Cleaning method of agarose microspheres
A technology of agarose microspheres and agarose heat, applied in separation methods, microsphere preparation, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of high recycling costs, environmental pollution, etc., achieve stable yields, easy cleaning process, The effect of high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] S1: Preparation of agarose microspheres: Weigh 4.0g of agarose powder in 100mL of purified water, heat it to dissolve completely, which is the water phase; weigh 12g of Span 80 in 300mL of liquid paraffin, stir well and control the temperature at 60~ 80°C, as the oil phase. Drop the water phase into the oil phase, stir at 60-80°C for 30-60 minutes, cool at 2-5°C / min to below 20°C, and let it solidify for 1 hour to form microspheres.
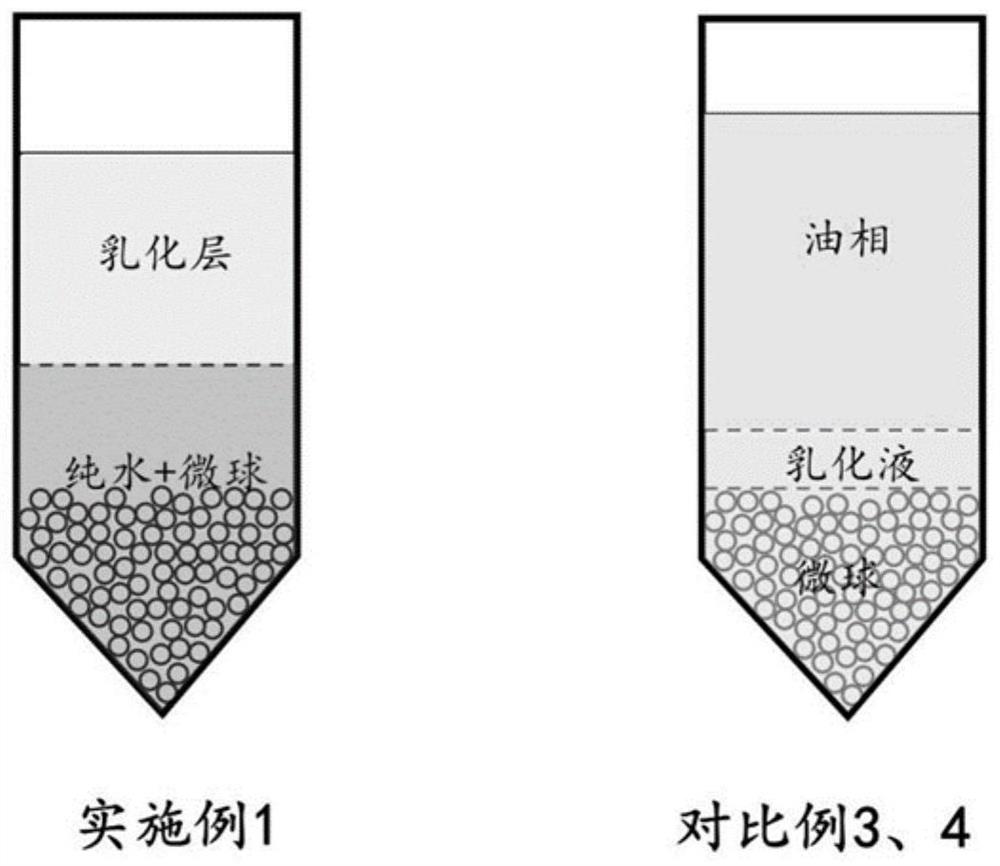
[0042] S2: After cooling and solidifying the emulsion into balls, let it stand at room temperature for 16-24 hours. After standing and stratifying, the upper layer of the emulsion is a clear oil phase, about 200mL, and the lower layer is an emulsified layer; suck out the upper oil phase to obtain Emulsion layer of microspheres.
[0043] S3: After adding an equal volume of purified water to the obtained emulsified layer, after stirring at a constant speed of 150 rpm for 10 minutes, let it stand for 15 minutes to separate the water phase fr...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Compared with embodiment 1, embodiment 2 only increases the number of repetitions of step S3. The number of repetitions of step S3 in step S4 in embodiment 2 is 4 times, and the rest of the steps are the same as in embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here. Table 2 records the mass of microspheres collected after step S3 each time.
[0049] Table 2 Effect of the number of operations in step S3 on the quality of the obtained microspheres
[0050] Operations 1 2 3 4 5 Mass of each microsphere / g 79.64 10.81 1.37 0.52 0.03 Total mass of microspheres / g 79.64 90.45 91.82 92.34 92.37 % of total mass 86.22% 97.92% 99.40% 99.97% ——
[0051] As can be seen from Table 2, when the number of operations of step S3 is the 4th time, almost all microspheres have been obtained, that is, when the number of times of repeating step S3 in step S4 is 3 times, all microspheres in the emulsified layer can be separate out. And step S3 needs t...
Embodiment 3~6
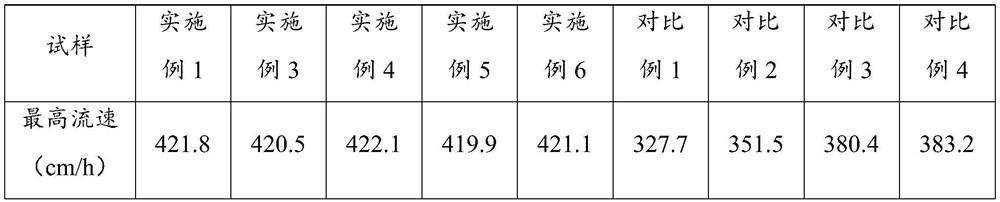
[0053] Compared with Example 1, Examples 3-6 are different in that the amount of purified water added and the stirring rate involved in step S3 are changed, and the rest of the steps are the same as in Example 1, and will not be repeated here. The specific parameters are shown in Table 3.
[0054] Table 3 Parameter changes of Examples 3 to 6 and the quality of the obtained microspheres
[0055] Example Volume ratio of purified water to emulsified layer Stirring rate / rpm Microsphere mass / g 3 0.5:1 150 70.73 4 3:1 150 92.17 5 1:1 50 91.35 6 1:1 200 91.78
[0056] Compared with Example 1, Examples 3 and 4 only changed the volume ratio of the purified water added in step S3 to the emulsified layer. It can be seen from Table 3 that the volume ratio of purified water to the emulsified layer will affect the quality of the finally obtained microspheres, and if the volume ratio is small, the quality of the obtained microspheres will decr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com