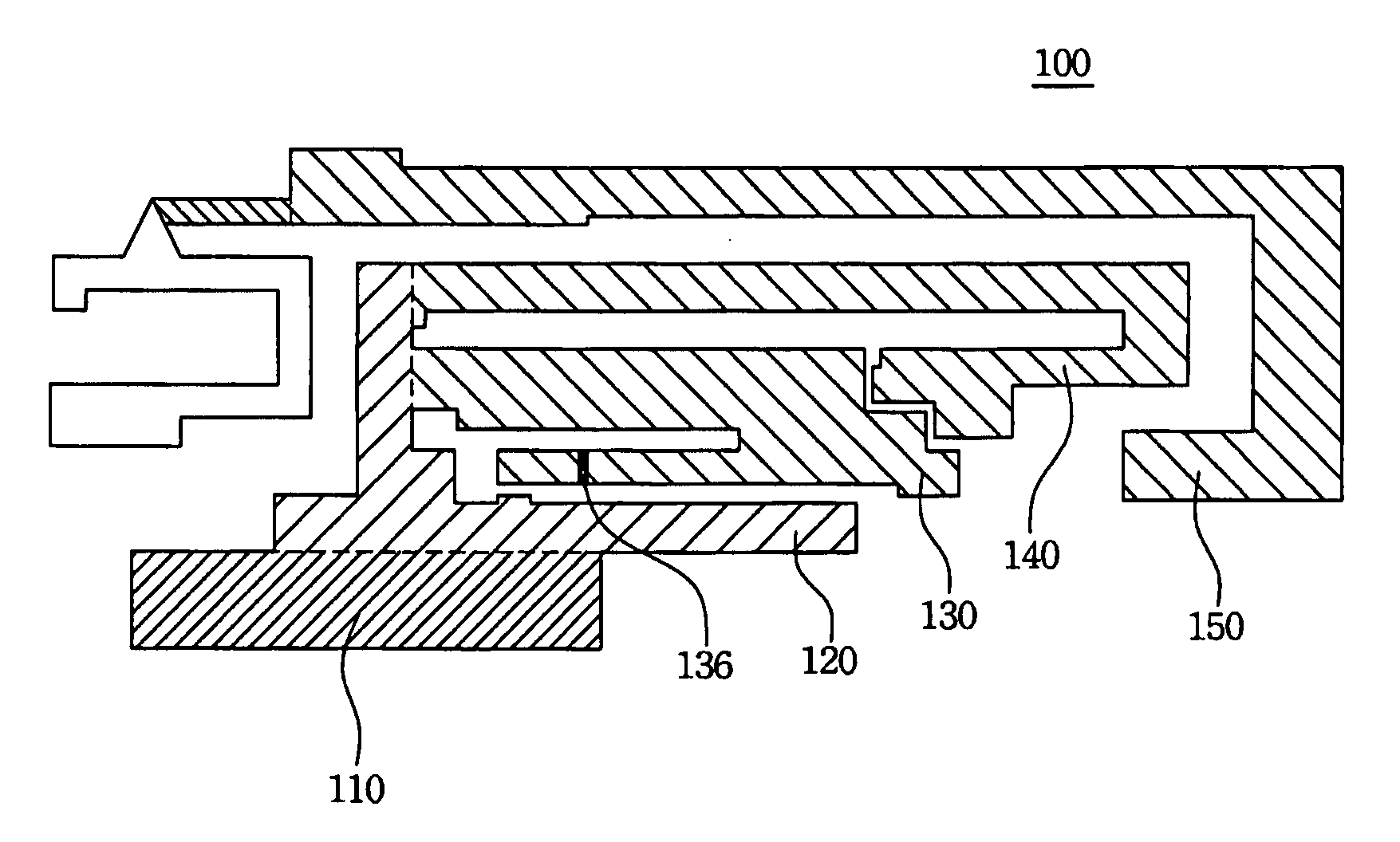
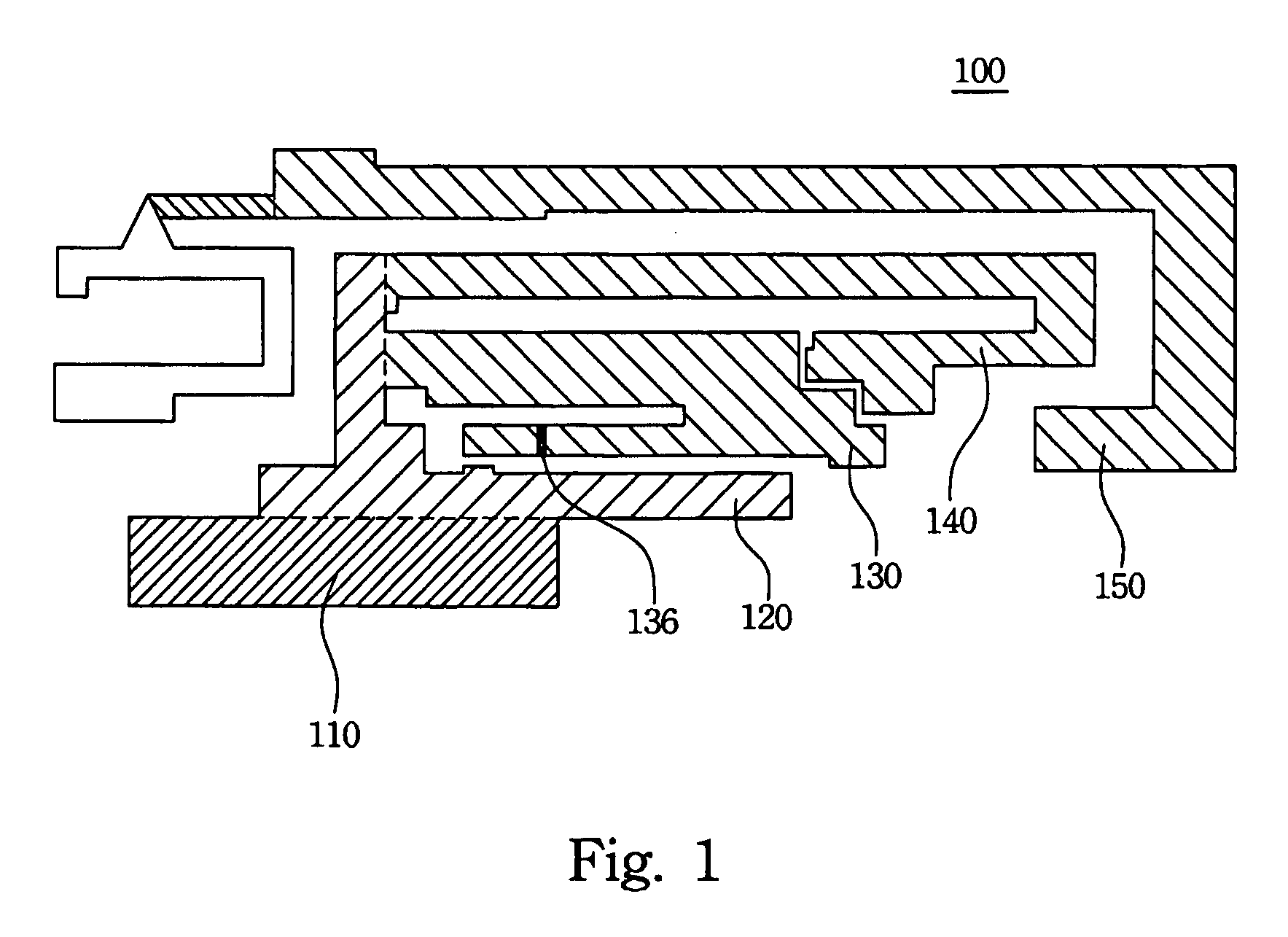
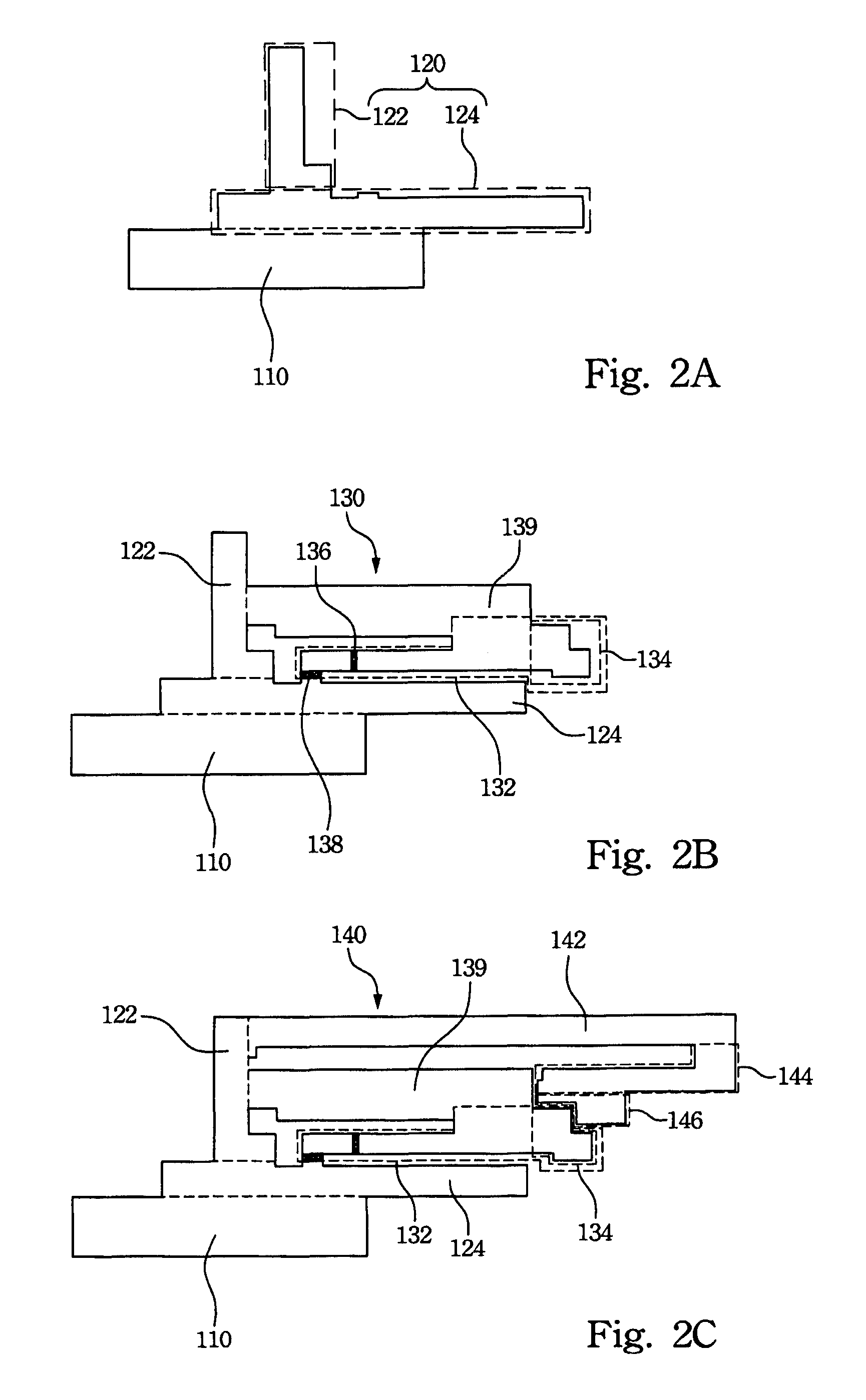
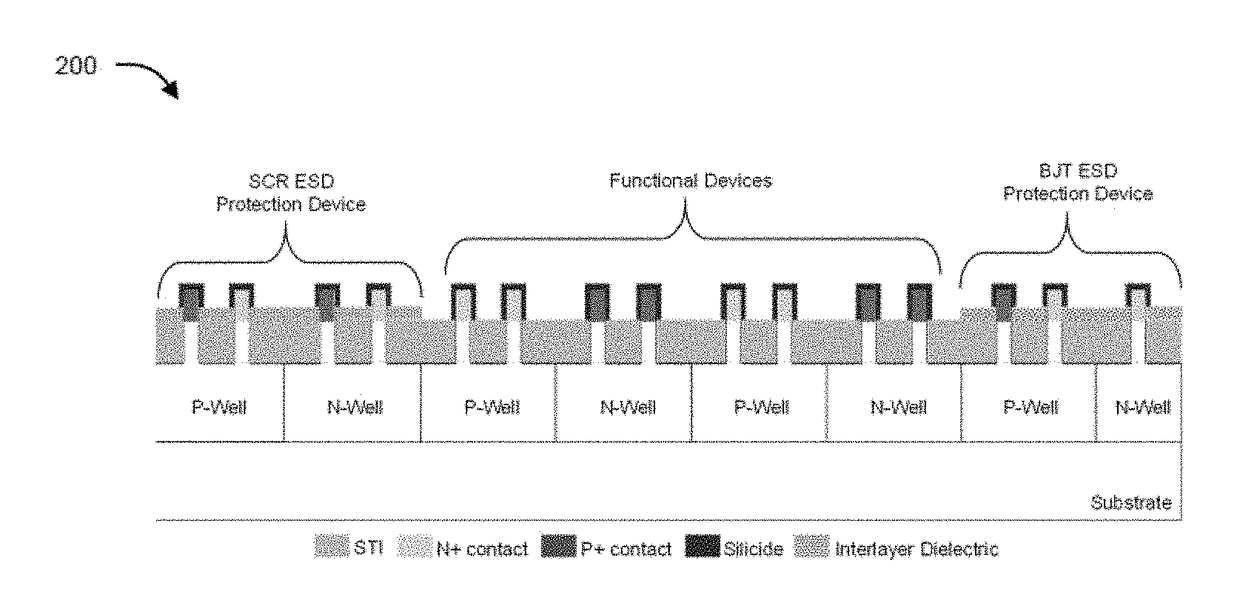
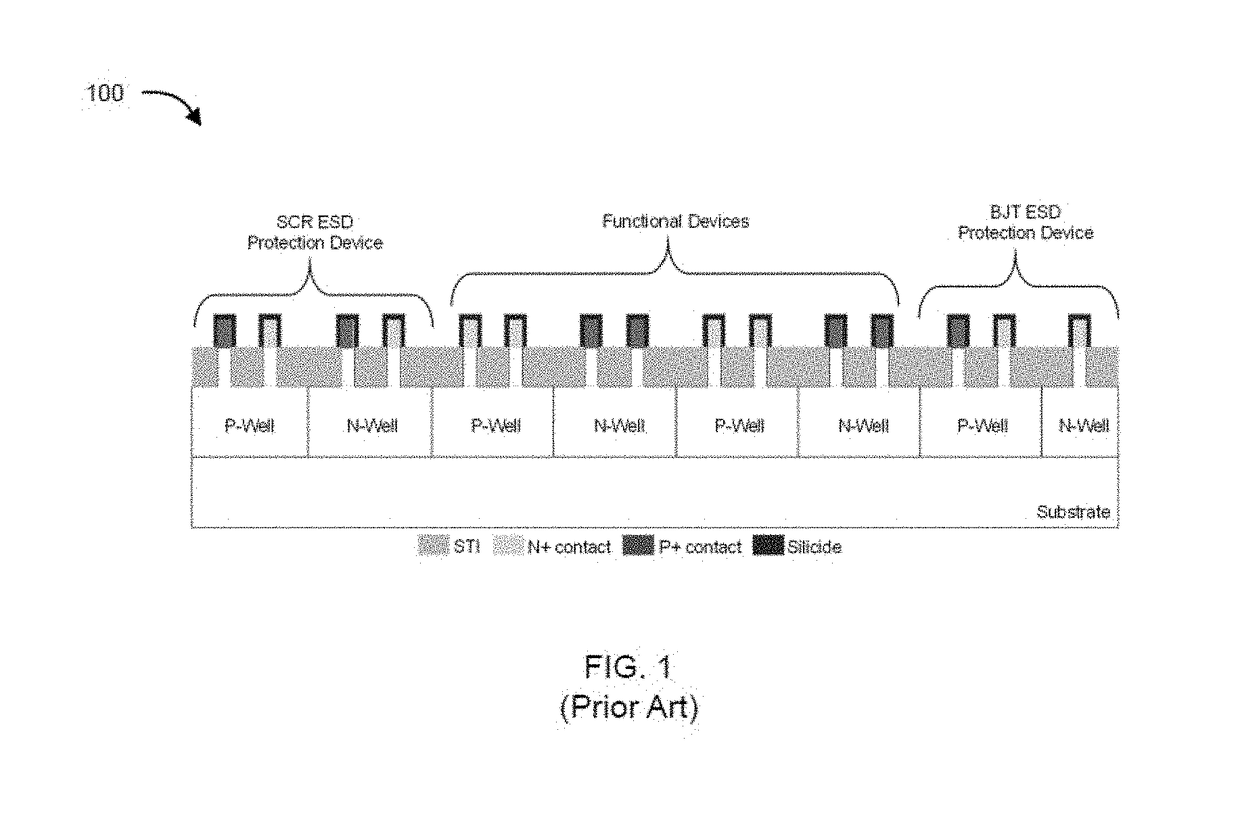
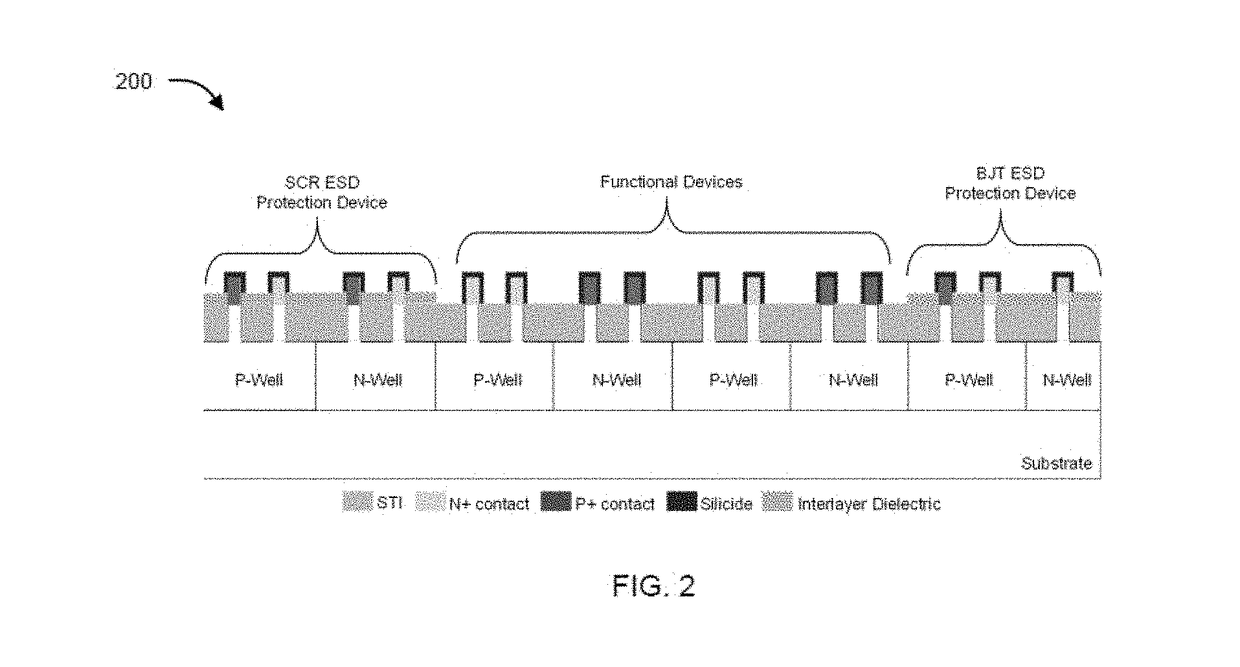
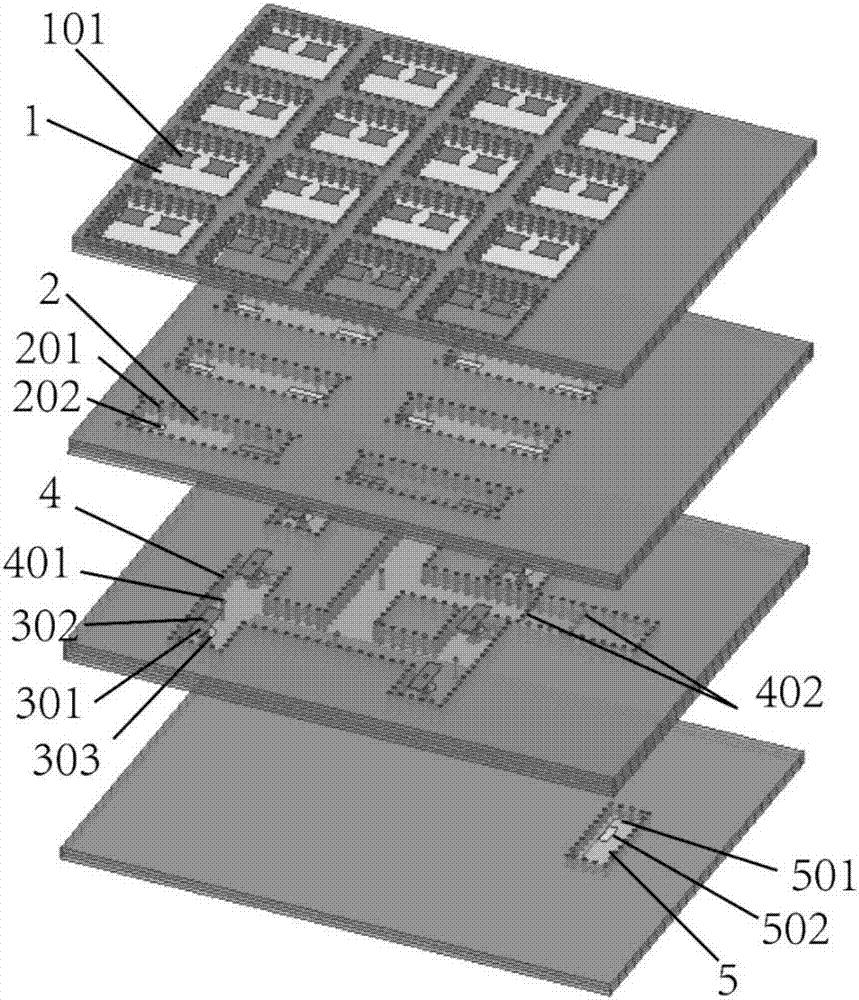
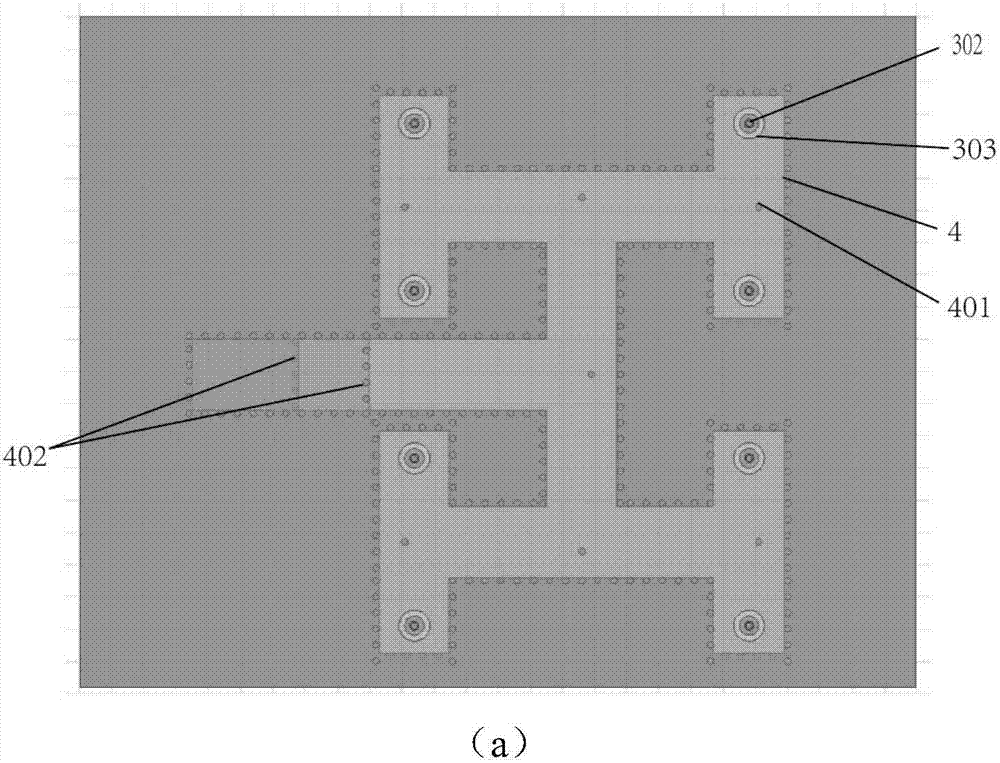
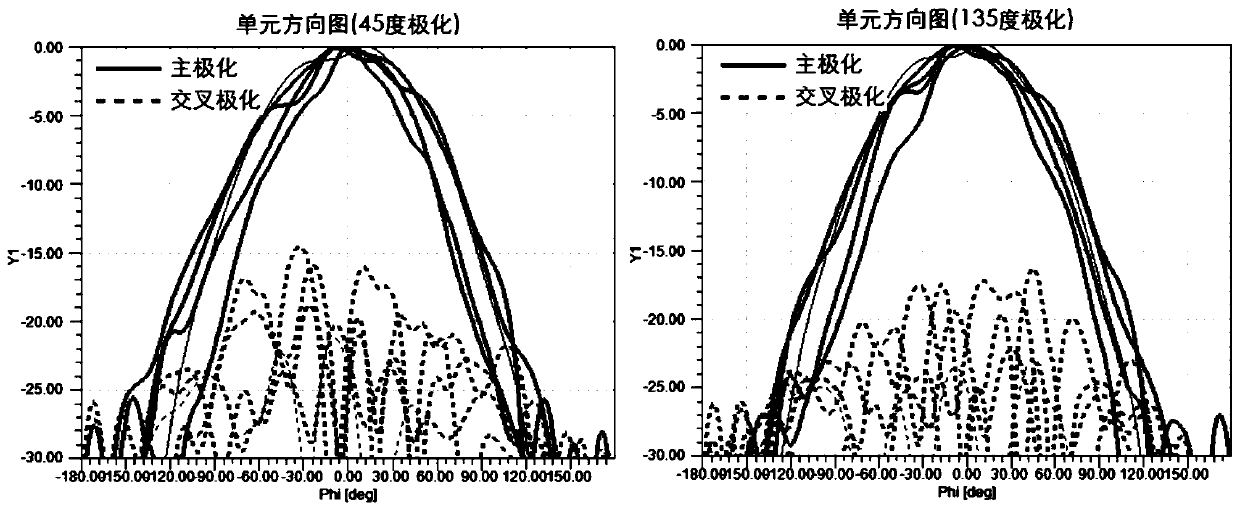
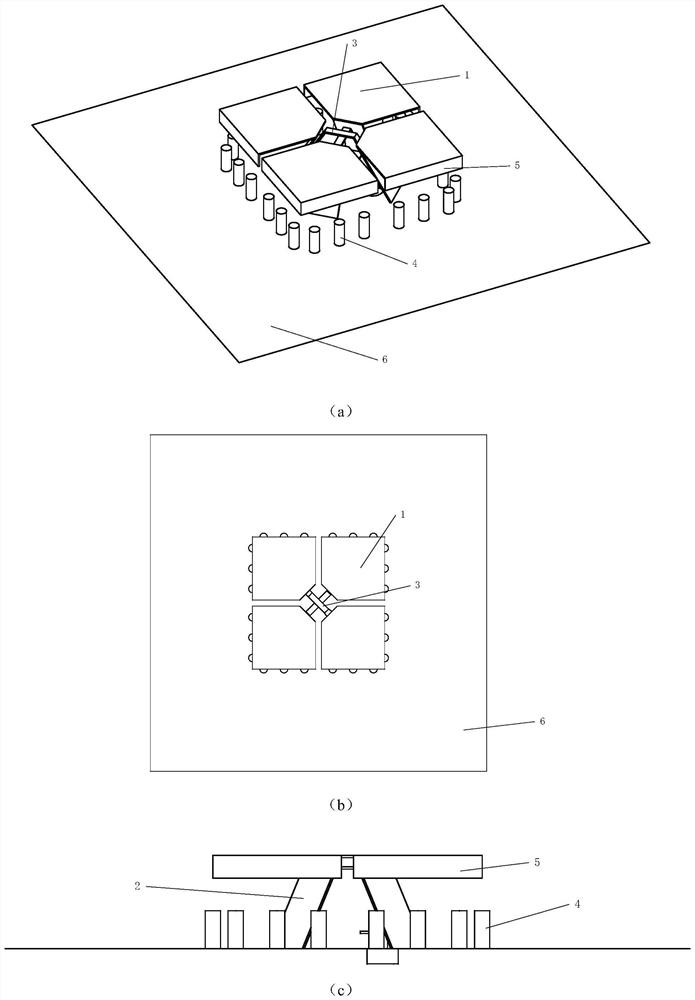
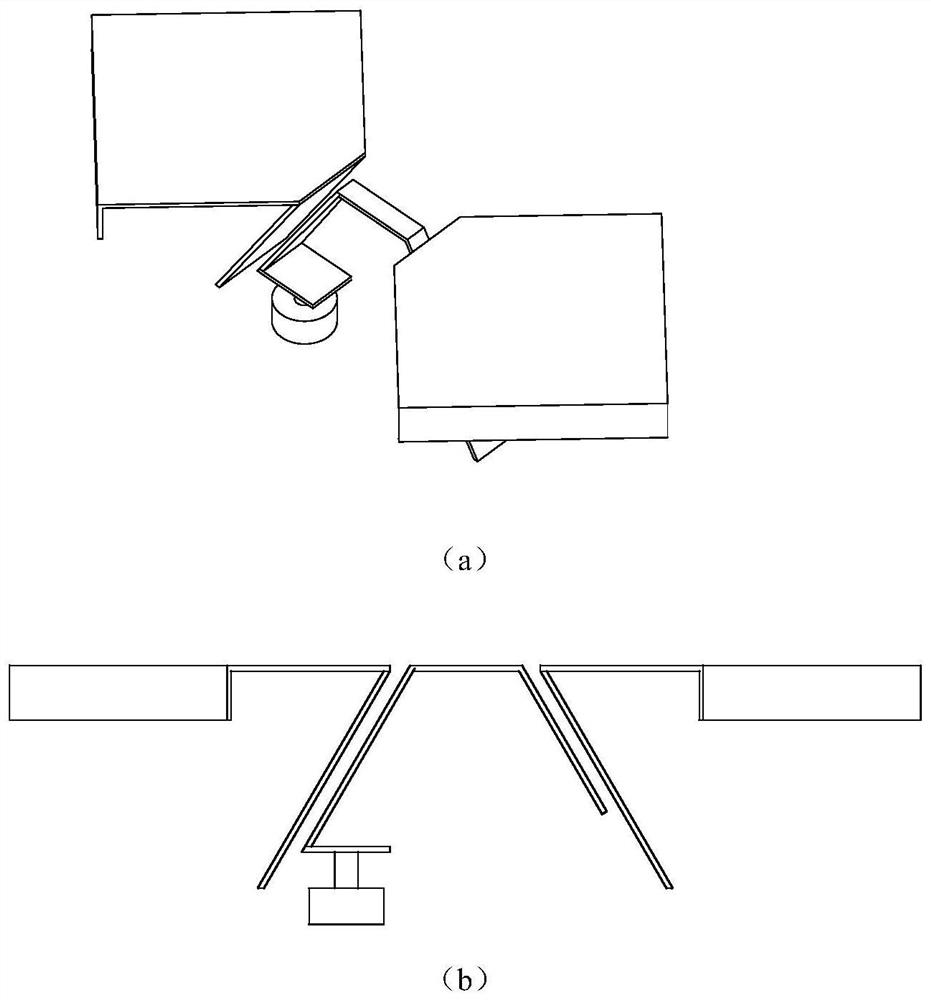
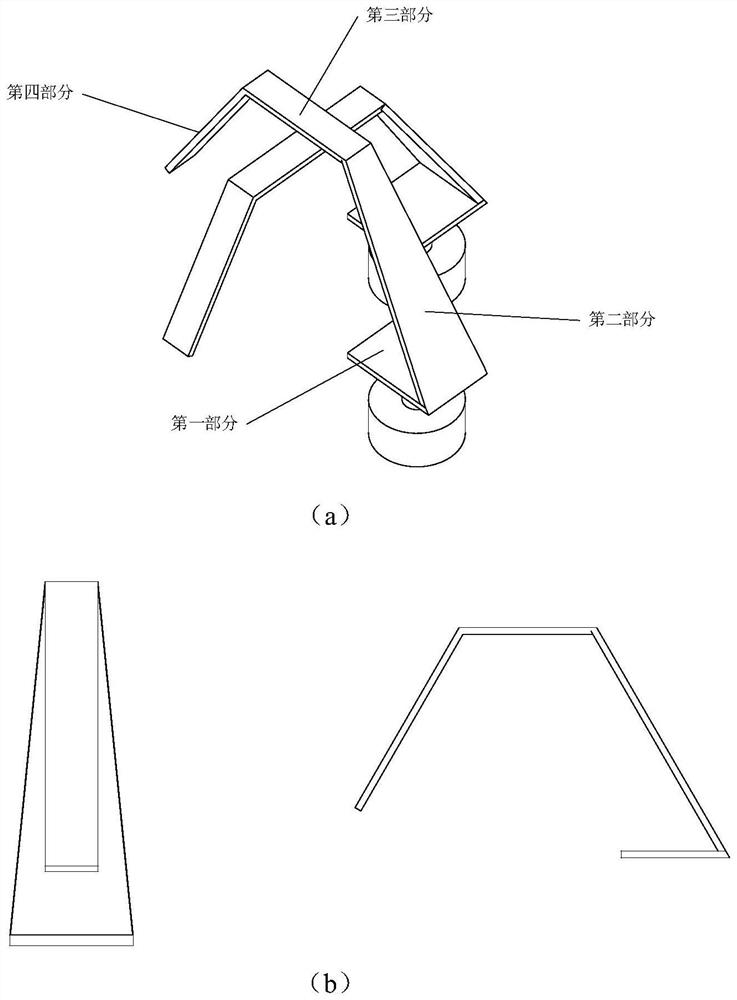
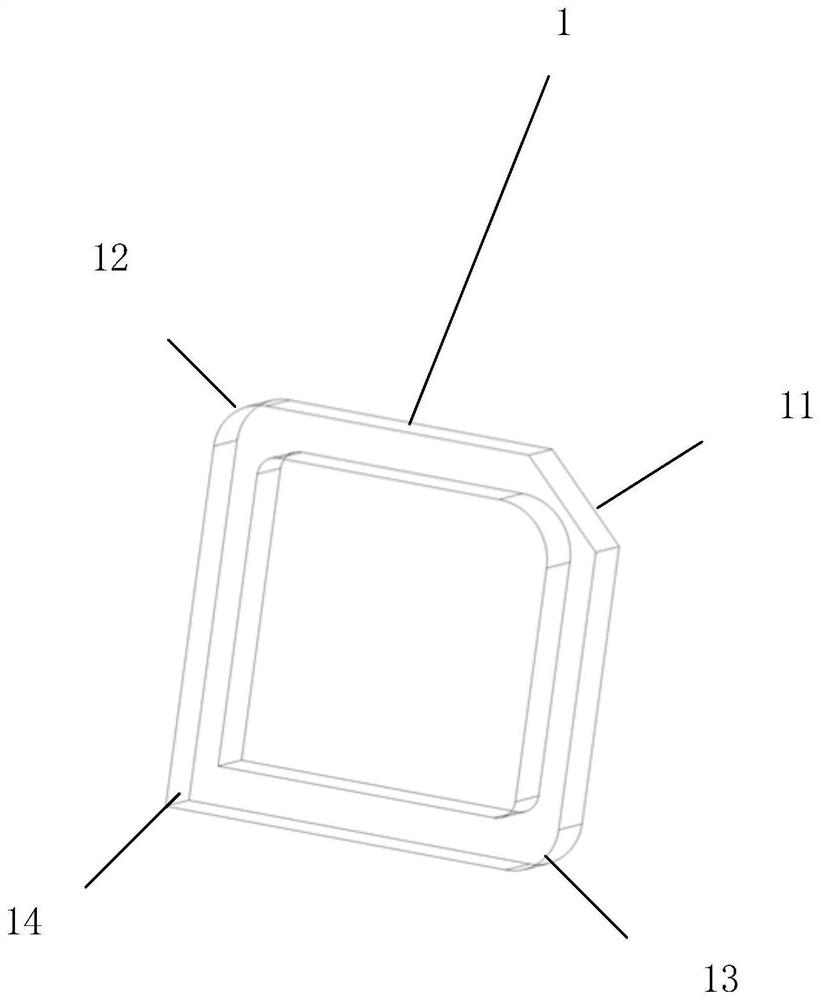
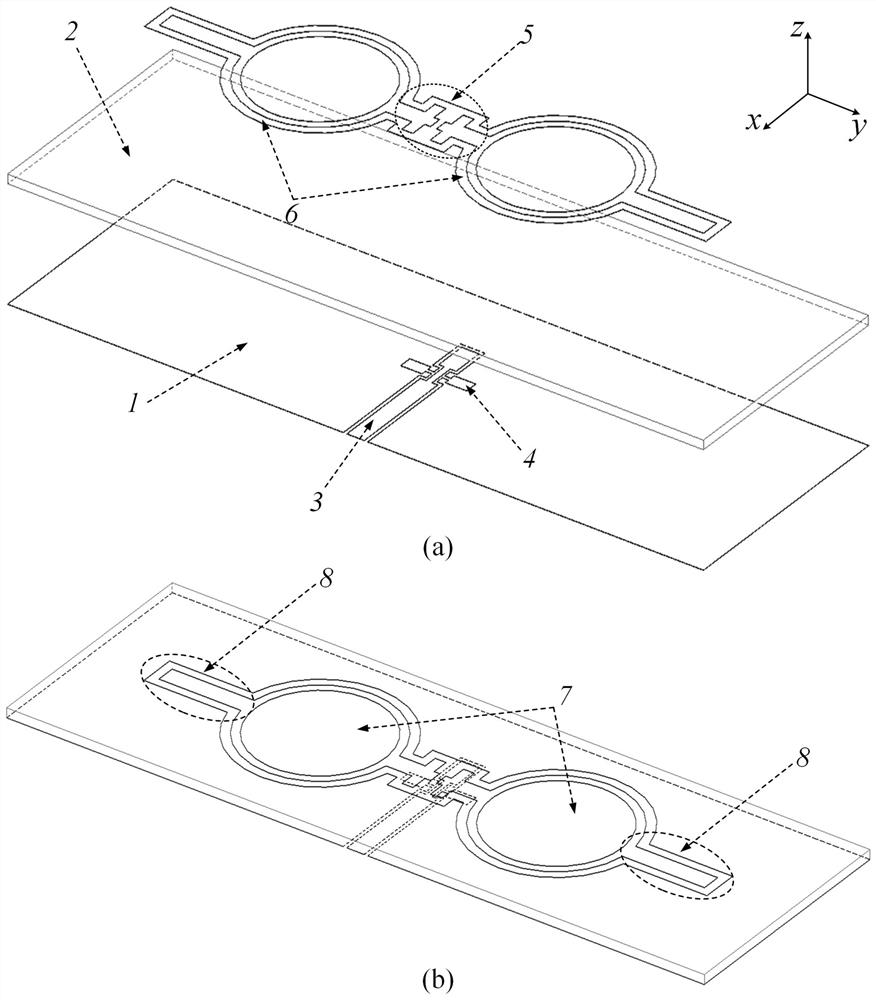
