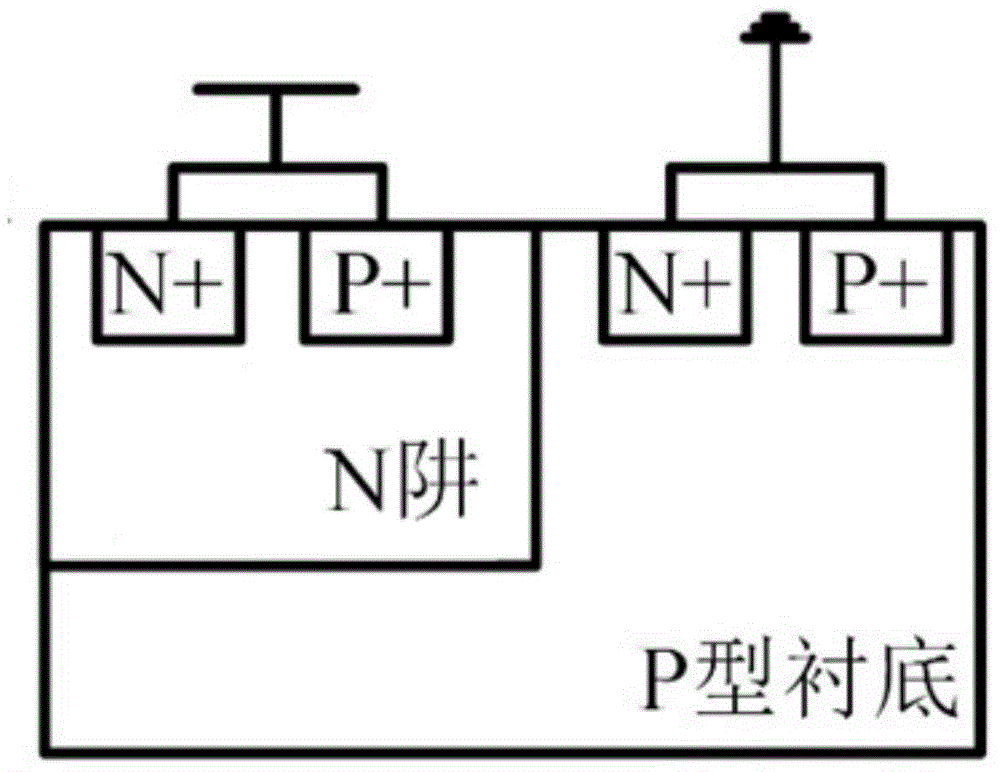
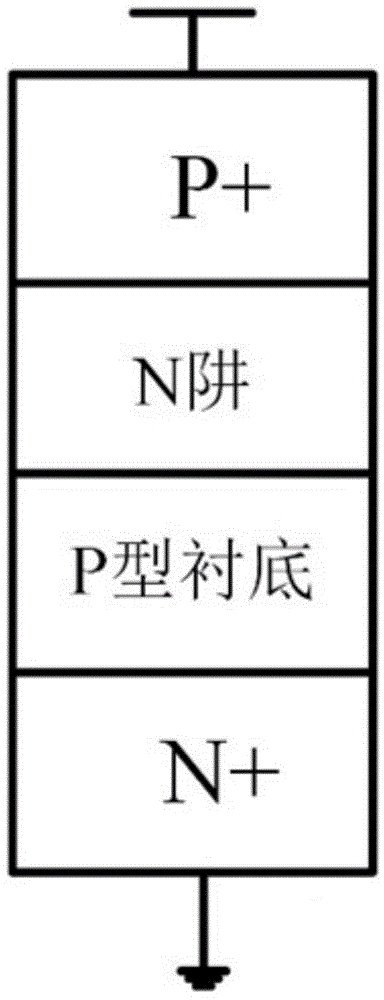
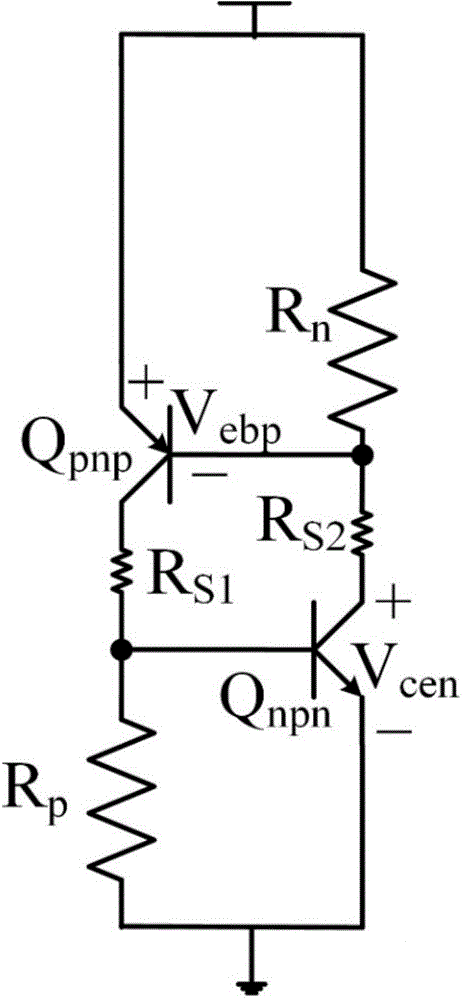
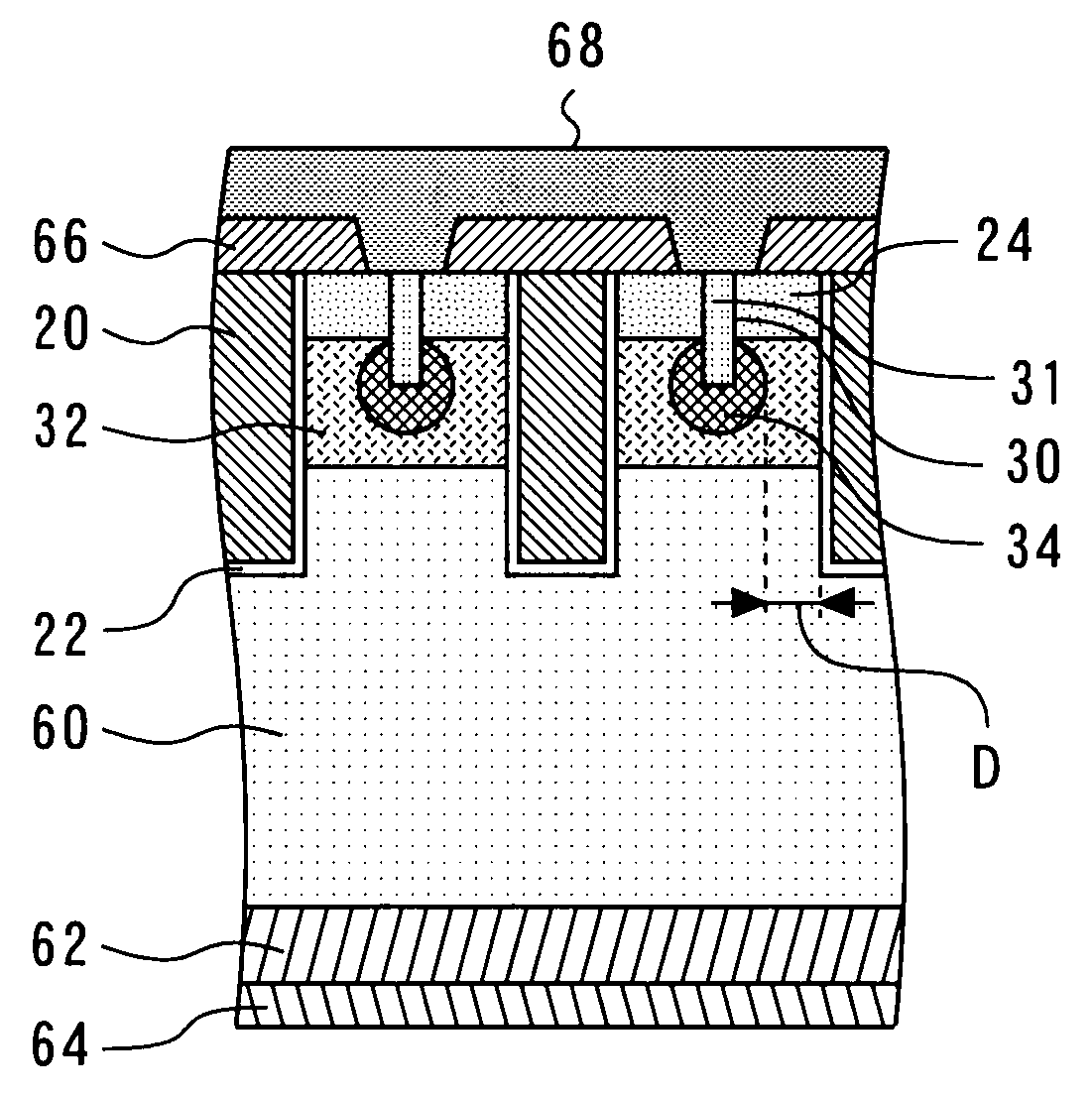
Patents
Literature
83results about How to "Avoid latch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
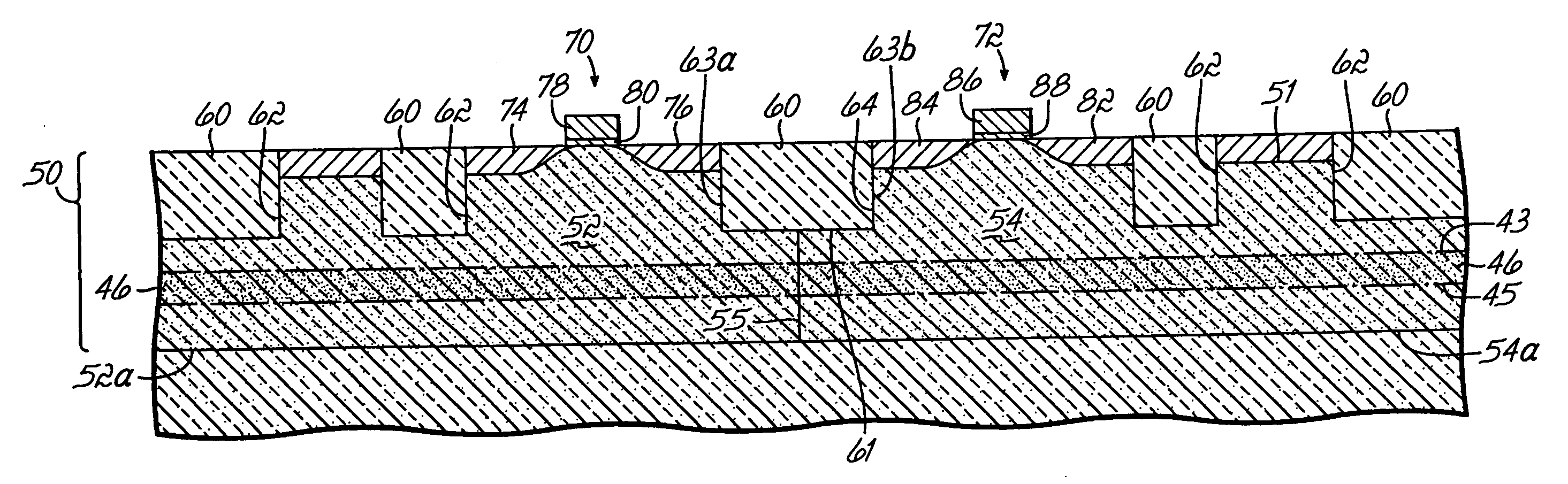
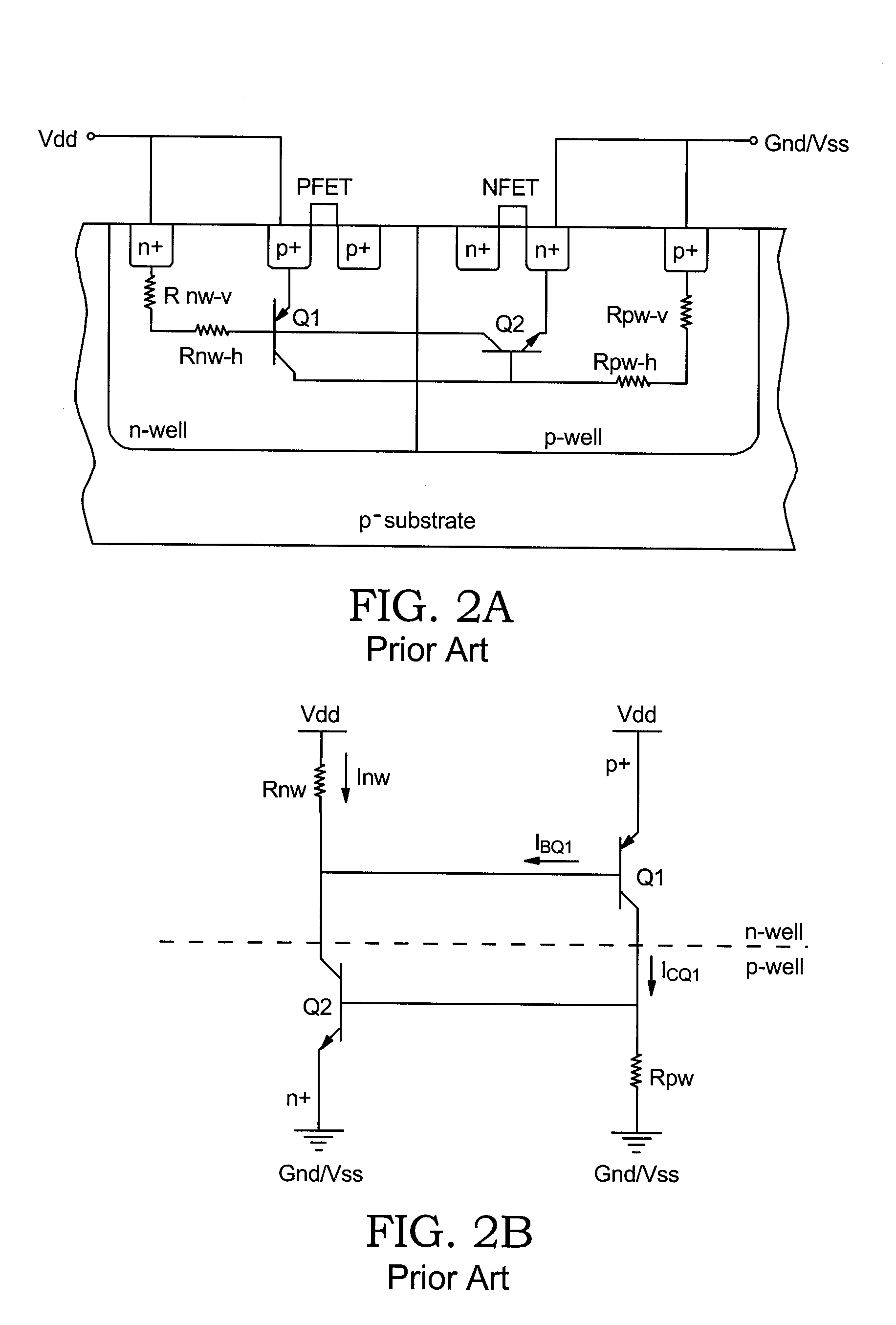
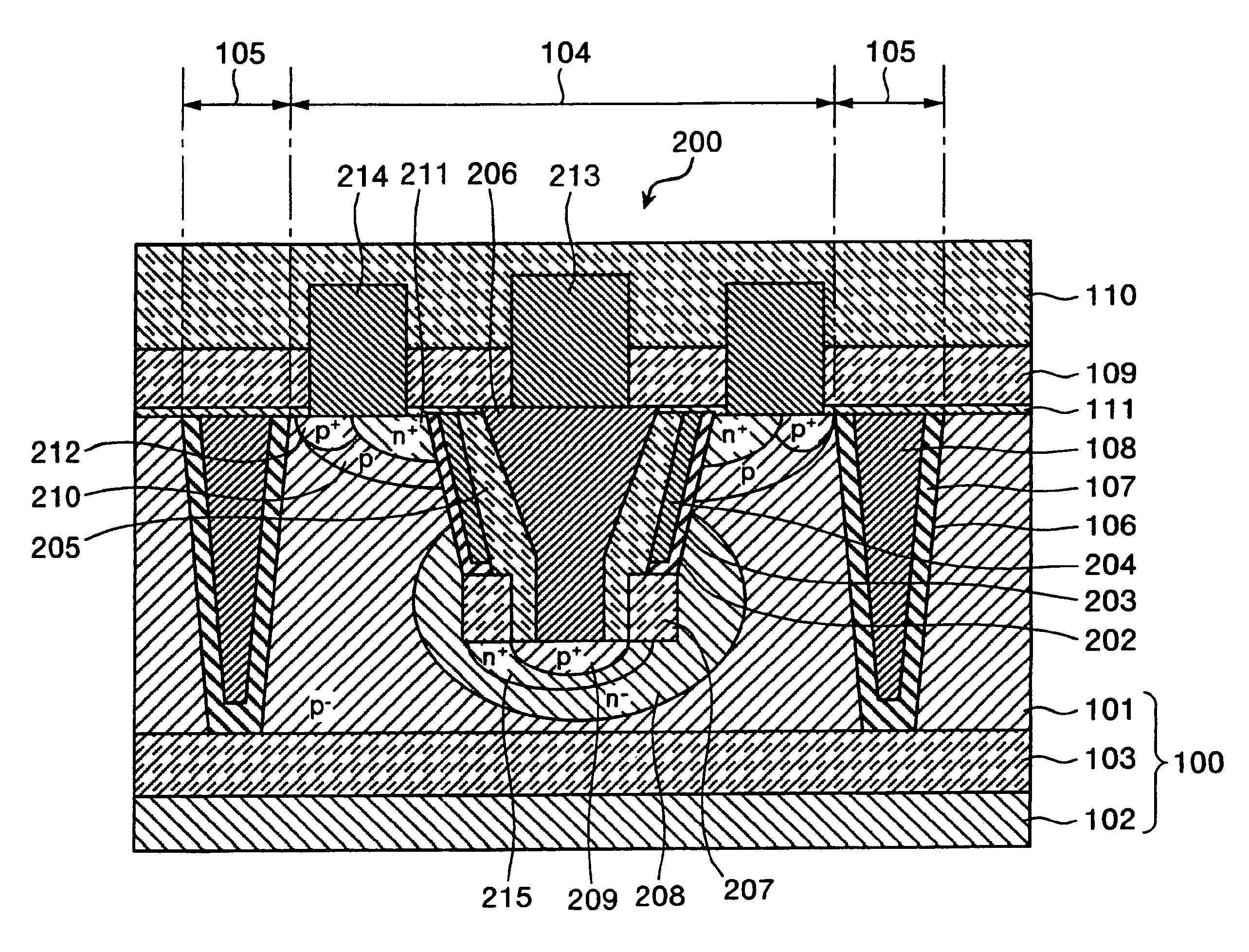
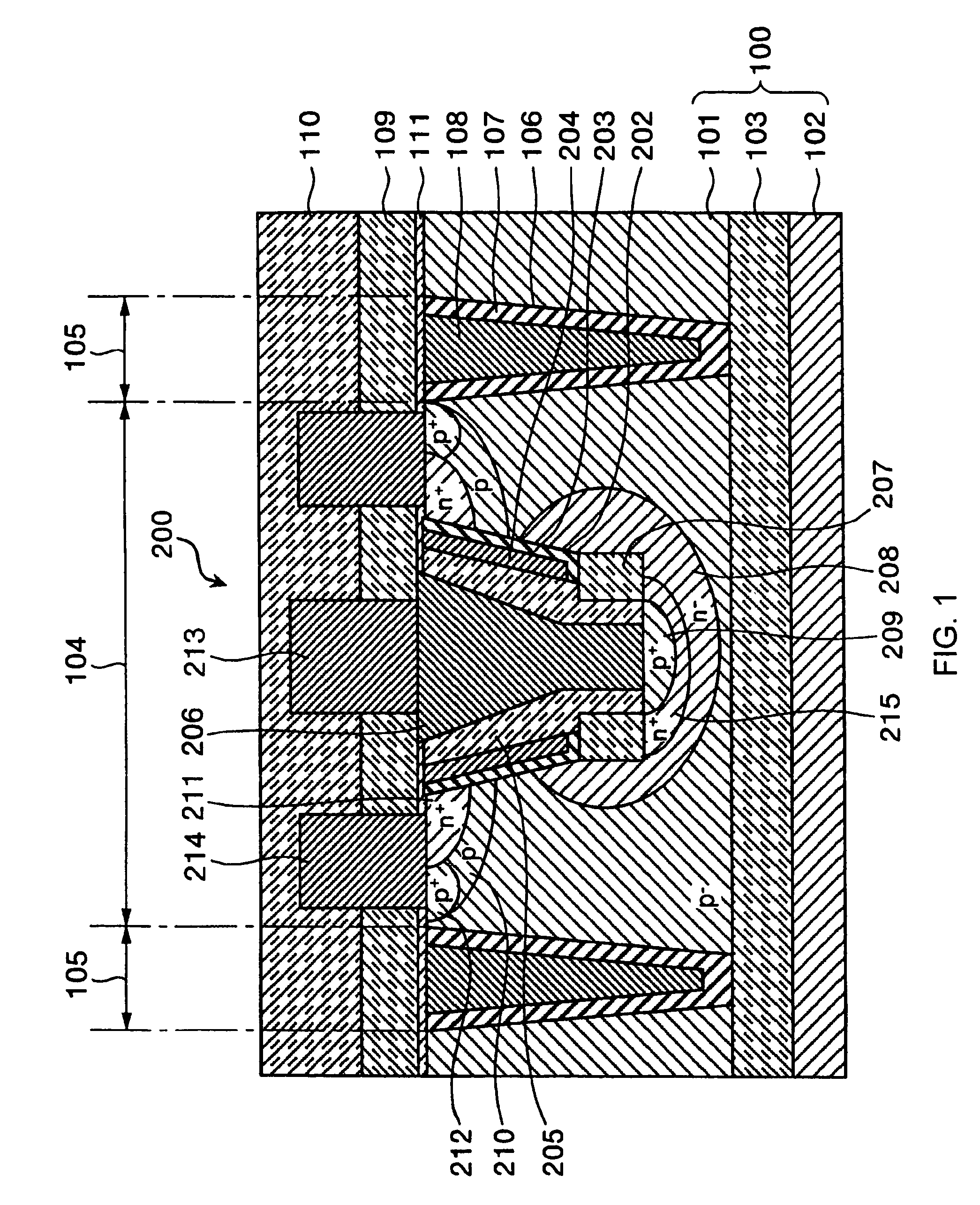
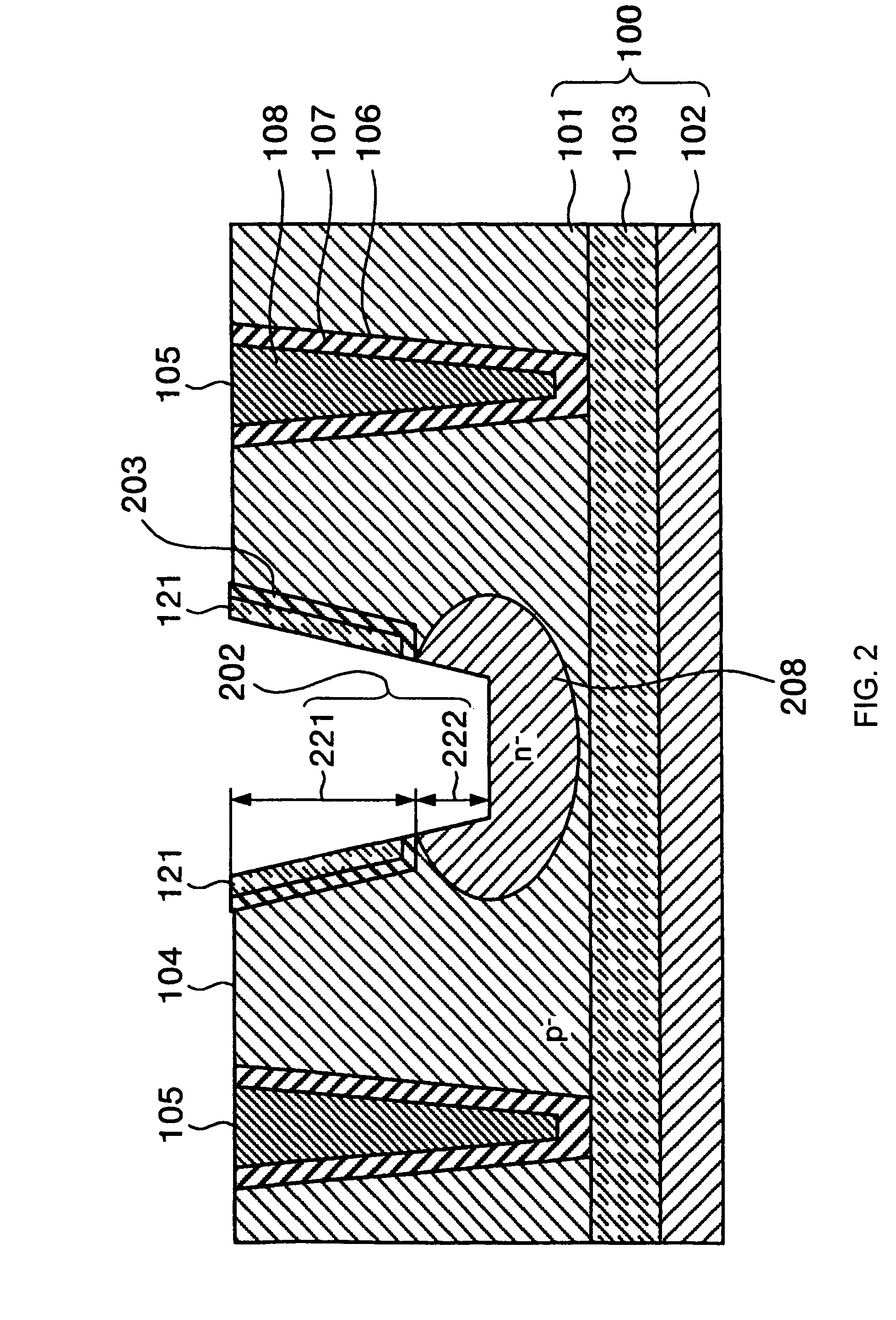
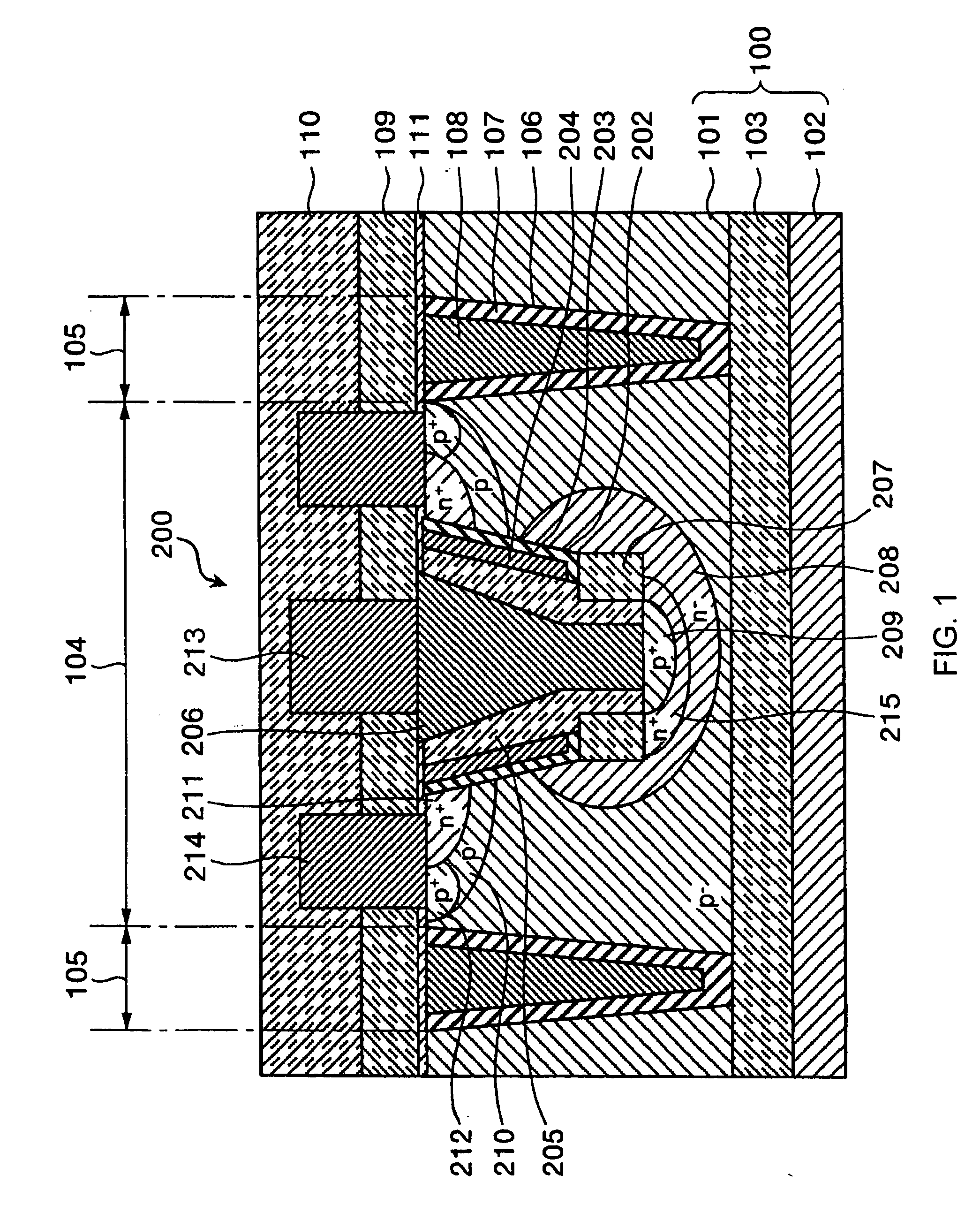
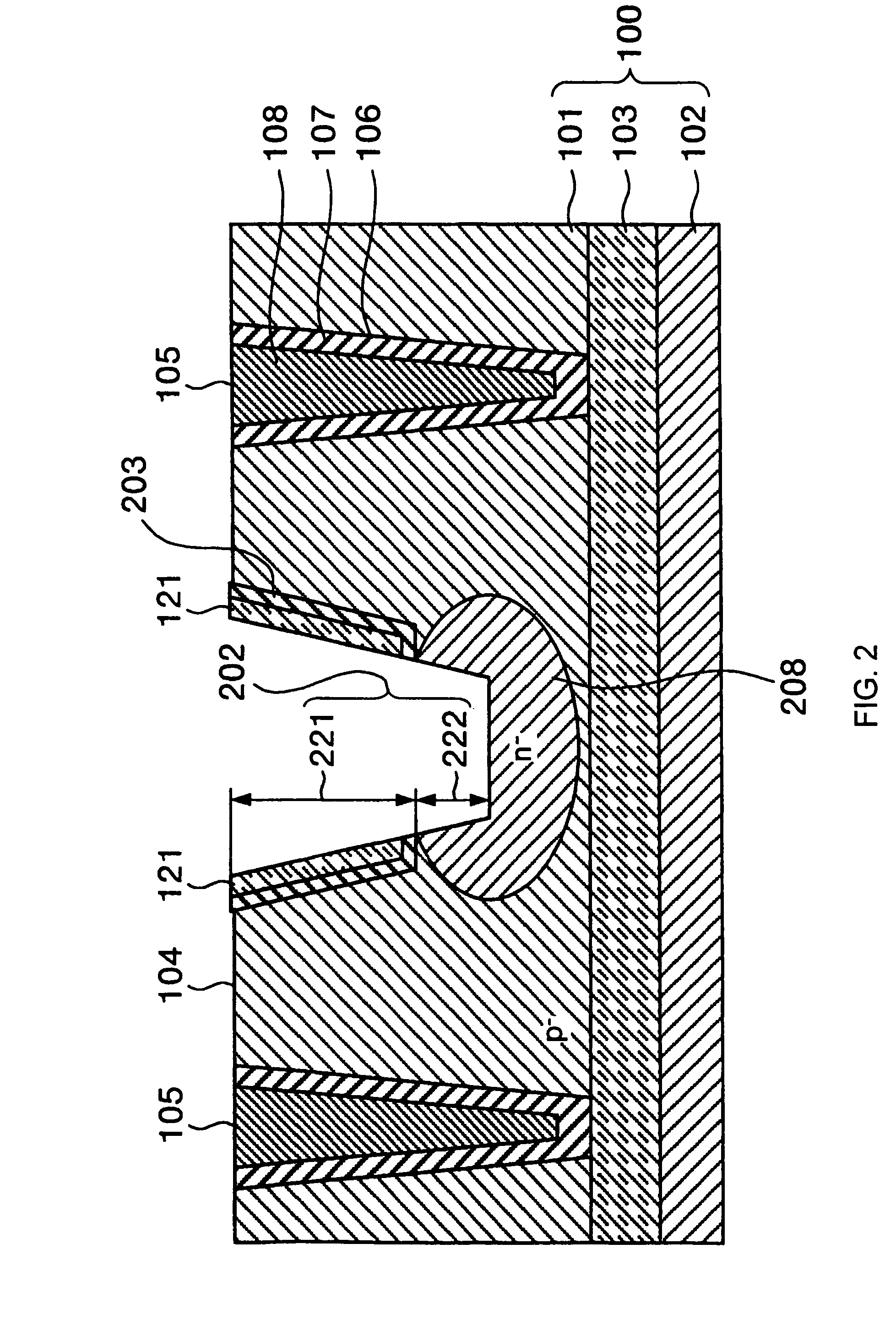
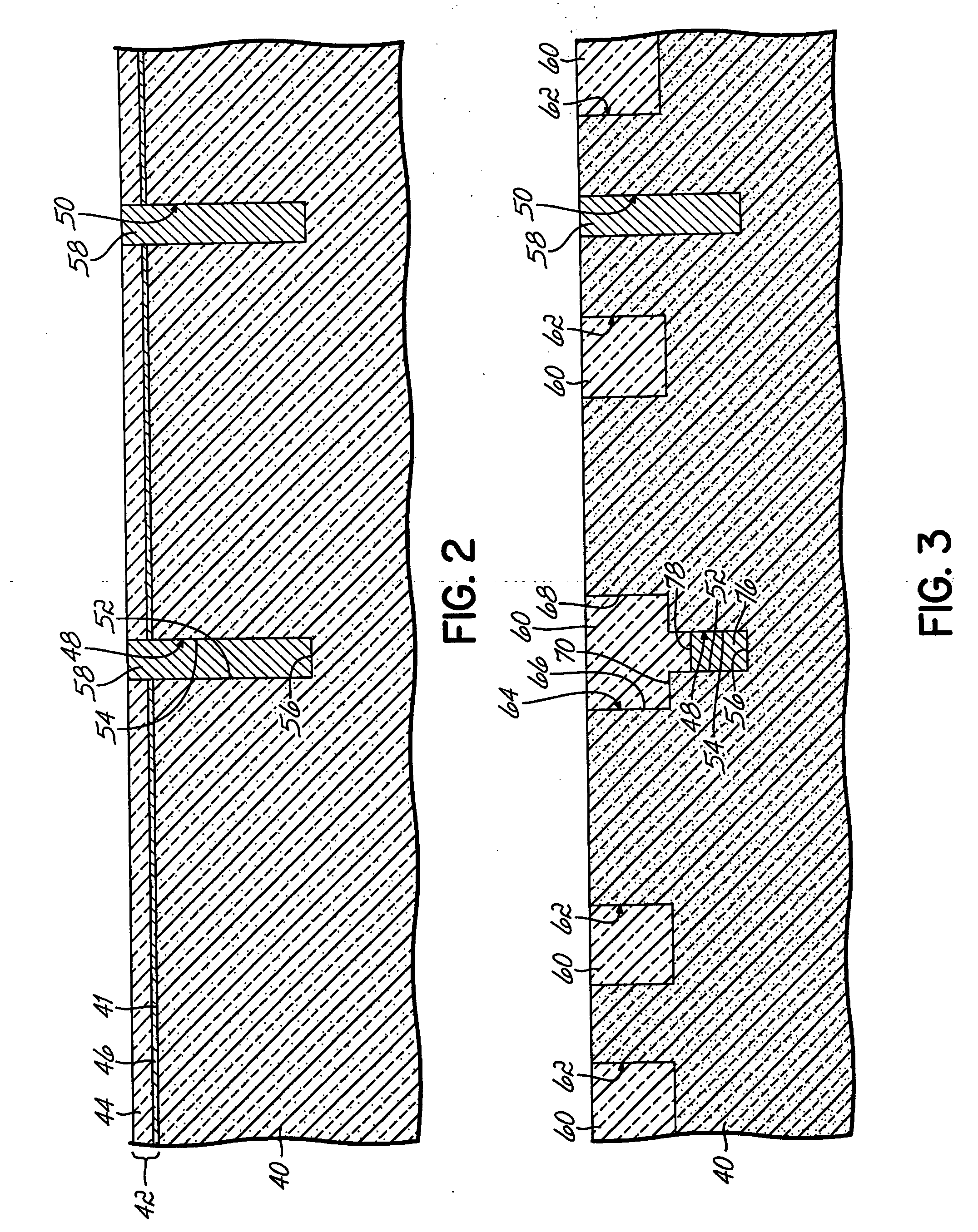
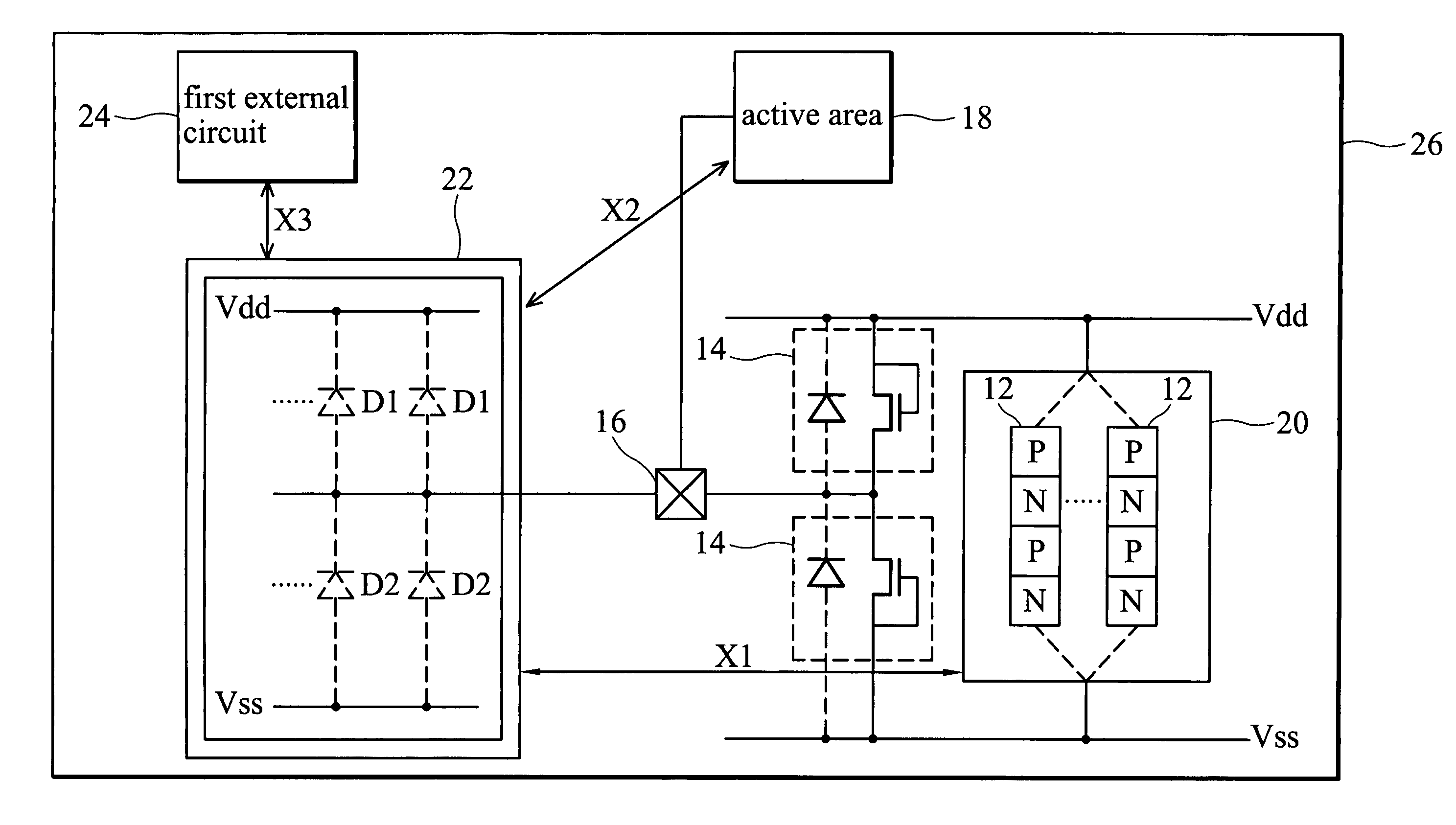
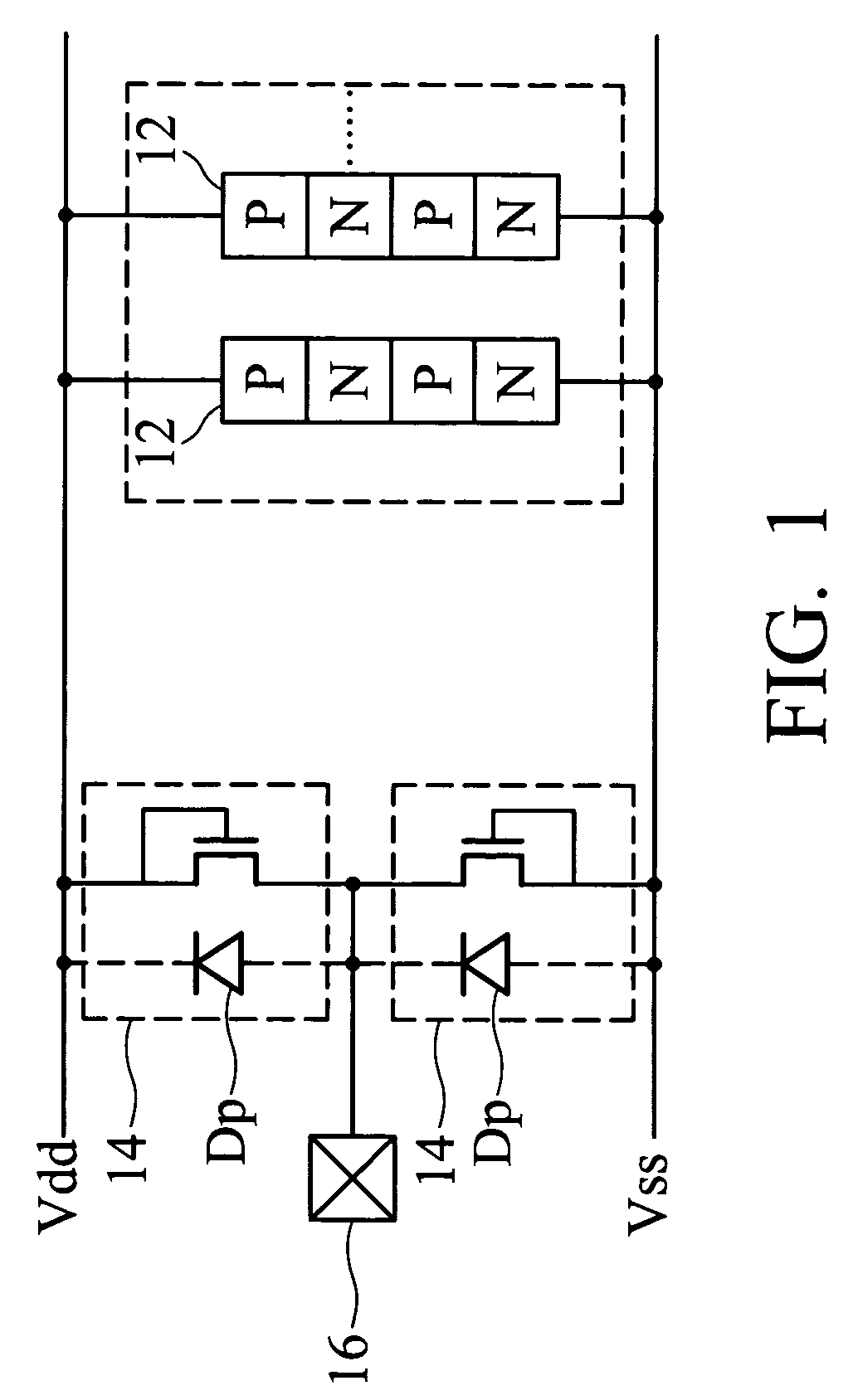
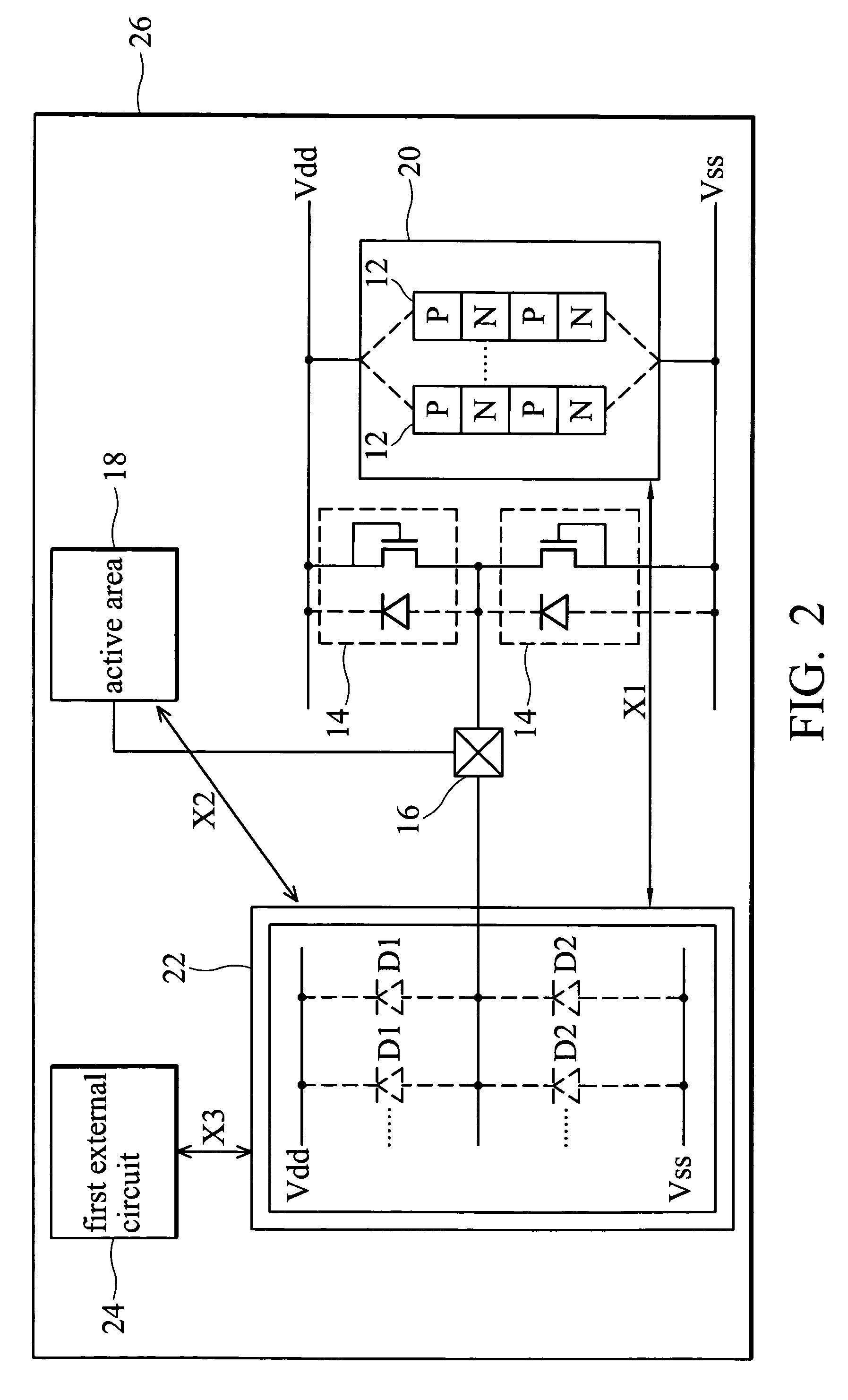
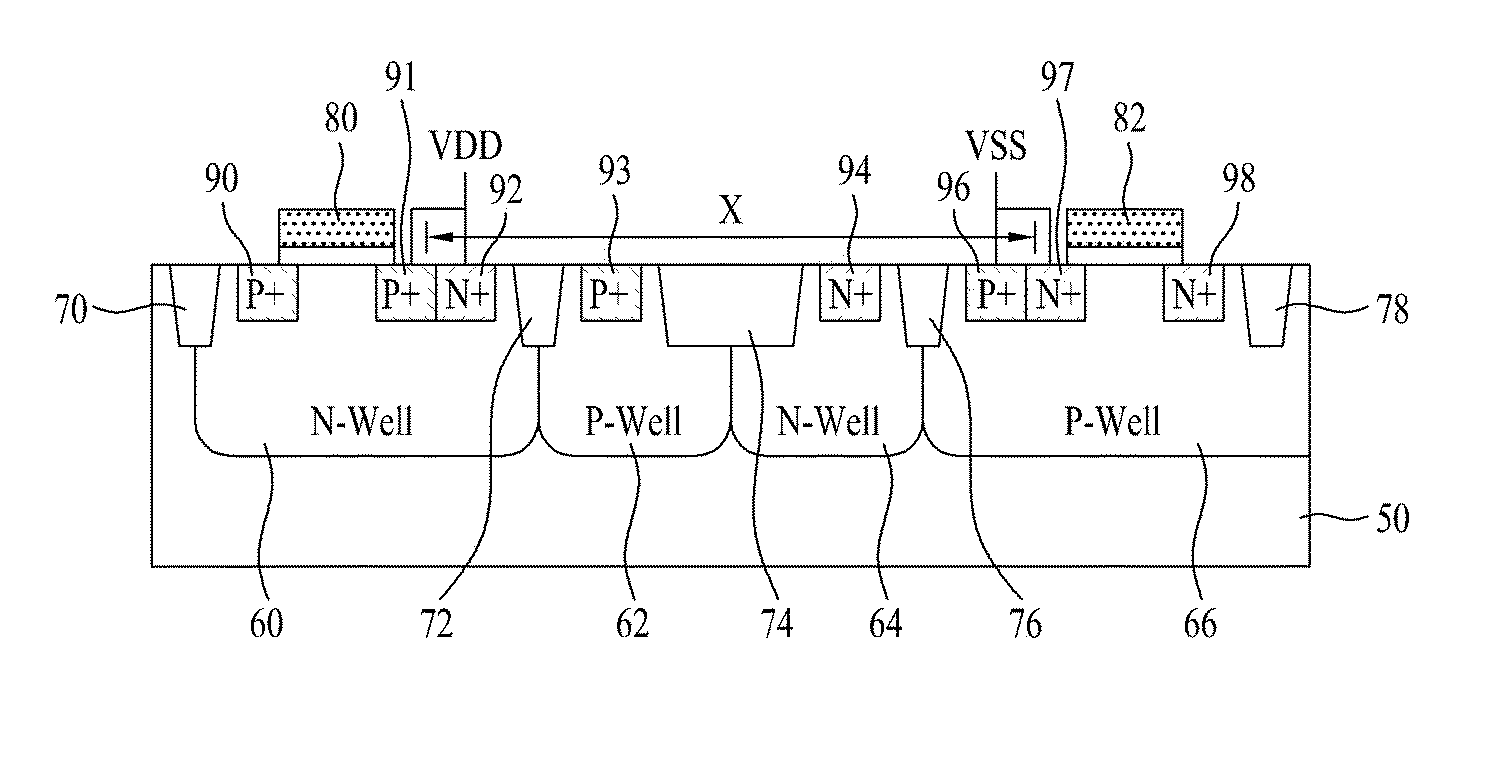
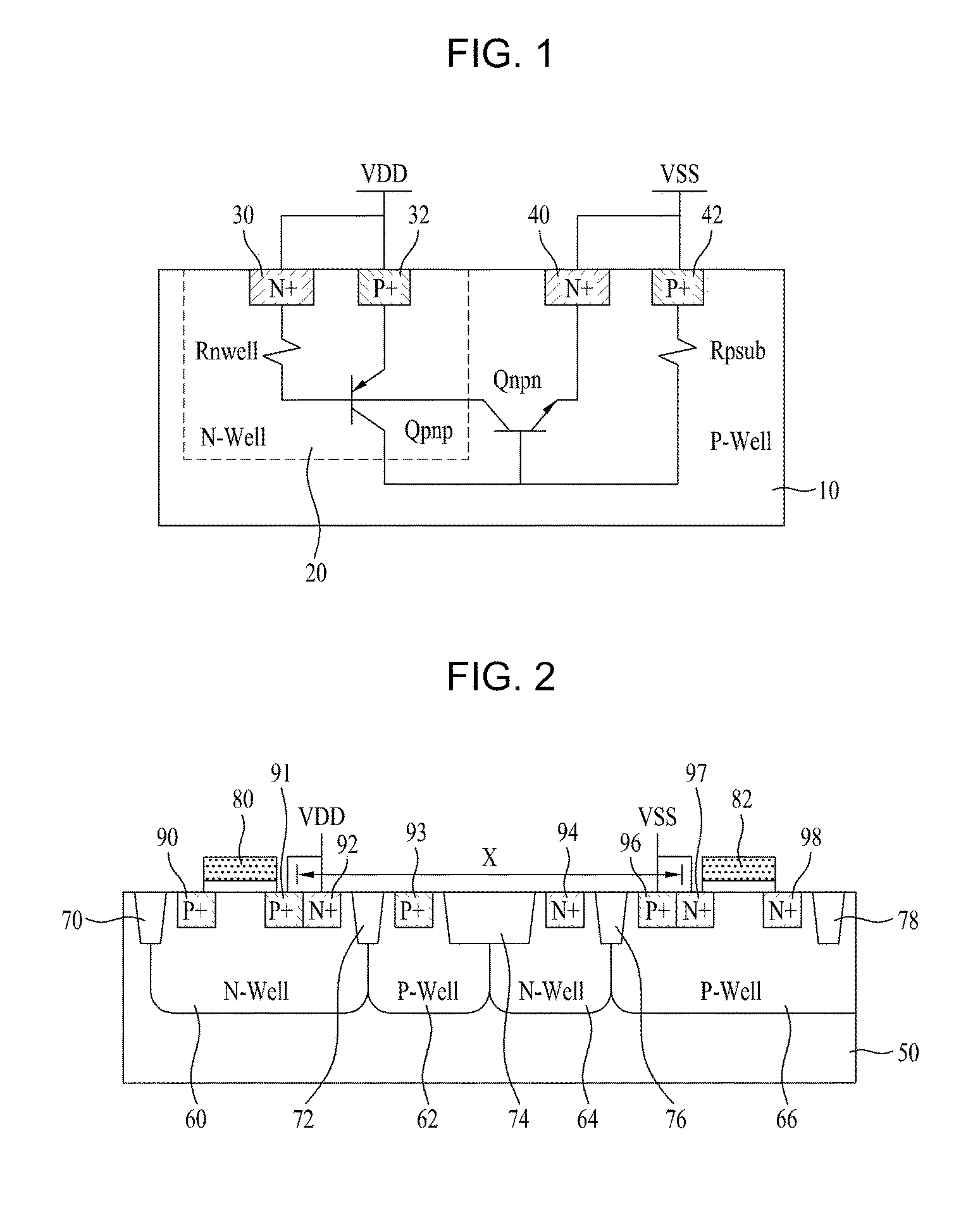
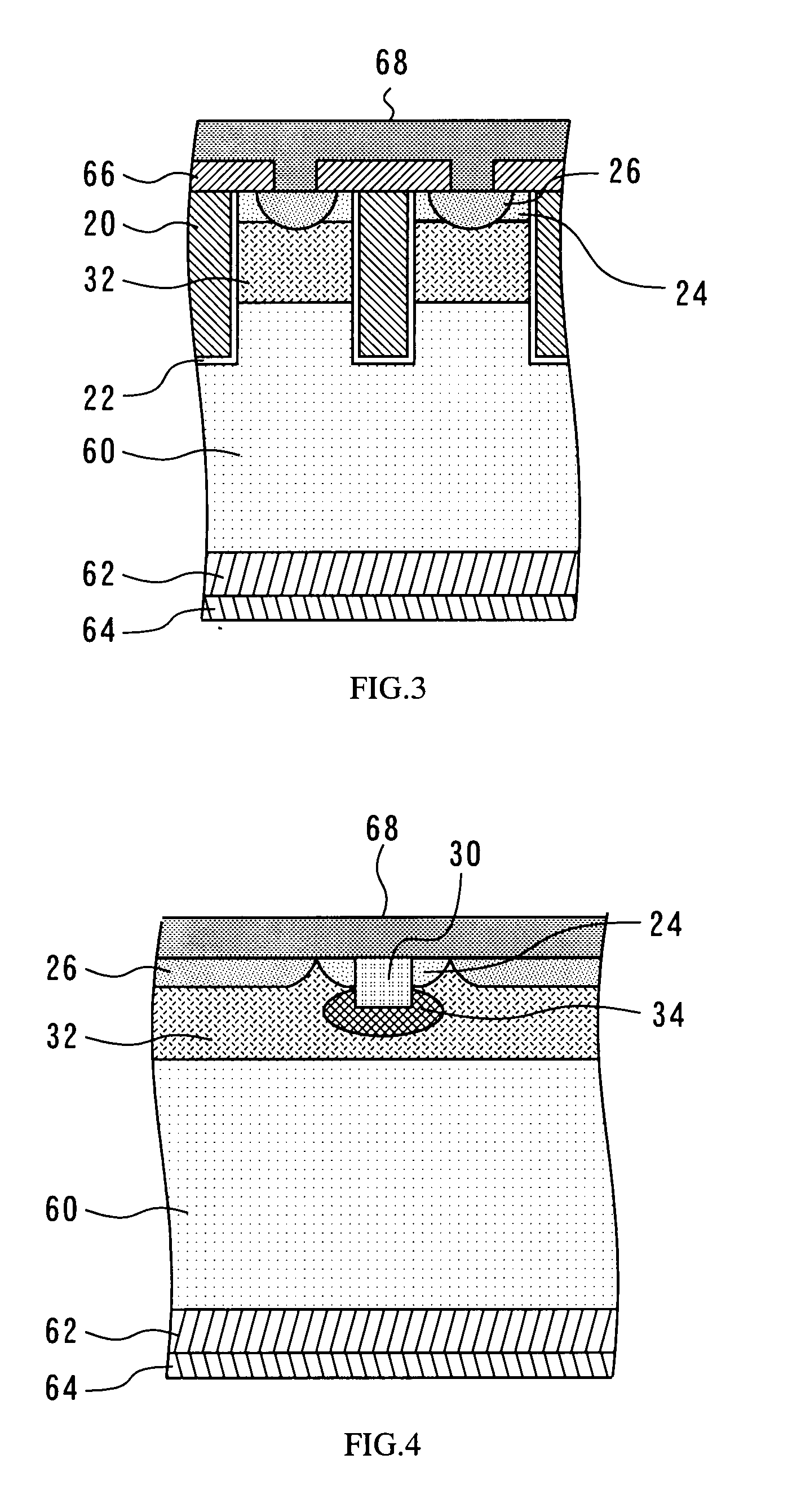
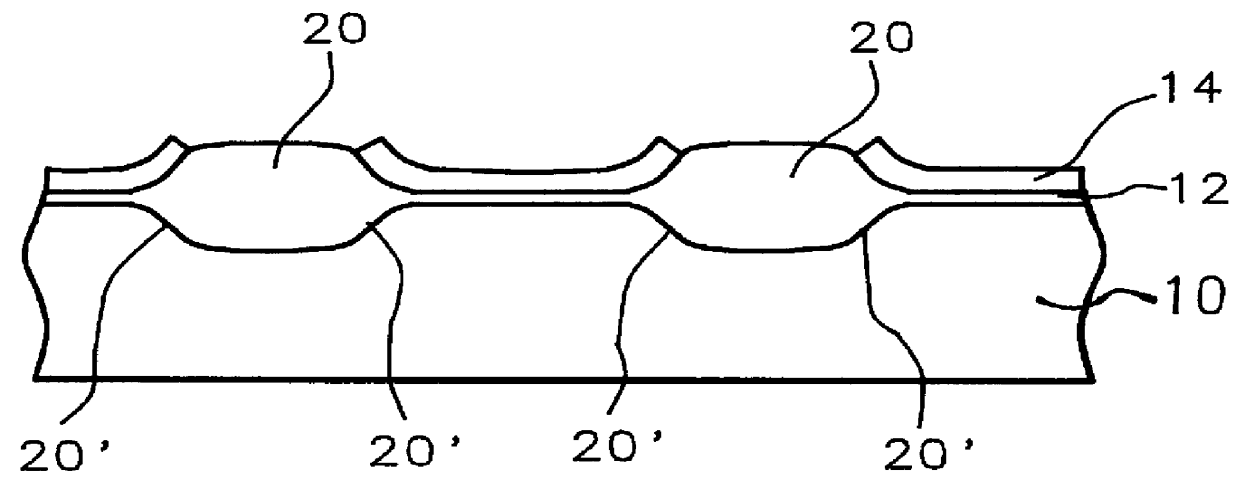
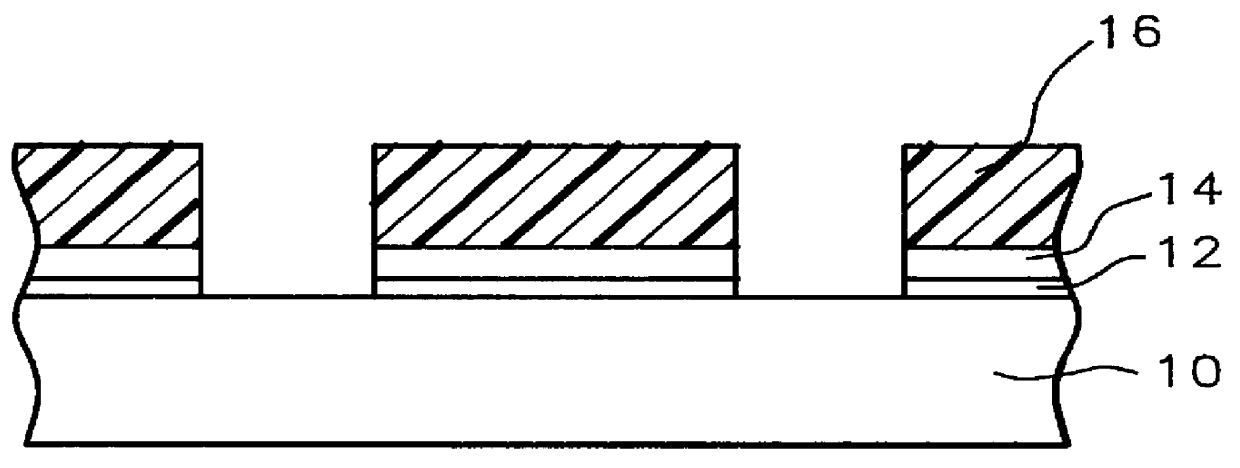
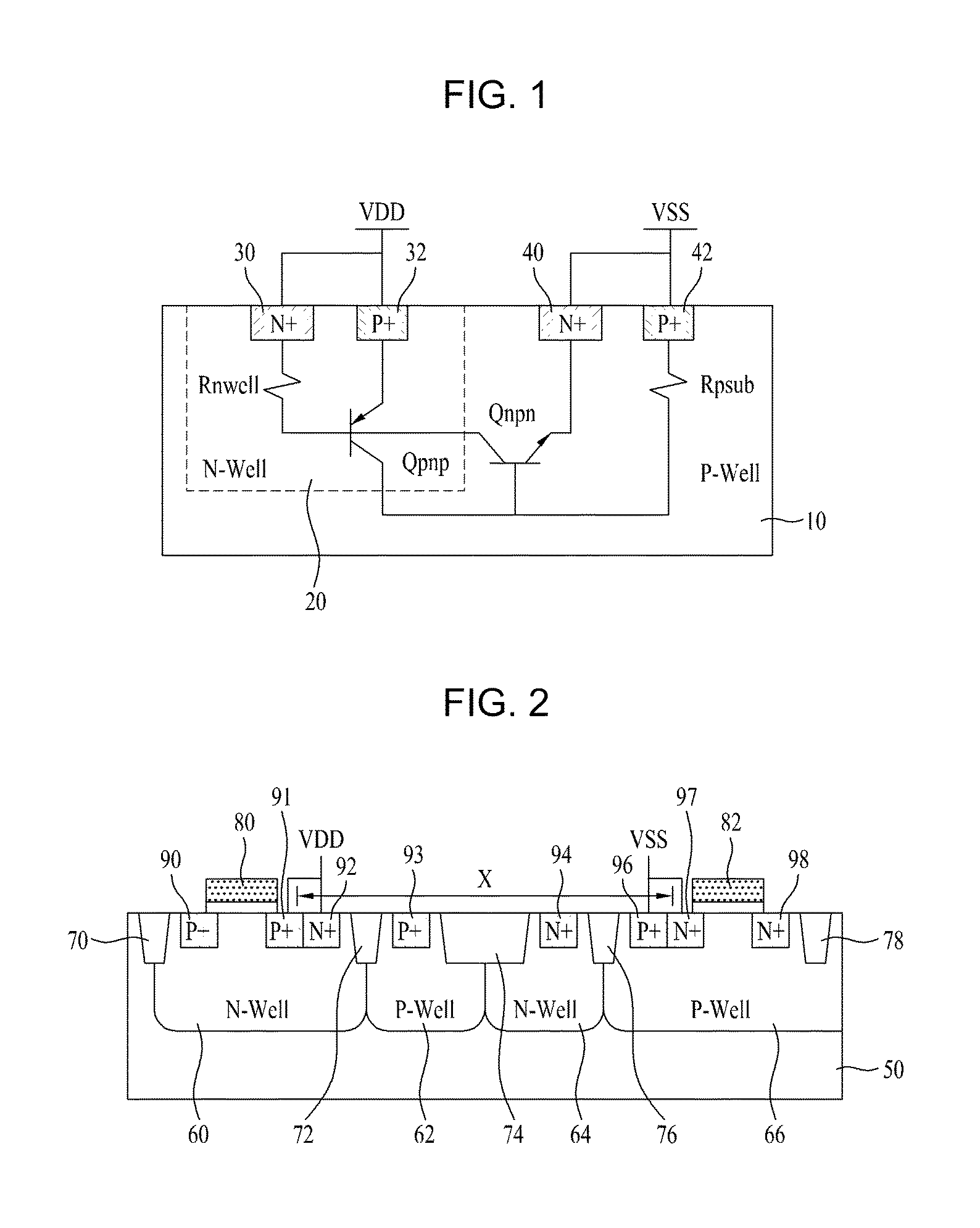
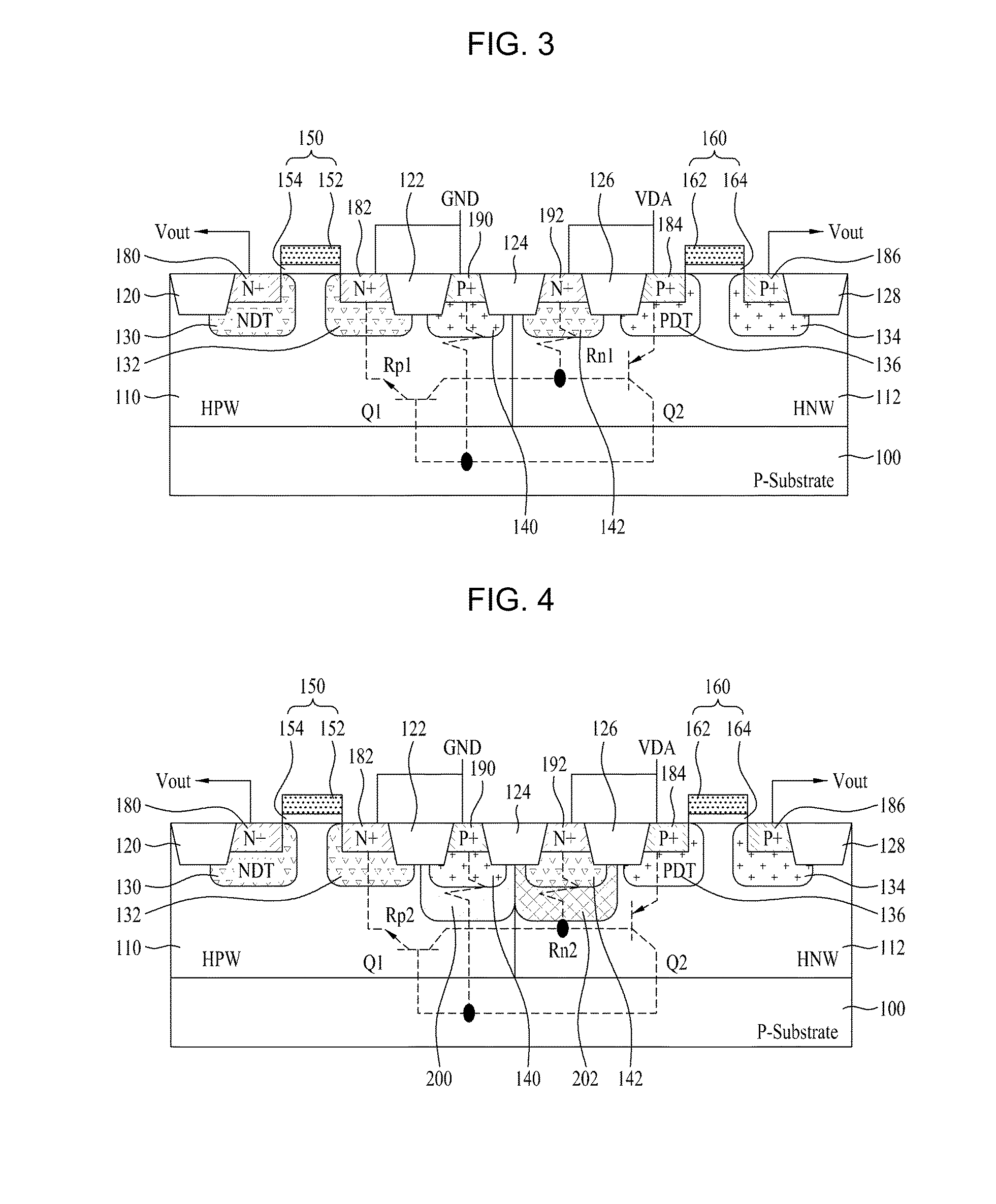
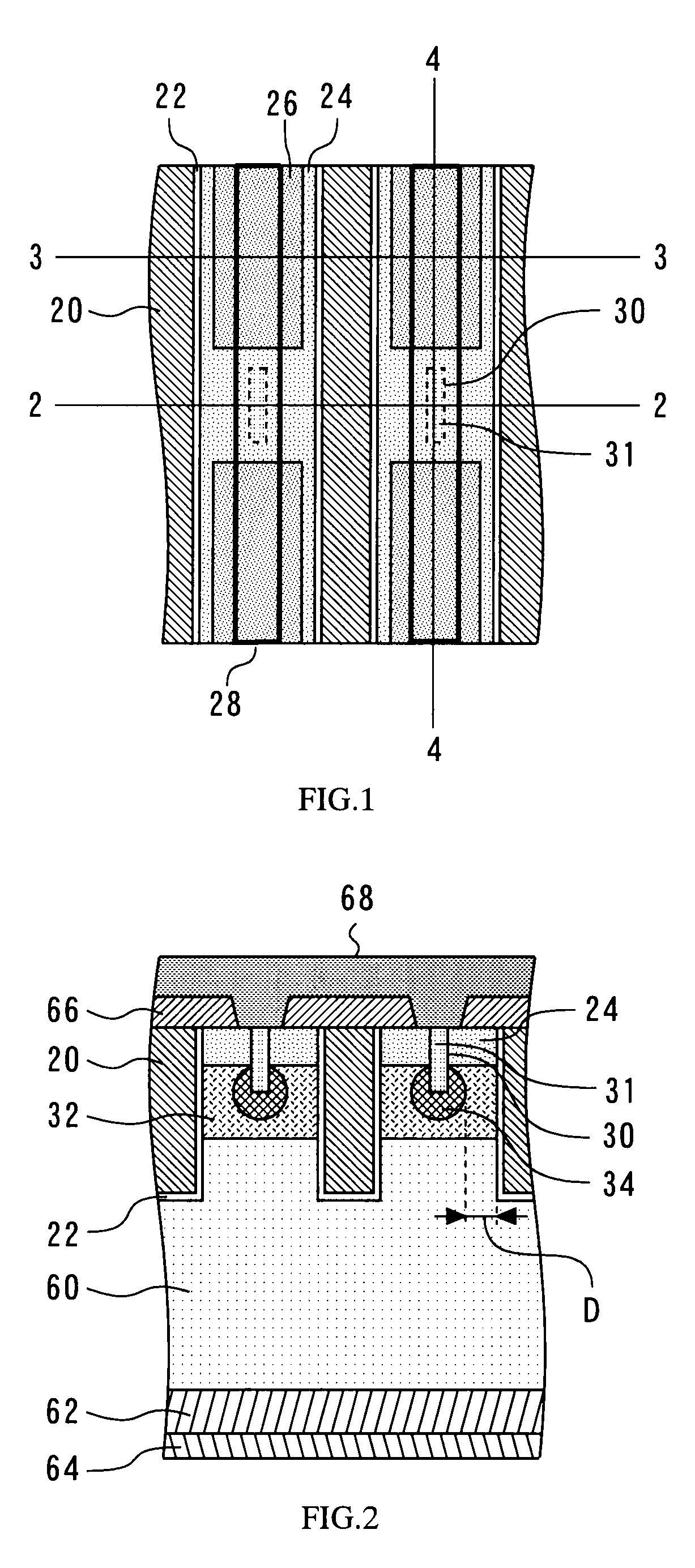
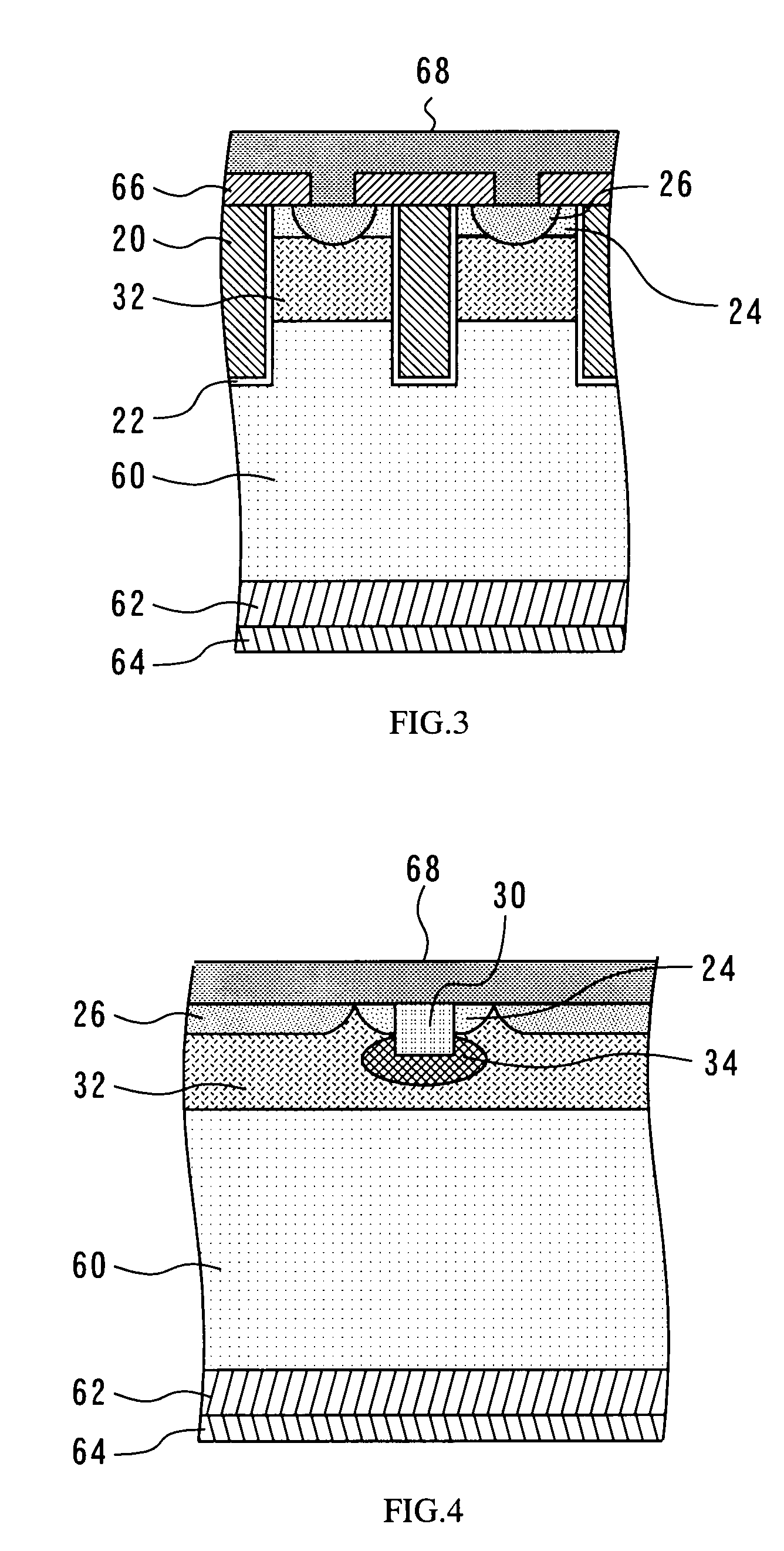
Methods and semiconductor structures for latch-up suppression using a buried damage layer
InactiveUS20070158779A1Improve latch-up immunityImprove suppressionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSSemiconductor structure
