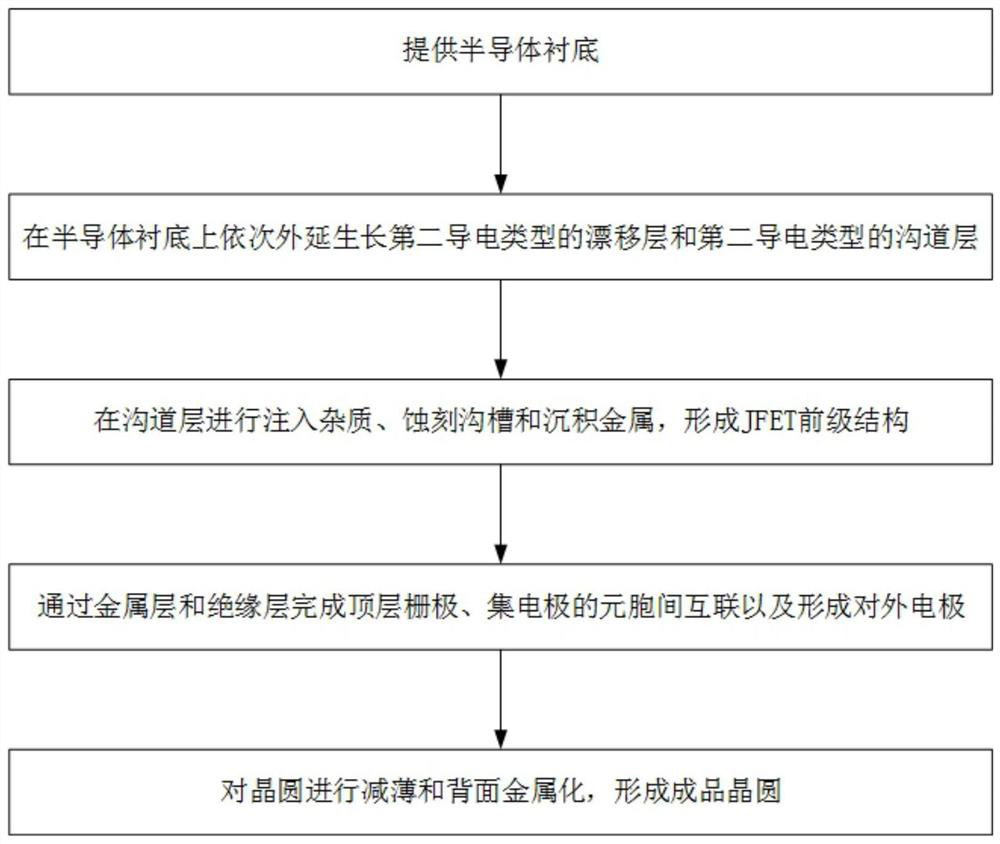
[0092] This embodiment is basically as attached image 3 Shown: a depletion mode power semiconductor structure processing technology, including the following content:
[0093] A semiconductor substrate is provided; the semiconductor substrate includes: a semiconductor substrate of a first conductivity type or a semiconductor substrate of a second conductivity type;
[0094] A drift layer of the second conductivity type and a channel layer of the second conductivity type are epitaxially grown sequentially on the semiconductor substrate; Before the drift layer of the conductivity type and the channel layer of the second conductivity type, a field stop / buffer layer of the second conductivity type is epitaxially grown on the semiconductor substrate;
[0095] Implant impurities, etch trenches and deposit metal in the channel layer to form the JFET front-end structure; specifically:
[0096] Selective implantation of impurities of the first conductivity type and impurities of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com