Monopolymer composite material based on planar silkworm cocoons and preparation method of monopolymer composite material
A composite material and polymer technology, applied in the field of composite materials, can solve the problems of difficult separation of fibers and polymers, incompatibility of the fiber-matrix interface, and degradation of composite material properties, and achieve excellent mechanical properties, good mechanical properties and acceptable performance. Biodegradable, easy to handle effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
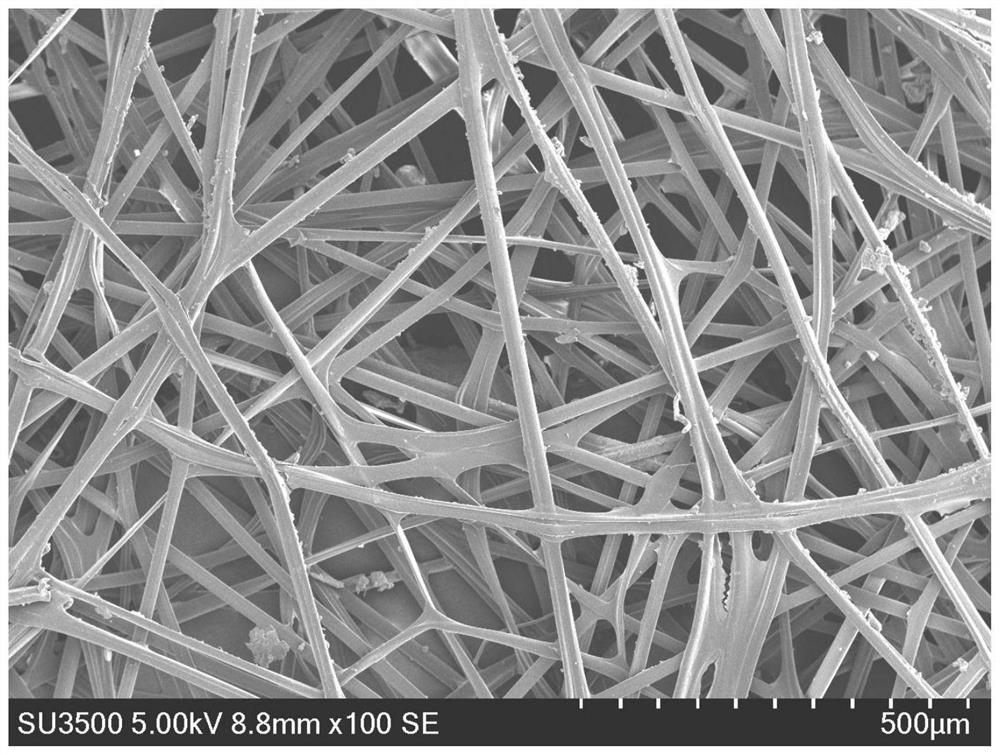
[0028] (1) Place cooked silkworms on a flat plate and spin silk to obtain a planar cocoon with a thickness of 1mm. The SEM photos of its surface morphology are as follows: figure 1 shown;
[0029] (2) Degumming the obtained planar cocoons in 0.5% (mass volume fraction) anhydrous sodium carbonate aqueous solution for 30 minutes, fully dissolved in 9.3M lithium bromide aqueous solution after drying, and then dialyzed in deionized water for 3 days , and then place the aqueous solution of silk protein obtained by dialysis in a -20°C refrigerator to freeze completely, and then use a freeze dryer to dry it in a low-temperature vacuum to finally obtain a solid silk protein;
[0030] (3) dissolving the silk protein solid obtained in step (2) with hexafluoroisopropanol to obtain a 15% (mass volume fraction) silk solution;
[0031] (4) Pour the silk solution obtained in step (3) into the flat silk cocoons, and make the solution submerge the flat silk cocoons, and then place the composi...
Embodiment 2
[0034] (1) placing the cooked silkworm on a flat plate to spin silk to obtain a planar cocoon with a thickness of 2mm;
[0035] (2) Degumming the obtained planar cocoons in 0.5% (mass volume fraction) anhydrous sodium carbonate aqueous solution for 30 minutes, fully dissolved in 9.3M lithium bromide aqueous solution after drying, and then dialyzed in deionized water for 3 days , and then place the aqueous solution of silk protein obtained by dialysis in a -20°C refrigerator to freeze completely, and then use a freeze dryer to dry it in a low-temperature vacuum to finally obtain a solid silk protein;
[0036] (3) dissolving the silk protein solid obtained in step (2) with hexafluoroisopropanol to obtain a 10% (mass volume fraction) silk solution;
[0037] (4) Pour the silk solution obtained in step (3) into the flat silk cocoons, and make the solution submerge the flat silk cocoons, and then place the composite system at room temperature to dry naturally;
[0038] (5) The mate...
Embodiment 3
[0040] (1) placing the cooked silkworm on a flat plate to spin silk to obtain a planar cocoon with a thickness of 0.5mm;
[0041] (2) Degumming the obtained planar cocoons in 0.5% (mass volume fraction) anhydrous sodium carbonate aqueous solution for 30 minutes, fully dissolved in 9.3M lithium bromide aqueous solution after drying, and then dialyzed in deionized water for 3 days , and then place the aqueous solution of silk protein obtained by dialysis in a -20°C refrigerator to freeze completely, and then use a freeze dryer to dry it in a low-temperature vacuum to finally obtain a solid silk protein;
[0042] (3) dissolving the silk protein solid obtained in step (2) with hexafluoroisopropanol to obtain a 20% (mass volume fraction) silk solution;
[0043] (4) Pour the silk solution obtained in step (3) into the flat silk cocoons, and make the solution submerge the flat silk cocoons, and then place the composite system at room temperature to dry naturally;
[0044] (5) The ma...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| bending strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com