Semiconductor structures and methods for suppressing latch-up in bulk CMOS devices. The structure comprises a damage layer formed in a substrate, a first doped well formed in the substrate, and a second doped well formed in the substrate proximate to the first doped well. The damage layer extends within the substrate to intersect the first and second doped wells. The damage layer may be formed by ion implantation followed by growth of an epitaxial layer to segregate the active device regions from the damage layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
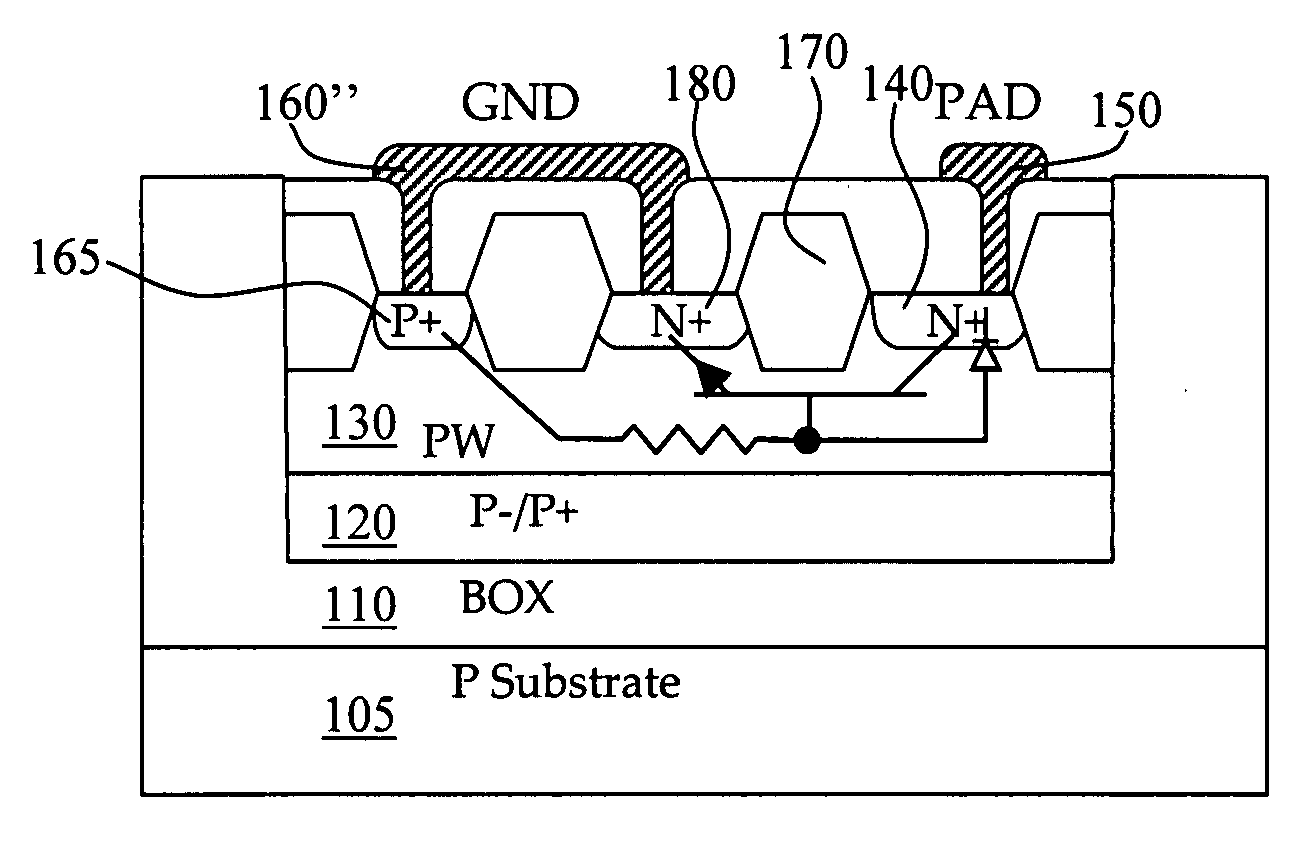
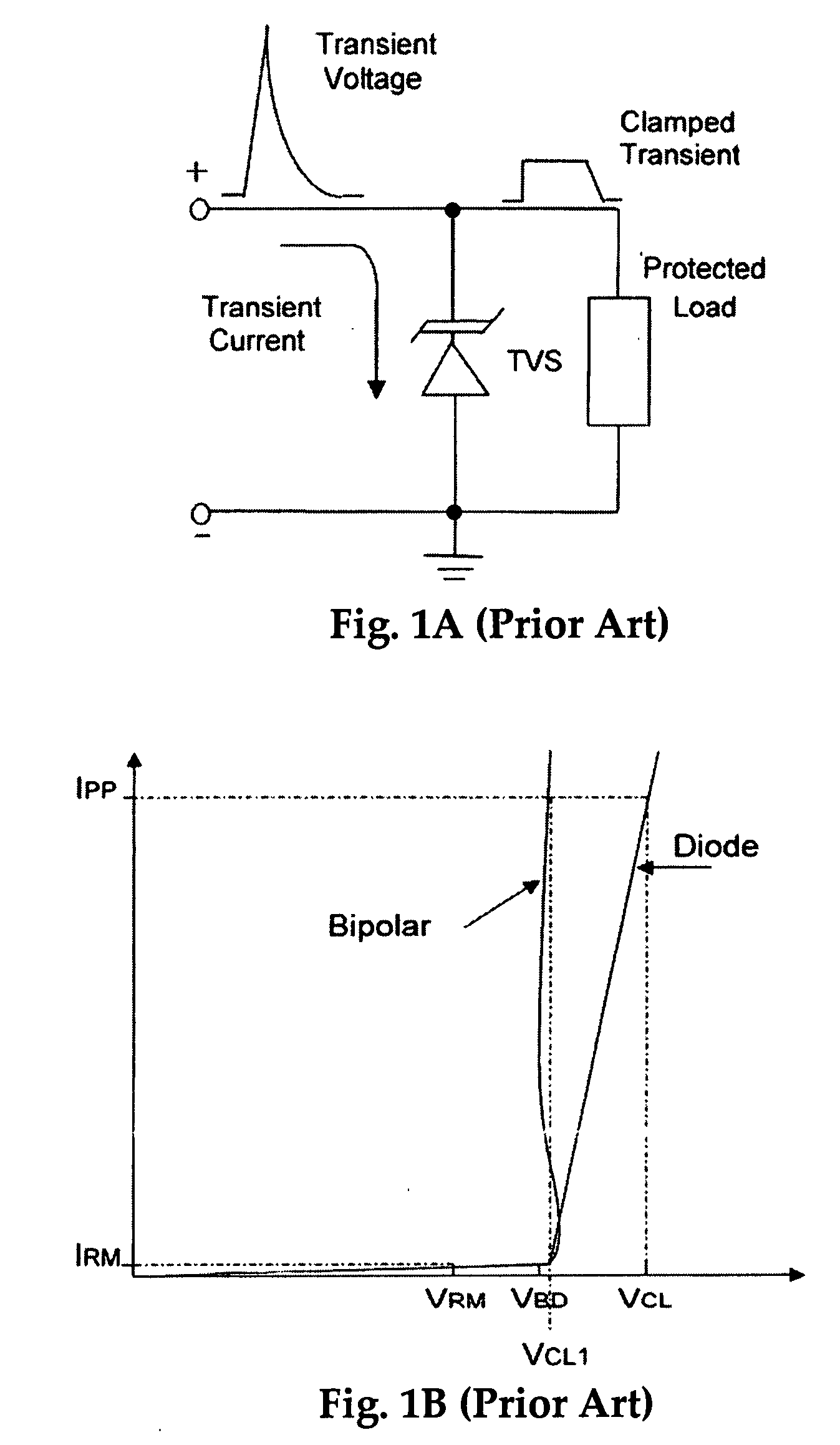
Transient voltage suppressor manufactured in silicon on oxide (SOI) layer
InactiveUS20090115018A1Reduce parasitic capacitanceAvoid latchSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerMicrometer
A transient voltage-suppressing (TVS) device supported on a semiconductor substrate is applied to protect an electronic device from a transient voltage. The TVS device includes a clamp diode functions with a high-side and a low side diodes for clamping a transient voltage disposed on a top layer of the semiconductor substrate insulated by a insulation layer constituting a TVS on silicon-on-insulator (SOI) device. In an exemplary embodiment, the insulator layer further includes a thick body oxide (BOX) layer having a thickness in the range of 250 Angstroms to 1 micrometer to sustain an application with a breakdown voltage higher than 25 volts. In another exemplary embodiment, the clamp diode further surrounded by a P-well and the P-well is formed on top of a P− / P+ substrate layer disposed above the insulator layer.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
Method and structure to suppress external latch-up
InactiveUS20050085028A1Easy to useLow densityTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
A method and structure for protection against latch-up is provided. Integrated circuits manufactured in accordance with the present disclosure feature well and substrate contacts of varying periodicity. Such a strategy enables maximizing the design of an integrated circuit as to the suppression of latch-up while concurrently optimizing available area on the chip allocable to circuit design. This method and structure is particularly beneficial to protect against cable discharge events and other discharge occurrences prone to injecting large current densities into an integrated circuit.