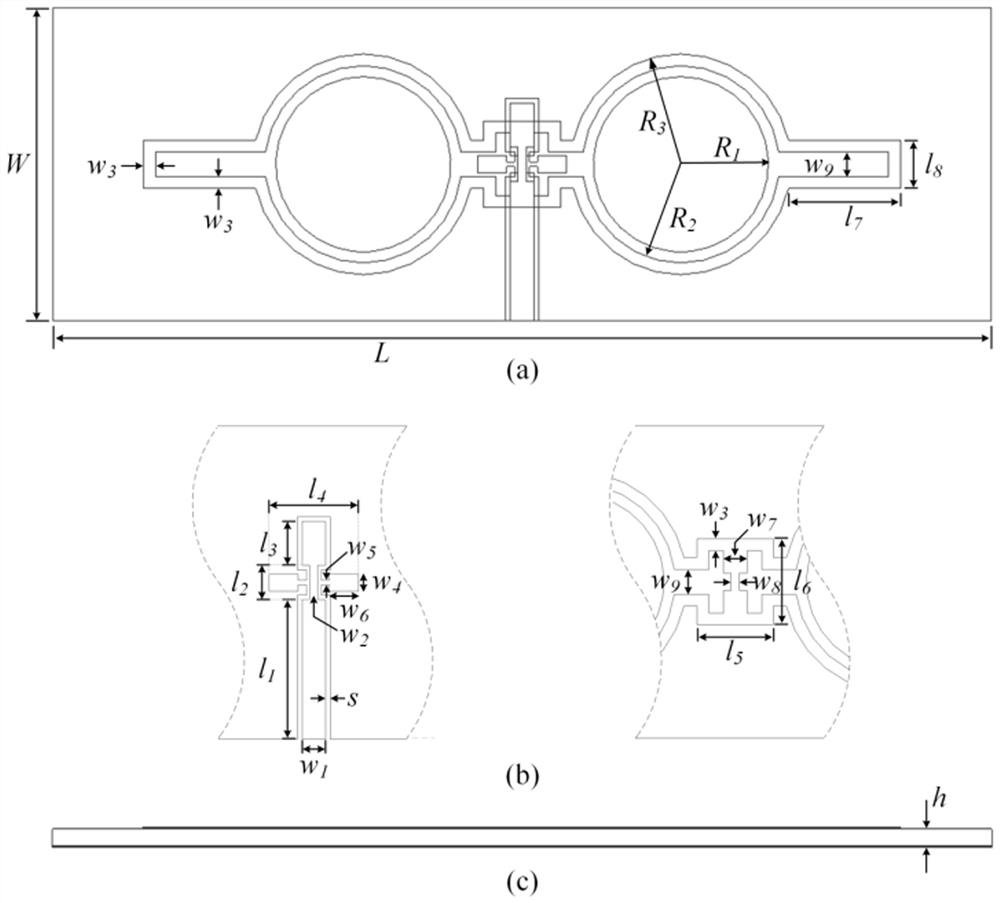
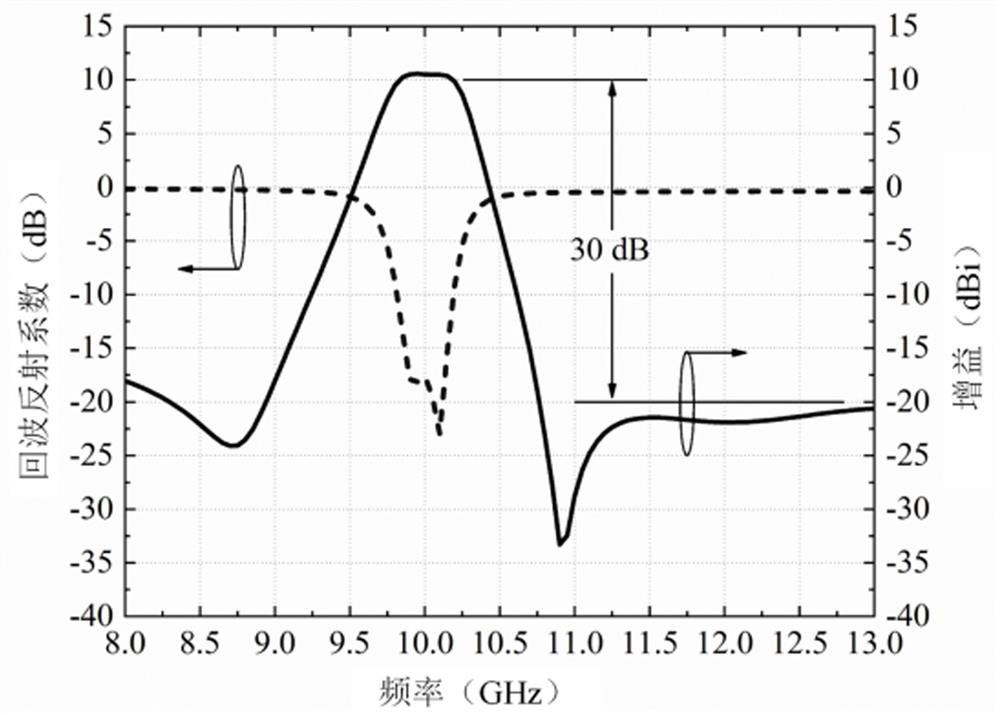
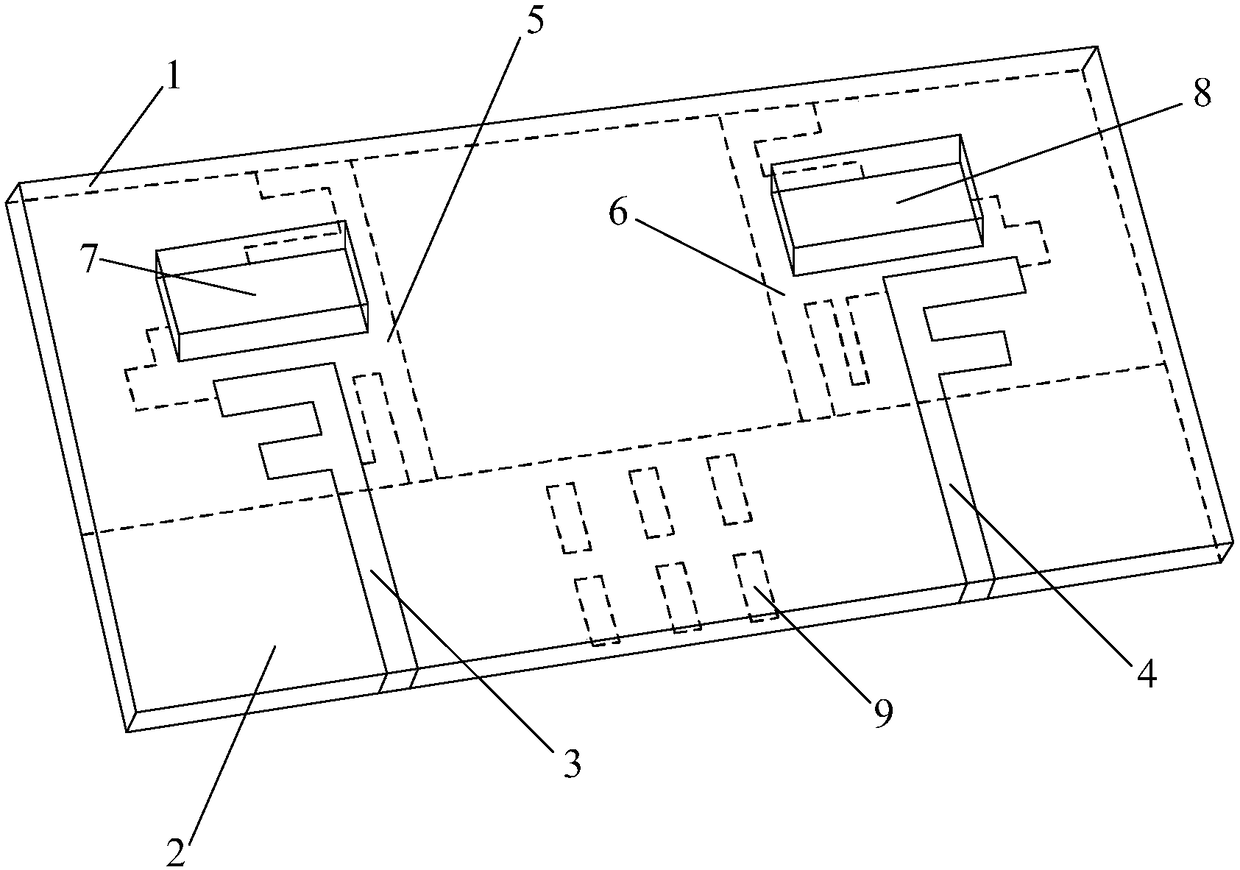
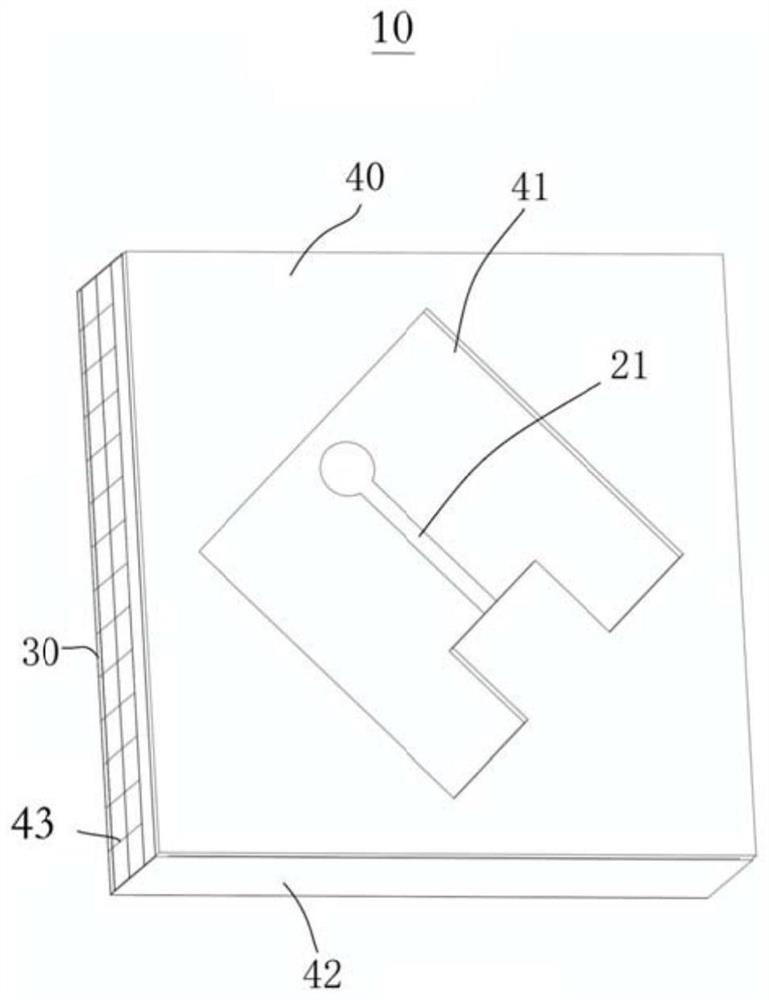
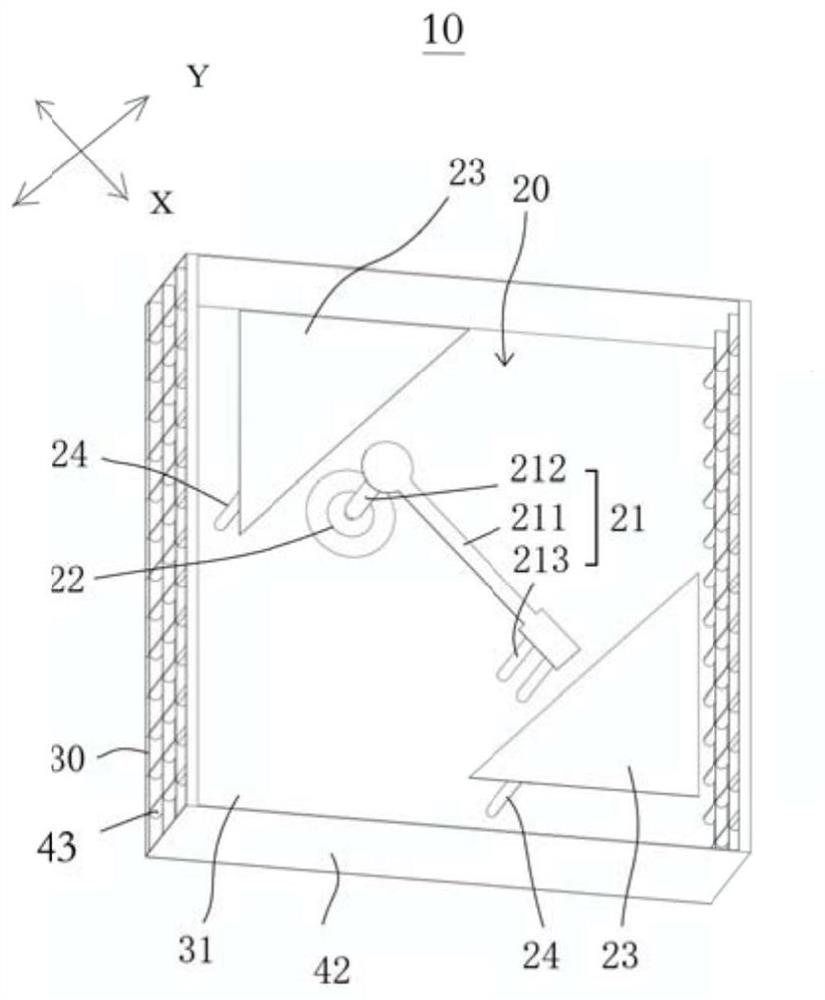
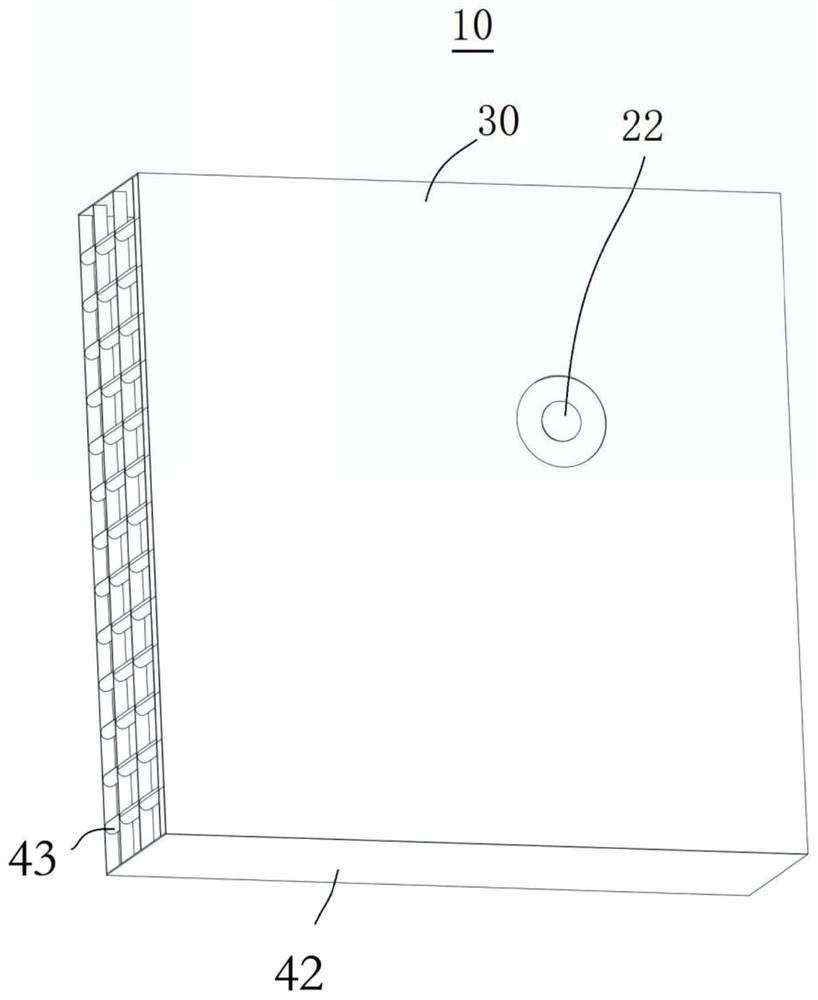
Patents
Literature
63 results about "Parasitic structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
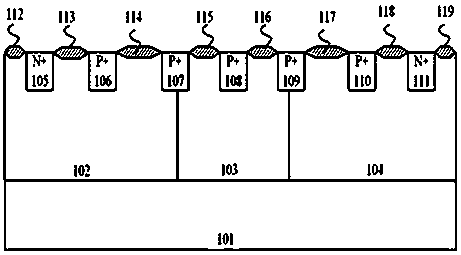
In a semiconductor device, a parasitic structure is a portion of the device that resembles in structure some other, simpler semiconductor device, and causes the device to enter an unintended mode of operation when subjected to conditions outside of its normal range. For example, the internal structure of an NPN bipolar transistor resembles two PN junction diodes connected together by a common anode. In normal operation the base-emitter junction does indeed form a diode, but in most cases it is undesirable for the base-collector junction to behave as a diode. If a sufficient forward bias is placed on this junction it will form a parasitic diode structure, and current will flow from base to collector.
