New lactic acid bacteria
A strain and amino acid technology, applied in bacteria, dairy products, microbial-based methods, etc., can solve problems such as expensive and complicated manufacturing processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0319] Example 1: Isolation of S. thermophilus exhibiting a full-stop phenotype.
[0320] Dilutions of cultures of the DGCC7984 strain were plated on the surface of M17 supplemented with 5 g / L sucrose agar plates. After incubation at 37°C for 48 hours, two isolated colonies of the DGCC7984 strain were picked and propagated in M17 liquid medium supplemented with 20 g / L sucrose at 37°C for 24 hours. These two subclones of the DGCC7984 strain were named DGCC12455 and DGCC12456. The acidifying properties of strains DGCC12455 and DGCC12456 were investigated as follows: both strains were inoculated into M17 liquid medium supplemented with 30 g / L lactose and then incubated overnight at 37°C. The culture was washed (v / v) in tryptone saline solution (tryptone 1 g / L, NaCl 8.5 g / L) as follows: the culture was centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 5 min; the pellet was resuspended in 10 mL of tryptone saline in solution. The washed culture was inoculated at 1% (v / v) into 100 mL of UHT semi-skimm...
Embodiment 2
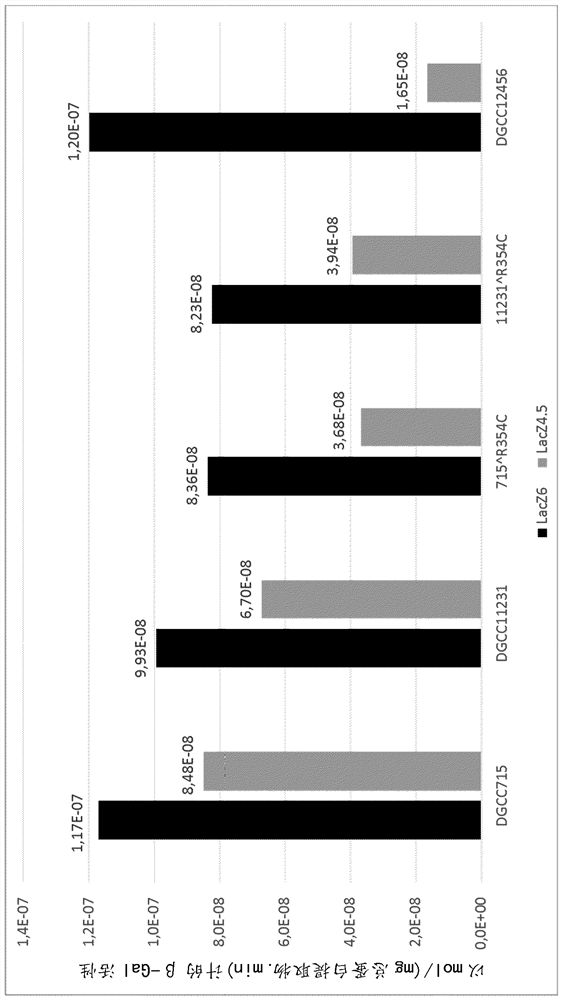
[0322] Example 2: DGCC12456 lacZ Identification of Genetic Differences in Genes
[0323] The genomes of strains DGCC7984 and DGCC12456 were sequenced and compared. Among them, in lacZ Differences between the two strains were identified in genes. lacZ Genes have been described (van den Bogaard et al., 2000; Vaughan et al., 2001) to encode β-galactosidase, the enzyme responsible for the hydrolysis of lactose into glucose and galactose. In the DGCC12456 genome, lacZ The C base at position 1060 of the gene was replaced with a T base, resulting in a non-conservative amino acid change, and the arginine at position 354 of β-galactosidase was replaced with a cysteine (R354C substitution). Therefore, DGCC7984 has a β-galactosidase-encoding lacZ Alleles, the sequence of the β-galactosidase is as defined in SEQ ID NO: 2, and the DGCC12456 strain has the sequence encoding the β-galactosidase lacZ Alleles, the sequence of the β-galactosidase is as defined in SEQ ID NO:4. In contra...
Embodiment 3
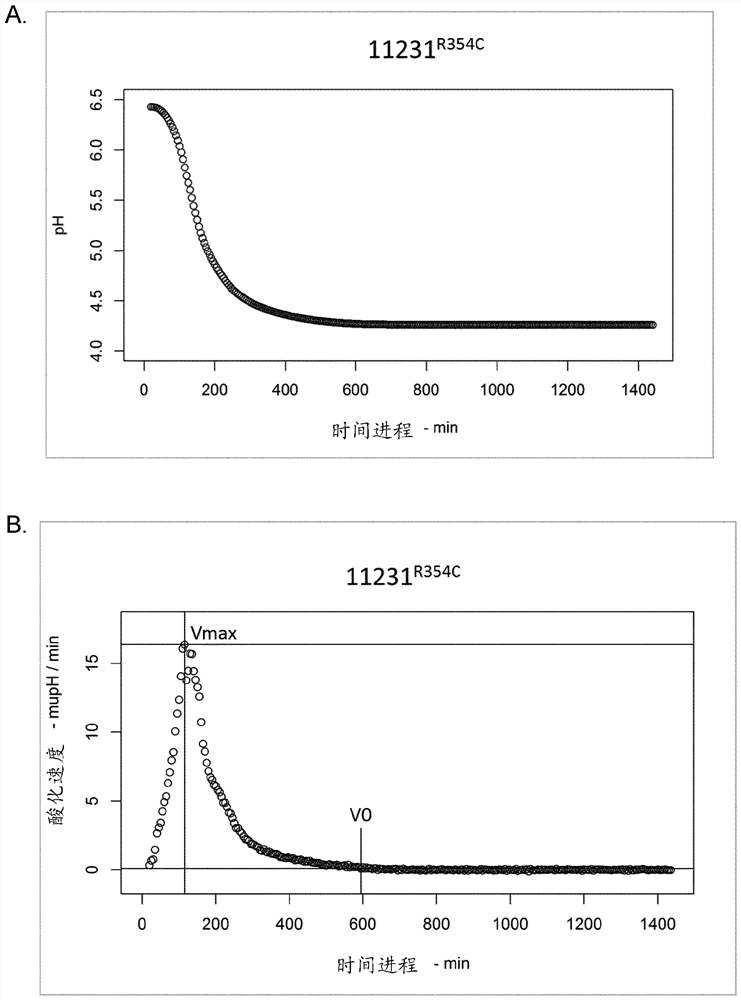
[0328] Example 3: Comparison of the acidification curves of S. thermophilus strains DGCC715 and DGCC11231 and their derivatives encoding a β-galactosidase having the sequence SEQ ID NO:4 instead of SEQ ID NO:2 (R354C substitution).
[0329] Builds are named 715 respectively R354C and 11231 R354C Derivatives of strains DGCC715 and DGCC11231. Inserted into the DGCC12456's lacZ Gene (encoding beta-galactosidase with cysteine (C) at position 354) to replace that of strains DGCC715 and DGCC11231 lacZ Gene. Indeed, from DGCC12456 DNA PCR amplified lacZ Gene. Competent cells of DGCC715 or DGCC11231 were prepared and transformed with amplified DNA. Transformants were verified by sequencing.
[0330] Evaluation of Streptococcus thermophilus strains DGCC715, DGCC11231, 715 R354C and 11231 R354C Capacity to ferment milk as described in the Materials and methods section [Assay C]. The pH was recorded over time using a CINAC device, and the results are presented at figure 2 A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com