Soybean sterile gene mutant, construction method and application in photosensitive fertility regulation
A construction method and soybean technology, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of long time and cumbersome process, and achieve the effect of reducing time, obvious economic value, and low precision requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
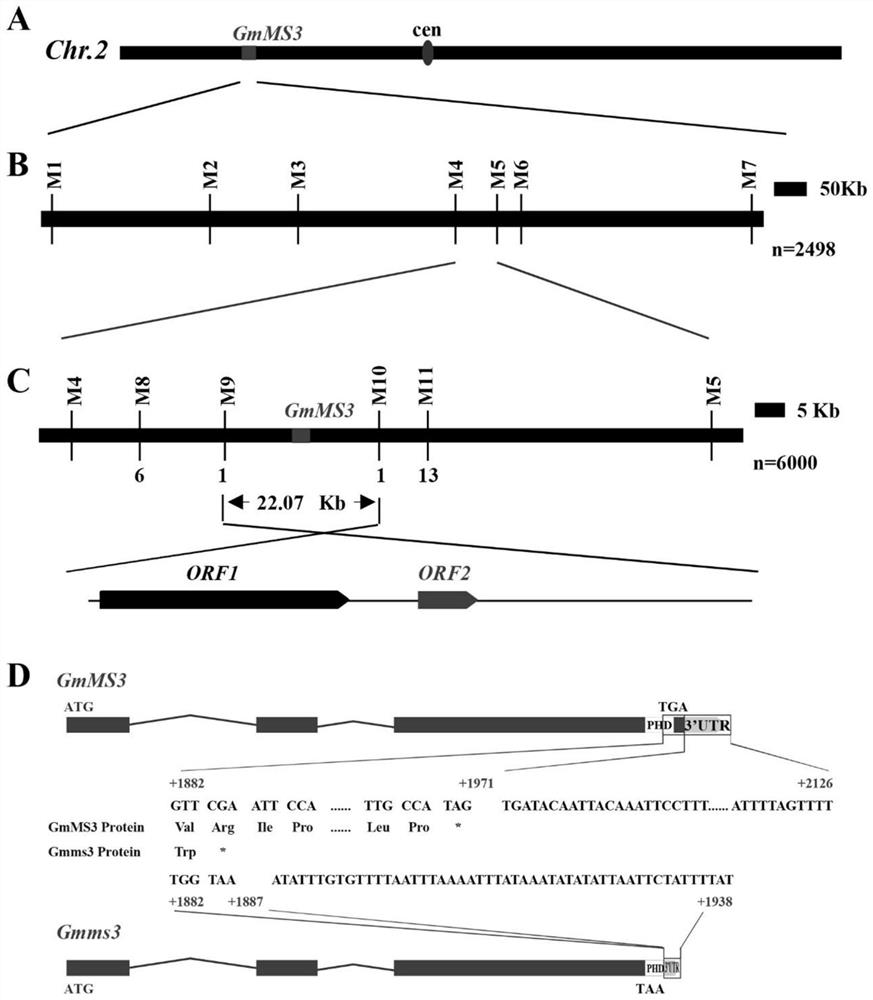
[0062] In this embodiment, the sterile mutant strain obtained from the Changchun test base is used as a material, and a soybean sterile gene mutant is provided by gene mapping method, the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID No. The difference in gene sequence is that the amino acid residue encoded by codons 10236294-10236296 of the wild-type ORF2 gene sequence is valine, while the amino acid residue encoded by nucleotides +1882-+1884 of the mutant in this example is is tryptophan, and the codon corresponding to nucleotides +1885 to +1887 of the mutant in this embodiment is the stop codon TAA.
