A kind of soi device resistant to total dose irradiation and preparation method thereof
An anti-total dose and device technology, applied in the direction of electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device components, etc., can solve the problems of limited protection ability, complex coating process, lead toxicity, etc., achieve excellent structural characteristics, simplify Preparation process, effect of shielding total dose effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
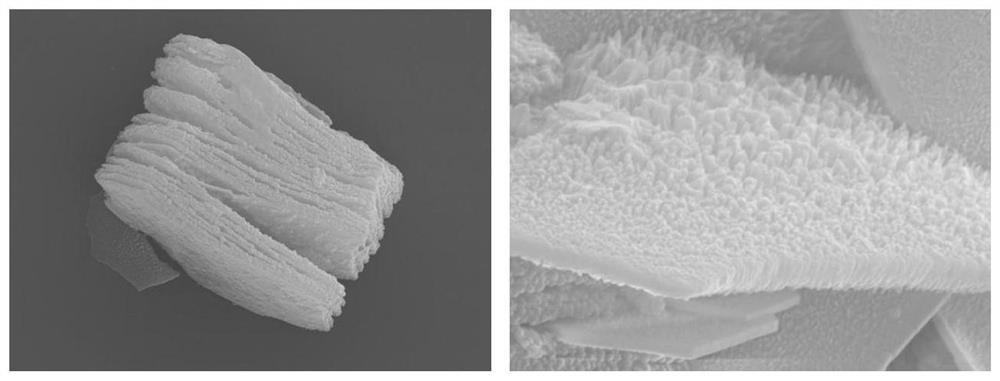
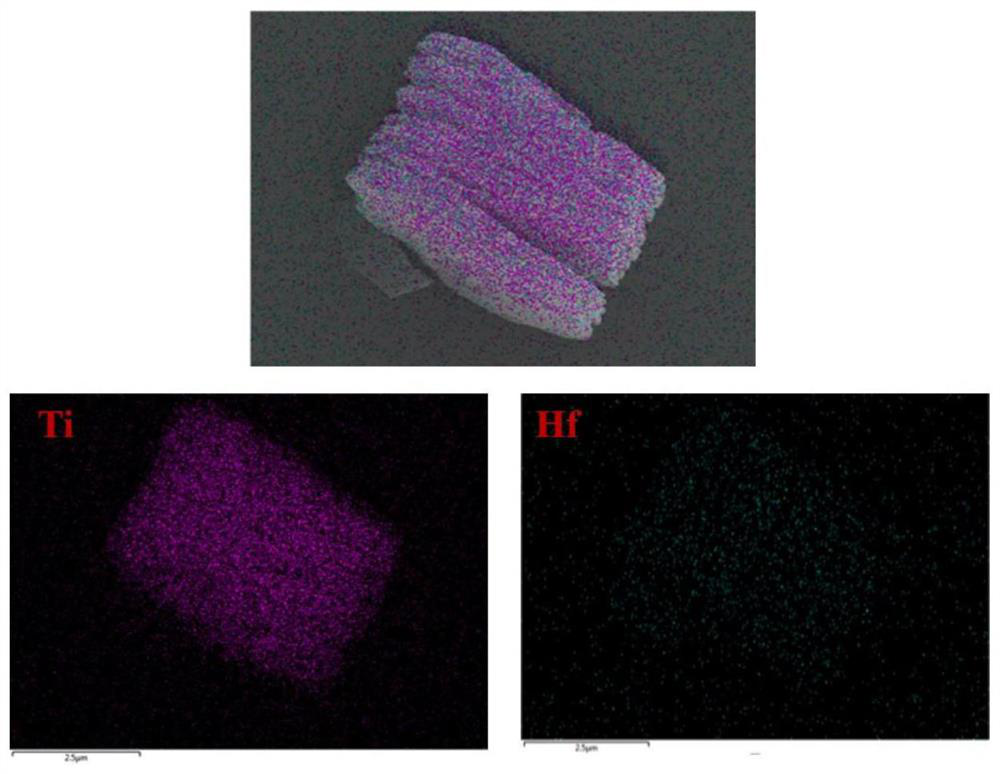
[0044] The Mxene etching was completed using method 1 (hydrofluoric acid etching), and then the Mxene was transferred into the chamber of the atomic layer deposition apparatus and subjected to high Z metal oxide HfO 2 Coating modification. The reaction temperature should be controlled at 200 °C, the pressure during the reaction should be controlled at 0.155torr, and the high-Z metal oxide source should be [(CH 3 )C 2 H 5 )N] 4 Hf, the pulse time is 0.15s, and the reaction time is 6s. After the pulse and the reaction are completed, high-purity nitrogen (99.999%) is used to purge the residual reactants and by-products in the pipeline and chamber for 60s. Then high-purity water was used as the oxygen source, the pulse time was 0.015s, and the reaction time was 6s. After the pulse reaction was completed, high-purity nitrogen (99.999%) was used to purge the residual reactants and by-products in the pipeline and chamber for 60s. The high-Z metal oxide source and the oxygen sourc...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2: The Mxene etching was completed by method 2 (HCl+LiF etching), and then the Mxene was transferred to the cavity of the atomic layer deposition device, and the high Z metal oxide HfO was carried out on it. 2 Coating modification. The reaction temperature should be controlled at 150°C, the pressure during the reaction should be controlled at 0.155torr, and the high-Z metal oxide source should be [(CH 3 )C 2 H 5 )N] 4 Hf, the pulse time is 0.15s, and the reaction time is 6s. After the pulse and the reaction are completed, high-purity nitrogen (99.999%) is used to purge the residual reactants and by-products in the pipeline and chamber for 60s. Then high-purity water was used as the oxygen source, the pulse time was 0.015s, and the reaction time was 6s. After the pulse reaction was completed, high-purity nitrogen (99.999%) was used to purge the residual reactants and by-products in the pipeline and chamber for 60s. The high-Z metal oxide source and the oxygen...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3: The Mxene etching was completed by method 3 (NaOH hydrothermal etching), and then the Mxene was transferred to the cavity of the atomic layer deposition device, and the high Z metal oxide HfO was carried out on it. 2 Coating modification. The reaction temperature should be controlled at 180°C, the pressure during the reaction should be controlled at 0.155torr, and the high-Z metal oxide source should be [(CH 3 )C 2 H 5 )N] 4 Hf, the pulse time is 0.15s, and the reaction time is 6s. After the pulse and the reaction are completed, high-purity nitrogen (99.999%) is used to purge the residual reactants and by-products in the pipeline and chamber for 60s. Then high-purity water was used as the oxygen source, the pulse time was 0.015s, and the reaction time was 6s. After the pulse reaction was completed, high-purity nitrogen (99.999%) was used to purge the residual reactants and by-products in the pipeline and chamber for 60s. The high-Z metal oxide source and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com