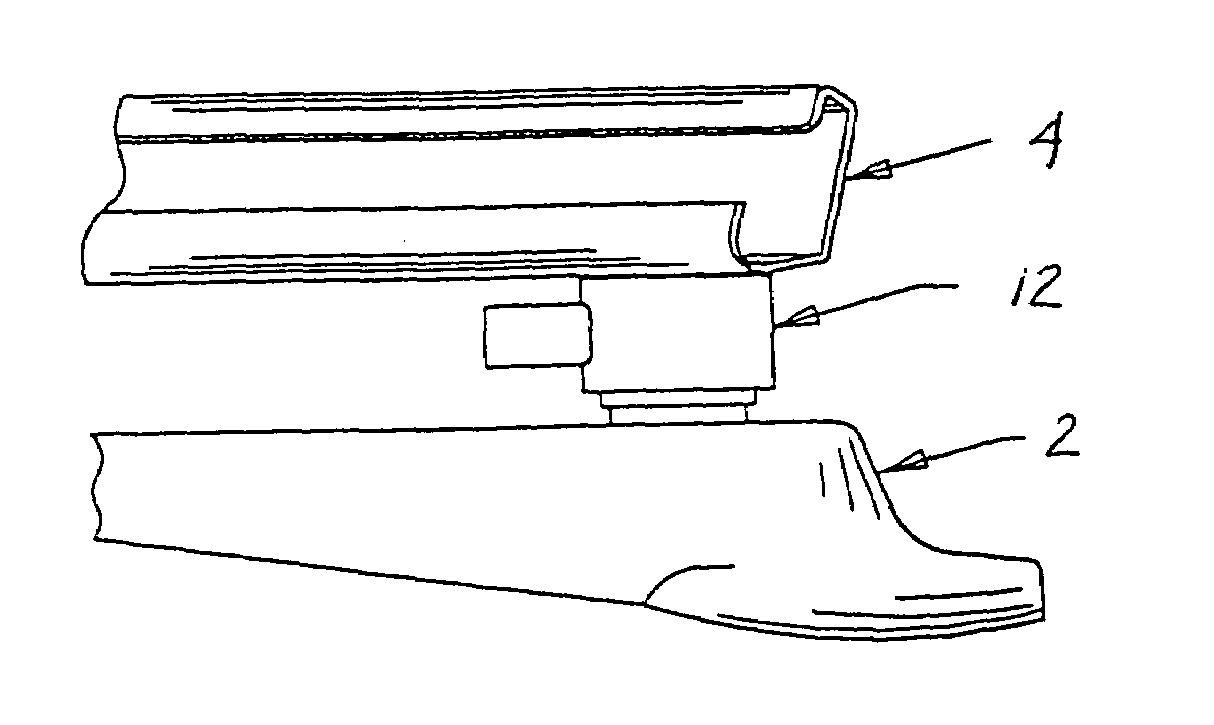
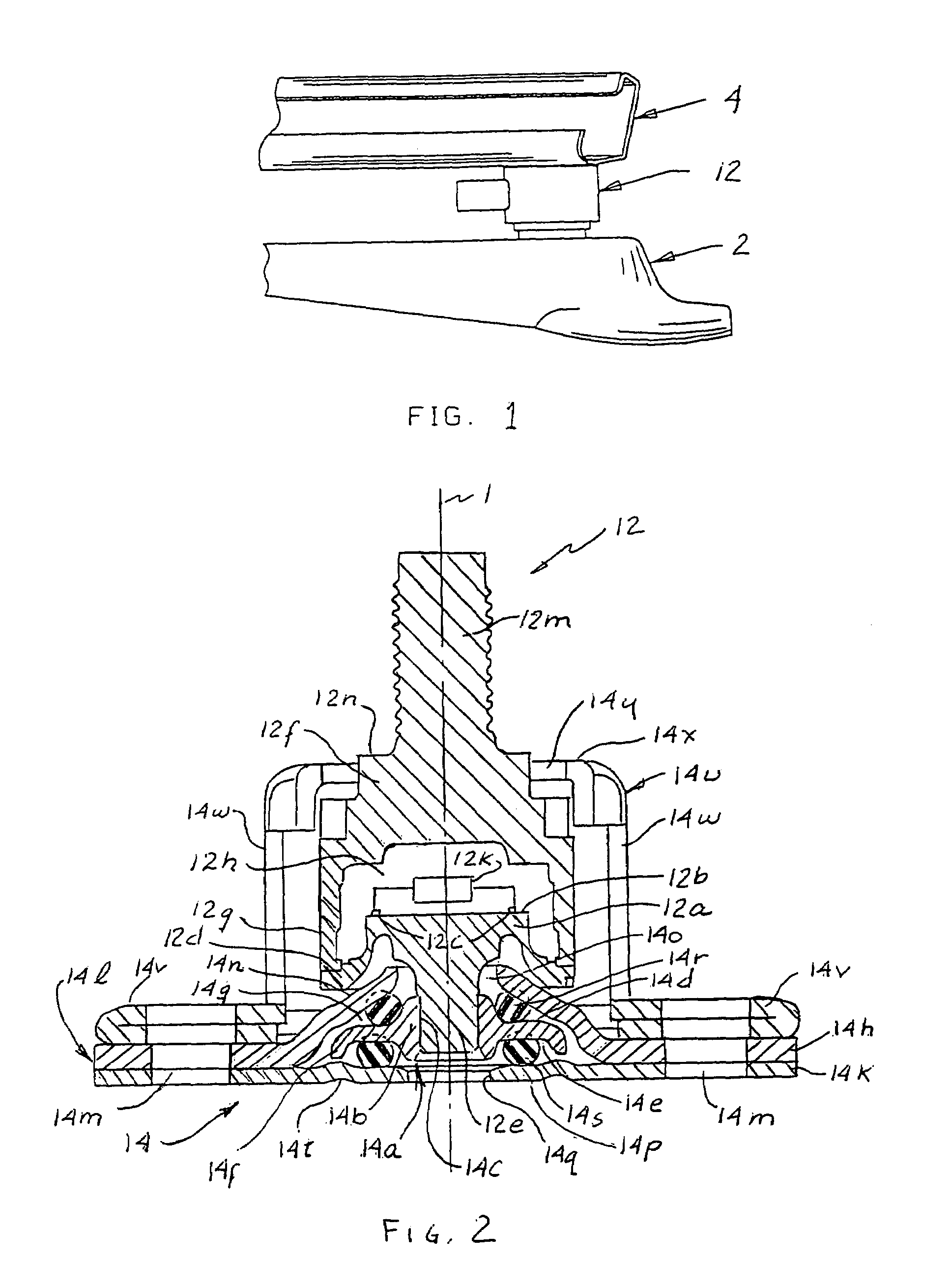
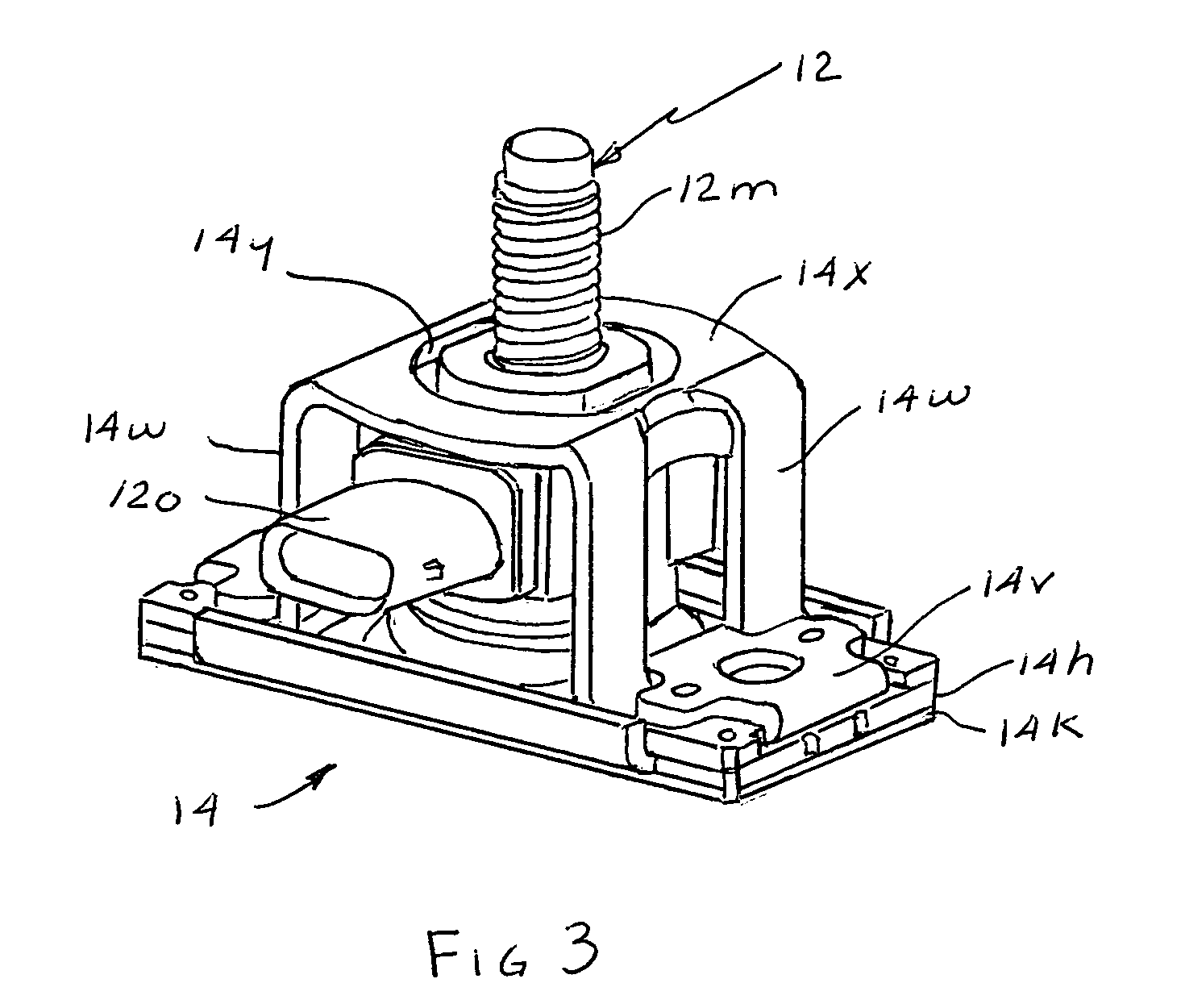
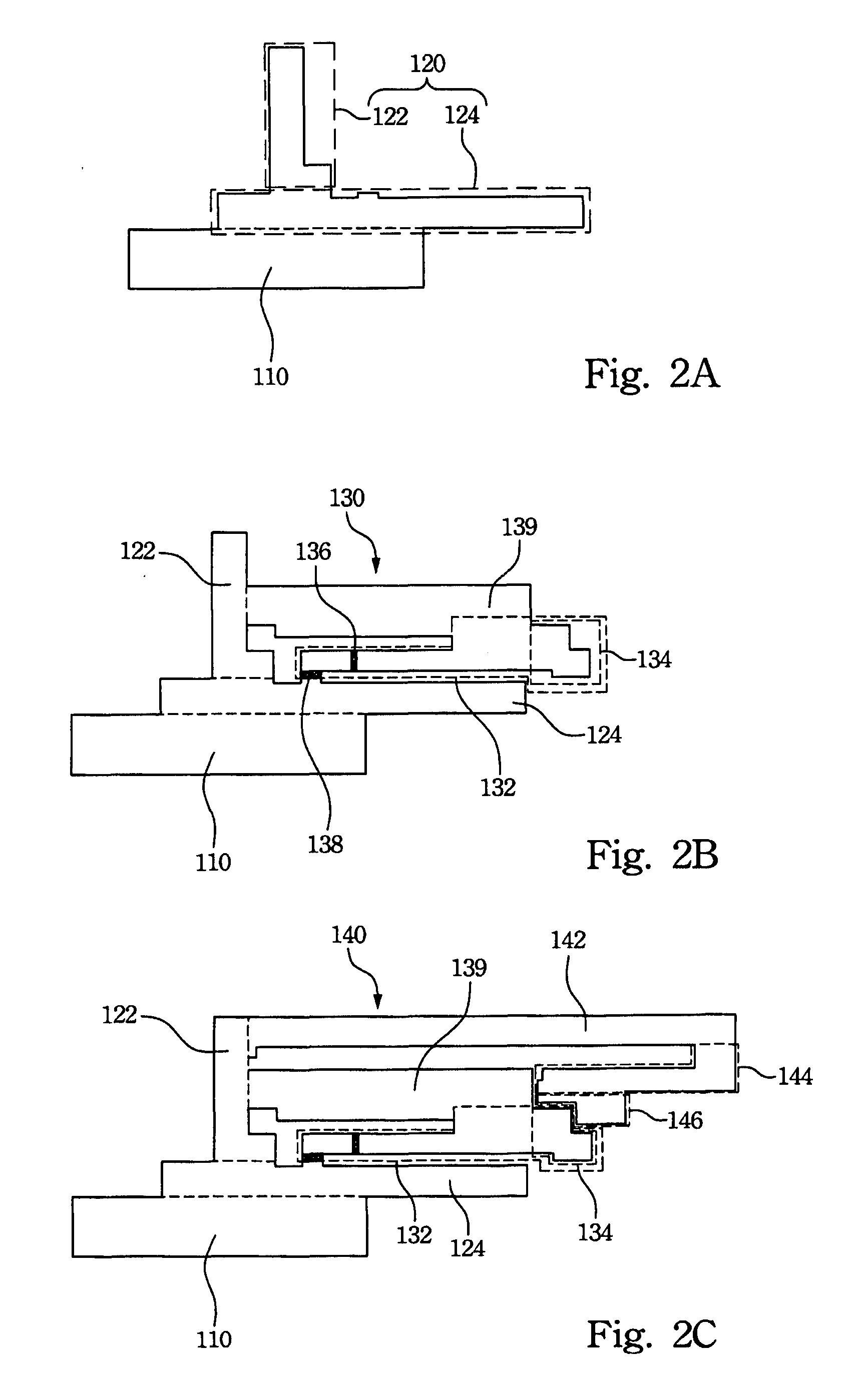
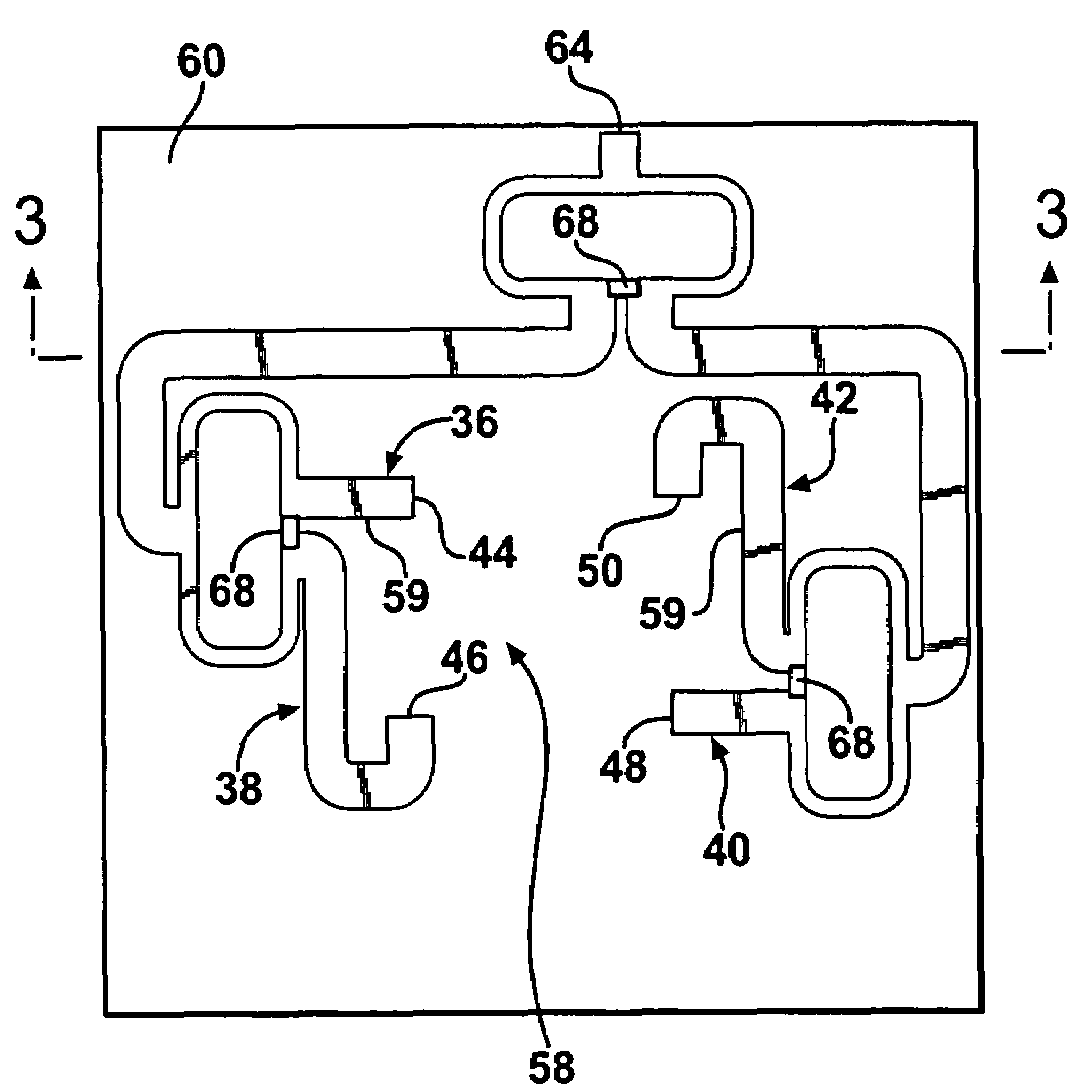
Sensor mounting apparatus for minimizing parasitic stress
ActiveUS7112749B2Minimize parasitic stressSufficiently robustVehicle seatsElectric devicesEngineeringParasitic structure
A compliant interface (14,16) for vehicular seat weight sensors minimizes parasitic stresses affecting sensor output. In one embodiment, an integral compliant interface (14) has an annular flange (14a) attached to a post extending from the sensor body with a first compliant member (14r) disposed between the annular flange and an upper elongated flange (14h) of a mounting bracket (14l) and a second compliant member (14s) disposed between the annular plate and a lower elongated flange (14k) to allow pivotal movement of the sensor limited by a motion stop member (14f) of annular flange (14b) engaging the lower flange. An overload cage (14u) may be placed over the sensor and attached to an additional flange (14l) to contain the sensor in the event of a failure of the mount in a catastrophic high speed crash. According to another preferred embodiment, an interface having upper and lower body members are formed with a sensor post receiving bore (16c) for attachment to the post. The body members are formed with spaced apart, radially extending face surfaces, each formed with an annular recess aligned with each other and with a compliant member received therein and fixed to the respective body members and extending beyond the face surfaces. The interface is received through a bore of a support plate to which the sensor is mounted with the compliant members engaging opposite face surfaces of the support plate allowing limited pivotal motion and with a compliant member limiting lateral movement of the interface relative to the support plate.
Owner:SENSATA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Radiation element structure for wind band dual polarization antenna
ActiveCN101505007AImprove balanceImprove return lossPolarised antenna unit combinationsOptoelectronicsBroadband
The invention provides a radial element structure of a broadband bipolarized antenna, which comprises a surface radiation unit, a medium plate, a feeding support and a reflecting plate; the surface radiation unit comprises array arms of semi-wave arrays; the feeding support is positioned between the medium plate and the reflecting plate; the invention also comprises a parasitic structure which is arranged at the bottom end of the array arm of the surface radiation unit to allow two adjacent array arms to be in capacitive joint; and the surface radiation unit and the parasitic structure are adhered on two sides of the medium plate respectively. The radial element structure can improve the balance of the arrays, effectively improves the crossed polarization property and strengthens the directivity of radiation in the direction of + / -60 degrees; and the radial element structure improves the back wave loss and the isolation degree of the arrays. The radial element structure has a more stable and reliable structure and is easier to be rapidly assembled and welded as an independent part.