[0063] The specific positioning method is as follows:
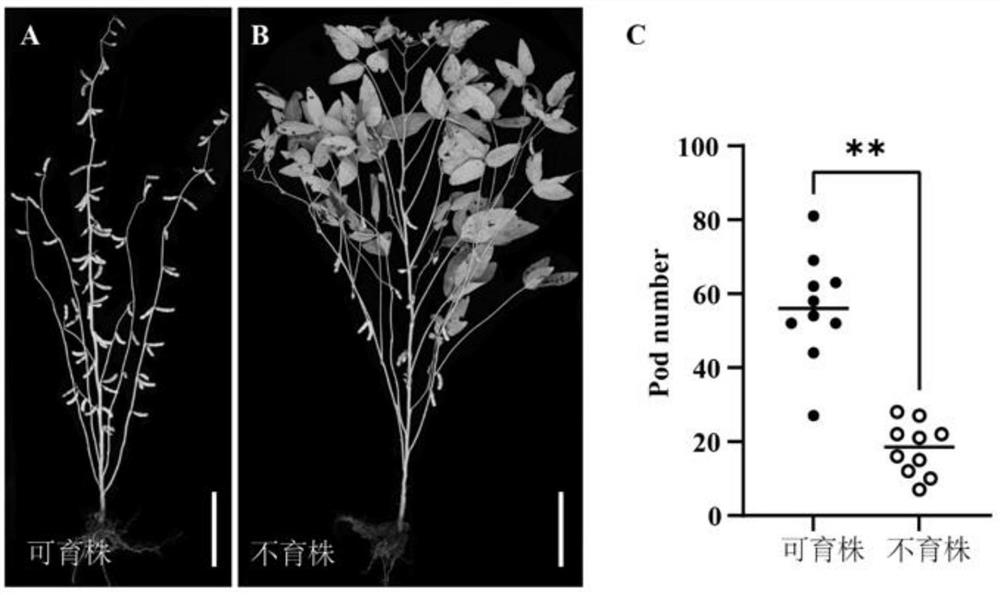
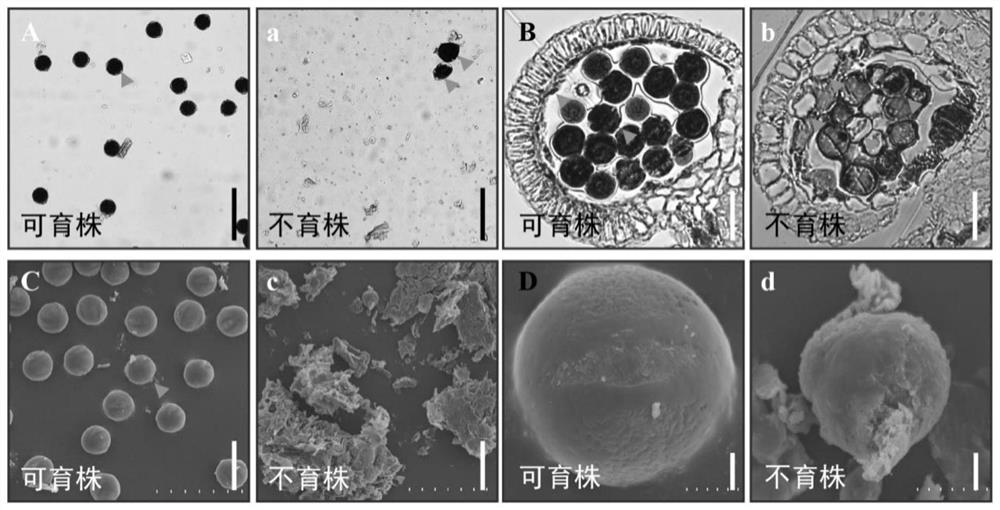
[0064] First, the results of mature period of the sterile plants in the Changchun Experimental Base of Jilin (43°50′N, from the first flowering stage to the final flowering stage: day and night time range 14:50′ / 9:10′-15:25′ / 8:35′) were studied. number of pods, the investigation was carried out and the results were as ...
Embodiment 2
[0070] This embodiment also provides a soybean sterility gene mutant, which differs from the embodiment 1 in that the amino acid residue encoded by nucleotides +1882-+1884 of the mutant in this embodiment is valine.
Embodiment 3
[0072] In order to verify the conclusion that the abnormal expression of the PHD-finger domain of the ORF2 gene of soybean chromosome 2 leads to the conclusion of fertility changes, this example uses CRISPR gene editing technology to construct the KNOCKOUT vector, and its two target sequences are respectively located in soybean 2. The positions 55bp-74bp and 64bp-83bp upstream of the PHD-finger domain of the chromosome ORF2 gene, and the KNOCKOUT vector was genetically transformed into the broad-adapted soybean variety Williams82, and T 1 transgenic plants.
[0073] The primer sequences targeting 55bp~74bp (primer pair 1) and 64bp~83bp (primer pair 2) are shown in Table 2:
[0074] Table 2 Primer sequences targeting 55bp~74bp and 64bp~83bp
[0075]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com