Owner:IBM CORP
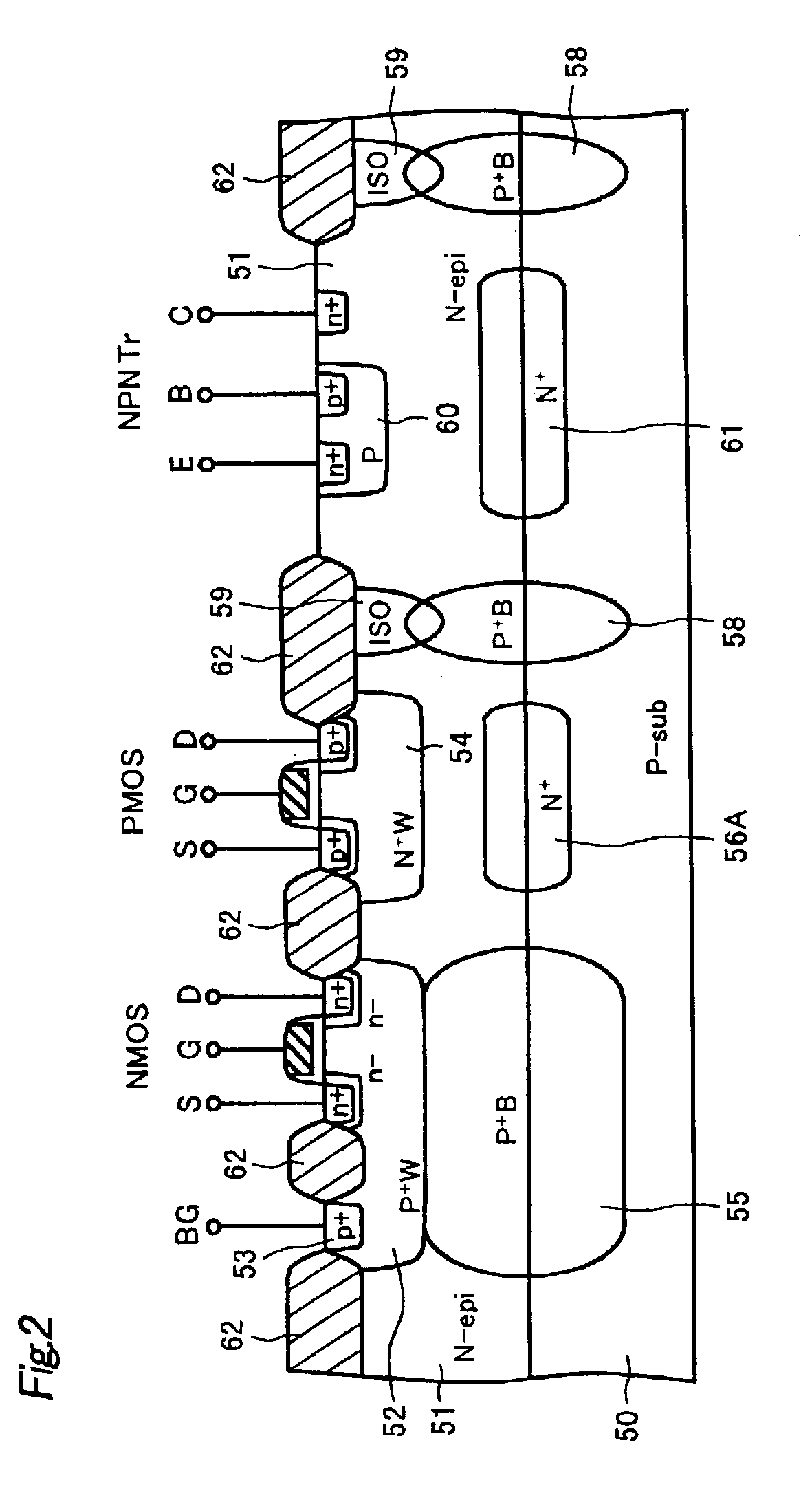
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS7109551B2Easy to integrateReduce switching lossesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSSemiconductor structure
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC HLDG CO LTD
Phase-locked loop and delay-locked loop including differential delay cells having differential control inputs
InactiveUS7176737B2Constant responseLinear responsePulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsDelay-locked loopEngineering
A differential delay cell is provided herein that not only receives a pair of differential input values, but also receives a pair of differential control values for delaying the differential input values to produce a pair of differential output values. As such, a delay cell is provided, which is truly differential, and therefore, capable of demonstrating a significant improvement in noise performance. The differential delay cell of the present invention also demonstrates high frequency stability around the center frequency, constant gain and increased tuning range capabilities. In this manner, the differential delay cell may be used in PLL or DLL designs as part of a low noise VCO or a low noise delay line, respectively.
Owner:RPX CORP
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050062101A1Easy to integrateReduce switching lossesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSDevice material
A semiconductor structure with device trench and a semiconductor device in the device trench, that enables realization of high integration, lowered on-resistance, reduction in switching losses and a high operation speed in a semiconductor device provided with a lateral IGBT, and that prevents malfunctions such as latchup when IGBTs or an IGBT and CMOS devices are integrated together. The structure includes an SOI substrate having a supporting substrate, an oxide film and a p−-semiconductor layer. An island-like element-forming region is isolated by a trench isolation region from surroundings. The trench isolation region includes an isolation trench with an insulation film on its inner wall. The device trench is formed in the element-forming region. A gate electrode is formed with a gate insulator film in the device trench. A collector region and an emitter region outside are provided respectively on the bottom and the outside of the device trench.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC HLDG CO LTD
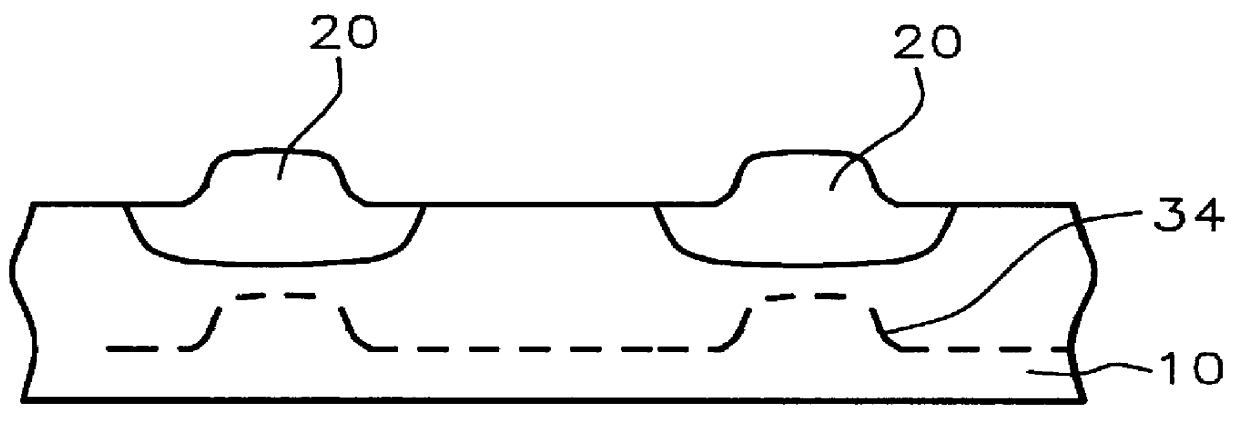
Methods and semiconductor structures for latch-up suppression using a buried conductive region
InactiveUS20070158755A1Retain cost effectivenessCost effectivenessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolid phasesCMOS
Semiconductor structures and methods for suppressing latch-up in bulk CMOS devices. The structure comprises a first doped well formed in a substrate of semiconductor material, a second doped well formed in the substrate proximate to the first doped well, and a deep trench defined in the substrate. The deep trench includes sidewalls positioned between the first and second doped wells. A buried conductive region is defined in the semiconductor material bordering the base and the sidewalls of the deep trench. The buried conductive region intersects the first and second doped wells. The buried conductive region has a higher dopant concentration than the first and second doped wells. The buried conductive region may be formed by solid phase diffusion from a mobile dopant-containing material placed in the deep trench. After the buried conductive region is formed, the mobile dopant-containing material may optionally remain in the deep trench.
Owner:IBM CORP
Charge pump device
InactiveUS6864525B2Large current capacityImprove efficiencyTransistorSolid-state devicesIsolation layerCrystalline silicon
A latch up in a charge pump device is prevented as well as a withstand voltage of an MOS transistor used in the charge pump device is increased with this invention. A first and a second N-type epitaxial silicon layers are stacked on a P-type single crystalline silicon substrate, and P-type well regions are formed in the second epitaxial silicon layer separated from each other. A P-type isolation layer is formed between the P-type well regions. A P+-type buried layer is formed abutting on a bottom of each of the well regions, an N+-type buried layer is formed abutting on a bottom of the P+-type buried layer, and a transistor for charge transfer is formed in each of the P-type well regions.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
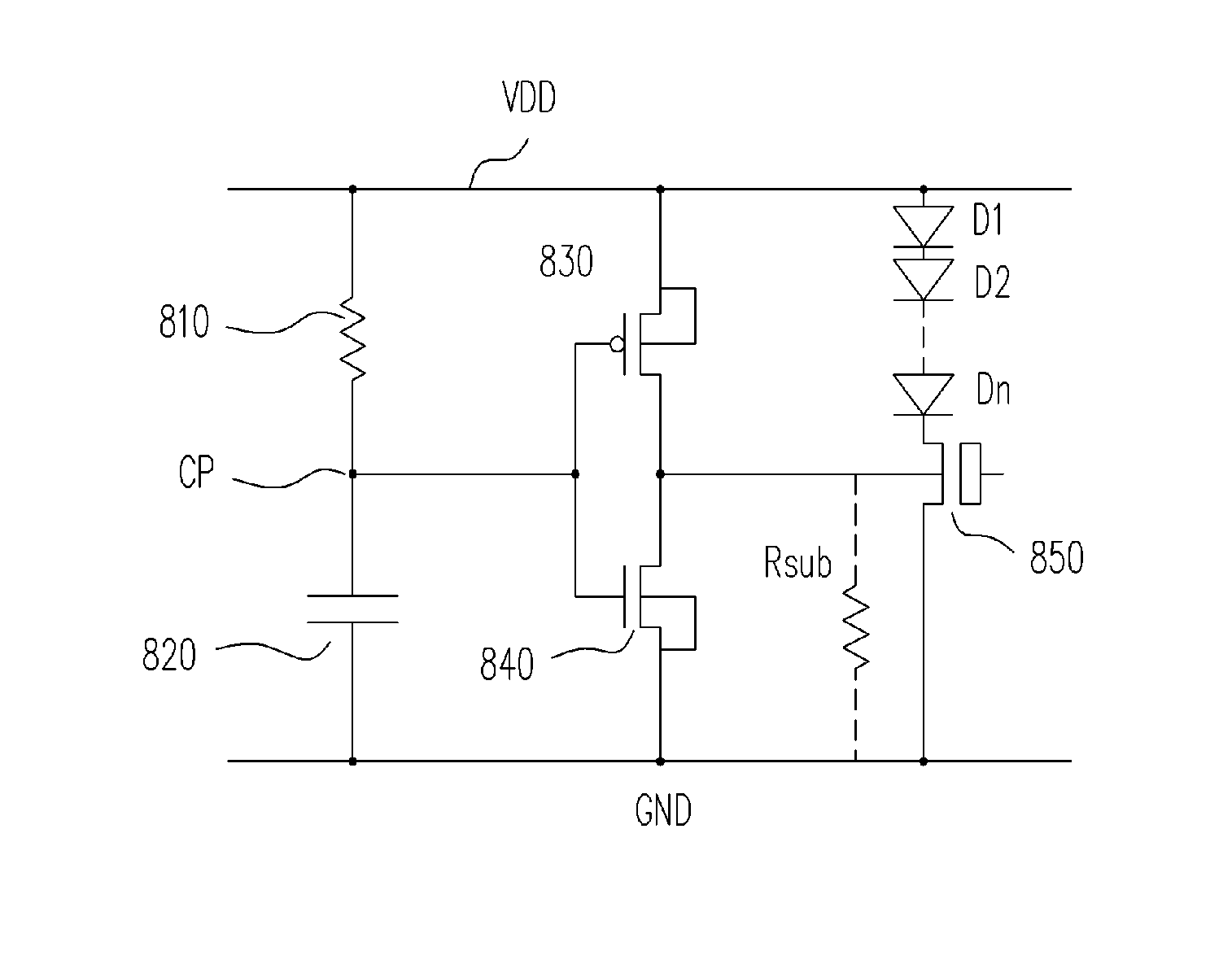
Electrostatic discharge protection apparatus for high-voltage products
InactiveUS20070127173A1Avoid latch-up issueAvoid latchTransistorEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectrostatic discharge protectionCapacitance
An electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection apparatus for high-voltage products is provided. The ESD protection apparatus includes a resistor, a capacitor, a first transistor, n diodes, and a main transistor, wherein n is an integer greater than 0. The holding voltage of the provided ESD protection apparatus is adjusted by determining the n value. The adjusted holding voltage is higher than the system voltage under normal operation, so that latch-up issues are avoided.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Distributed switches to suppress transient electrical overstress-induced latch-up
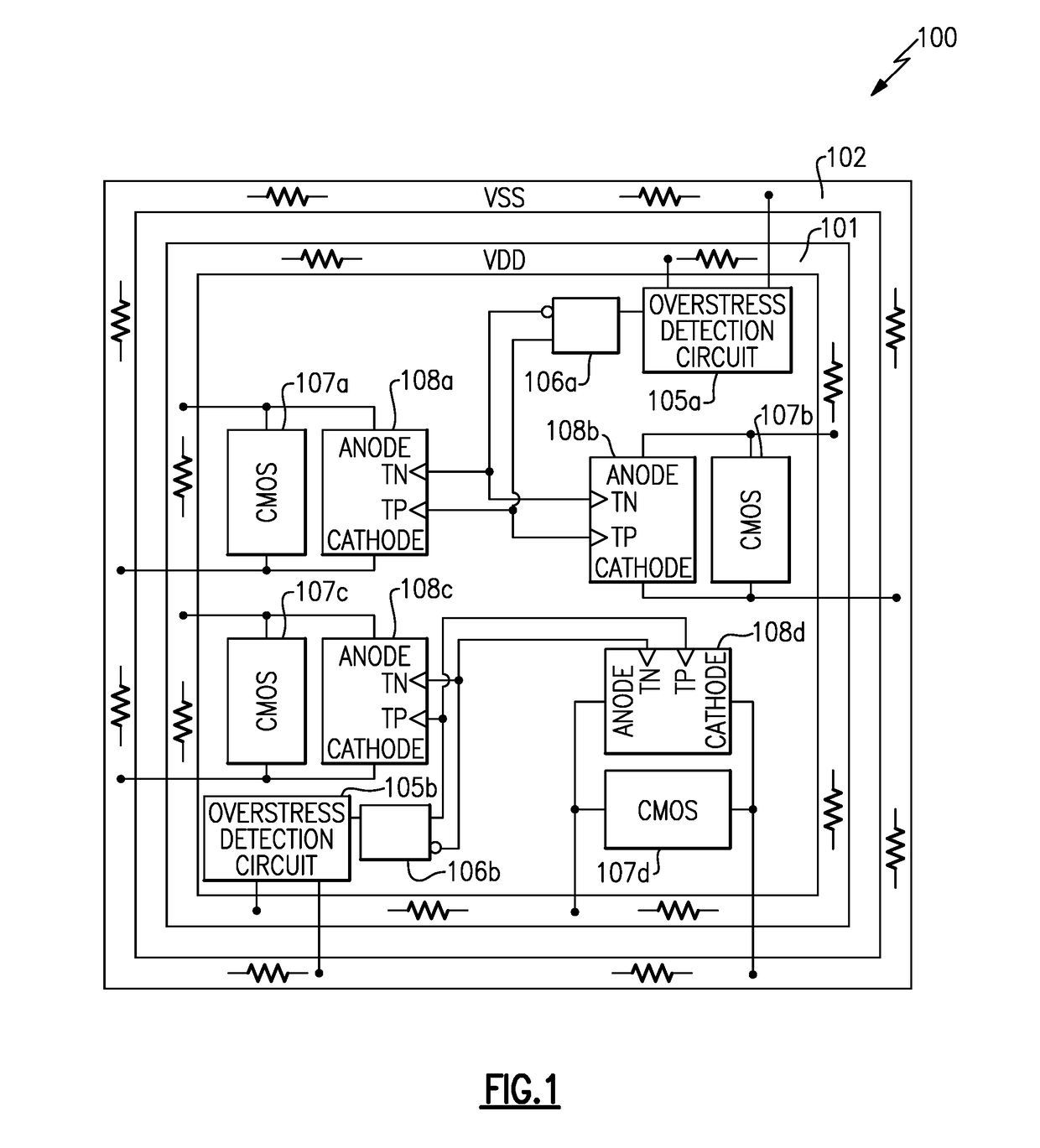
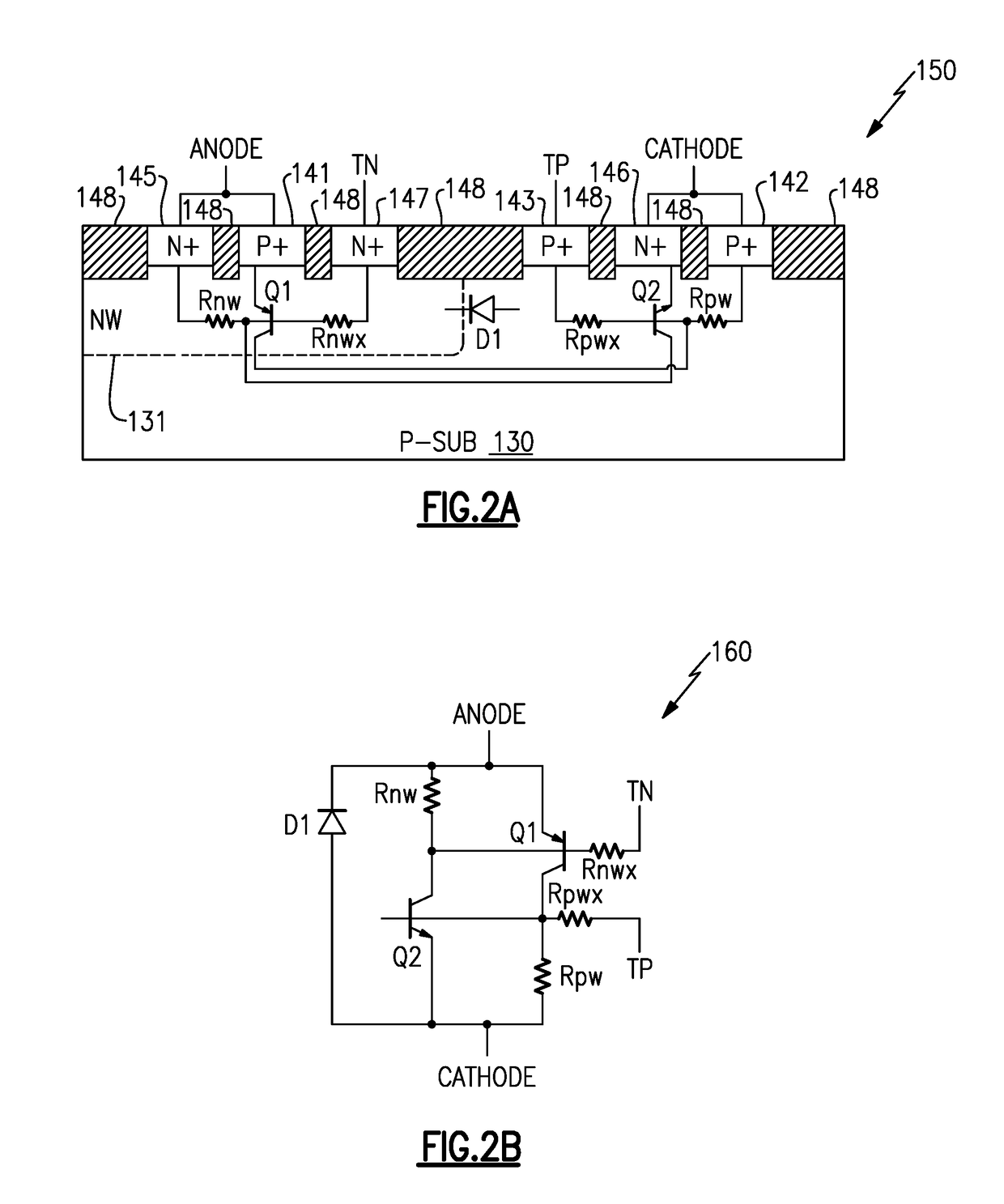
ActiveUS20180226788A1Prevent lockoutAvoid latchTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor chipEngineering
Distributed switches to suppress transient electrical overstress-induced latch-up are provided. In certain configurations, an integrated circuit (IC) or semiconductor chip includes a transient electrical overstress detection circuit that activates a transient overstress detection signal in response to detecting a transient electrical overstress event between a pair of power rails. The IC further includes mixed-signal circuits and latch-up suppression switches distributed across the IC, and the latch-up suppression switches temporarily clamp the power rails to one another in response to activation of the transient overstress detection signal to inhibit latch-up of the mixed-signal circuits.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Forage for improving later-period production performance of laying hens and eggshell quality
ActiveCN103931908AIncrease egg productionImprove feed utilizationFood processingAnimal feeding stuffSodium bicarbonateAnimal Foraging
A forage for improving later-period production performance of laying hens and eggshell quality comprises, in parts by weight, 45-50 parts of corn, 10-15 parts of soybean meal, 8-12 parts of wheat, 5-10 parts of corn germ cake, 3-6 parts of alfalfa meal, 4-6 parts of calcium particles, 4-6 parts of brewer's grains, 3-5 parts of calcium powder, 2-4 parts of corn gluten meal, 0.5-1 part of calcium hydrogen phosphate, 0.1-0.2 part of bentonite, 0.2-0.4 part of plant grease, 0.0005-0.0008 part of betaine, 0.2-0.4 part of edible salt, 0.2-0.4 part of lysine, 0.1-0.2 part of composite vitamins, 0.1-0.2 part of choline, 0.1-0.2 part of composite trace elements, 0.1-0.2 part of sodium bicarbonate, 0.1-0.2 part of methionine and 0.002-0.006 part of phytase. The forage is capable of satisfying nutrition demands of laying hens at a later period, improving laying rate and eggshell thickness, and improving eggshell quality.