Owner:MOBILE ANTENNA TECH SHENZHEN +5
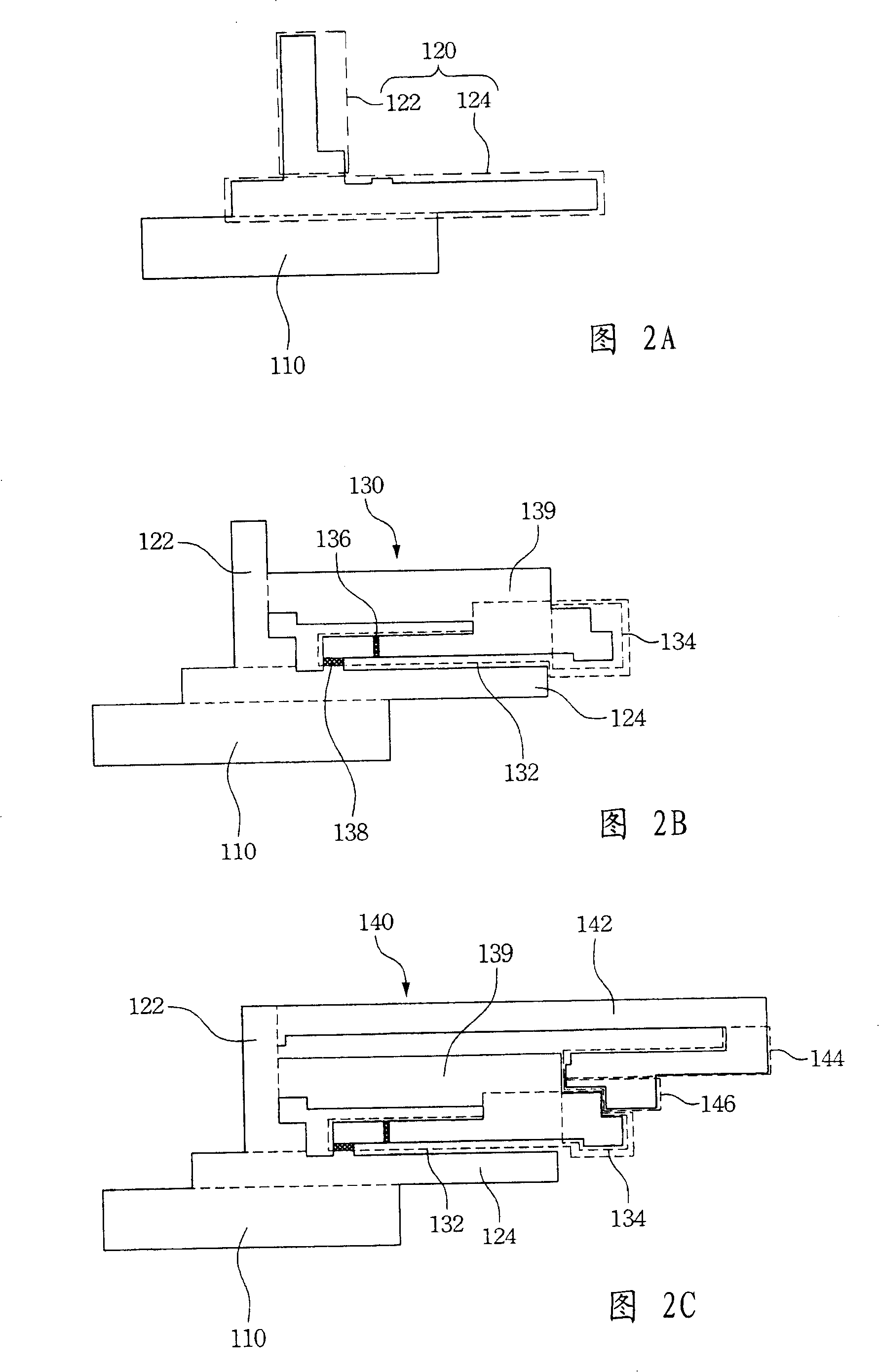
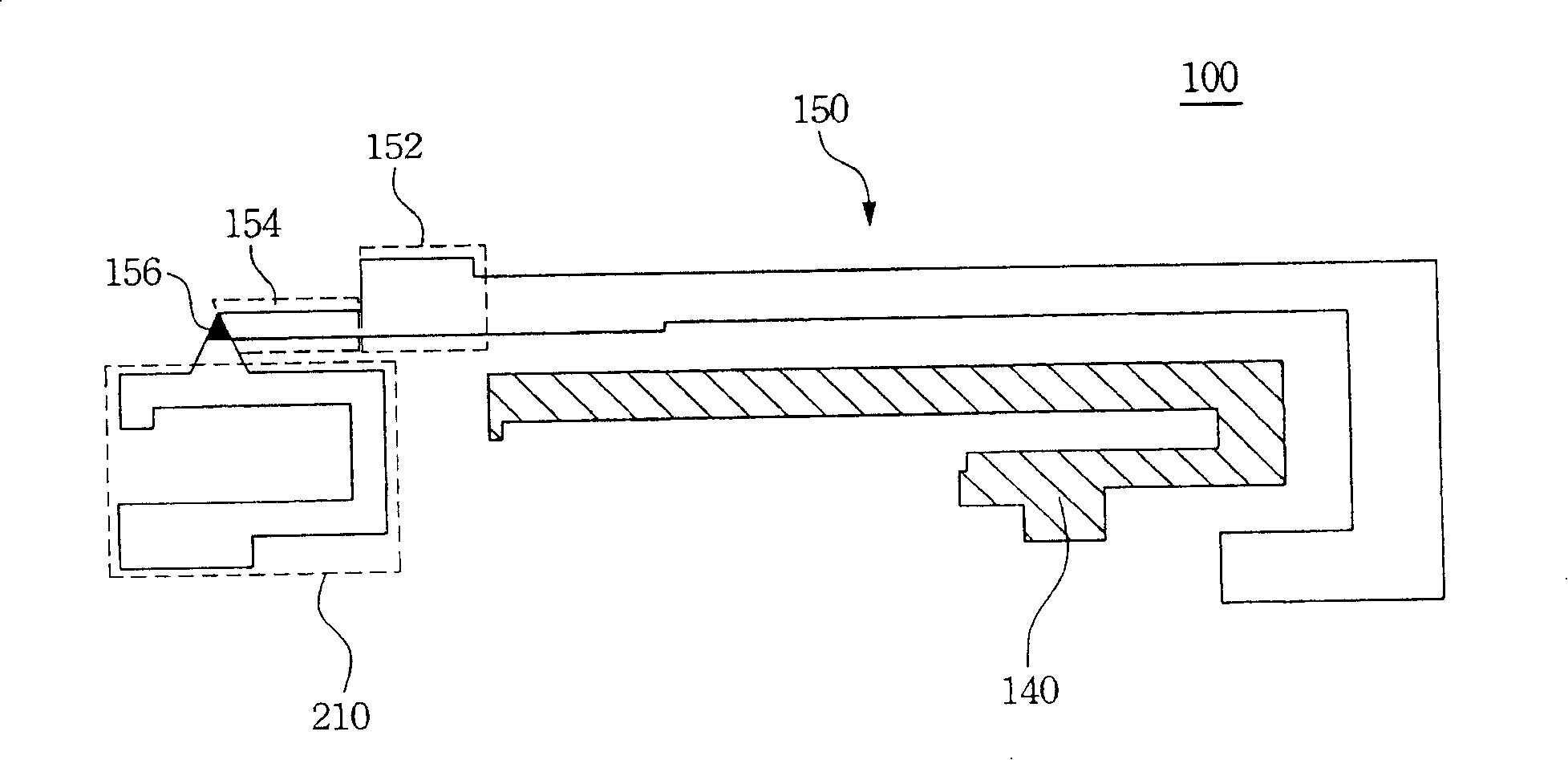
Multi-frequency antenna
ActiveUS20080136711A1High frequency responseImprove receiving efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsOptoelectronicsParasitic structure
A multi-frequency antenna for receiving a first frequency and second frequency signals comprises a grounding element, a first conductive member, a first radiation member, and a second radiation member. The first conductive member connects to the grounding element. The first radiation member and the second radiation member connect to the first conductive member separately. The multi-frequency antenna further comprises a parasitic structure. The parasitic structure structurally encircles the second radiation member and the encirclement is a partial encirclement. Moreover, the parasitic structure connects to the grounding element.
Owner:WISTRON NEWEB
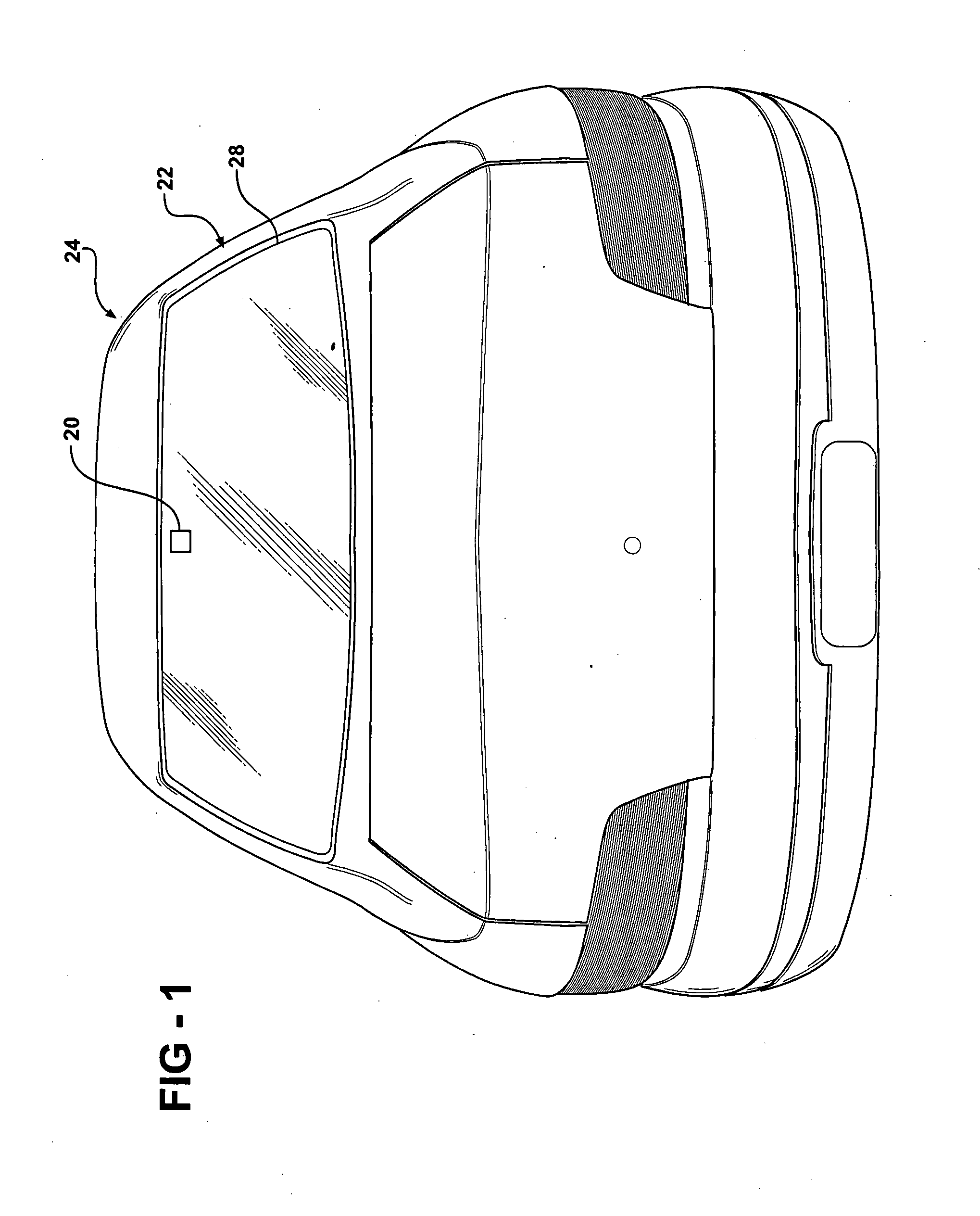
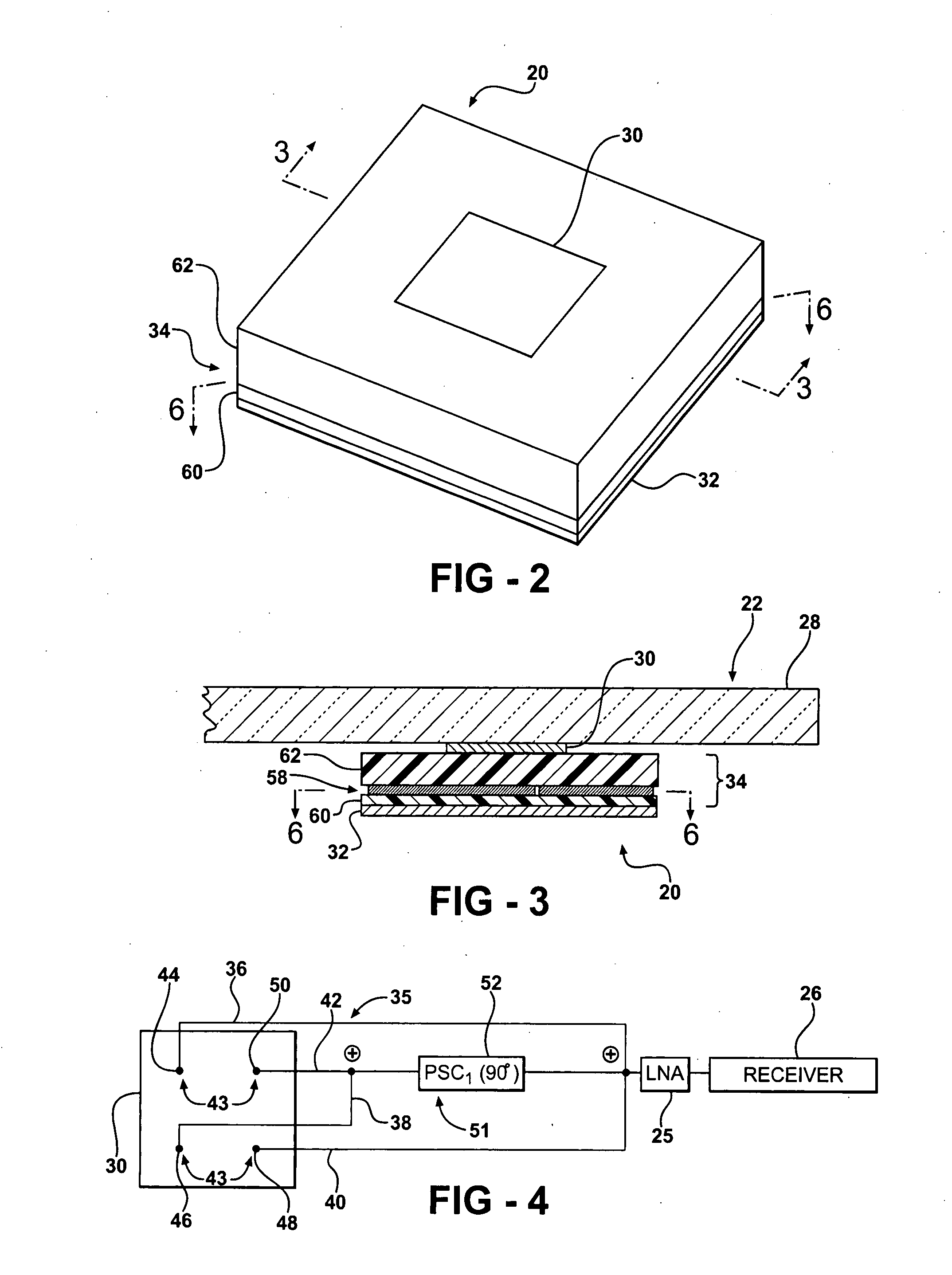
Beam tilting patch antenna using higher order resonance mode
ActiveUS20080129636A1Improve visibilitySmall dimensionSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesParasitic structureCircularly polarized radiation
A patch antenna receives circularly polarized RF signals from a satellite. The antenna includes a radiating element. A plurality of feed lines feed the radiating element at a plurality of feed points. The feed points are spaced apart to generate a circularly polarized radiation beam solely in a higher order mode at a desired frequency. The antenna may include a plurality of parasitic structures. The feed point spacing and / or the parasitic structures tilt the radiating beam away from an axis perpendicular to the radiating element. Thus, the patch antenna provides excellent RF signal reception from satellites at low elevation angles.
Owner:AGC AUTOMOTIVE AMERICAS CO A DIV OF AGC FLAT GLASS NORTH AMERICA INC
Beam tilting patch antenna using higher order resonance mode
ActiveUS7505002B2Improve visibilitySmall dimensionSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesParasitic structureCircularly polarized radiation
A patch antenna receives circularly polarized RF signals from a satellite. The antenna includes a radiating element. A plurality of feed lines feed the radiating element at a plurality of feed points. The feed points are spaced apart to generate a circularly polarized radiation beam solely in a higher order mode at a desired frequency. The antenna may include a plurality of parasitic structures. The feed point spacing and / or the parasitic structures tilt the radiating beam away from an axis perpendicular to the radiating element. Thus, the patch antenna provides excellent RF signal reception from satellites at low elevation angles.
