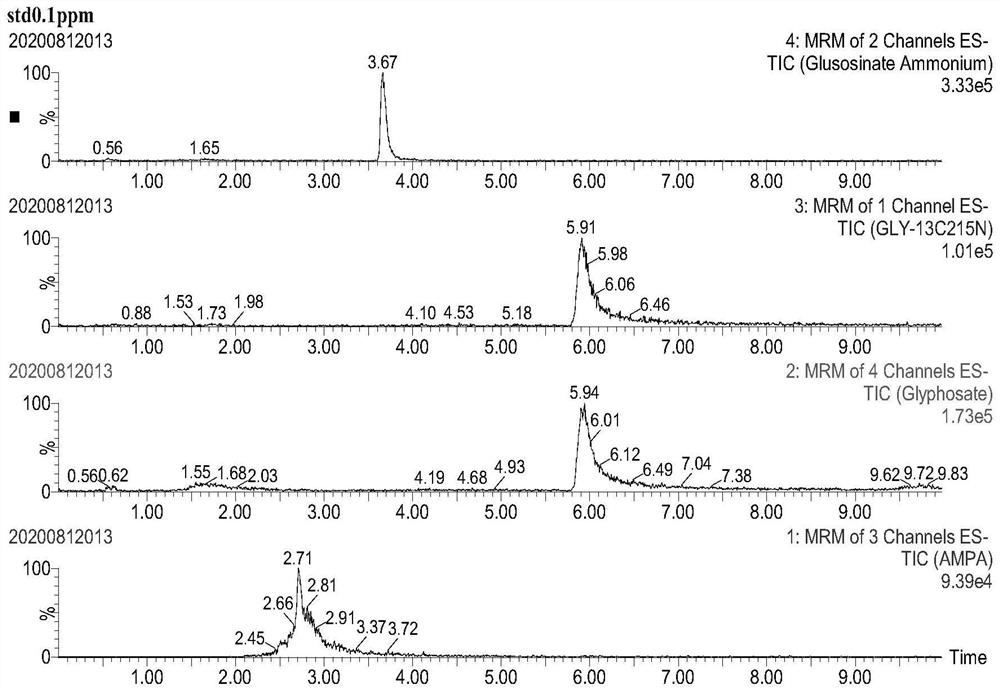
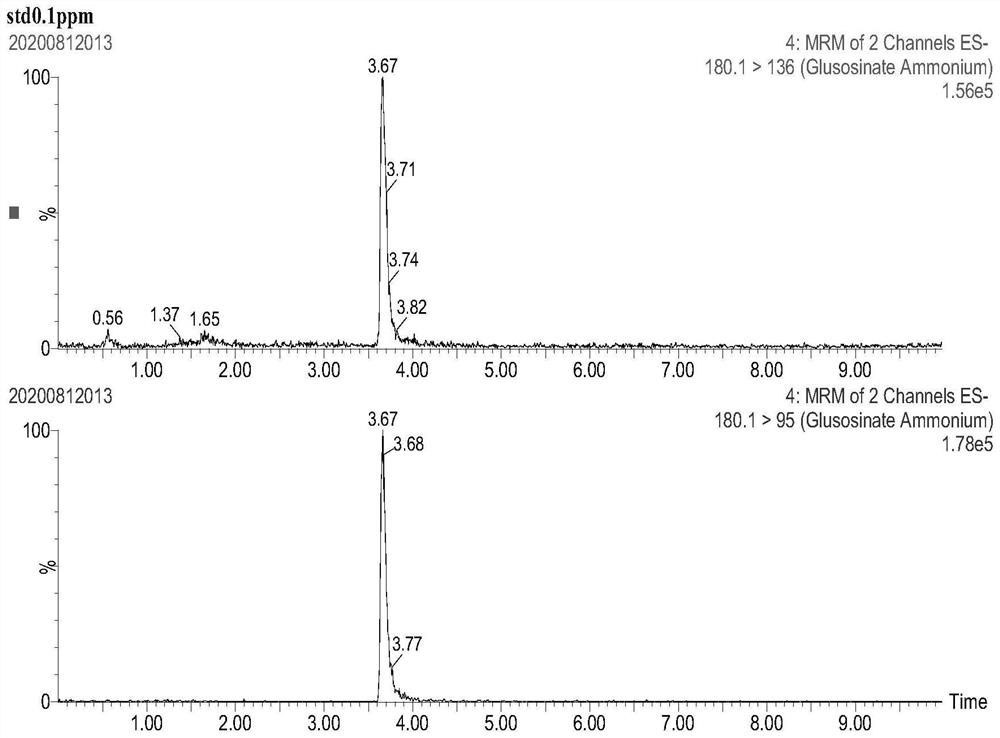
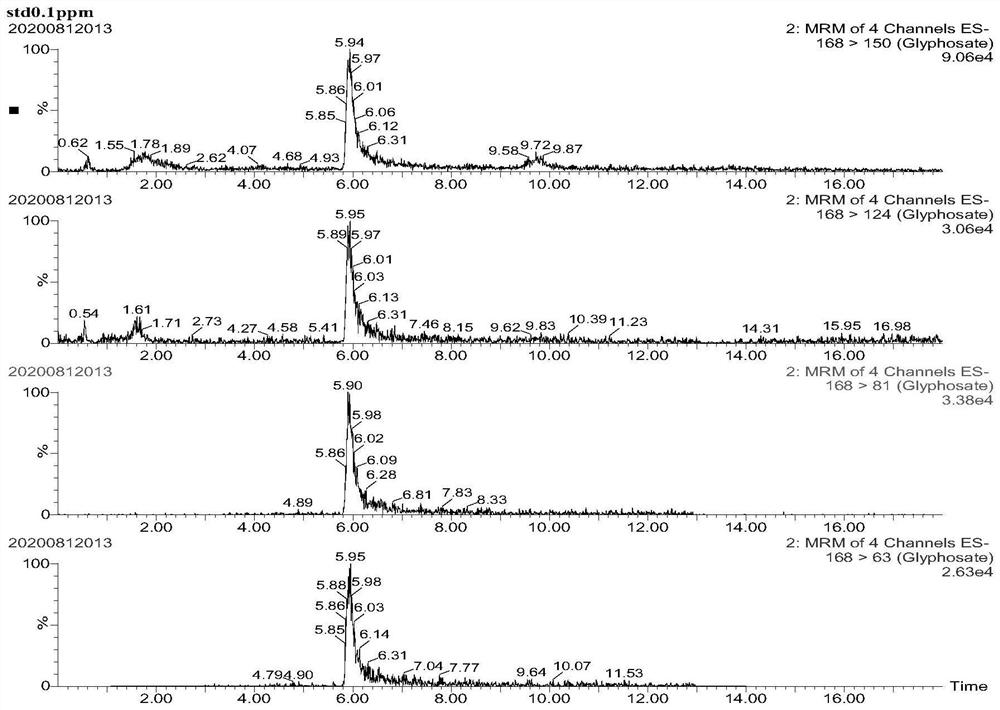
Method for determining residual quantity of glyphosate, glufosinate-ammonium and metabolite aminomethylphosphonic acid of glyphosate and glufosinate-ammonium in agricultural products
A technology of aminomethylphosphonic acid and medium glyphosate, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, measuring devices, and other chemical processes, can solve the problems of reproducibility and poor precision of analysis results, and achieve short time-consuming, High detection efficiency and accurate quantitative results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Determination of glyphosate, glufosinate-ammonium and aminomethylphosphonic acid residues in rice samples.
[0046] (1) Sample pretreatment
[0047] Weigh 2g of rice sample into a 50mL EP tube, pulverize it thoroughly, then add 10mL of deionized water and 10mL of dichloromethane in turn, mix and shake for 60min, then centrifuge at 8000r / min for 10min, take 5mL of the supernatant; 10mL of methanol and 10mL of water were used to activate the C18 solid-phase microextraction column. After the activation was completed, let it stand for 5 minutes; take the above-mentioned clear liquid onto the column for purification treatment. It is worth noting that the flow rate of the clear liquid through the SPE column should not exceed 6 μL / s , collect the effluent; finally, the purified sample is detected by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.
[0048] (2) Preparation of standard working solution:
[0049] Use the rice that has been tested to be free of glyphosate, glufosinate a...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Determination of glyphosate, glufosinate-ammonium and aminomethylphosphonic acid residues in lettuce samples.
[0105] (1) Sample pretreatment