Owner:四川圣迪乐村生态食品股份有限公司
IGBT with current carrier storage layer and additional hole passage
InactiveCN102157551AIncrease the minority carrier concentrationPrevent openingSemiconductor devicesCharge carrierConductivity modulation
The invention discloses an insulate gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) with a current carrier storage layer and an additional hole passage, and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor power devices. In the IGBT, an N-type current carrier storage layer (5) and a large P<+> tagma (4) structure are introduced on the basis of a conventional planar non-pouch-through IGBT. The N-type current carrier storage layer (5) improves a conductivity modulation effect close to an emitter and the large P<+> tagma (4) structure plays a role in providing an additional passage for a hole so that the latch-up resistance is improved. Due to the design of the N-type current carrier storage layer (5) and the large P<+> tagma (4), the flow path of a hole current of the conventional IGBT is optimized, so that a safety operation area of a device is enlarged and the sensitivity of latch current density to a temperature is reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
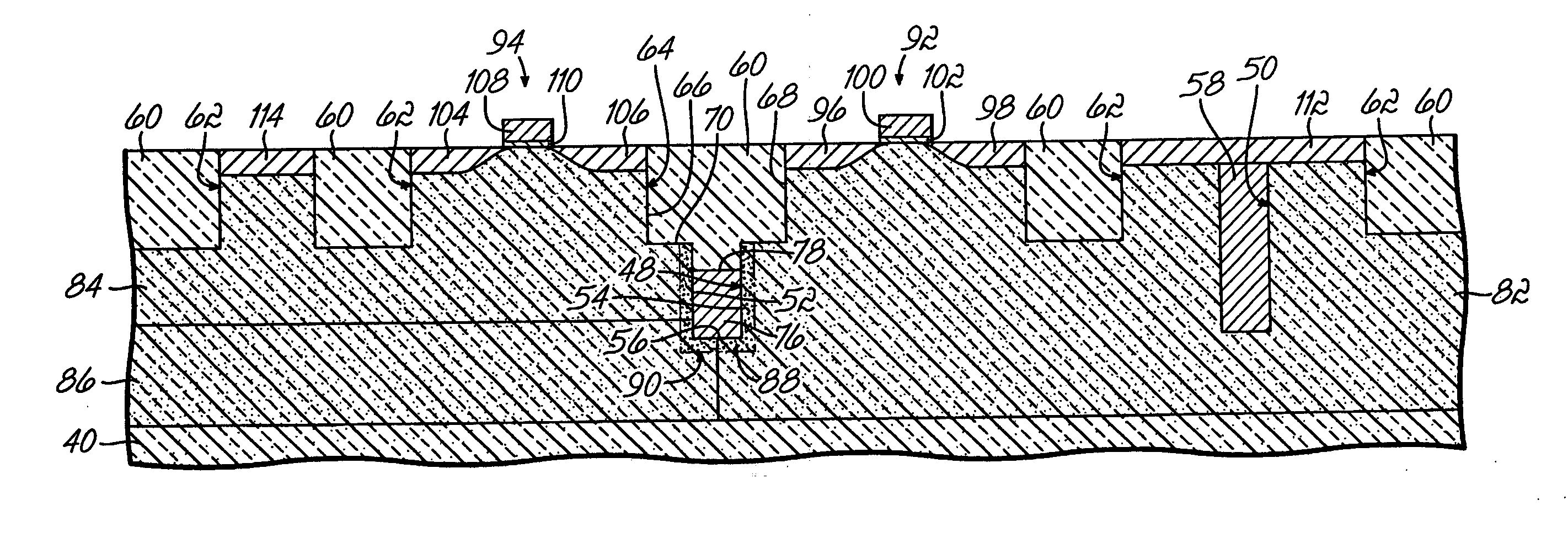
Memory cell array latchup prevention
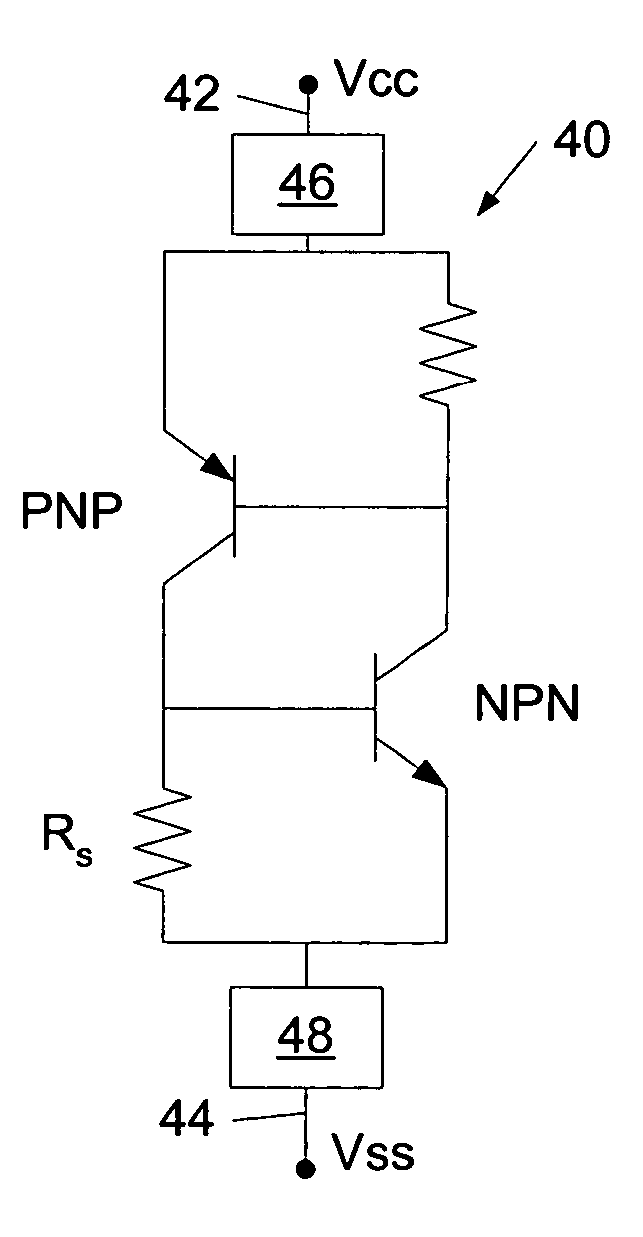
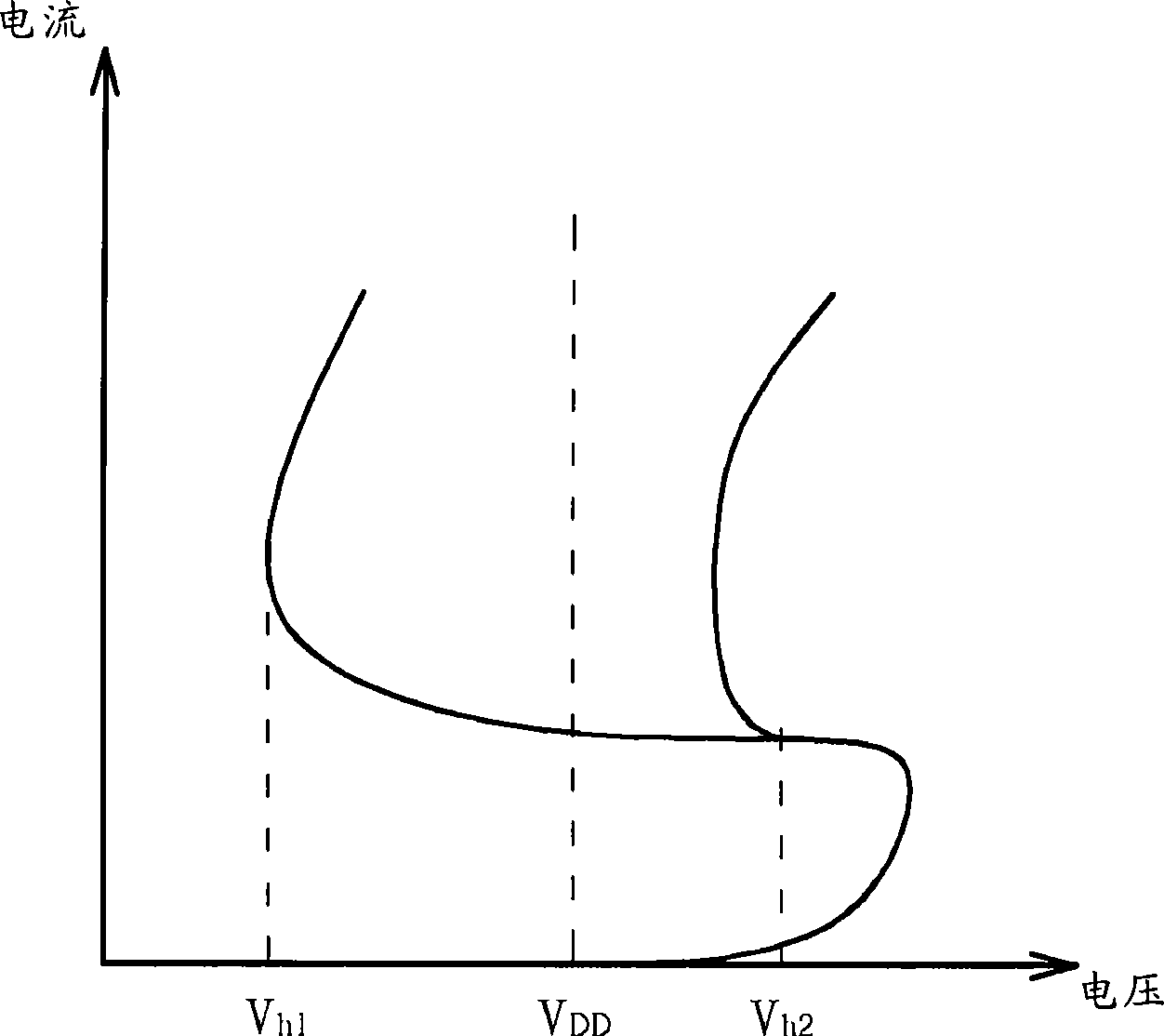
ActiveUS7773442B2Prevent lockoutLatch up within the circuit may be preventedTransistorReliability increasing modificationsCMOSCurrent limiting
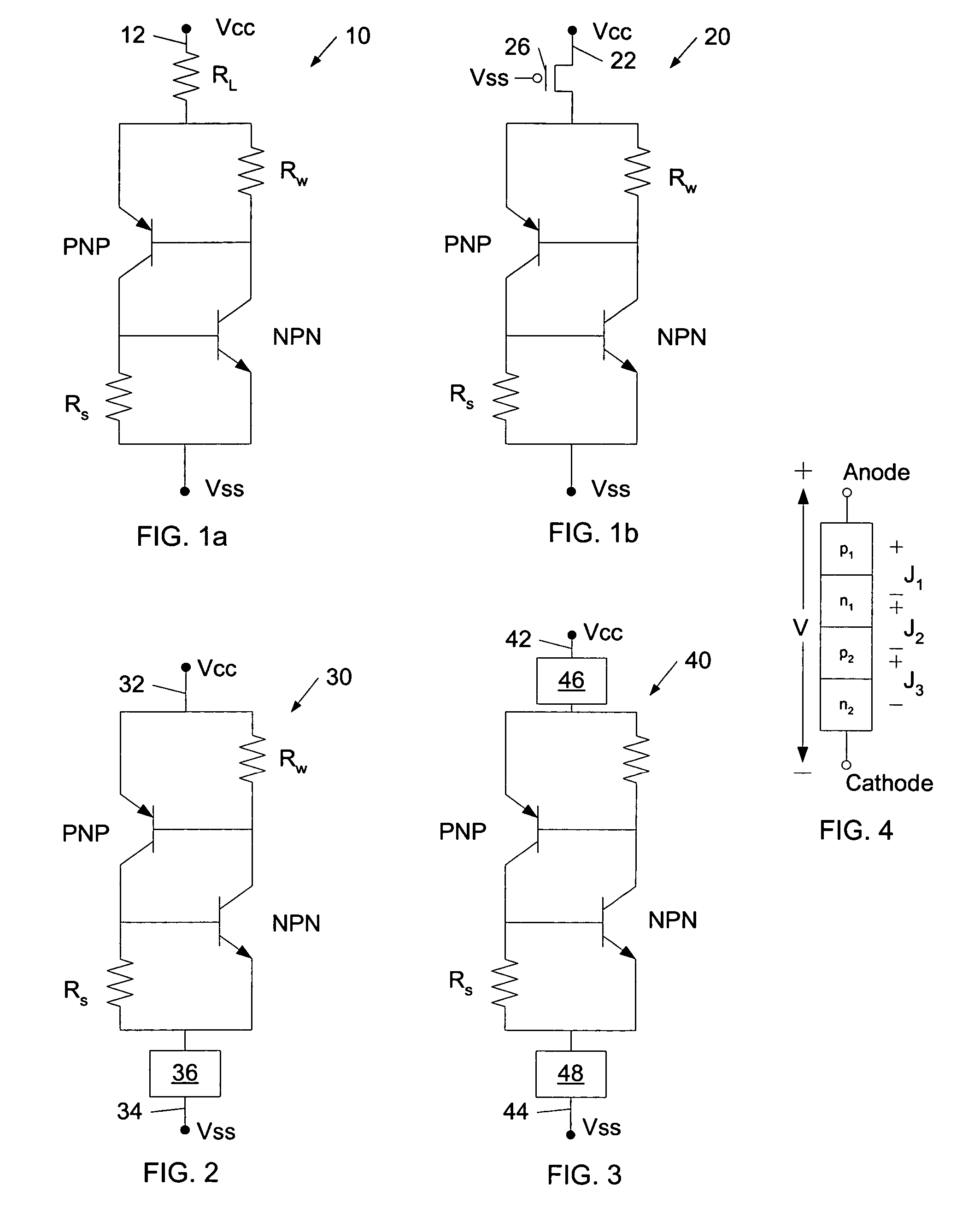
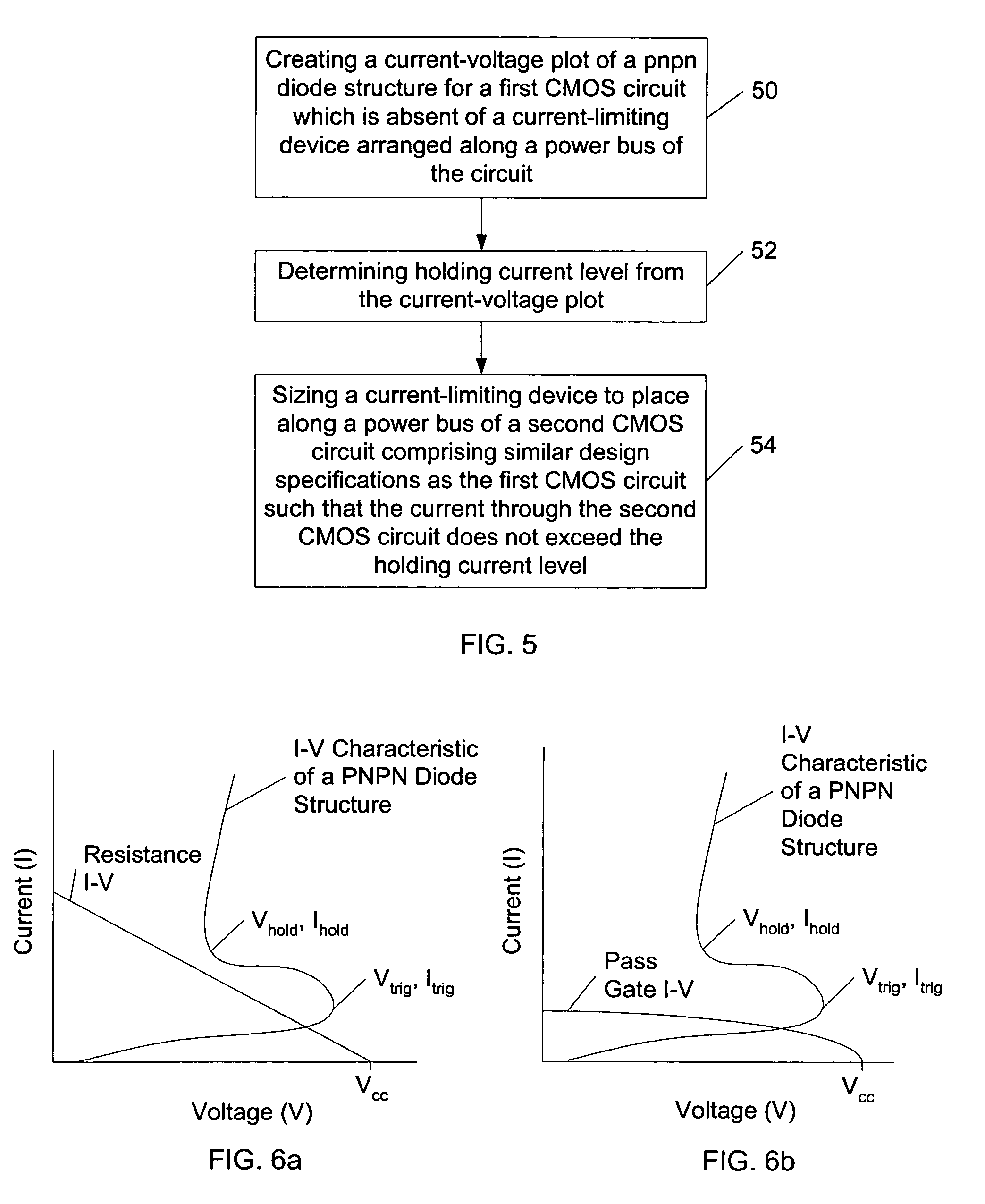
A complementary field-effect (CMOS) circuit is provided which includes a current-limiting device arranged along a power-supply bus or a ground bus of the circuit. The current-limiting device is configured to prevent latch up of the CMOS circuit. More specifically, the current-limiting device is configured to maintain a junction of the parasitic pnpn diode structure as reverse-biased. A method is also provided which includes creating a current-voltage plot of a pnpn diode arranged within a first CMOS circuit which is absent of a current-limiting device arranged along a power bus of the circuit. In addition, the method includes determining a holding current level from the current-voltage plot and sizing a current-limiting device to place along a power bus of a second CMOS circuit comprising similar design specifications as the first CMOS circuit such that the current through the second CMOS circuit does not exceed the holding current level.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
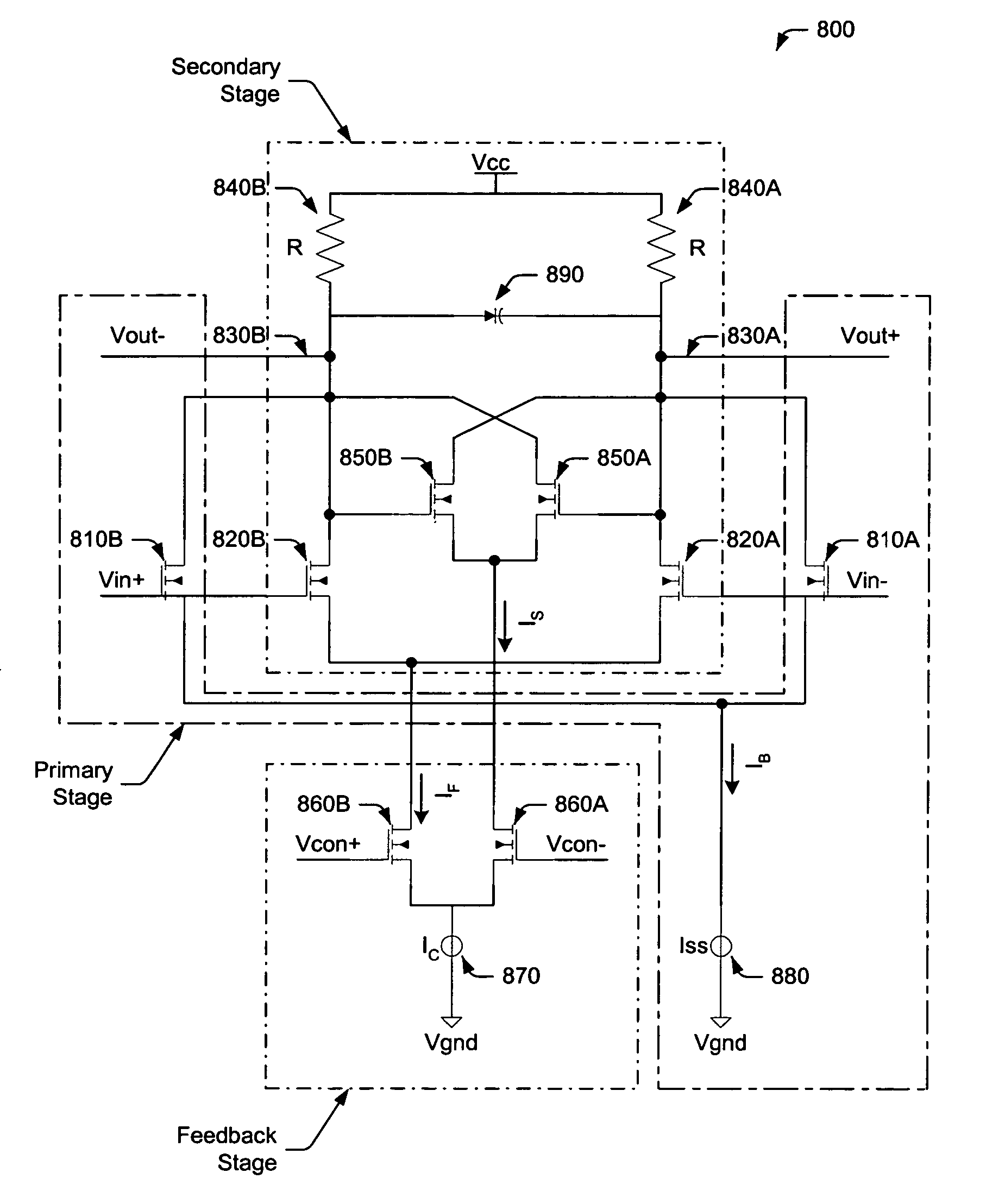
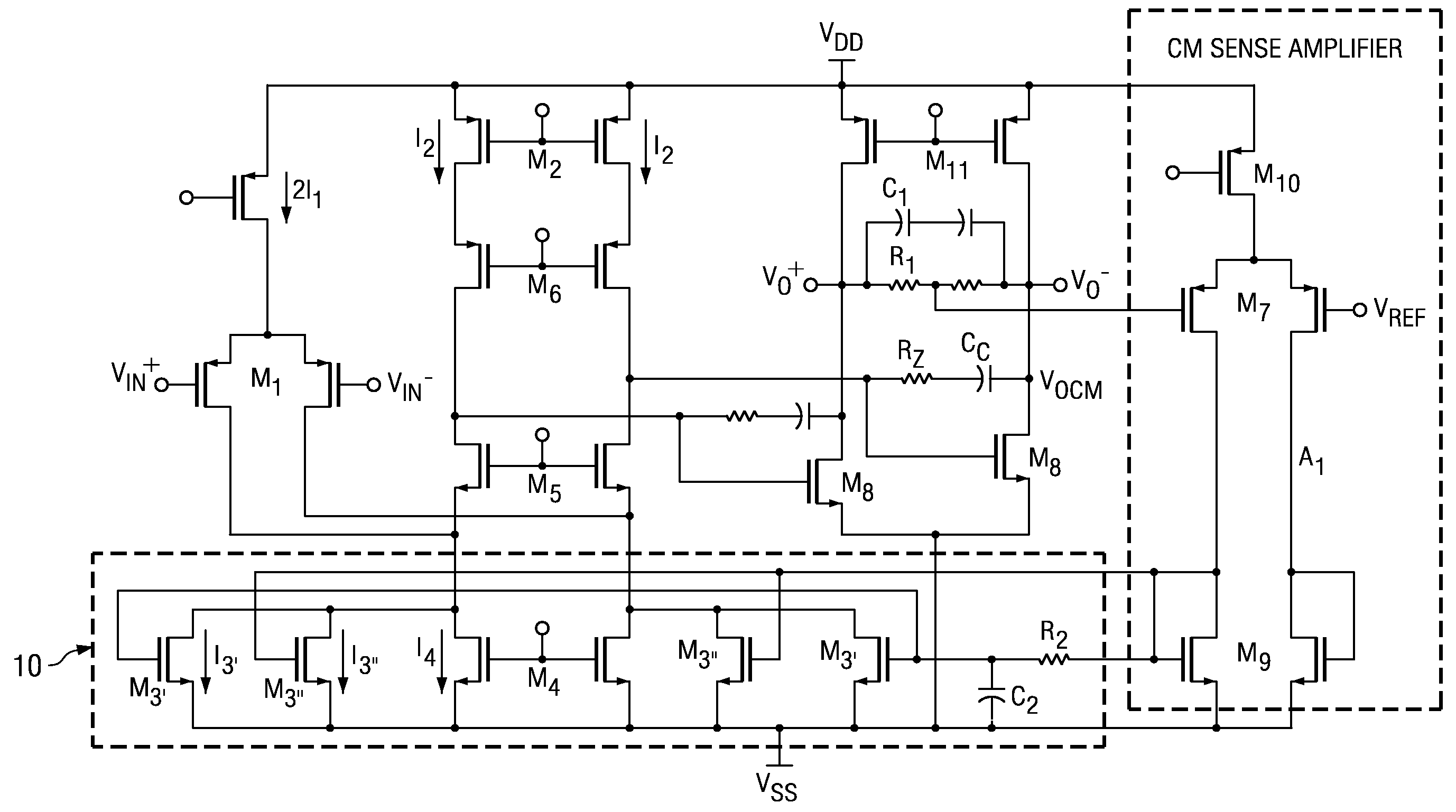
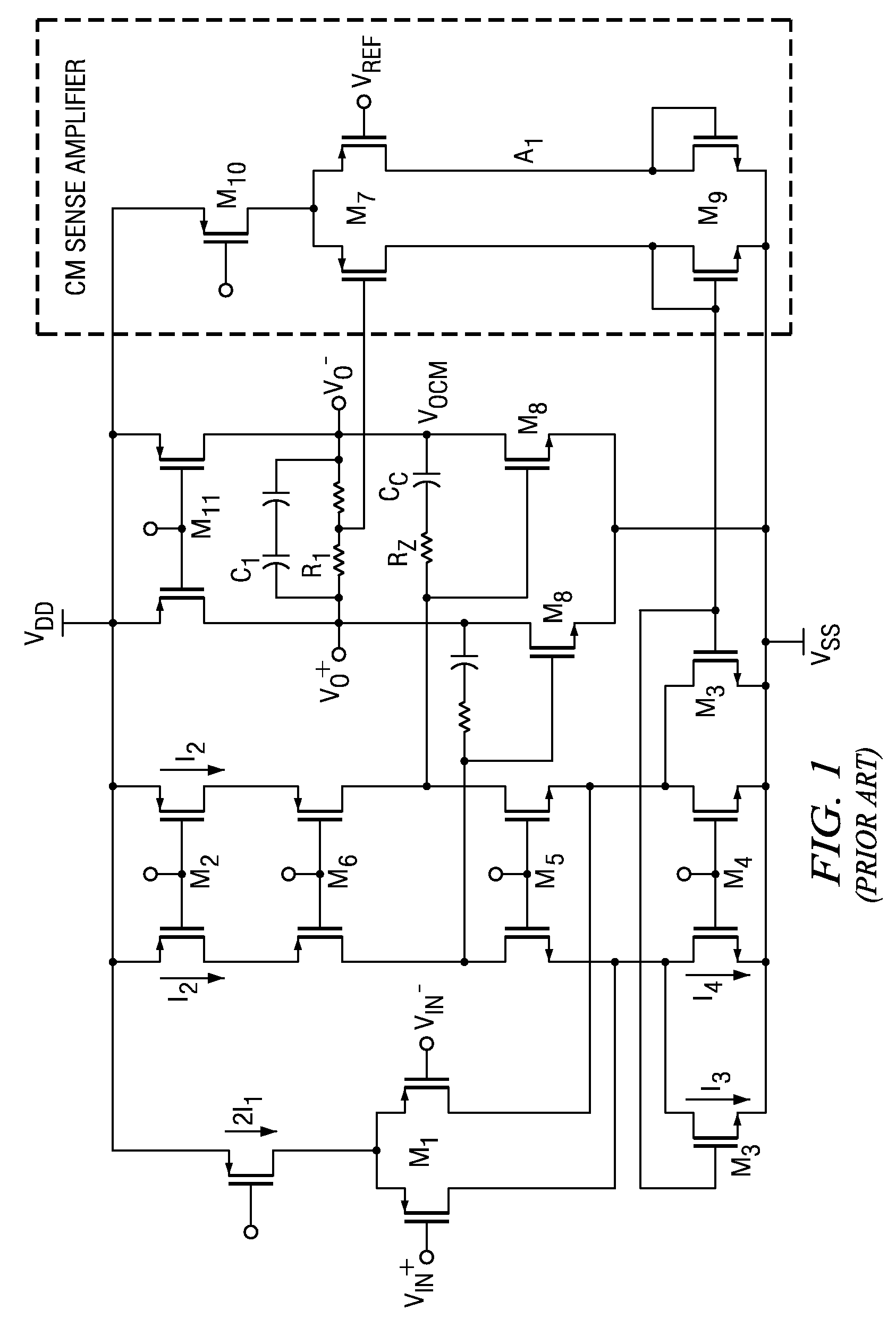
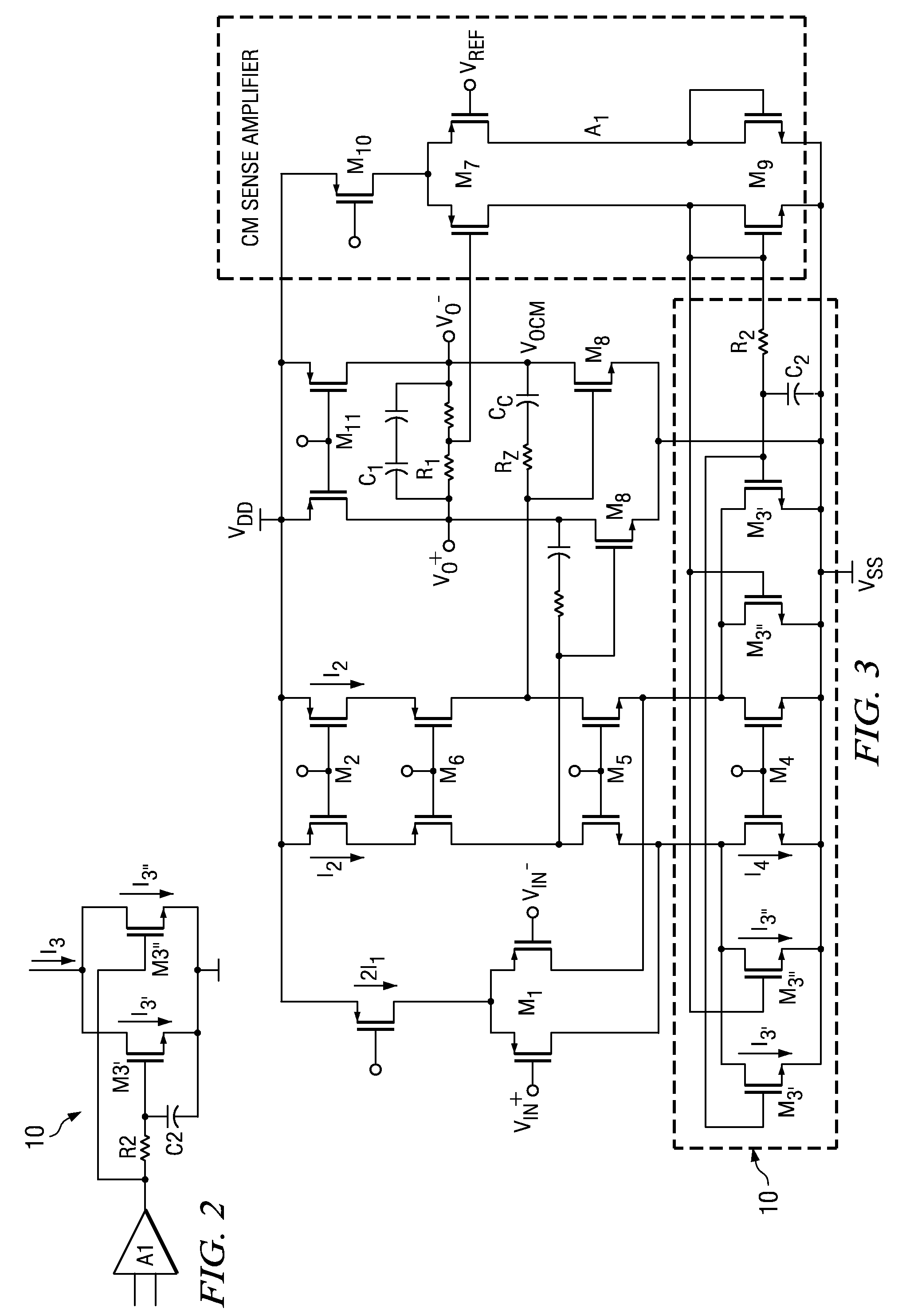
Multi-path common mode feedback for high speed multi-stage amplifiers
ActiveUS7453319B2Large transconductance gainLow transconductance gainDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesFast pathAudio power amplifier
The invention includes methods and systems for providing a multi-path common mode feedback loop in an amplifier system. Embodiments include techniques for dividing a common mode feedback current path to provide a slow common mode feedback current path and a fast common mode feedback current path. The slow and fast paths are configured for controlling common mode feedback current within a small bandwidth.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
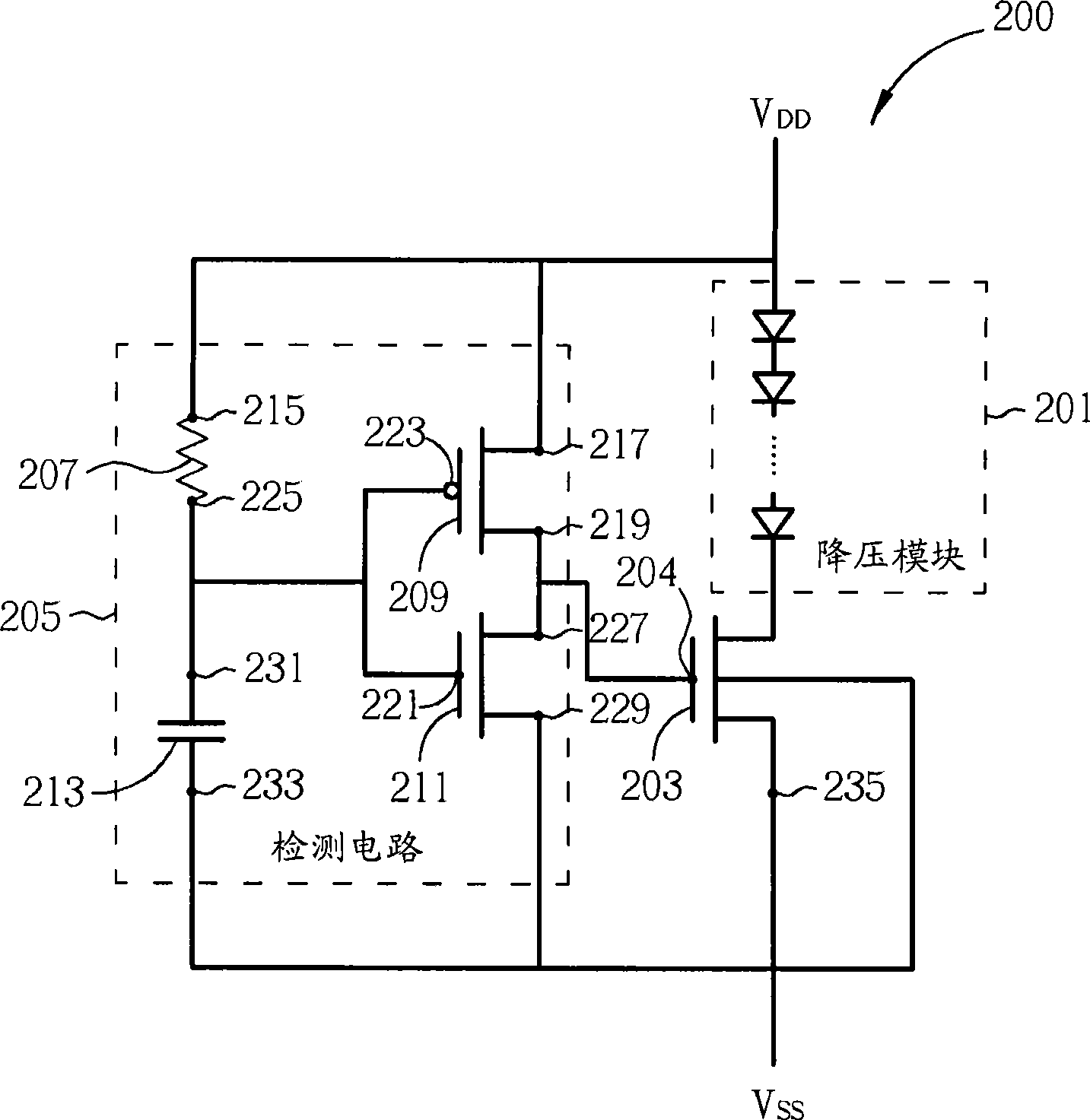
Electrostatic discharging protection circuit
InactiveCN101488665AAvoid latchEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectrostatic discharge protectionEngineering
A static discharge protection circuit comprises: a step-down module that is coupled between a first voltage level and a second voltage level, wherein the first voltage level is higher than the second voltage level; a grid trigger switch that is coupled between the first voltage level and the second voltage level; and a detection circuit that is coupled with the grid trigger switch and used for detecting static discharge events so as to control the grid trigger switch.
Owner:RAYDIUM SEMICON
Latchup prevention method for integrated circuits and device using the same
ActiveUS7221027B2Minimize impactAvoid latchTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringVoltage source
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
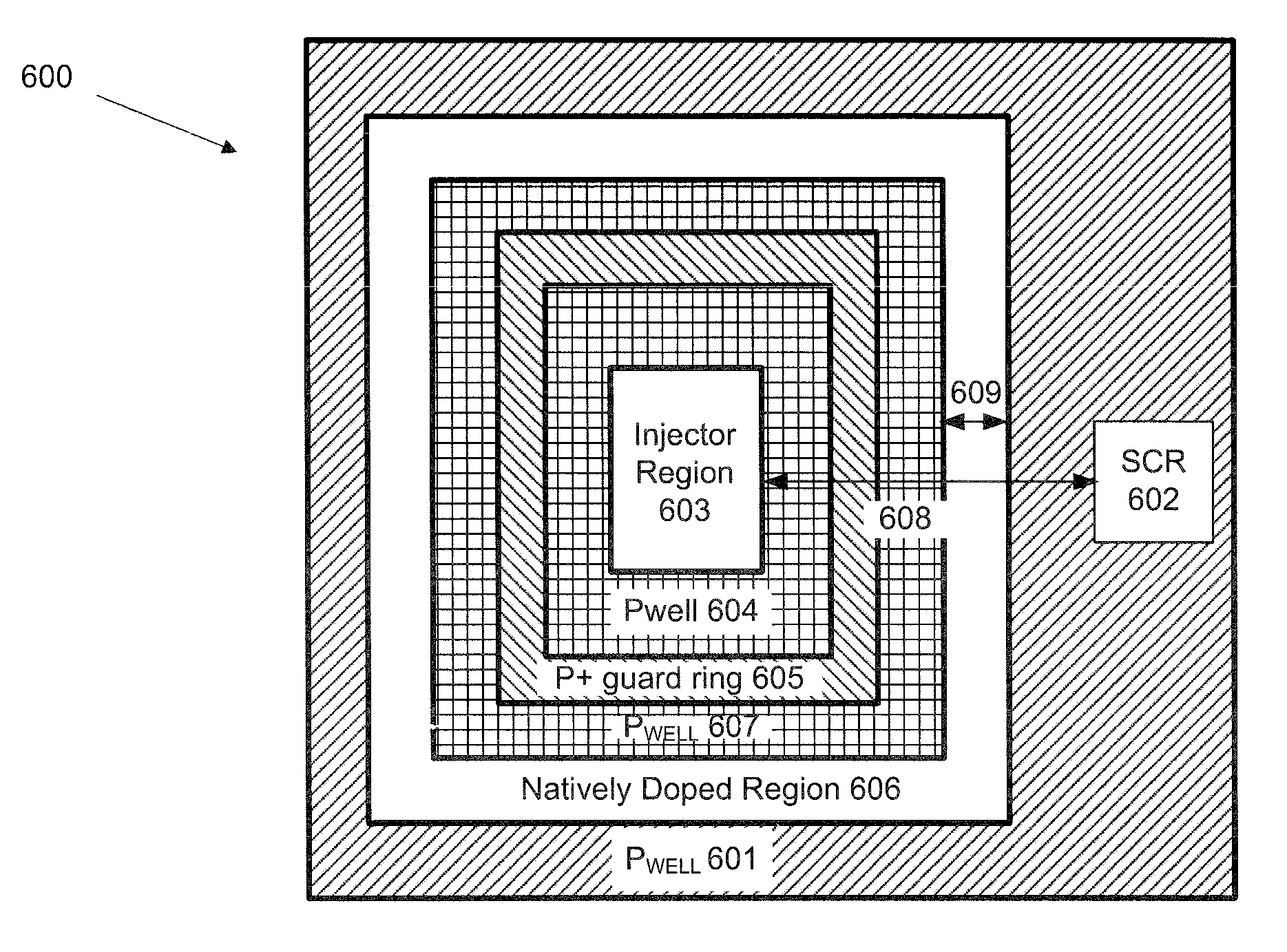
Semiconductor device for latch-up prevention
ActiveUS7777248B1Improve performanceReduce sizeThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInjectorHigh resistance