Owner:AGC AUTOMOTIVE AMERICAS CO A DIV OF AGC FLAT GLASS NORTH AMERICA INC
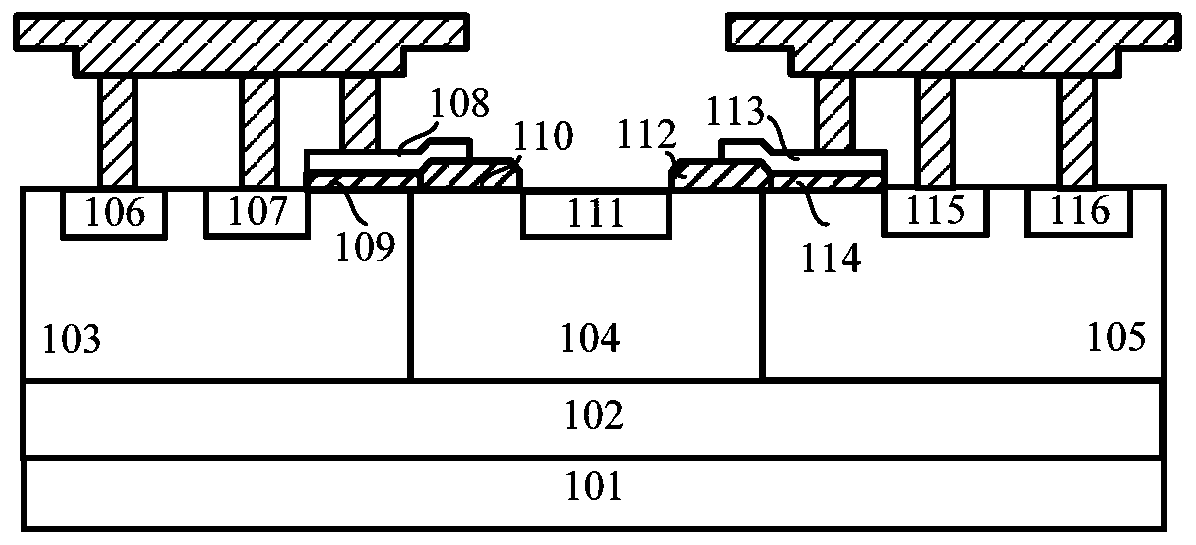
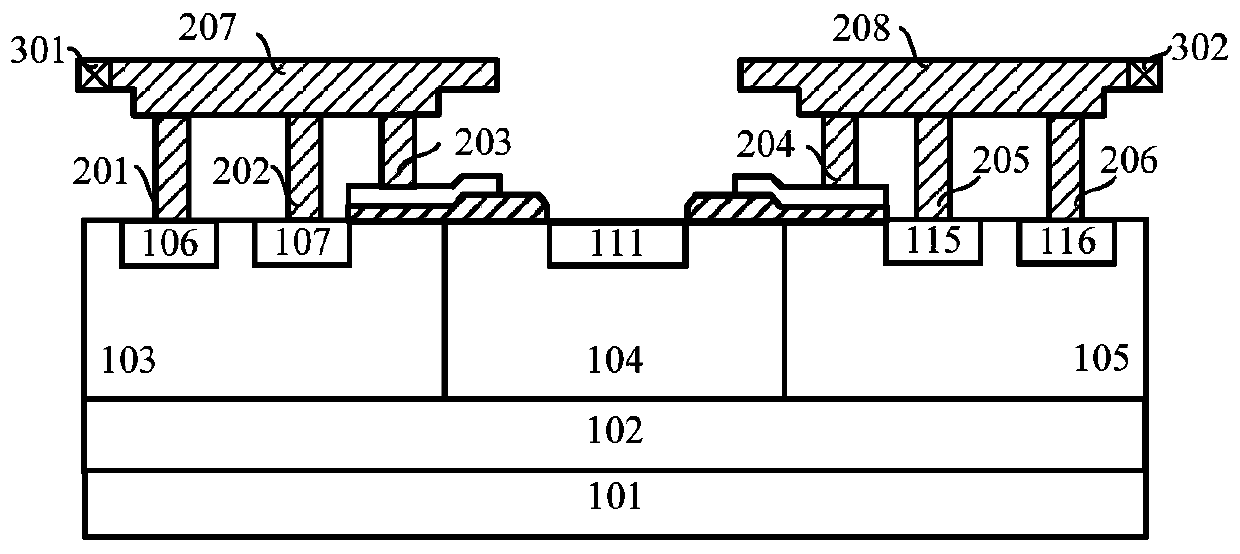
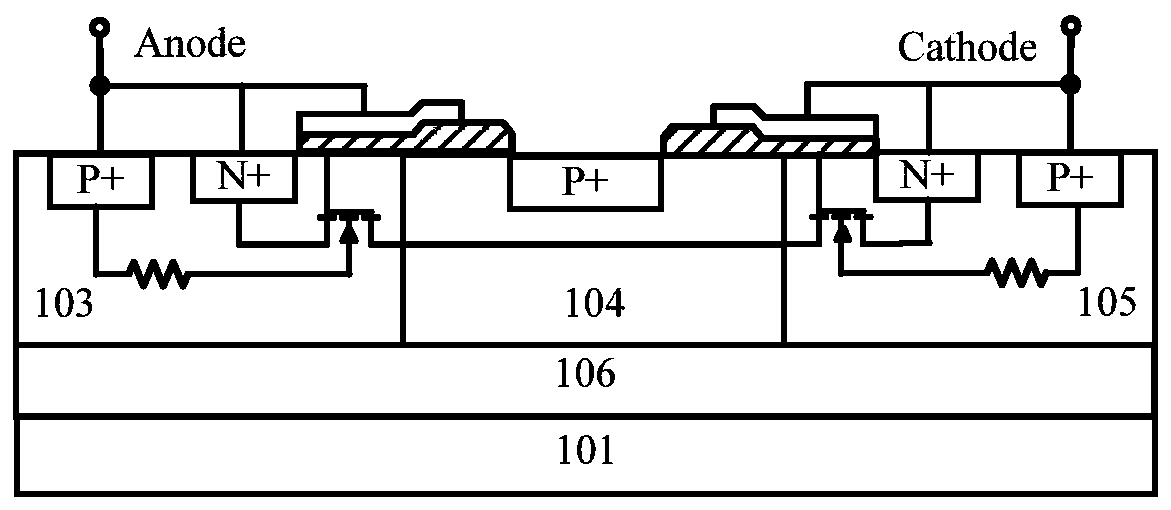
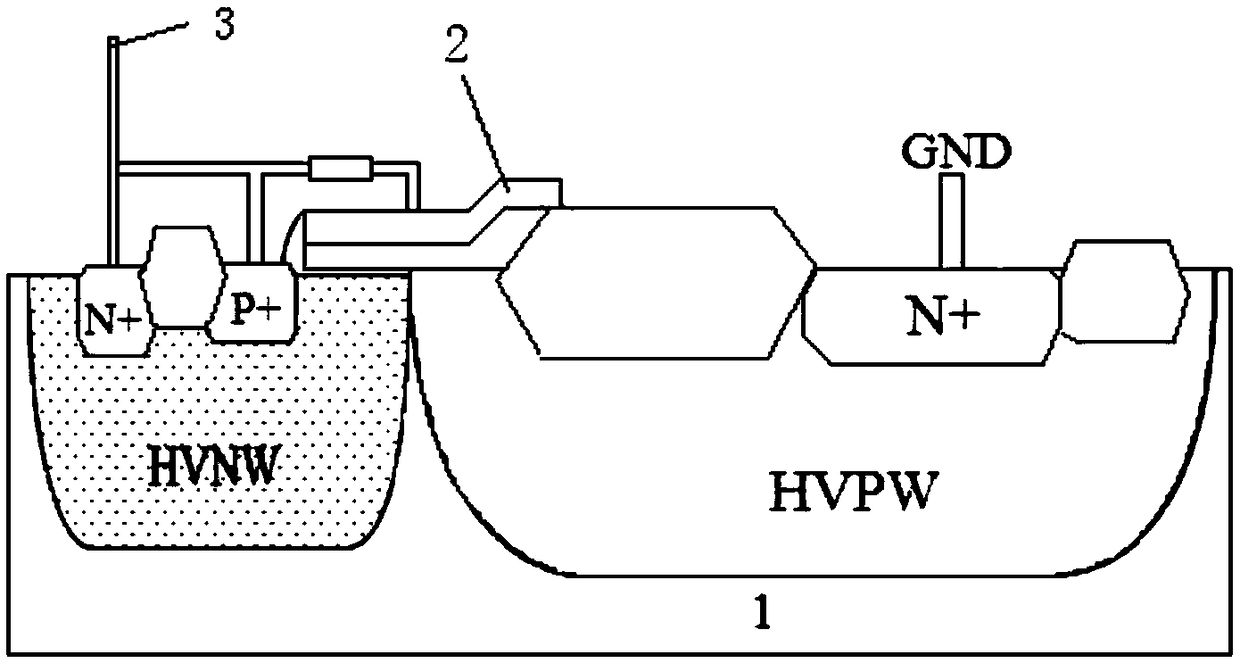
Bidirectional ESD protection structure with embedded low trigger voltage PNP structure
PendingCN107731814AInhibition hysteresisIncrease holding voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesStructure typeHigh voltage
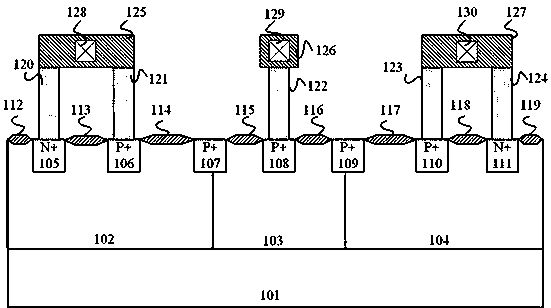
The invention discloses a bidirectional ESD protection structure with an embedded low trigger voltage PNP structure. The bidirectional ESD protection structure is used for ESD protection devices on ICchips and composed of a P substrate, N traps, a P trap, a first N+ injection region, a first P+ injection region, a first P+ span bridge, a second P+ injection region, a second P+ span bridge, a third P+ injection region, a second N+ injection region, metal anodes, metal cathodes and mulitple field oxygen isolation regions. Under the function of high-voltage ESD pulses, on the one hand, a spurious SCR current assistant protection path is formed by the first P+ injection region, the first N trap, the P trap, the second N trap and the second N+ injection region, so that the failure current of the devices can be increased, and the ESD robustness of the devices can be improved; on the other hand, a spurious PNP structure is formed by the first P+ injection region, the first N trap, the firstP+ span bridge, the P trap and the second P+ injection region, so that the maintenance voltage of the devices is increased, and the latch-resisting capability of the devices is improved. The ESD protection device is of a symmetrical structure, and can achieve the bidirectional ESD protection function and reduce the occupied layout area.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
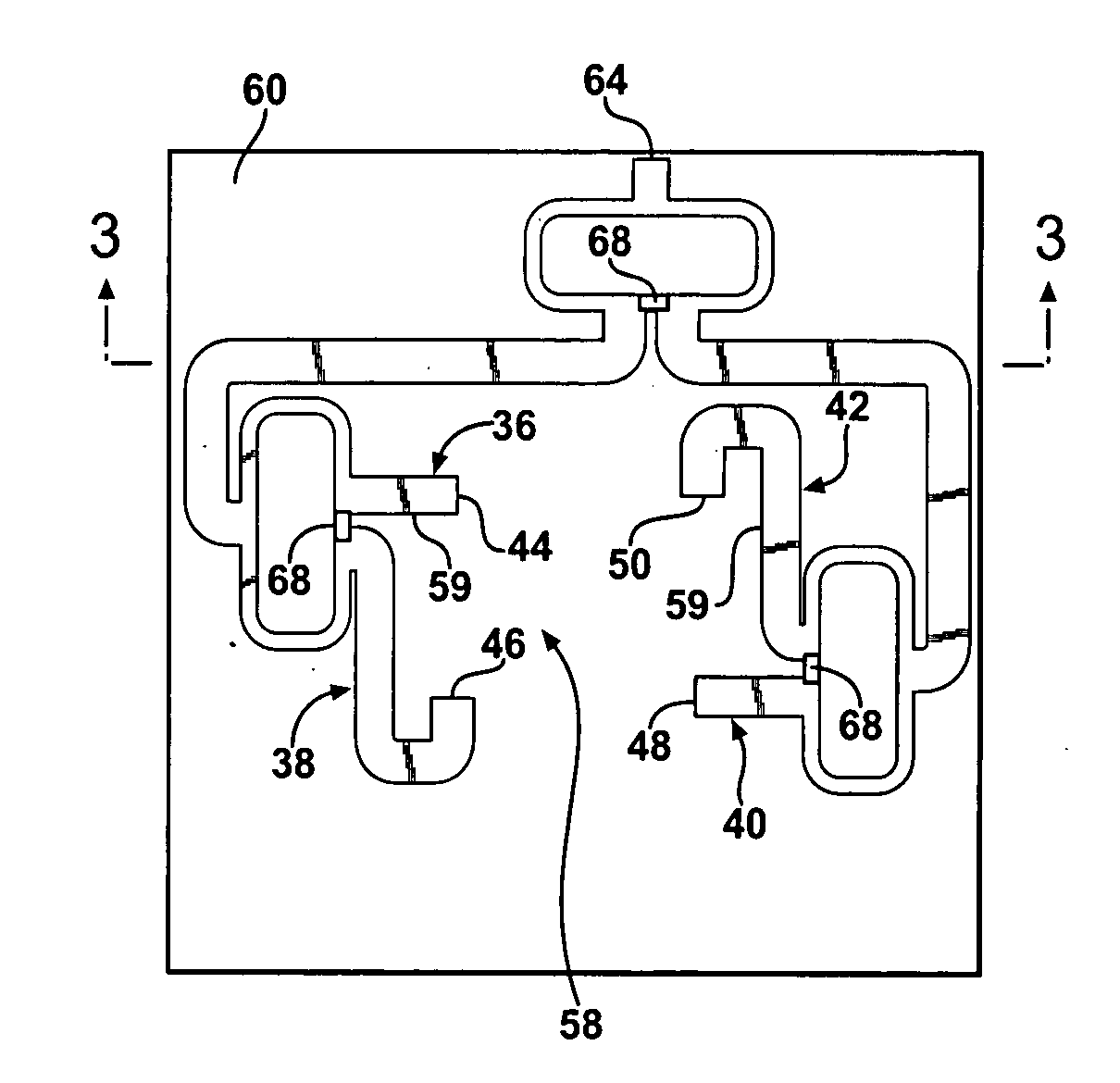
Middle distance flat-plate wireless power transmission system based on magnetic resonance coupling
InactiveCN104734368ARealize integrationReduce consumptionElectromagnetic wave systemCircuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionDielectric substrate
The invention provides a middle distance flat-plate wireless power transmission system based on magnetic resonance coupling. A complanation structure is adopted by the wireless power transmission system, and the system can be processed through a plate-making mode of a printed circuit board. Coil coplanar design is further adopted by the system, by placing an exciting coil (102) and a transmitting terminal resonance coil (101) on the same side of a dielectric substrate, meanwhile, by placing a loading coil and a receiving terminal resonance coil on the same side of the dielectric substrate, a bottom layer of the printed circuit board can be used for adding adjustable electronic parts and components, matching a circuit and rectifying a voltage regulator circuit, and the integration level of the system is improved. A parasitism structure is further adopted by the system, by utilizing a parasitic coil to the resonance coils, the coupling intensity among magnetic coupling resonance coils is strengthened, the transmission efficiency is improved, and the transmission distance is increased. The invention further provides a design and application scheme of a point-to-multipoint wireless power transmission system, and the wireless charging and electricity supplying to multiple consumer electronics, communication equipment and LED lighting equipment are achieved simultaneously.
Owner:喻易强 +1
Multi-frequency antenna
ActiveUS7705784B2High frequency responseImprove efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsOptoelectronicsParasitic structure
A multi-frequency antenna for receiving a first frequency and second frequency signals comprises a grounding element, a first conductive member, a first radiation member, and a second radiation member. The first conductive member connects to the grounding element. The first radiation member and the second radiation member connect to the first conductive member separately. The multi-frequency antenna further comprises a parasitic structure. The parasitic structure structurally encircles the second radiation member and the encirclement is a partial encirclement. Moreover, the parasitic structure connects to the grounding element.
Owner:WISTRON NEWEB
Semiconductor devices and methods to enhance electrostatic discharge (ESD) robustness, latch-up, and hot carrier immunity
ActiveUS20180247929A1High latch-up immunityEnhanced life expectancyTransistorThyristorSalicideEngineering
The present disclosure relates to non-planar ESD protection devices. The present disclosure provides a device structure and method of fabricating the structure that is essentially immune to latch-up and possess high ESD robustness and reliability. In an aspect, the present disclosure provides a mixed silicidation and selective epitaxy (epi) FinFET processes for latch-up immunity together with ESD robustness, thereby allowing achievement of ESD efficient parasitic structures together with latch-up immune and reliable functional devices. The present disclosure provides a dual silicidation scheme where ESD protection element(s) have fins that are partially silicided, and functional devices have fins that are fully silicided. The present disclosure also provides a hybrid contact and junction profile scheme where ESD protection element(s) have fins that are partially silicided with or without deep junctions depending on their application, and functional devices have fins that are fully silicided with the silicide edge crossing the junction. On the other hand, a dual Epi scheme is implemented such that ESD protection elements have fins with Epi contact, and functional devices have fins that are fully silicided without Epi (raised S / D) contact.