[0106] Weigh 5g lettuce sample in a 50mL EP tube, pulverize it thoroughly, then add 10mL deionized water and 10mL dichloromethane in turn, mix and shake for 60min, then centrifuge at 8000r / min for 10min, take 9mL supernatant, and then Add 1mL of acetonitrile; use 10mL of methanol and 10mL of water to activate the C18 solid-phase microextraction column successively, and let it stand for 5 minutes after the activation; take the above-mentioned clear liquid onto the column for purification treatment. It is worth noting that the flow rate cannot be faster than 6μL / s, the effluent was collected; finally, the purified sample was detected by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.
[0107] (2) Preparation of standard working solution
[0108] Use the lettuce that has been tested to be free of glyphosate, glufosinate and aminomethy...
Embodiment 3
[0117] Determination of glyphosate, glufosinate-ammonium and aminomethylphosphonic acid residues in potato samples.
[0118] (1) Sample pretreatment
[0119] Weigh 5g of potatoes into a 50mL EP tube, crush them thoroughly, then add 10mL of deionized water, 10mL of dichloromethane and 2mL of dichloromethane in turn, mix and shake for 60min, then centrifuge at 8000r / min for 10min, take 9mL of the supernatant Then add 1mL acetonitrile; use 10mL methanol, 10mL acetonitrile and 10mL water to activate the C18 solid-phase microextraction column successively, and let it stand for 5min after the activation is completed; take the above-mentioned clear solution to the column for purification treatment, it is worth noting that, The flow rate cannot be faster than 1 drop / s, and the effluent is collected; finally, the purified sample is detected by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.
[0120] (2) Preparation of standard working solution
[0121] Use the tested potatoes that do not co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com