A semiconductor device is provided for preventing Latch-up in Silicon Controlled Rectifiers (SCRs) when these SCRs become activated. Embodiments of the invention use a natively doped region having high resistance to separate the NPN transistor from the PNP transistor that form the SCR, and / or to isolate the entire SCR from the injector source in order to prevent latch-up. The high resistance of the natively doped region allows to achieve the separation resistance needed in a smaller space, as compared to the space required to achieve the same separation resistance in a well. Accordingly, the invention provides for more robust and cost effective latch-up prevention devices.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Charge pump device
InactiveUS6881997B2Reduce well resistanceReduce resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesIsolation layerCrystalline silicon
In a charge pump device, occurrence of a latch up can be prevented and current capacity can be increased. An N-type epitaxial silicon layer is formed on a P-type single crystalline silicon substrate, P-type well regions are formed in the N-type epitaxial silicon layer separated from each other, and P-type lower isolation layers and P-type upper isolation layers are formed between the P-type well regions. Then a charge transfer MOS transistor is formed in each of the P-type well regions. The P-type single crystalline silicon substrate is biased to a ground potential or a negative potential.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
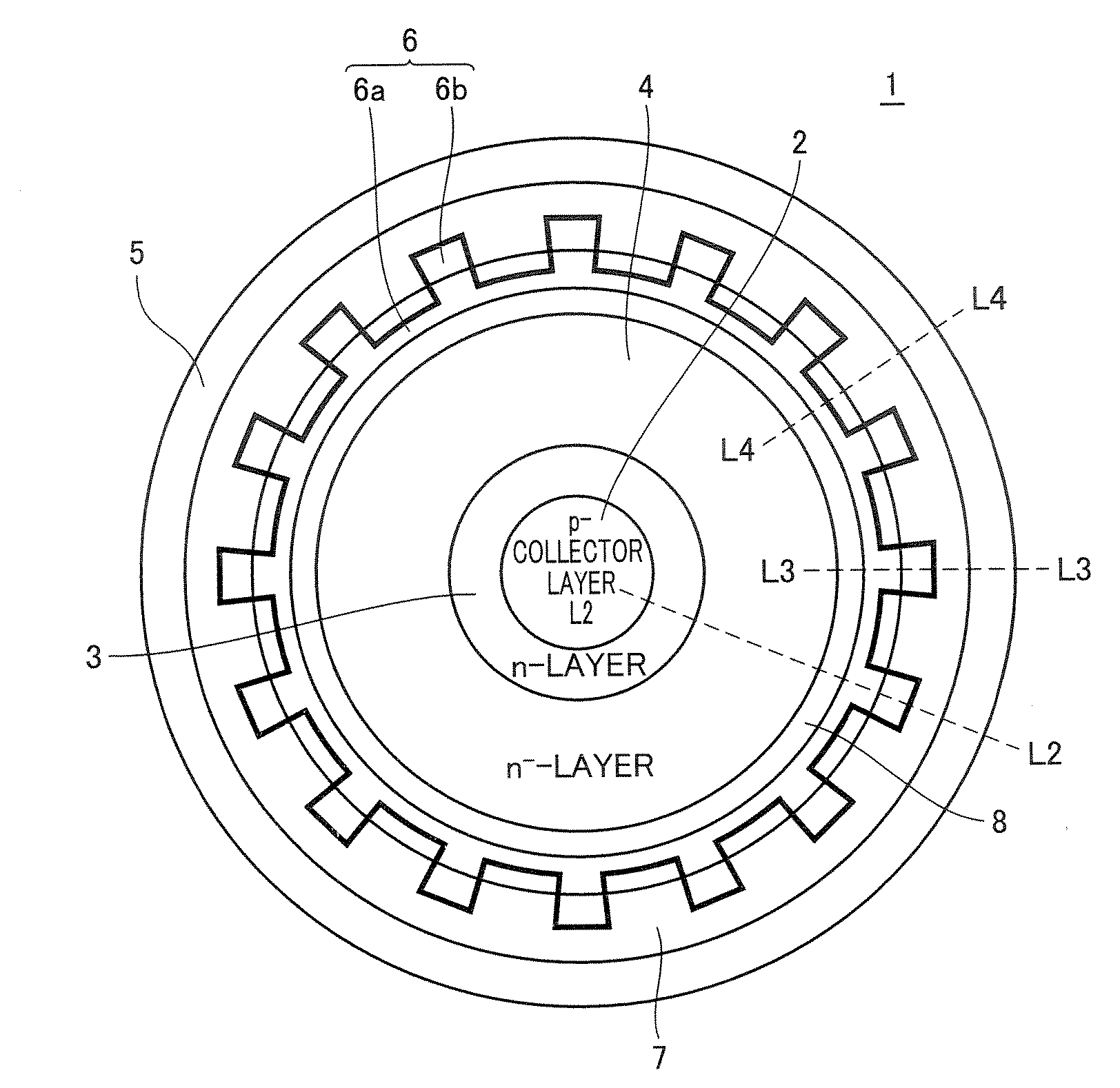
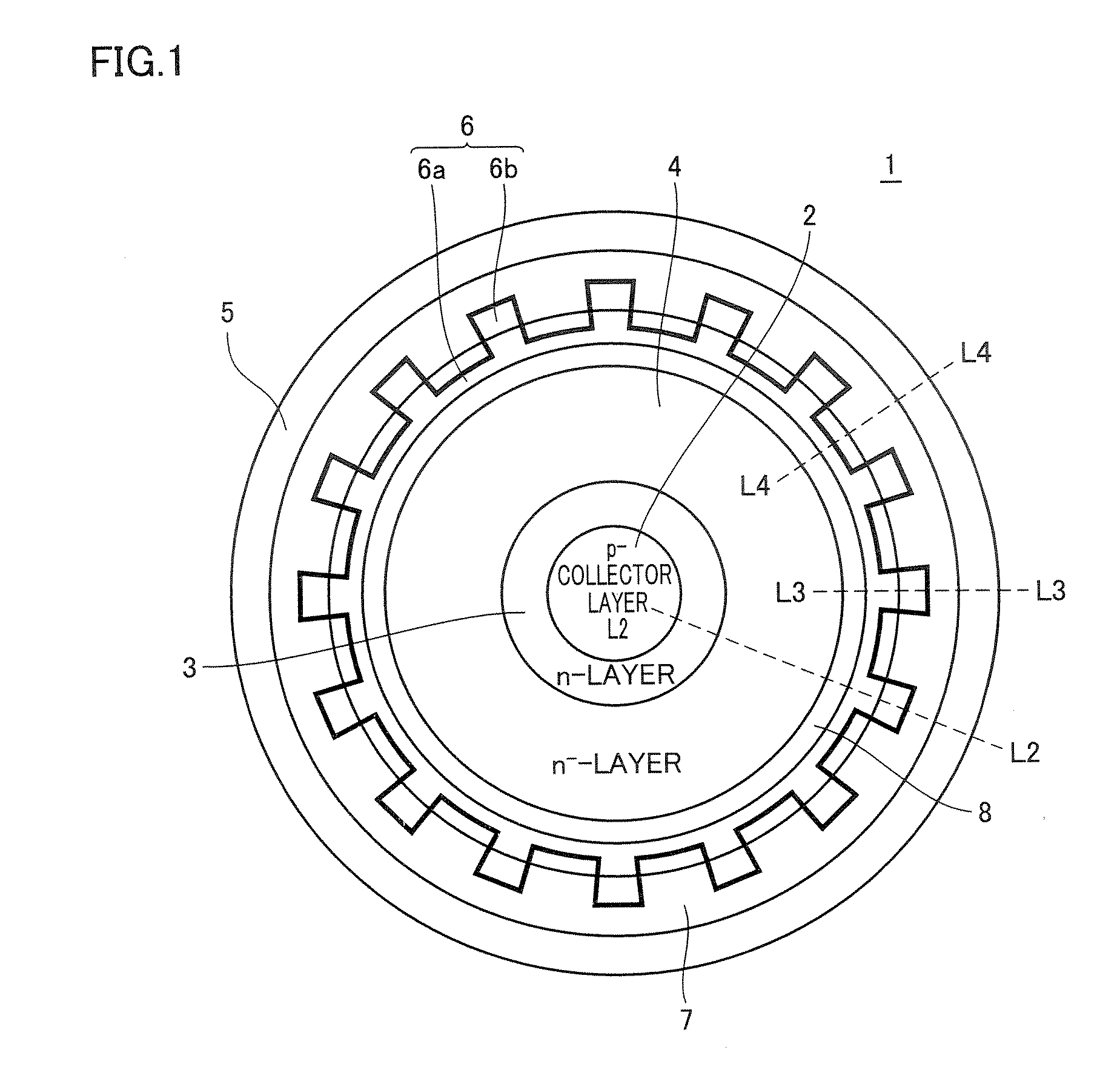
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20080006906A1Increase the number ofImprove immunityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorSemiconductor device
An n+-emitter layer arranged under an emitter electrode is formed of convex portions arranged at predetermined intervals and a main body coupled to the convex portions. A convex portion region is in contact with the emitter electrode, and a p+-layer doped more heavily than a p-base layer is arranged at least below the emitter layer. In a power transistor of a lateral structure, a latch-up immunity of a parasitic thyristor can be improved, and a turn-off time can be reduced.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
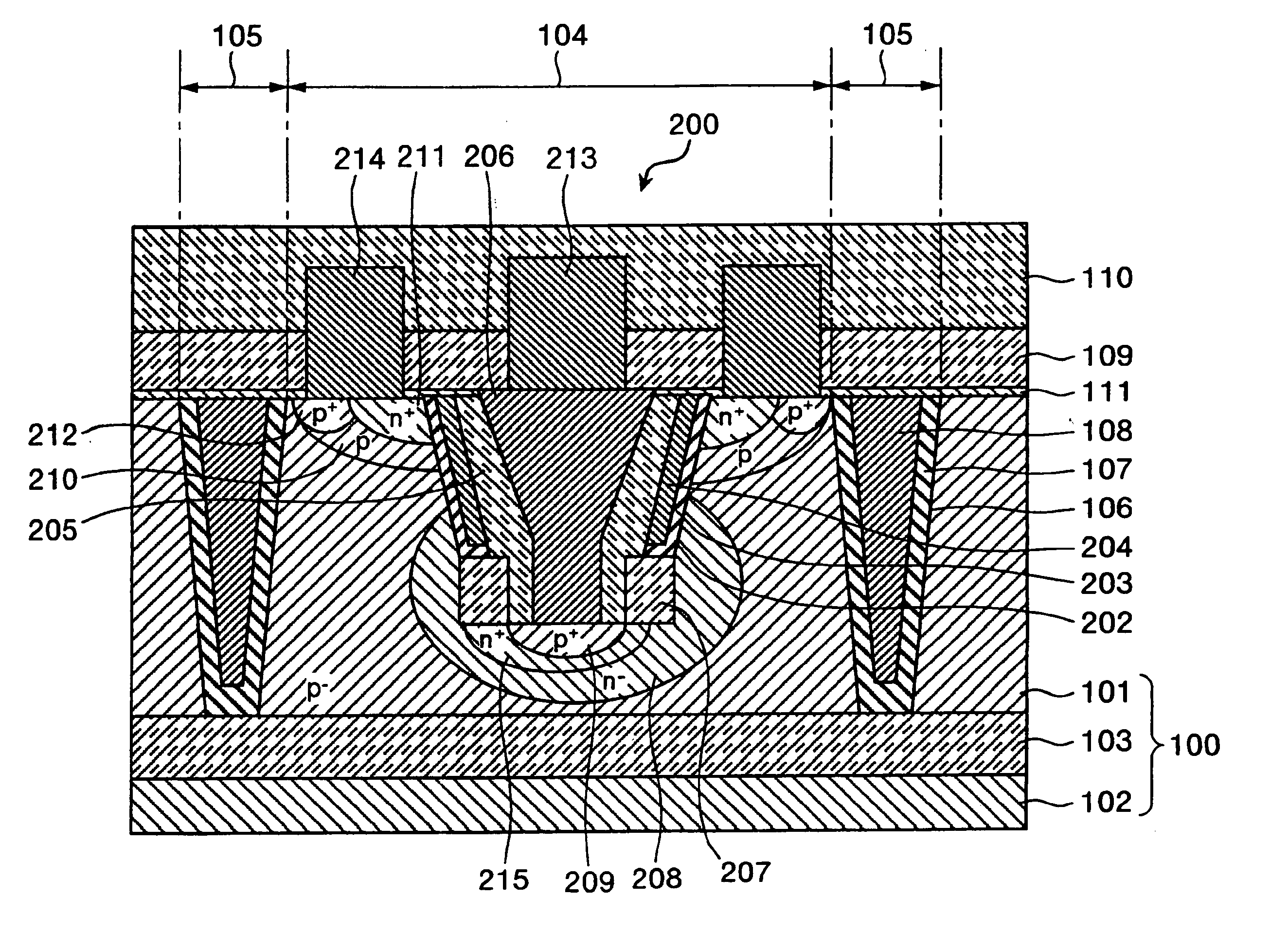
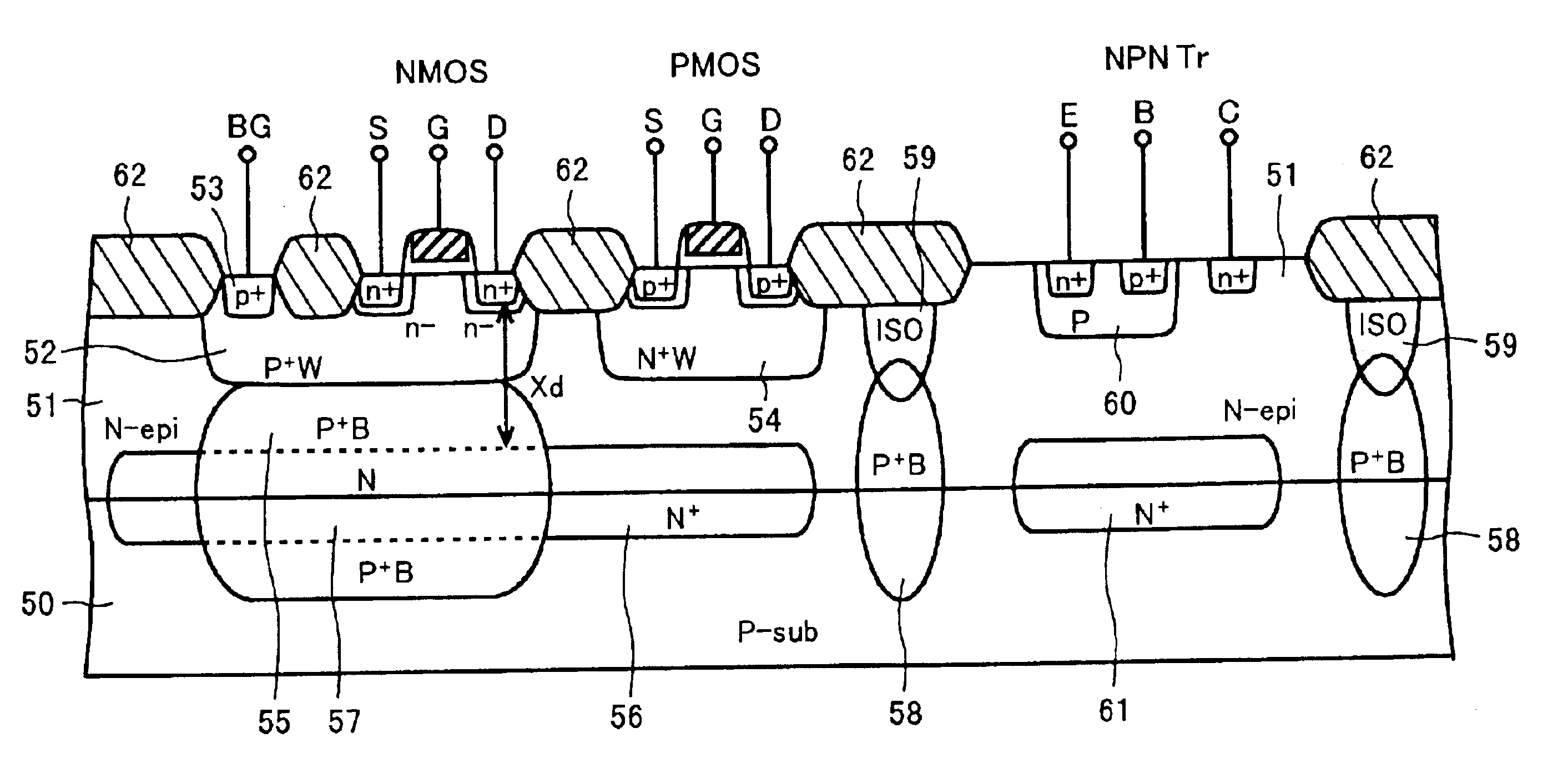
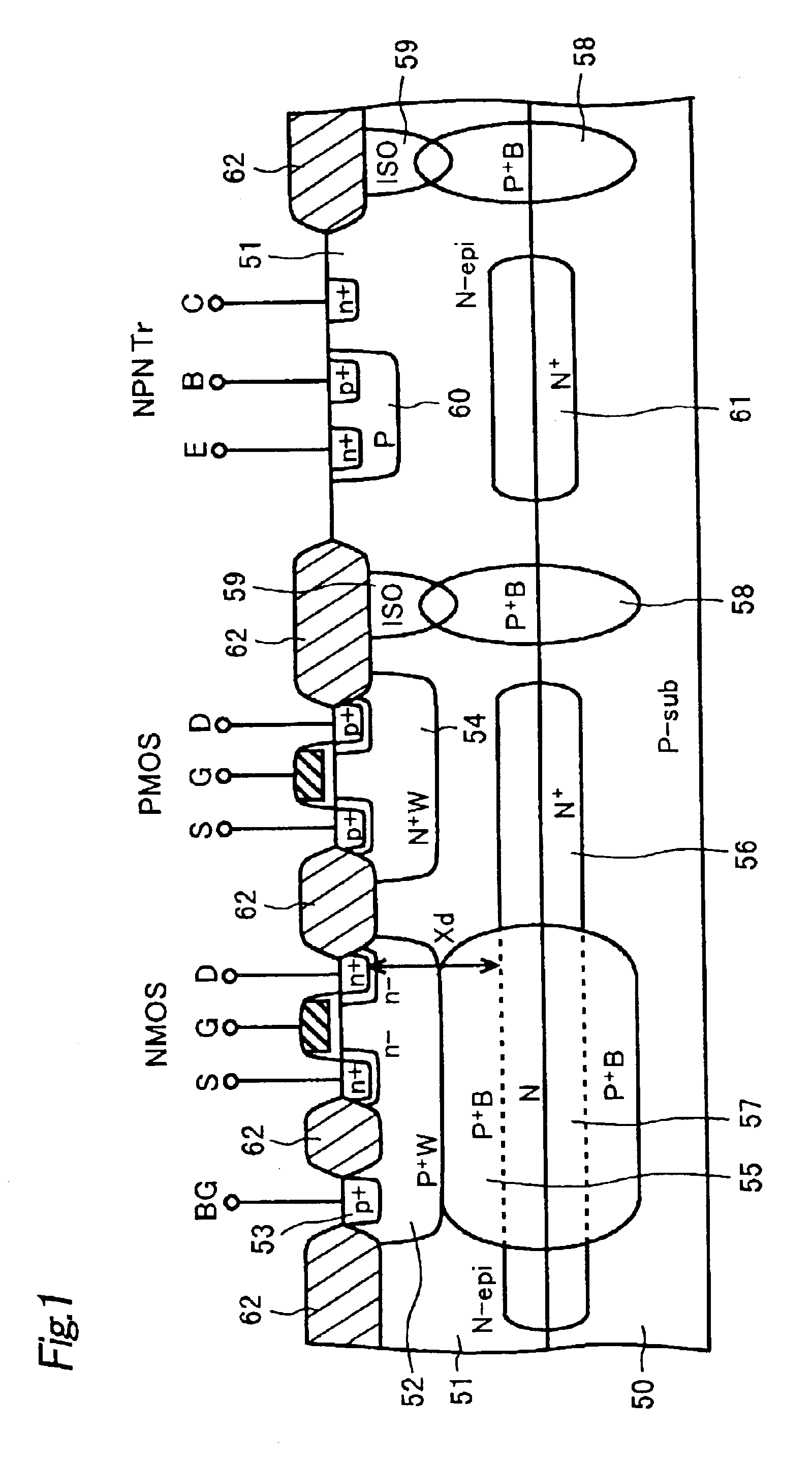
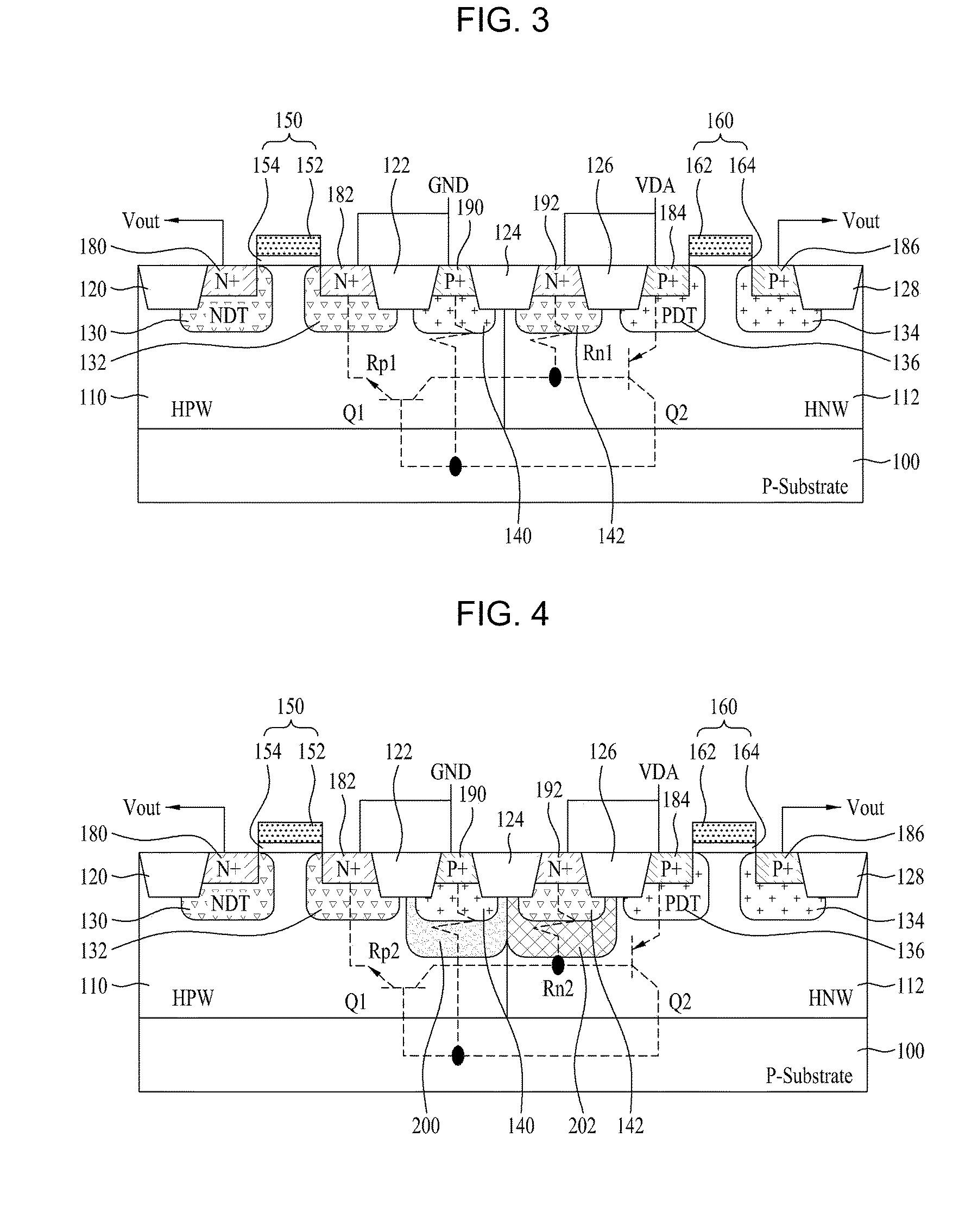
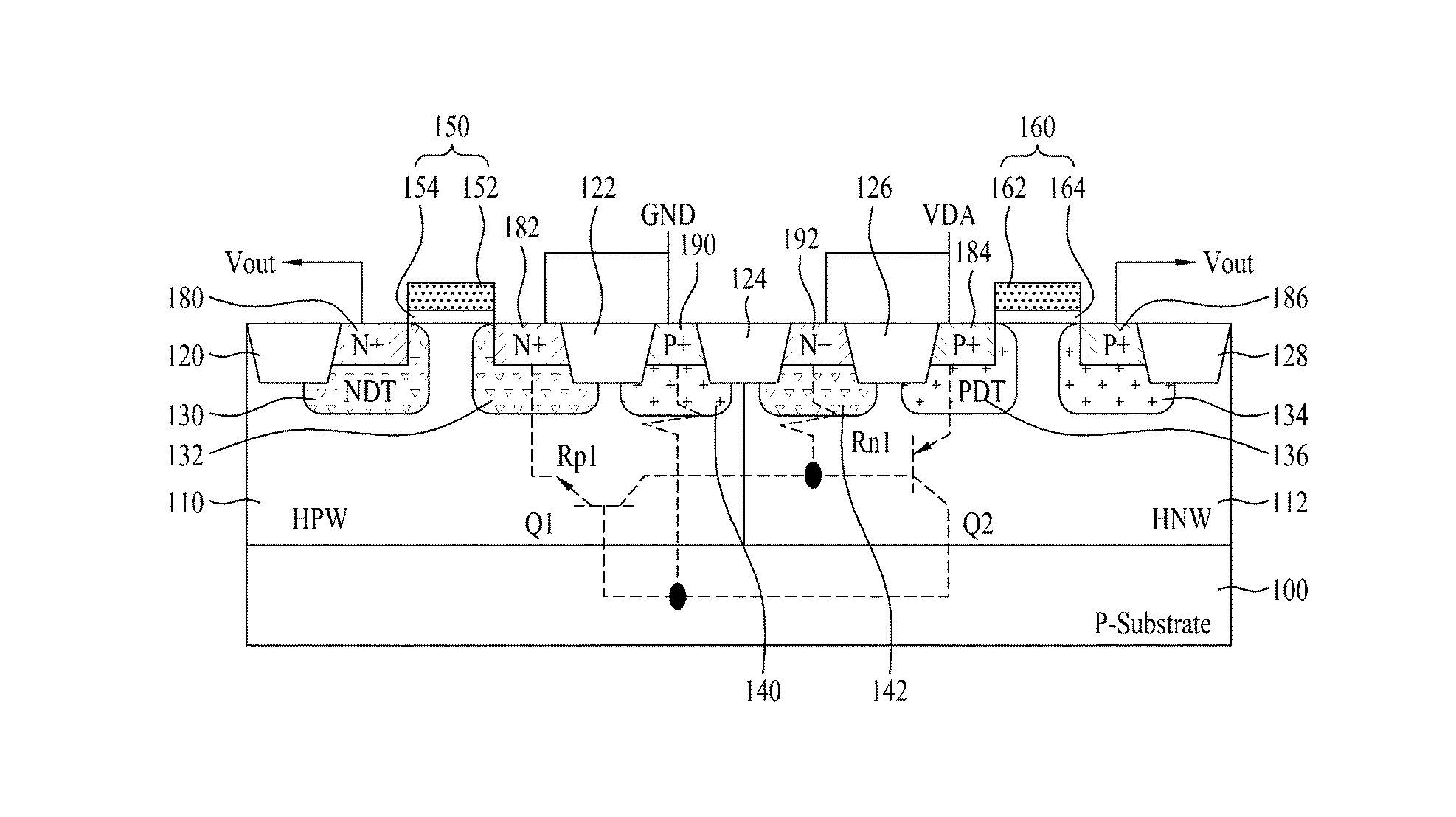
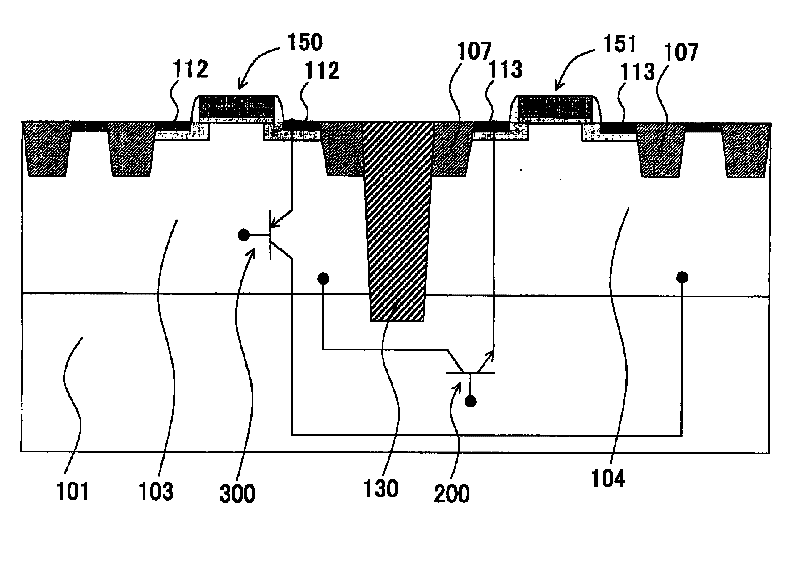
Semiconductor Device and Method for Manufacturing the Same
Disclosed are a semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing the same. The semiconductor device includes at least two of first and second conductive-type high-voltage transistors and first and second conductive-type low-voltage transistors. The first conductive-type high-voltage transistor include a first conductive-type well in a semiconductor substrate, a device isolation film in the first conductive-type well, a gate pattern on the first conductive-type well, second conductive-type drift regions in the semiconductor substrate at opposite sides of the gate pattern, second conductive-type source and drain regions in the second conductive-type drift region, a pick-up region to receive a bias voltage, and a first latch-up inhibiting region under the pick-up region. Accordingly, it is possible to reduce and prevent latchup without using a double guard ring and to eliminate an additional process to form first and second latch-up inhibiting regions.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
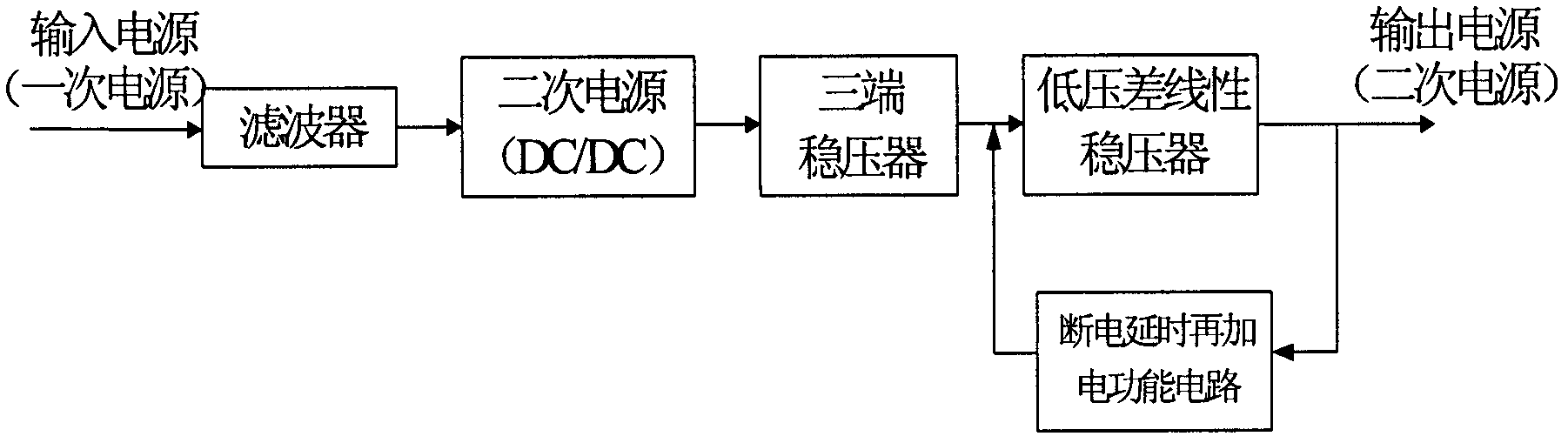
Secondary power source with latch-up resistance function
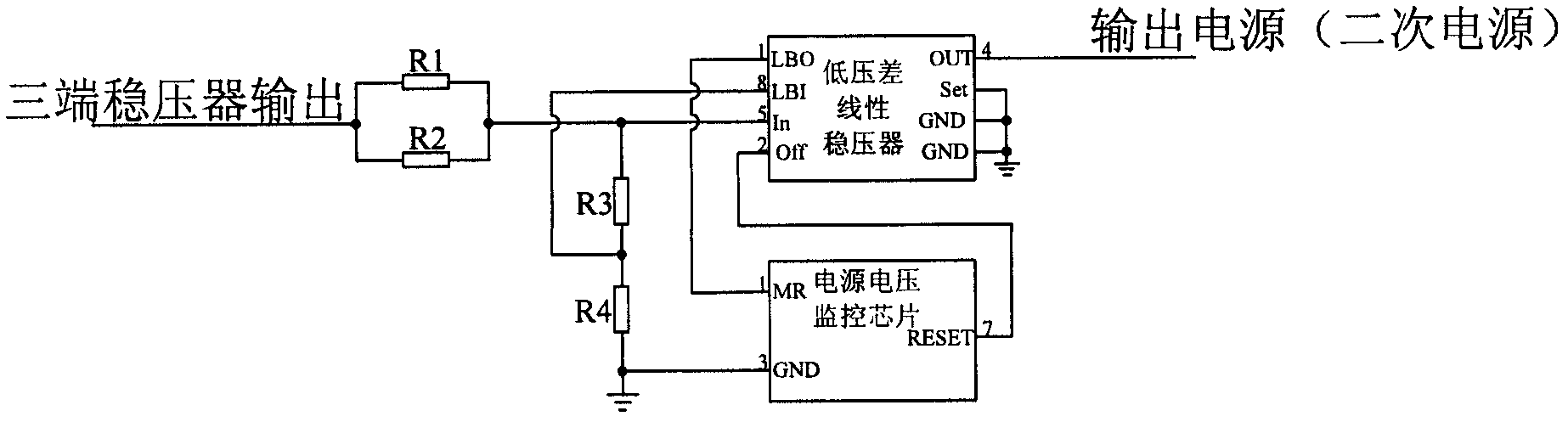
InactiveCN102684476AImprove output qualityStable jobApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationLinear regulatorElectricity
The invention provides a secondary power source with a latch-up resistance function, which comprises an input filter, a DC / DC (Direct Current / Direct Current) transducer, a three terminal regulator, a low dropout linear regulator and a power-off delay secondary power-up function circuit. The external primary power supply voltage is sequentially filtered through the input filter and reduced and isolated through the DC / DC transducer, and then is transmitted to the three terminal regulator for primary voltage regulation filtering; the output of the three terminal regulator is transmitted to the low dropout linear regulator for secondary voltage regulation filtering; and the needed secondary voltage is generated by the low dropout linear regulator and