Owner:INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE
Integrated substrate chamber millimeter wave array antenna
ActiveCN107154531AHigh gainIncreased effective radiation aperture areaAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsResonanceMetal sheet
The invention discloses an integrated substrate chamber millimeter wave array antenna. The antenna comprises an antenna array, a power division module and an external switching module, wherein the external switching module is used for leading electromagnetic waves from metal waveguide to the power division module, the electromagnetic waves are divided by the power division module into multiple paths of electromagnetic waves for output, the electromagnetic waves enter into an integrated substrate chamber of an antenna unit, high-order mode resonance is generated in the integrated substrate chamber through expanding a radiation aperture of the integrated substrate chamber, gain of the millimeter wave array antenna is improved, high-order mode field distribution of the electromagnetic waves in the integrated substrate chamber is adjusted through a parasitic structure, so the high-order mode radiation direction of the electromagnetic waves in the integrated substrate chamber is turned to be in a normal direction of the integrated substrate chamber, and normal operation of the antenna array is realized, moreover, the parasitic structure employs an I-like metal sheet, current length of the metal sheet can be improved, and bandwidth of the antenna array is enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High-isolation dual polarization station antenna unit facing 5G application
InactiveCN108365331AImprove return lossReduce lossRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationSelf interferenceHigh isolation
The present invention relates to a high-isolation dual polarization station antenna unit facing 5G application. The unit comprises a dielectric slab, a coaxial feeder, a back panel and an SMA feeder arranged in order from top to bottom. The front and back surfaces of the dielectric slab are etched with a first bow-tie dipole antenna and a second bow-tie dipole antenna which are vertically arrangedat +-45 degrees, each bow-tie dipole antenna is formed by two symmetrically arranged dipole antenna arms, and each dipole antenna arm comprises one optimized fractional parasitic structure. The high-isolation dual polarization station antenna unit facing 5G application forms a station antenna unit with low loss and high isolation features and low loss and high loss and high isolation through theoptimized fractional parasitic structure so as to reduce the loss of the antenna itself and reduce the self interference between antennas.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
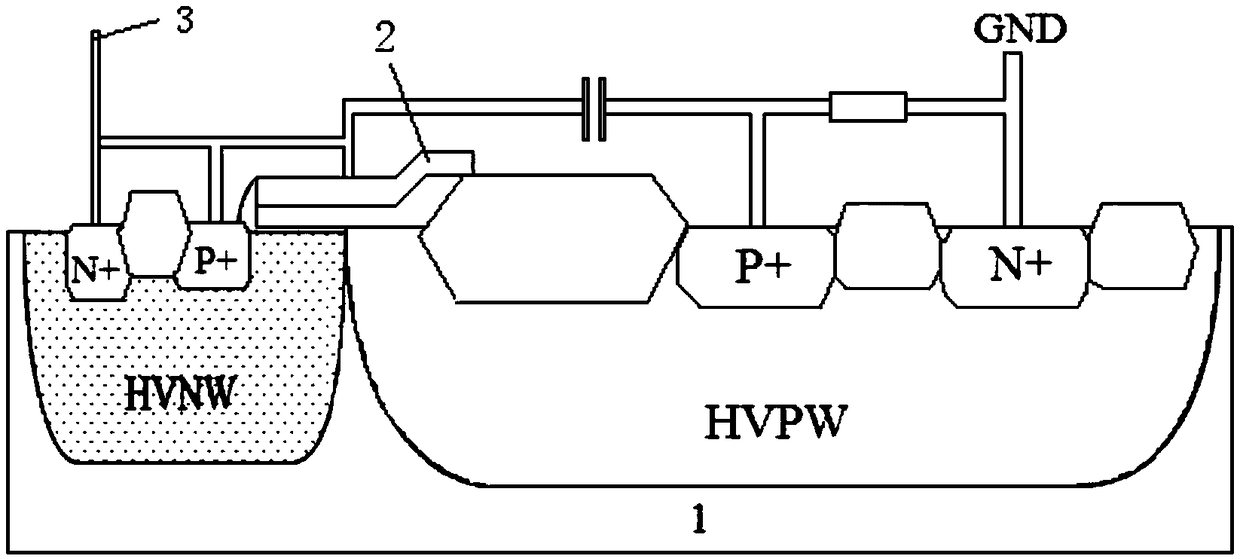
Bidirectional high-voltage ESD protection device of full-symmetric LDMOS triggered SCR structure
ActiveCN110880500AEnhanced ESD robustnessImprove pressure resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesDischarge efficiencyEngineering
The invention discloses a bidirectional high-voltage ESD protection device of a full-symmetric LDMOS triggered SCR structure, and belongs to the field of electrostatic discharge protection and surge resistance of integrated circuits. The protection device is mainly composed of a P substrate, a deep N well, a first P well, an N well, a second P well, a first P + injection region, a first N + injection region, a first polysilicon gate, a first thin gate oxide layer, a first field oxide isolation region, a second P + injection region, a second field oxide isolation region, a second polysilicon gate, a second thin gate oxide layer, a second N + injection region and a third P + injection region. The two NLDMOSs are embedded to form an auxiliary trigger SCR current path in which the on-state NLDMOS and the off-state NLDMOS are connected in series. The voltage withstanding capability of the device is improved, so that the device meets the ESD protection requirement of a high-voltage power supply domain, the ESD robustness of the device is enhanced, the discharge efficiency of the device in unit area is improved, the carrier concentration of a base region in a parasitic SCR structure is reduced, and the maintaining voltage of the device is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Multi-frequency antenna structure
ActiveCN111403899AEasy to applySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsSoftware engineeringParasitic structure
The invention provides a multi-frequency antenna structure. The multi-frequency antenna structure comprises a first antenna unit, a second antenna unit, a reflecting plate and a first parasitic structure of the first antenna unit, wherein the working frequency bands of the first antenna unit and the second antenna unit are different, and the distance between the antenna unit with the higher working frequency band and the reflecting plate is lessthan the distance between the antenna unit with the lower working frequency band and the reflecting plate; the first antenna unit is adjacent to the second antenna unit; the distance between the first antenna unit and the second antenna unit is less than 0.5 time of the vacuum wavelength of the minimum working frequency band in the two antenna units; the distance between the first antenna unit and the first parasitic structure is less than 0.5 times of the vacuum wavelength of the working frequency band of the first antenna unit, and the distance between the second antenna unit and the first parasitic structure is less than 0.5 times of the vacuum wavelength of the working frequency band of the second antenna unit. Therefore, the problems ofpolarization rejection ratio deterioration and the like of the directional diagram of the first antenna unit can be optimized, and the performance of the second antenna unit cannot be obviously influenced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Branch loading and parasitic structure-based base station antenna
ActiveCN110233332AReduce horizontal sizeOvercoming technical problems with large dimensionsRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsBase station antenna arrayMiniaturization
The invention discloses a branch loading and parasitic structure loading-based small-size base station antenna unit. The branch loading and parasitic structure loading-based small-size base station antenna unit comprises a radiation patch, angular metal structures, a parasitic ring structure, a microstrip feeder, a coaxial feeder, short-circuit metal, a reflection plate, three different dielectricplates and a feeding floor, wherein the four angular metal structures are respectively arranged at tail ends of four dipole arms, the parasitic ring structure is arranged right below the radiation patch, and the reflection plate comprises a horizontal structure and metal baffle plates around the horizontal structure. By loading the angular metal posts at the tail ends of the dipole arms and loading the metal ring structure below the radiation patch, the size of the radiation patch is reduced by 25%, the impedance matching is good, and the radiation performance is stable; and with a structurethat the feeding floor and the reflection plate are separated, the antenna is flexible to assemble, and the antenna is suitable for mass production. The antenna can be applied to a base station antenna array under a limited space size condition.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Broadband high-gain circularly polarized filtering antenna
ActiveCN114566796AHigh gainGood circular polarization performanceRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsDielectric substrateEngineering
The invention discloses a broadband high-gain circularly polarized filtering antenna, and relates to the field of radio frequency communication. The antenna comprises four layers of dielectric substrates from bottom to top, a first metal ground is printed on the upper surface of the first layer of dielectric substrate, a slot coupling feed network is printed on the second layer of dielectric substrate, a radiation structure is printed on the upper surface of the third layer of dielectric substrate, and a parasitic structure is printed on the lower surface of the fourth layer of dielectric substrate. The first metal ground is a square metal copper surface, the radiation structure is a square chamfered radiation patch, and the parasitic structure is a square slotted parasitic patch; the slot coupling feed network comprises a microstrip feed line and a double-Y-shaped slot, the double-Y-shaped slot is printed on a second metal ground, and the second metal ground and the microstrip feed line are printed on the upper surface and the lower surface of the second dielectric substrate respectively. By using the slot coupling feed network to excite the radiator structure with the circular polarization radiation function and the filtering function, good broadband circular polarization radiation characteristics and high-roll-off filtering characteristics are generated.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
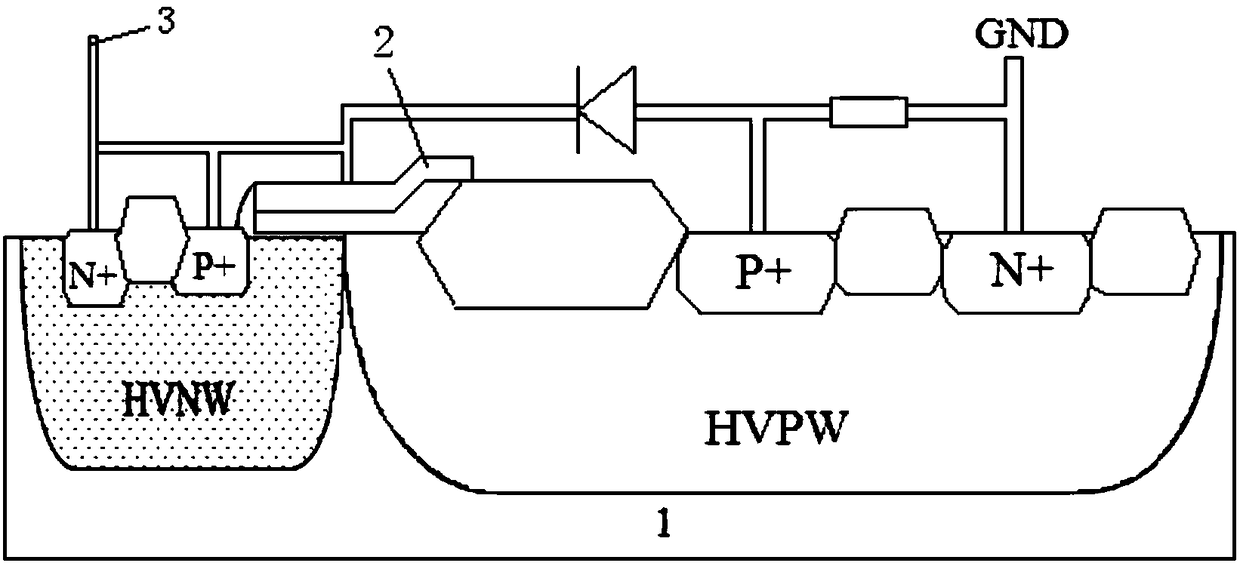
High-voltage electrostatic protection device and equivalent circuit
ActiveCN109148438ALower the trigger voltageTrigger voltage optimizationTransistorSolid-state devicesLDMOSHemt circuits
The invention discloses a high-voltage electrostatic protection device, a trigger circuit is arranged at the drain end of a high-voltage P-LDMOS, when the circuit is working normally, the trigger circuit is in an off state, and when static electricity comes, the trigger circuit is in an on state, so that the parasitic SCR structure in the high-voltage P-LDMOS is triggered to be turned on to discharge electrostatic charge. The invention discloses an equivalent circuit of the high-voltage electrostatic protection device. The invention can effectively protect the internal high-voltage device.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Multi-frequency antenna
ActiveCN101207236AImprove transmission efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsParasitic structurePhysics
The invention relates to a multi-frequency antenna, which is used for receiving the signals of a first frequency and a second frequency. The invention at least comprises a grounding part, a first conducting component, a first radiation part and a second radiation part. The first conducting component is mutually connected with the grounding part. The first radiation part and the second radiation part are respectively connected on the first conducting component. In addition, the multi-frequency antenna also comprises a parasitic structure surrounding the second radiation part, and the parasitic structure is mutually connected with the grounding part.
Owner:WISTRON NEWEB
ESD protection device capable of modulating trigger voltage and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109935584ARealize adjustableMeet the requirementsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZener diodeAvalanche diode
The invention discloses an ESD protection device capable of modulating a trigger voltage and a preparation method thereof. One or more tunneling diodes are formed in the device. An avalanche diode isreplaced by a Zener diode on a parasitic structure, and the avalanche breakdown is replaced by tunneling breakdown on the breakdown principle, so that an electrical breakdown point of a parasitic SCRis changed, the trigger voltage is effectively reduced, and the trigger voltage is modulated according to the change of the structure. Meanwhile, the invention discloses a preparation method of the ESD protection device capable of modulating the trigger voltage, and the preparation method is used for preparing the ESD protection device capable of modulating the trigger voltage. The ESD protectiondevice formed by modulating the trigger voltage and capable of modulating the trigger voltage can meet the requirement of an ESD protection window under the FinFET technology, and it is guaranteed that the trigger voltage is lower than the damage voltage of a protected unit.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF TECH
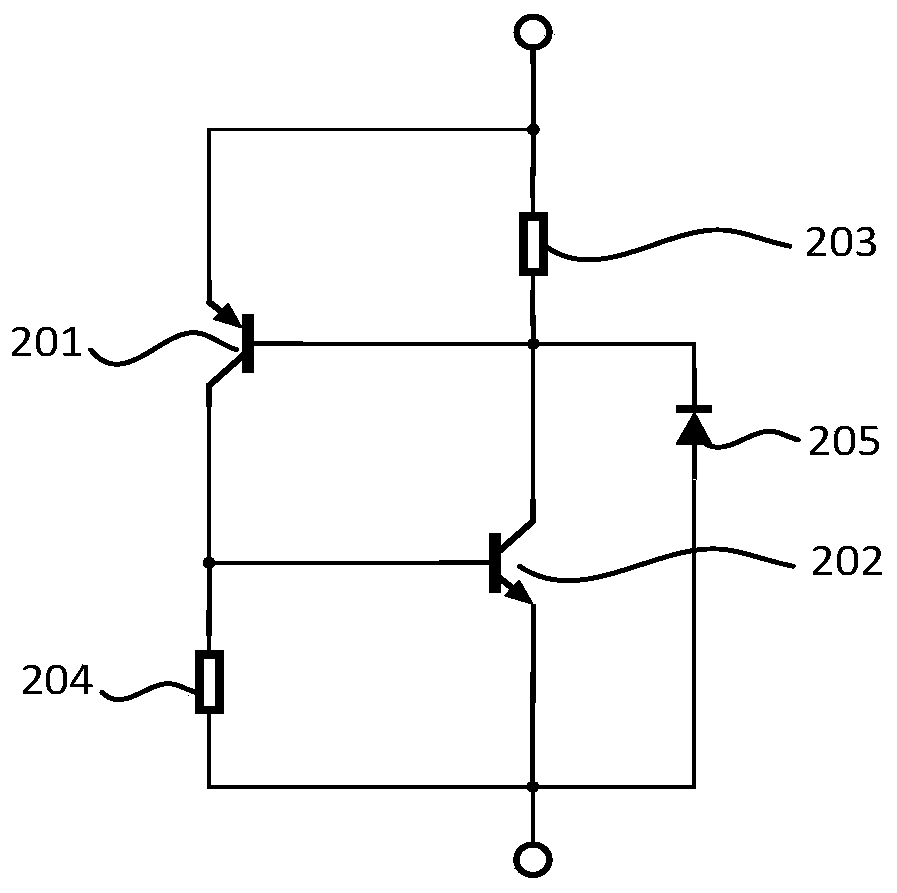
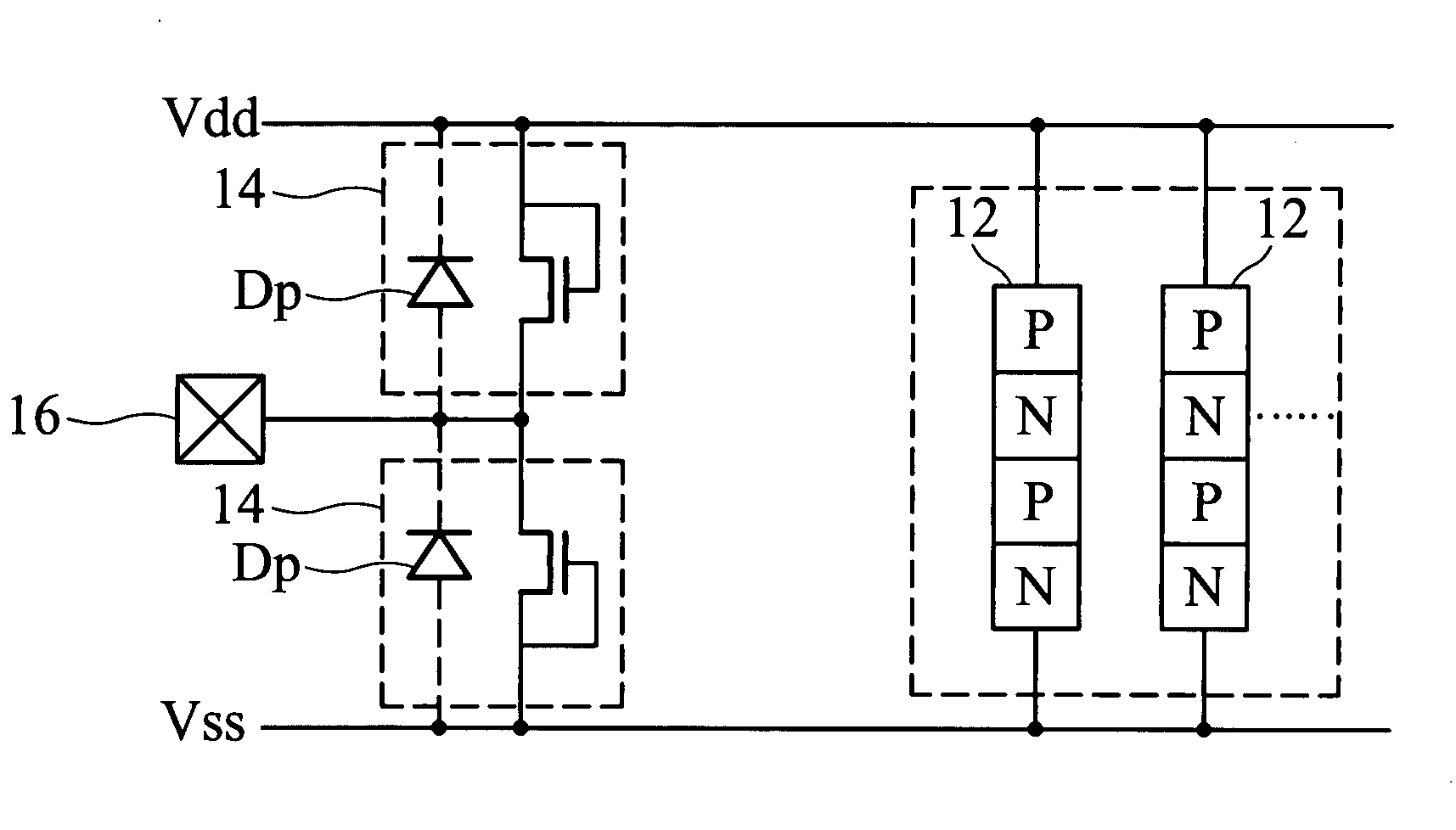
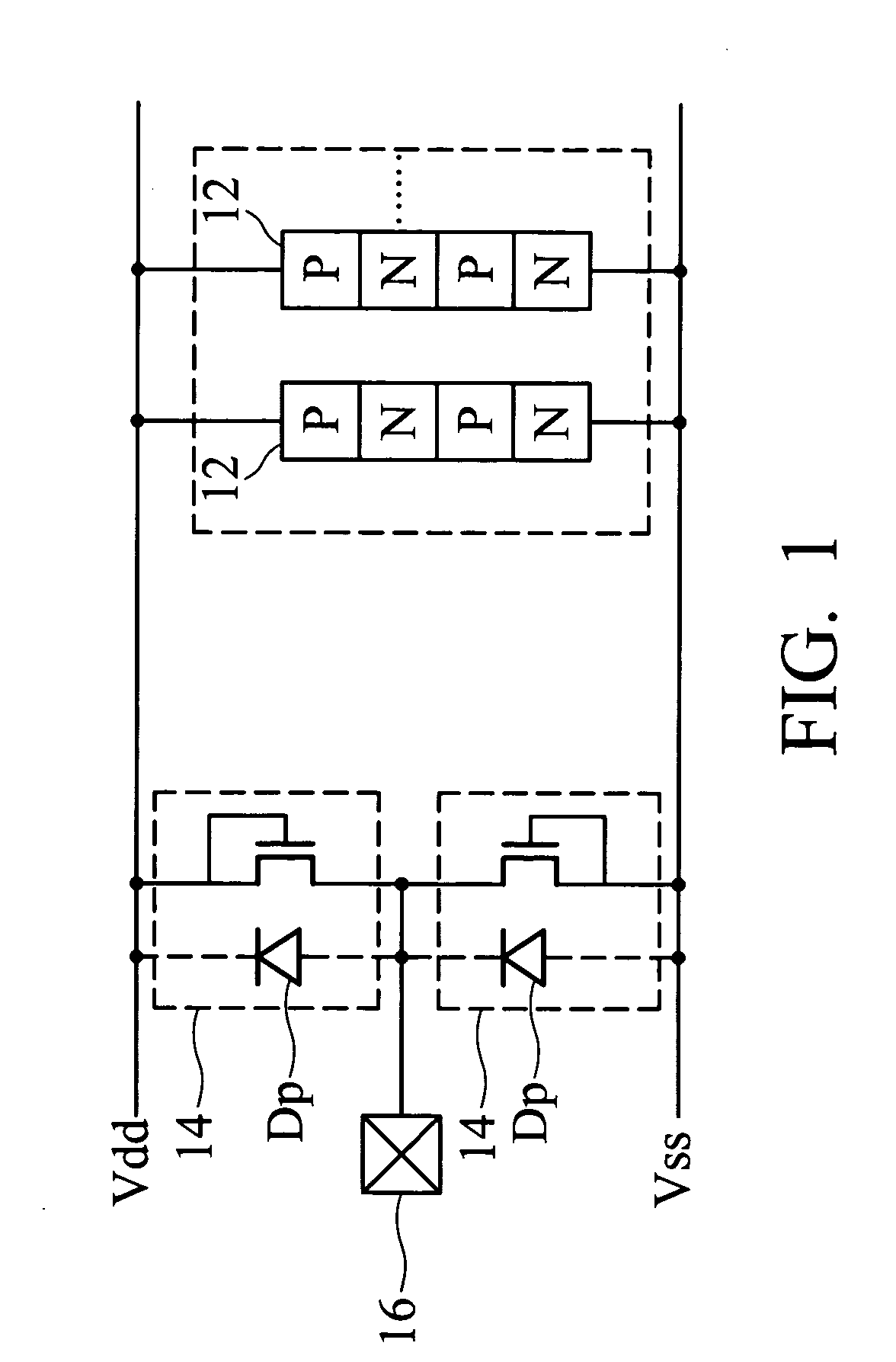
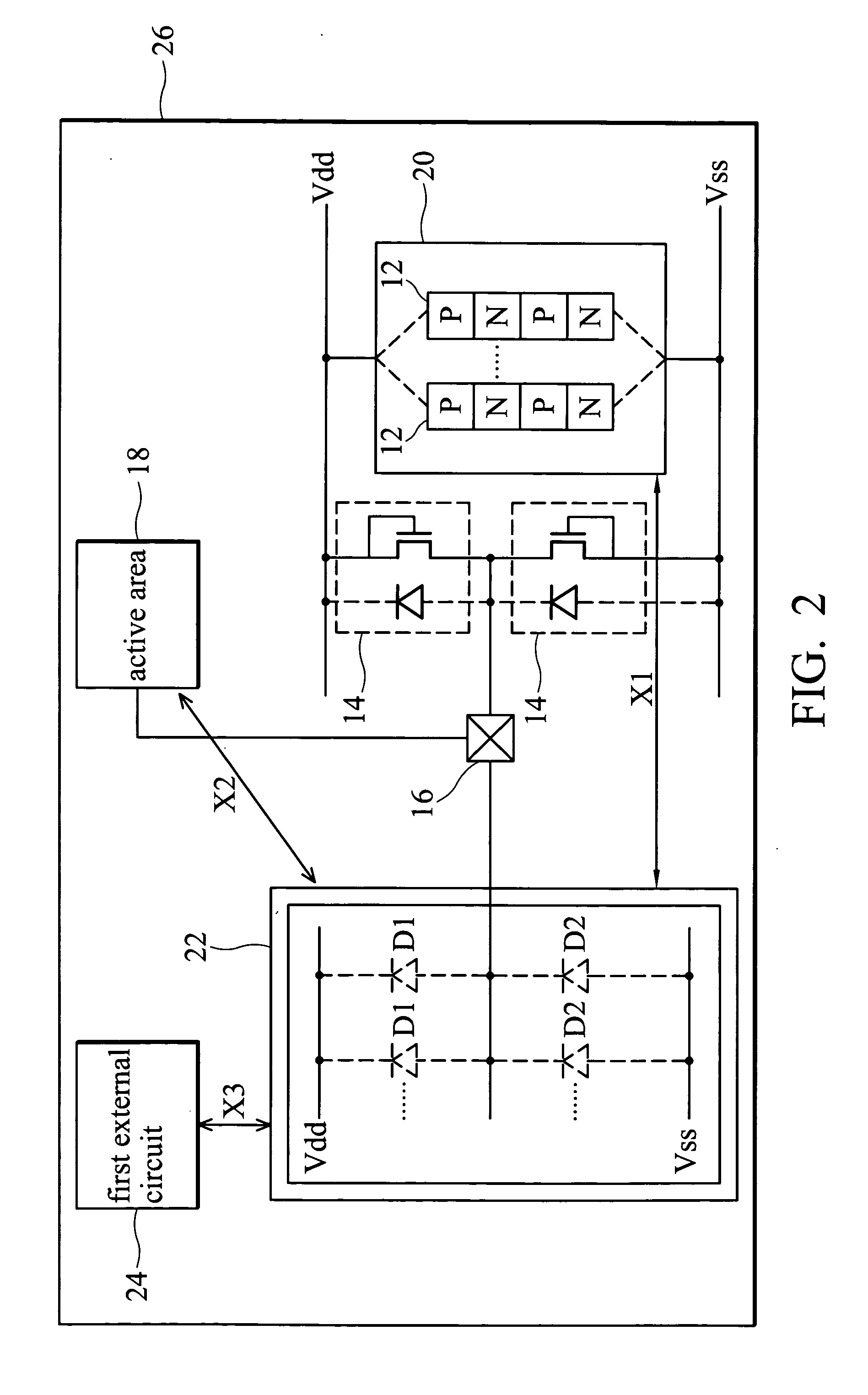
Latchup prevention method for integrated circuits and device using the same
ActiveUS20050259372A1Minimize impactAvoid latchTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringVoltage source
An integrated circuit preventing latchup. In the integrated circuit, an internal circuit is disposed in a substrate and has a parasitic SCR structure. At least one ESD protection circuit and active area are disposed on the substrate and coupled to a pad. A first current shunting diode has an anode coupled to the pad and a cathode coupled to a first voltage source. A second current shunting diode has a cathode coupled to the pad and an anode coupled to a second voltage source. Minority-carriers guard rings surround the first current shunting diode and the second shunting diode. Distance between the first and second current shunting diodes and the internal circuit, the active area and the ESD protection circuit exceed 80 μm.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Low-profile low-cross-polarization dual-polarization electromagnetic dipole antenna
ActiveCN114498003AIncreased cross-polarization ratioStable Half Power BeamwidthRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationEngineeringImpedance matching
The invention discloses a low-profile low-cross-polarization dual-polarization electromagnetic dipole antenna, and belongs to the technical field of mobile communication base station antennas. The antenna comprises two pairs of electric dipoles, two pairs of magnetic dipoles, a feed structure, a metal column and a metal reflecting plate, the electric dipole comprises two horizontal metal patches and four vertical metal patches; the magnetic dipole is a rectangular metal patch, and an included angle between the magnetic dipole and the metal reflecting plate is 60 degrees; the feed structure comprises a pair of orthogonally placed inverted L-shaped feed structures and two SMA joints, and each inverted L-shaped feed structure is divided into four parts which are connected in sequence; and the metal column is positioned between the metal reflecting plate and the vertical metal patch. According to the antenna, the low profile is kept, and meanwhile, the cross polarization ratio in a + / -60-degree sector is increased through the coupling effect of the parasitic structure, and the half-power beam width is stabilized; and the vertical metal patch which is bent downwards and the metal column structure are introduced, so that good impedance matching in a frequency band can be realized only by performing simple parameter optimization.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Broadband low-profile miniaturized AMC cavity monopole antenna
ActiveCN114374092AAchieved weightReduce weightSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsSquare arrayAntenna bandwidth
The broadband low-profile miniaturized AMC cavity monopole antenna comprises a monopole antenna body, parasitic structures, a broadband AMC structure and a metal cavity, the monopole antenna body is installed on the side wall of the cavity, the parasitic structures are located on the two sides of the monopole antenna body and are flush with the opening face of the cavity, and the broadband AMC structure is a square patch type AMC structure with an air layer. The dielectric substrate is located between the monopole antenna and the bottom surface of the cavity, a square array is printed on the dielectric substrate, and an air layer is arranged between the dielectric substrate and the bottom surface of the cavity. According to the invention, the monopole and the parasitic structure are placed on the side wall of the cavity, so that wide beam coverage in the broadband of the antenna is realized, the space of the cavity is effectively utilized, and miniaturization and light weight of the antenna are realized; moreover, based on the broadband AMC structure, the profile of the antenna is reduced by 40% under the condition of keeping 32% bandwidth of the cavity monopole antenna, and the whole antenna has good impedance and radiation characteristics in a small-size cavity.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Earth plate slot radiation n-type parasitic structure multi-frequency planar monopole antenna
ActiveCN110783703ASimple structureImproved port matching performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric substrateEngineering
The invention discloses an earth plate slot radiation n-type parasitic structure multi-frequency planar monopole antenna, comprising: a square dielectric substrate; a monopole rectangular radiation arm disposed on the upper surface of the square dielectric substrate; an n-type metal parasitic structure disposed on the upper surface of the square dielectric substrate; and a metal earth plate disposed on the lower surface of the square dielectric substrate. The monopole rectangular radiation arm is a rectangular metal patch. The axis of the monopole rectangular radiation arm in parallel to a long arm passes through the center of the upper surface of the square dielectric substrate. A short side of the monopole rectangular radiation arm coincides with a first side of the upper surface of thesquare dielectric substrate, and the centers of two edges coincide with each other to serve as a feed port of the earth plate slot radiation n-type parasitic structure multi-frequency planar monopoleantenna. Two groups of rectangular slot structures are etched symmetrically on the metal earth plate. The earth plate slot radiation n-type parasitic structure multi-frequency planar monopole antennasolves the technical problems that the antenna of an existing wireless mobile communication system has a single operating frequency and thus leads to an increase in system complexity and a decrease inreliability.
Owner:YULIN UNIV
Novel millimeter-wave low-profile planar differential double-helix antenna
PendingCN111585014AIncrease circular polarization gainMeet the needs of easy integrationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMetal stripsDielectric plate
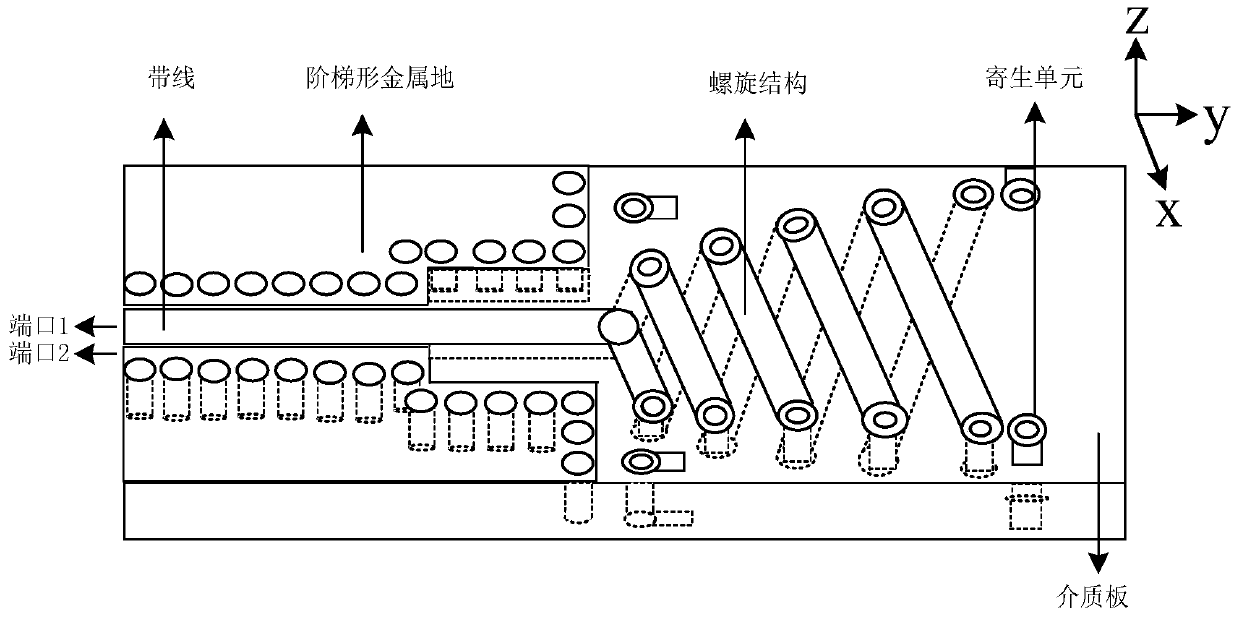
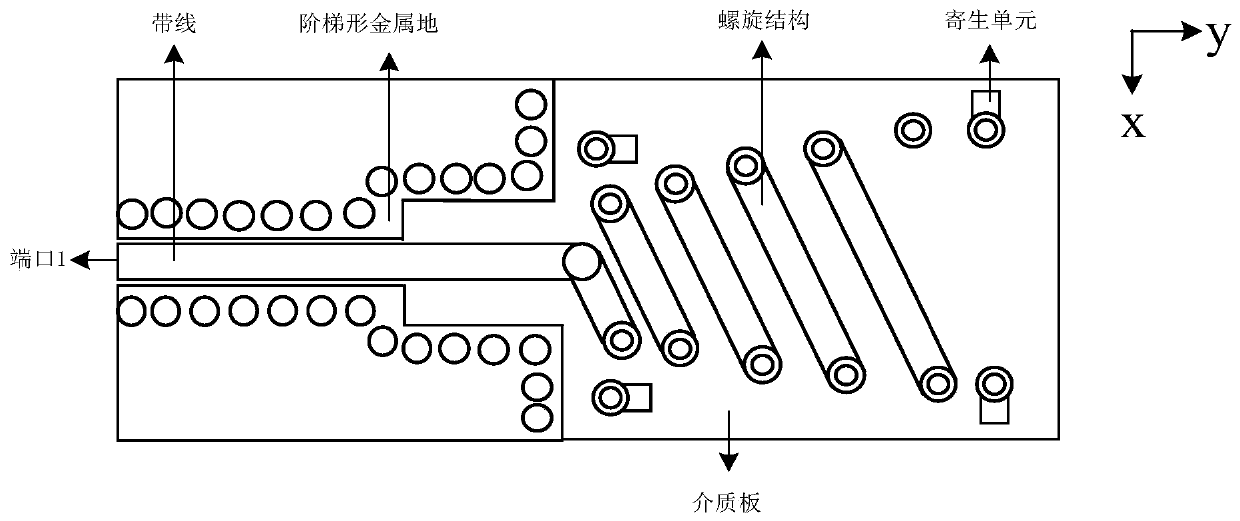
The invention discloses a novel millimeter-wave low-profile planar differential double-helix antenna. The antenna consists of three parts: a first part has a feed structure, the differential feed is realized through strip lines located at two sides of the front bottom of the same dielectric plate, and the two sides of the front bottom are completely symmetrical; a second part is of a planar helixstructure, one end of the helix is connected with the strip line, and the other end axially extends, the planar helix is formed by connecting metal strips printed on the front surface and the bottom surface of the dielectric plate with the metalized via holes in a staggered manner and is of a double-helix structure, the diameter of the helix is gradually increased, and the structures of the frontsurface and the bottom surface of the dielectric plate are in 180-degree rotational symmetry; and a third part is of a parasitic structure and is composed of a metallized via hole and metal strips printed on the two sides of the front bottom of the dielectric plate. The parasitic unit is disposed around the helix. The antenna has the advantages of being low in profile, wide in bandwidth, stable incircular polarization gain, good in radiation directivity, simple in structure, easy to process and the like, and has a good application prospect in the 5G millimeter wave frequency band.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Planar low-profile micro-strip filtering antenna based on band-pass filter prototype
ActiveCN113314838ASimple structureIncrease the level of out-of-band rejectionRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsCoplanar waveguideBand-pass filter
The invention provides a planar low-profile micro-strip filtering antenna based on a band-pass filter prototype, belongs to the technical field of communication. The planar low-profile micro-strip filtering antenna comprises a dielectric substrate and a floor. The invention provides a filtering antenna technology based on the band-pass filter prototype, which can be used for realizing radiation filtering response with a high out-of-band rejection level under the condition that an additional filtering circuit and a complex parasitic structure are not used. Meanwhile, the physical form of the provided filtering antenna is a microstrip coupling line feed double-patch radiator, and the filtering antenna is very simple in structure and easy to process. A coplanar waveguide-slot line-microstrip line conversion structure is used as a Balun and a power divider, aims to excite a differential coupling line, and improves the frequency selectivity and the out-of-band rejection level by introducing a hybrid electromagnetic coupling feed technology. The micro-strip filtering antenna has a low profile and a compact structure, and is beneficial to miniaturization and integration design of a radio frequency front end.
Owner:成都频时科技有限公司
High-isolation multi-input multi-output antenna based on parasitic structures
InactiveCN108232436AAchieve coverageImprove isolationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMulti inputArray element
The invention discloses a high-isolation multi-input multi-output antenna based on parasitic structures. The high-isolation multi-input multi-output antenna comprises an array element cell; the arrayelement cell comprises two antenna elements which adopt the same structure and are back on to each other, each of the antenna elements comprises a substrate and a ground plate arranged at the lower part on the back surface of the substrate, the substrate and the ground plate are of an integrated structure, and a first parasitic structure and a second parasitic structure are arranged on the back surface of the substrate; a first F-shaped structure and a second F-shaped structure are arranged on the front surface of the substrate; the first parasitic structure and the second parasitic structureare symmetrically arranged about a center line of the substrate, and the first F-shaped structure and the second F-shaped structure are symmetrically arranged about the center line of the substrate; the first parasitic structure and the second parasitic structure from a low-frequency radiation unit and a reflection unit of the antenna element. With the adoption of the invention, the isolation of the antenna is improved.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Ultra-low profile double-frequency single-layer small mobile antenna based on MGAA unit
ActiveCN114552219ASolve miniaturizationHigh profile solutionSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMobile antennasDielectric substrate
The invention belongs to the technical field of small mobile antennas, and discloses an MGAA unit-based ultra-low profile double-frequency single-layer small mobile antenna, which comprises a dielectric substrate, a metal floor, an MGAA unit, a rectangular parasitic microstrip and a coaxial feeder, the MGAA unit and the rectangular parasitic microstrip are attached to the upper side of the dielectric substrate, and the metal floor is attached to the lower side of the dielectric substrate; the MGAA unit is funnel-shaped and is located at the middle position of the dielectric substrate, and the center position of the MGAA unit is connected with an inner conductor of the coaxial feeder line for feeding so as to radiate low-frequency linearly polarized electromagnetic waves; the rectangular parasitic micro-strips are located on the left side and the right side of the center of the MGAA unit and used for radiating high-frequency linearly polarized waves. According to the invention, the MGAA unit is introduced into the dual-frequency design of the mobile communication equipment to solve the problems of miniaturization, high profile and multiband characteristic of the antenna, and the dual-frequency work of the antenna is realized by adding the parasitic structure.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A bidirectional esd protection device with composite structure
ActiveCN110896072BLower the trigger voltageReduce hysteresisTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringParasitic structure
The invention discloses a bidirectional ESD protection device with a composite structure, which belongs to the fields of electrostatic discharge protection and anti-surge of integrated circuits. The device is mainly composed of a P-type lightly doped substrate, an N-type doped well, a first P-type medium-doped well, a second P-type medium-doped well, a first P-type heavily doped implant region, a first N-type heavily doped implant region, second P-type heavily doped implant region, second N-type heavily doped implant region, first polysilicon gate and its covered first thin gate oxide layer, third N-type heavily doped implant region The doping implantation region, the fourth N-type heavily doped implantation region, the second polysilicon gate and its covered second thin gate oxide layer, and the fifth N-type heavily doped implantation region. The present invention improves the base concentration of the parasitic NPN transistor inside the device through the layout design and the use of the P-type doped well, reduces the magnification of the internal parasitic NPN transistor, weakens the positive feedback degree of the parasitic SCR structure, and can increase the maintenance voltage of the device and enhance ESD robustness.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Antenna structure and antenna array
ActiveCN112909506AImprove experienceGood product competitivenessParticular array feeding systemsSimultaneous aerial operationsEngineeringBroadband
The embodiment of the invention provides an antenna structure and an antenna array. The antenna structure comprises a first antenna assembly, and the first antenna assembly comprises a first three-dimensional antenna with one end grounded or connected with a reference potential, a single antenna port connected with the other end of the first three-dimensional antenna and a first parasitic structure arranged adjacent to the first three-dimensional antenna. In the antenna structure, the first three-dimensional antenna is only connected with a single antenna port, so that the number of ports required by the antenna can be reduced, that is, power consumption is reduced from the antenna dimension, heat is reduced, and stable overall antenna performance is maintained; meanwhile, a first parasitic structure is arranged adjacent to the first three-dimensional antenna. Therefore, the first antenna assembly can cover multi-frequency and broadband wavebands, such as the multi-frequency and broadband 5G millimeter wavebands, so that the user experience and the comprehensive competitiveness of the product can be remarkably improved.
Owner:ETHETA COMM TECH SHENZHEN CO LTD
High-gain long-distance ultrahigh-frequency vehicle-mounted RFID tag antenna and installation accessory therefor
InactiveCN105024153ASmall sizeLow design profileAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsTag antennaIn vehicle
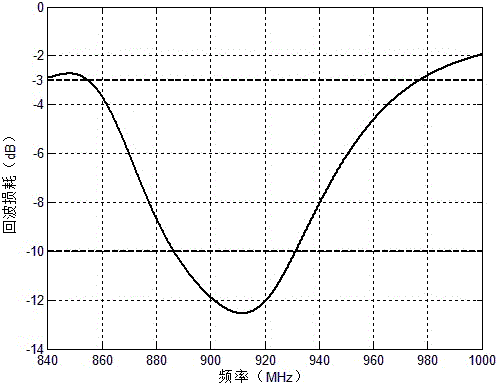
The invention relates to a high-gain long-distance ultrahigh-frequency vehicle-mounted RFID tag antenna. The antenna consists of a metal patch and a flexible thin layer, wherein the metal patch comprises a tree-shaped branch, a rectangular ring, a parasitic structure, and a closed structure. The tag antenna comprises is low in profile, is small in size and is deformable. The tag antenna can be disposed at different positions of a vehicle, such as a windscreen, a vehicle transom window, and a vehicle chassis. The tag antenna not only meets an RFID engineering standard (S<11> is less than -3dB) within the complete ultrahigh-frequency RFID wave band (860MHz-960MHz), but also meets an RFID engineering excellent index (S<11> is less than -10dB) within a wider band width (886MHz-931MHz). The gain of the tag antenna reaches 12.8 dBi, the gain of a right front side of vehicle running reaches 6.5 dBi, and the maximum reading distance can reach 40 meters or more. The tag antenna is high in flexibility, and is high in universality. The tag antenna especially meets the requirements of all-weather operation in a vehicle management system, and is wide in application range.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Multi-frequency antenna
ActiveCN101207236BImprove transmission efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsParasitic structurePhysics
The invention relates to a multi-frequency antenna, which is used for receiving the signals of a first frequency and a second frequency. The invention at least comprises a grounding part, a first conducting component, a first radiation part and a second radiation part. The first conducting component is mutually connected with the grounding part. The first radiation part and the second radiation part are respectively connected on the first conducting component. In addition, the multi-frequency antenna also comprises a parasitic structure surrounding the second radiation part, and the parasiticstructure is mutually connected with the grounding part.
Owner:WISTRON NEWEB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com