then is output. The power-off delay secondary power-up function circuit utilizes a detection resistor, a resistance-voltage-dividing network and a power supply voltage monitoring chip to form a voltage monitoring circuit for the secondary power source; when the voltage is lower than a threshold value through detection, the low dropout linear regulator is closed automatically, the latch of a CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) device is released because of power-off, and the output voltage gets back to normal again after the secondary power-up is performed, so that the power-off delay secondary power-up function is achieved, and the latch of the CMOS device can be released reliably.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
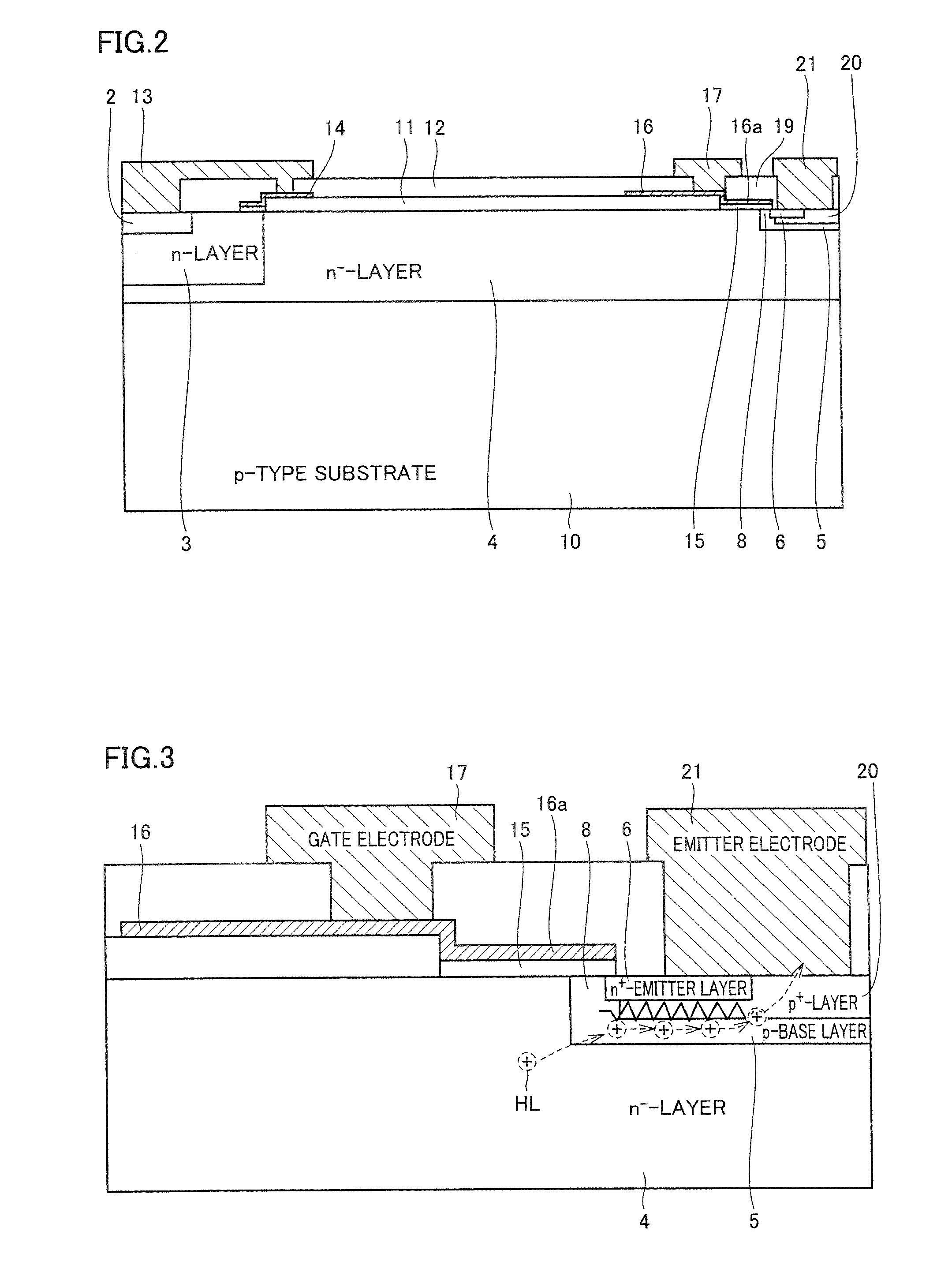
Semiconductor device
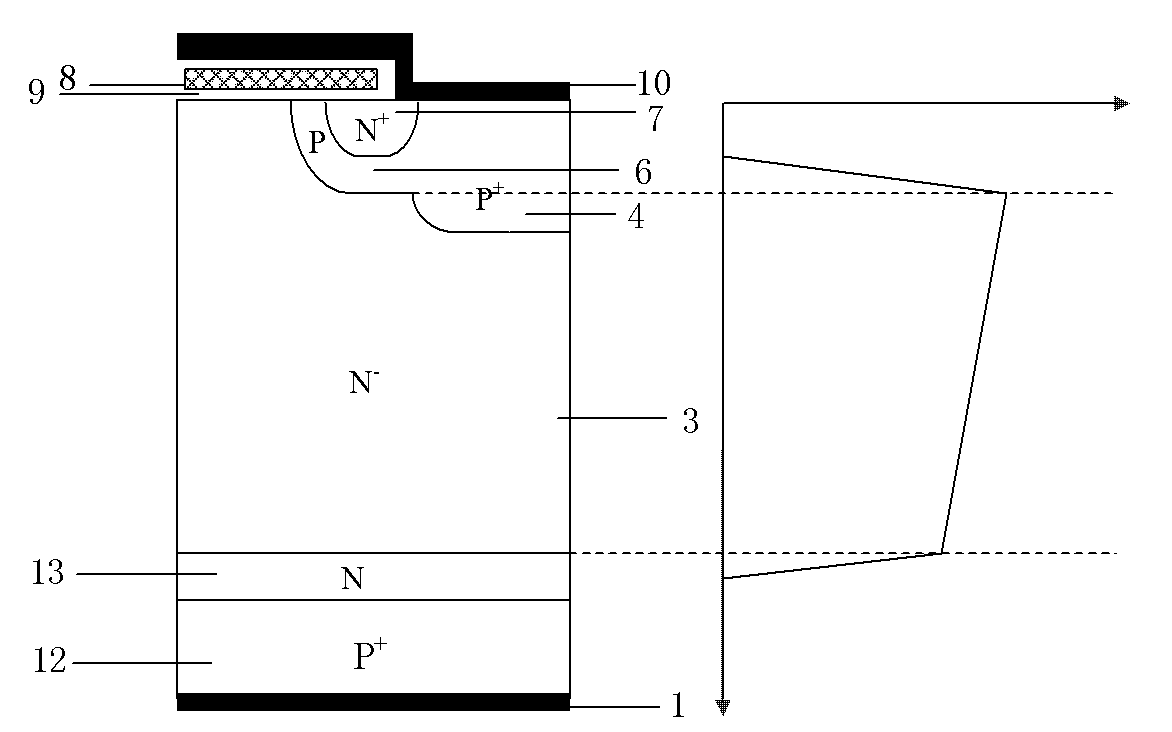
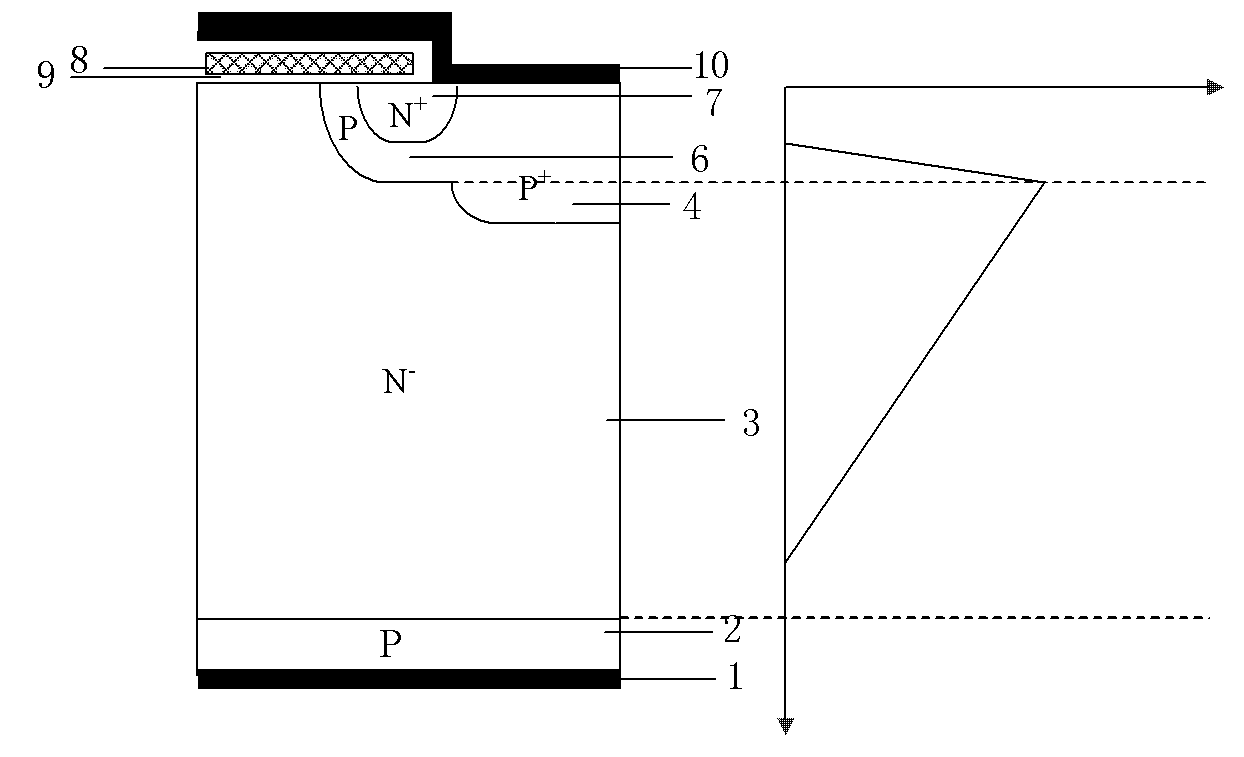
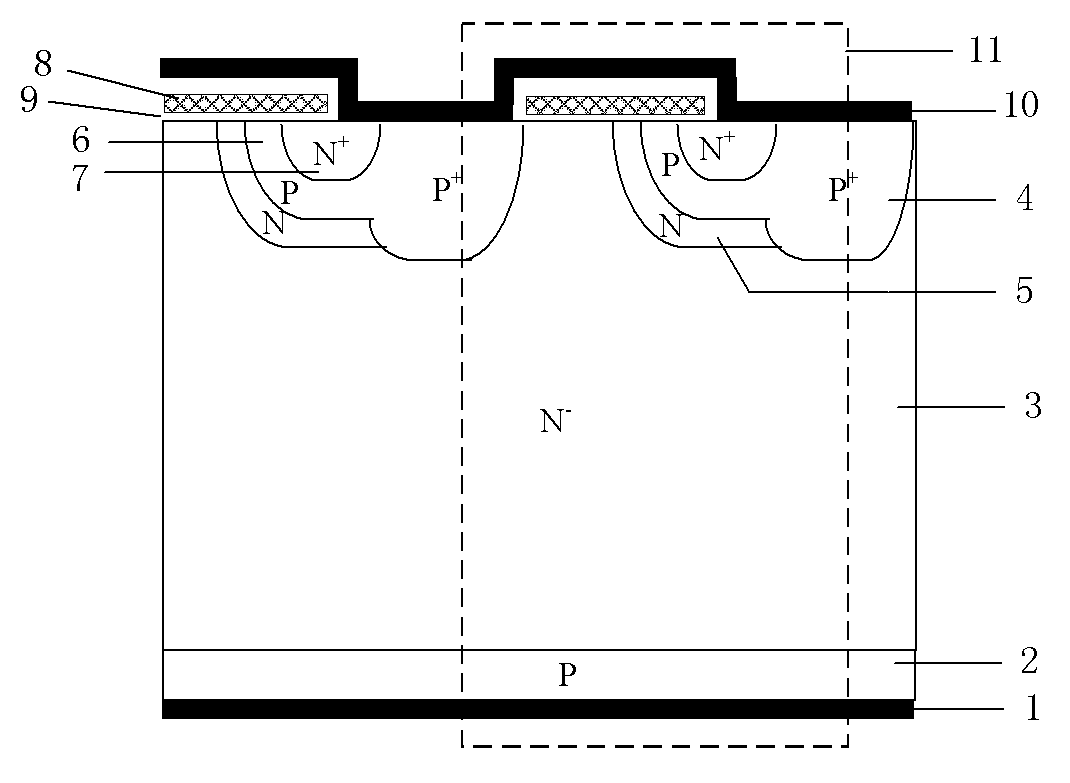
ActiveUS20100193836A1Improve rbsoaSuppress latch-upSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsElectrically conductive
A semiconductor device includes a substrate of a first conductivity type, a base region of a second conductivity type, a source region of the first conductivity type, a collector region of the second conductivity type, a trench gate, which is formed in a trench via a gate insulation film, an electrically conductive layer, which is formed within a contact trench that is formed through the source region, a source electrode, which is in contact with the electrically conductive layer and the source region, and a latch-up suppression region of the second conductivity type, which is formed within the base region, in contact with the electrically conductive layer, and higher in impurity concentration than the base region. The distance between the gate insulation film and the latch-up suppression region is not less than the maximum width of a depletion layer that is formed in the base layer by the trench gate.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Vehicle hood latch protector
InactiveUS20060082165A1Difficult and time-consumeAvoid latchBurglar prevention lockingAnti-theft devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:AUTOGUARD DEVICES
Method of making an improved field oxide isolation structure for semiconductor integrated circuits having higher field oxide threshold voltages
InactiveUS6054368ARaise the threshold voltageReduce leakage currentTransistorSolid-state devicesRefresh cycleLOCOS
A method and structure for forming a modified field oxide region having increased field oxide threshold voltages (Vth) and / or reduced leakage currents between adjacent device areas is achieved. The method involves forming a field oxide using the conventional local oxidation of silicon (LOCOS) using a patterned silicon nitride layer as a barrier to oxidation. After forming the LOCOS field oxide by thermal oxidation and removing the silicon nitride, a conformal insulating layer composed of silicon oxide is deposited and anisotropically etched back to form sidewall insulating portions over the bird's beak on the edge of the LOCOS field oxide, thereby forming a new modified field oxide. P-channel implants are formed in the device areas. Then a second implant is used to implant through the modified field oxide to provide channel-stop regions with modified profiles that increase the field oxide Vth and / or reduce leakage current between device areas. This improved field oxide / channel-stop structure is particularly useful for reducing the leakage current on DRAM cells thereby increasing the refresh cycle times.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
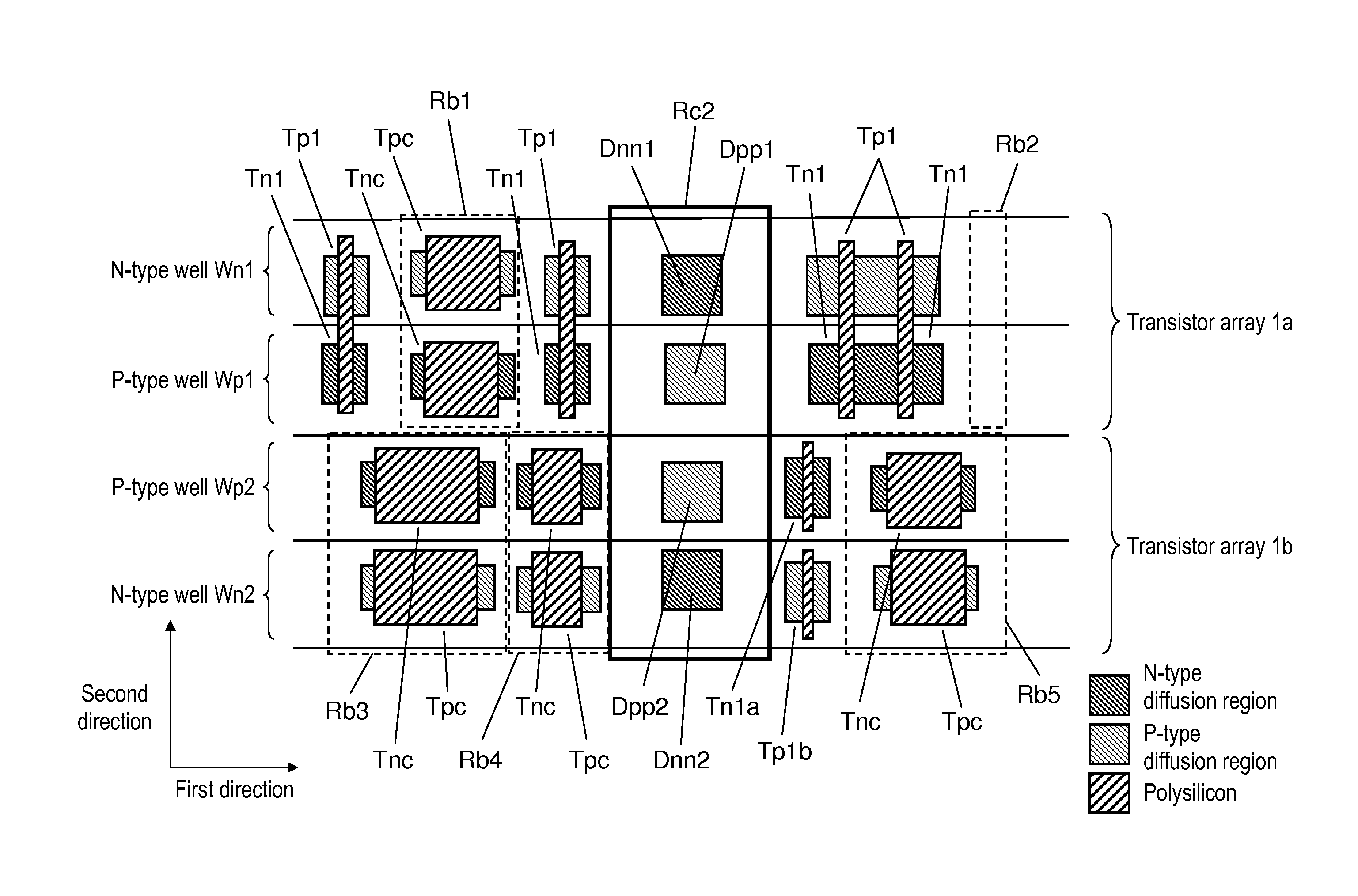
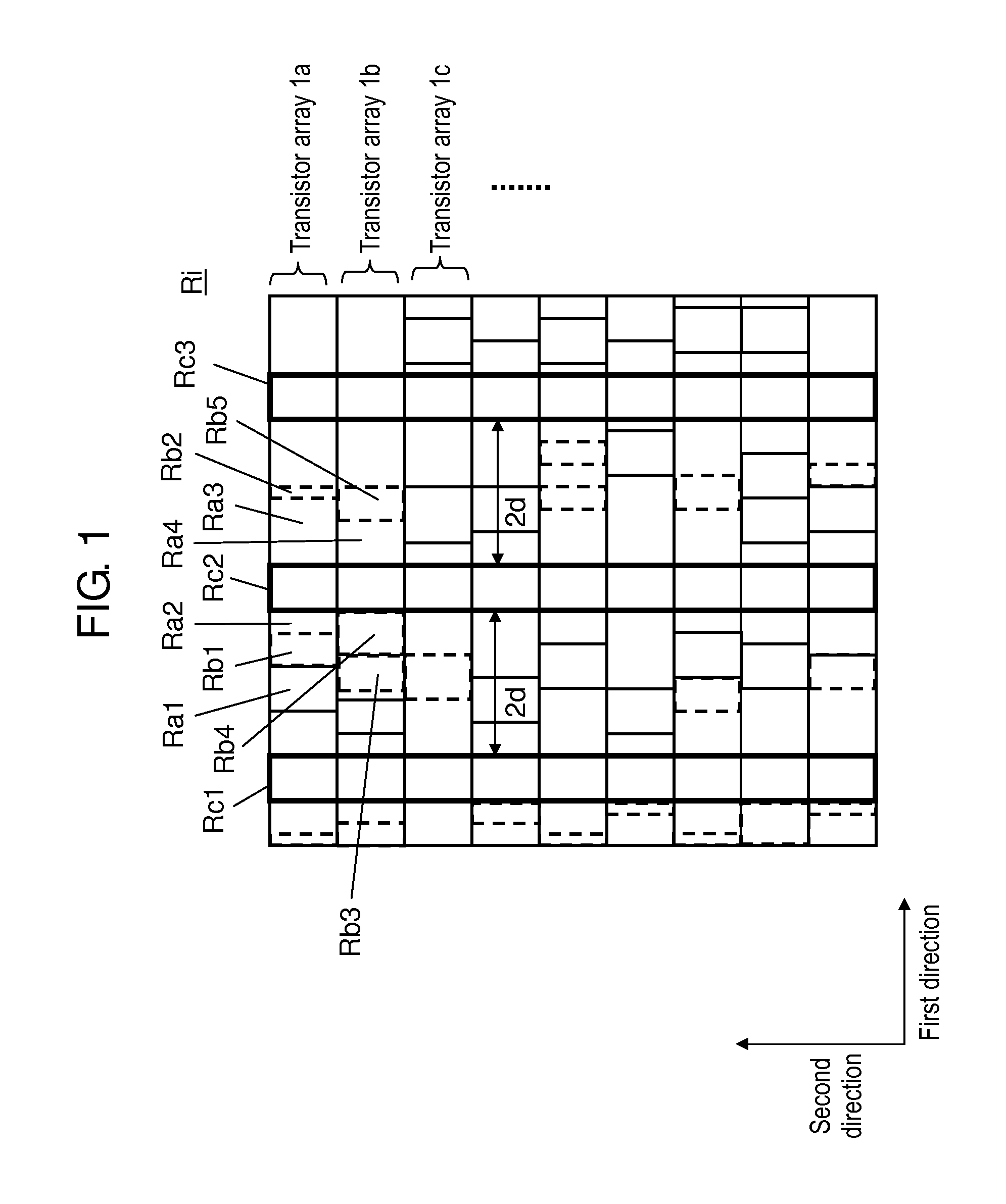
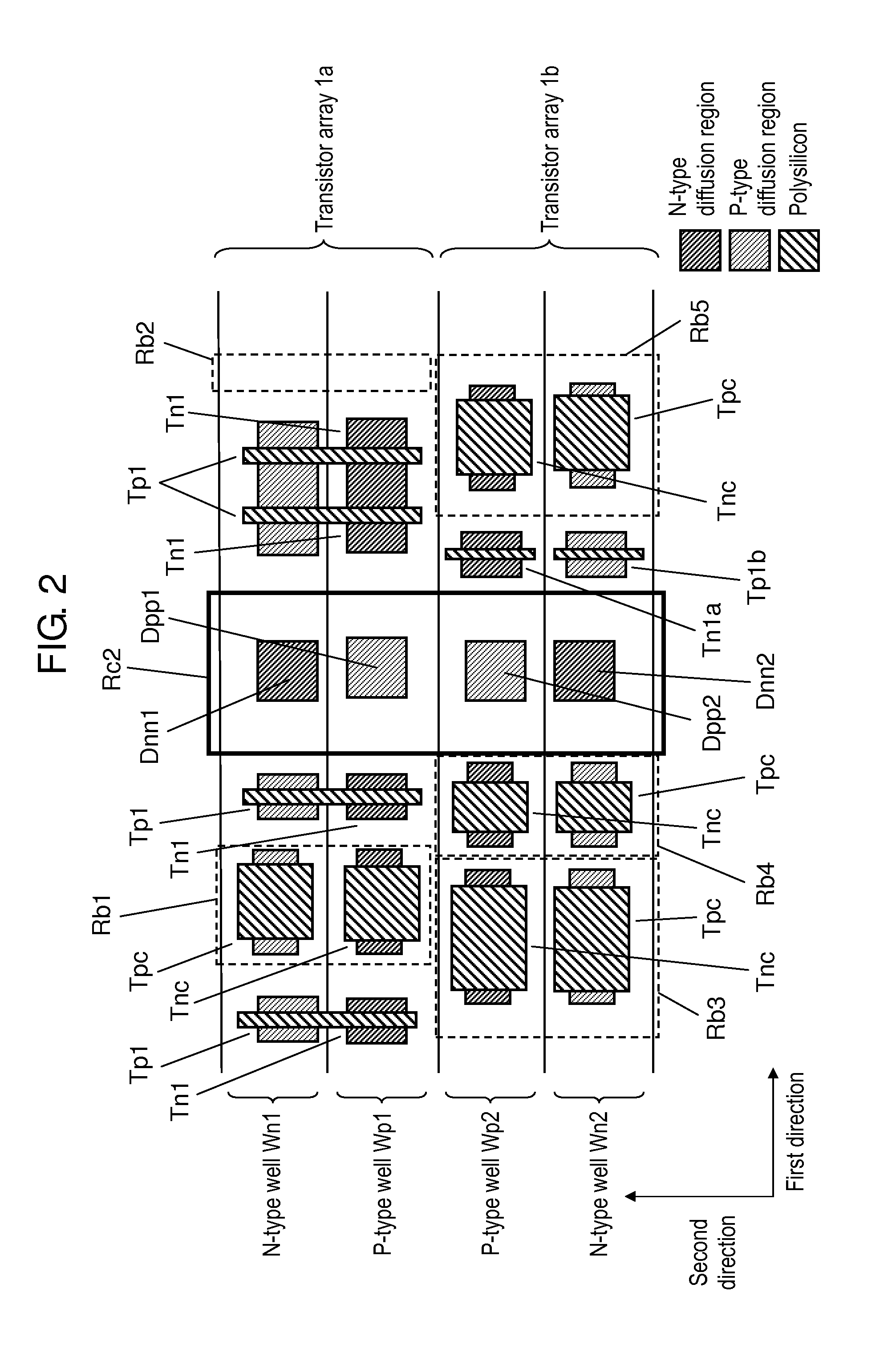
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
ActiveUS20140299920A1Increase the areaReduce in quantitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceEngineering
The present disclosure provides a layout of a semiconductor integrated circuit device that can assure a lot of substrate contact regions, and can surely suppress latch-up without increasing an area of a whole semiconductor integrated circuit and without significantly decreasing a decoupling capacitance element. In a margin region, a transistor serving as a decoupling capacitance and a substrate contact are disposed as a pair on a P-type well. In the margin region, a transistor serving as a decoupling capacitance and a substrate contact are disposed as a pair on an N-type well.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
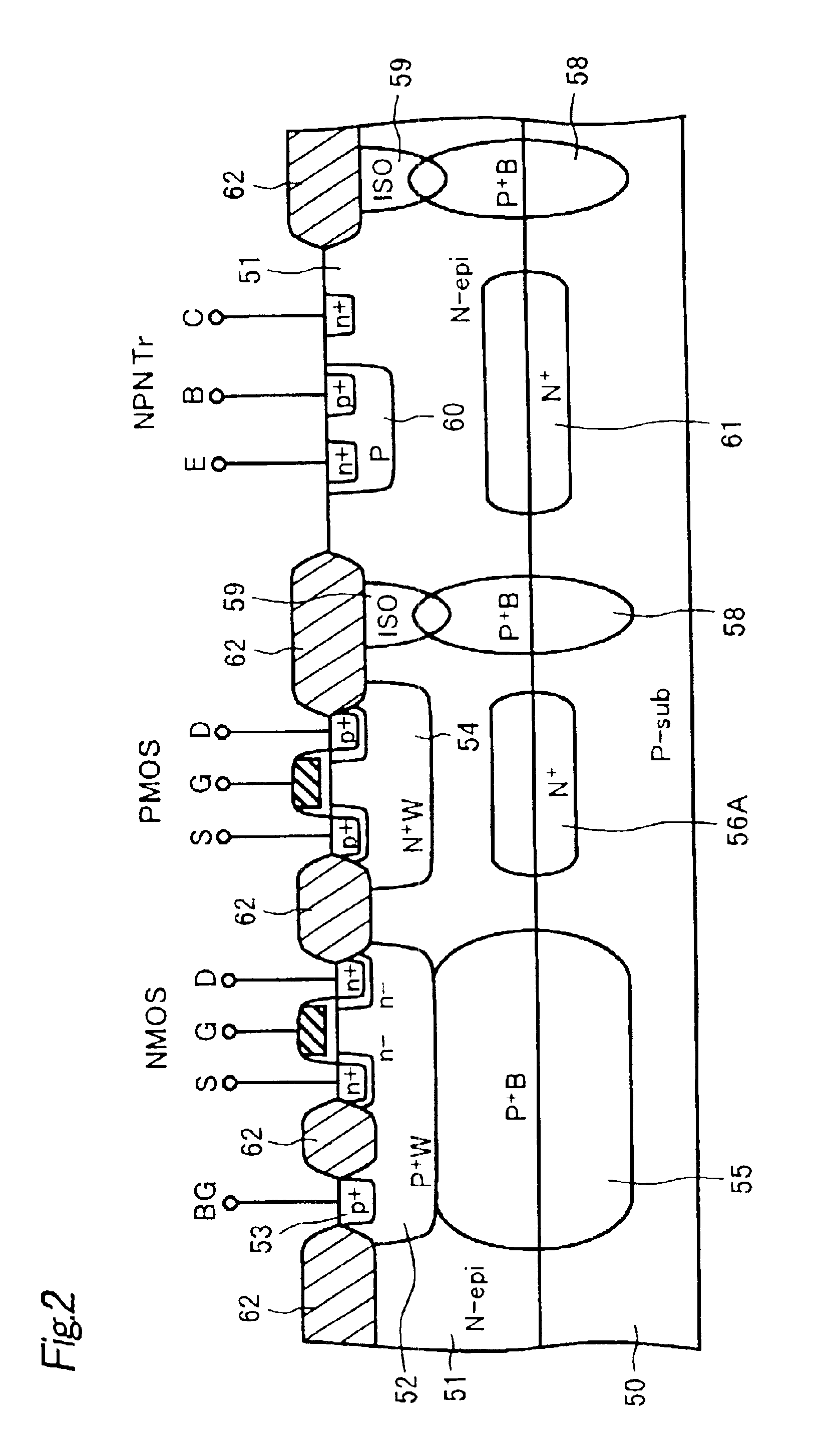
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
Disclosed are a semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing the same. The semiconductor device includes at least two of first and second conductive-type high-voltage transistors and first and second conductive-type low-voltage transistors. The first conductive-type high-voltage transistor include a first conductive-type well in a semiconductor substrate, a device isolation film in the first conductive-type well, a gate pattern on the first conductive-type well, second conductive-type drift regions in the semiconductor substrate at opposite sides of the gate pattern, second conductive-type source and drain regions in the second conductive-type drift region, a pick-up region to receive a bias voltage, and a first latch-up inhibiting region under the pick-up region. Accordingly, it is possible to reduce and prevent latchup without using a double guard ring and to eliminate an additional process to form first and second latch-up inhibiting regions.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
Adventure door
Owner:IVIE CALVIN L
Adjustable maintaining voltage type electronic static discharge protecting circuit
ActiveCN104392983AVenting is effectiveFully ventedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesVoltage regulator moduleComputer module
The invention relates to the field of electronic static discharge (ESD) protecting circuits of integrated circuit chips, and in particular relates to an instantaneously-triggered and adjustable maintaining voltage type ESD protecting circuit. The adjustable maintaining voltage type electronic static discharge protecting circuit comprises an instantaneous triggering module, a release device controlled silicon and a maintaining voltage regulating module; the maintaining voltage regulating module is connected with the controlled silicon and comprises a resistor R2, a capacitor C2, an inverter INV1, a PMOS (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) Mp1 and a PMOS MP2. With the adoption of the adjustable maintaining voltage type electronic static discharge protecting circuit, the maintaining voltage can be kept to be greatly less than the power supply voltage when then chip is in an idle state, and thus the electronic static charge can be fully released; when the chip is in a working state, the maintaining voltage is more than the power supply voltage to avoid the latch-up effect.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS7800183B2Improving RBSOAAvoid latchSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrench gateImpurity
A semiconductor device includes a substrate of a first conductivity type, a base region of a second conductivity type, a source region of the first conductivity type, a collector region of the second conductivity type, a trench gate, which is formed in a trench via a gate insulation film, an electrically conductive layer, which is formed within a contact trench that is formed through the source region, a source electrode, which is in contact with the electrically conductive layer and the source region, and a latch-up suppression region of the second conductivity type, which is formed within the base region, in contact with the electrically conductive layer, and higher in impurity concentration than the base region. The distance between the gate insulation film and the latch-up suppression region is not less than the maximum width of a depletion layer that is formed in the base layer by the trench gate.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Semiconductor device and its production method
InactiveCN102315219AIncrease impurity concentrationAvoid latchTransistorSolid-state devicesImpuritySemiconductor device
The invention provides a semiconductor device and its production method. The semiconductor device in the invention includes: a semiconductor substrate of a first conductive type; a first well region of the first conductive type formed in the semiconductor substrate; an epitaxial region of a second conductive type formed in the semiconductor substrate and arranged in a region adjacent to the first well region; a buried region of the second conductive type that is formed in a region at a lower part of the epitaxial region and that has an impurity concentration higher than that of the epitaxial region; a trench formed at boundaries between the first well region and the epitaxial region, and between the first well region and the buried region; a first semiconductor element that is formed on the first well; and a second semiconductor element that is formed on the epitaxial region.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com