Preparation method of boron trifluoride and boron trifluoride mixed gas
A boron trifluoride and mixed gas technology, applied in the field of chemical engineering, can solve the problems of too many gas impurities, unable to further increase the use demand, low boron trifluoride yield, etc., to improve the content of F element, and to achieve high reaction conversion efficiency. , the effect of less by-products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
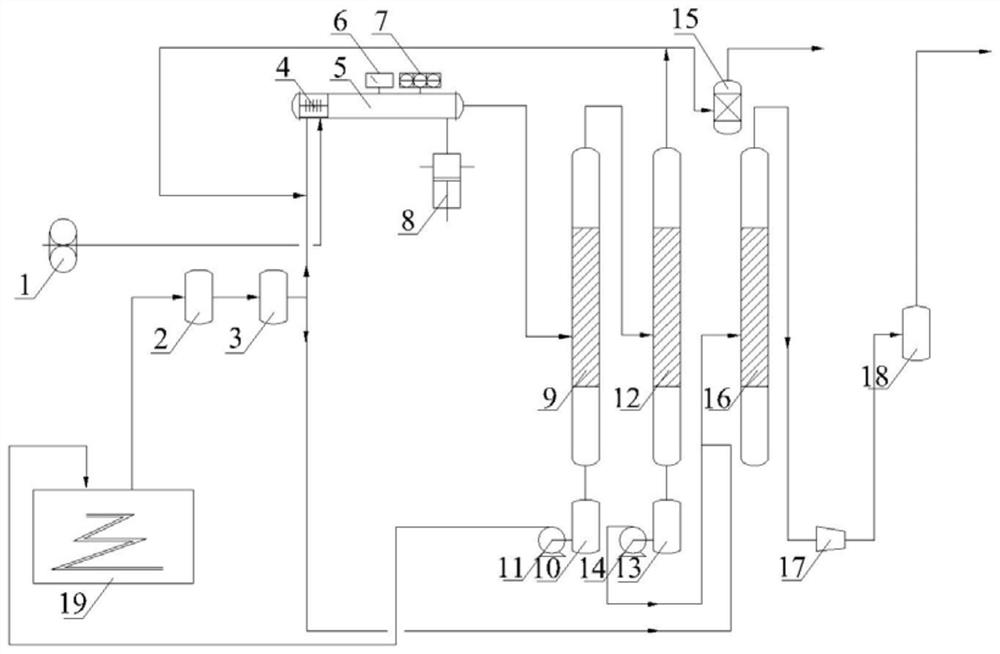
[0033] The fluorination reactor is a circular pipe fluorination reactor, the length of the reaction tube is 4.8m, and the inner diameter is 65mm.
[0034] Before the reaction, the pressure in the reaction tube was pumped to 180Pa by a vacuum pump, and the temperature was normal temperature, and then the reaction gas was slowly added to react, wherein the molar ratio of diborane and fluorine gas was controlled to be 1:19.1, and the mass ratio of diborane was 3.2%; in the specific reaction process, diborane enters the above-mentioned fluorination reactor after adjusting the flow rate to 1.8g / h, and the fluorine-containing mixed gas (the mass percentage of fluorine gas is 86%, and the rest is nitrogen) is adjusted to the flow rate of 55.0 g / h, enter the above-mentioned fluorination reactor to react;
[0035] The mixed gas obtained by the reaction is pressurized to a pressure of 0.15 MPa, and is successively subjected to the first-stage condensation separation and the second-stage...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the molar ratio of diborane and fluorine gas is controlled to be 1:16.9, and the mass ratio of diborane is 3.2%; in the specific reaction process, the flow rate of diborane is adjusted to 1.8g Enter the above-mentioned fluorination reactor after / h; the fluorine-containing mixed gas (the mass percentage of fluorine gas is 76%, and the rest is nitrogen) adjust the flow rate to 55.0g / h, enter the fluorination reactor according to the conditions described in Example 1 reaction;
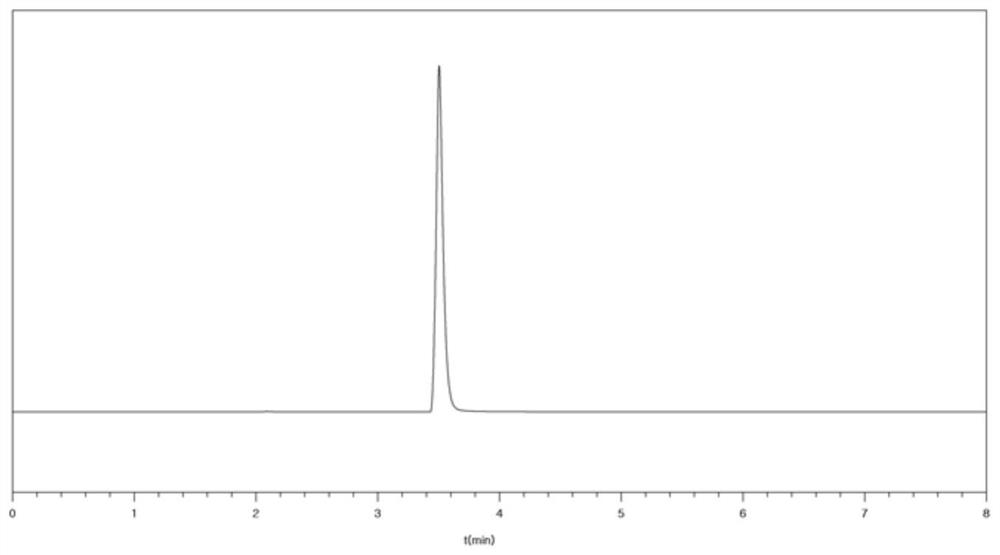
[0039] The mixed gas prepared by the reaction is pressurized to a pressure of 0.25 MPa, and the first stage and the second stage are condensed and separated successively, wherein the first stage separation condensation temperature is controlled at -25 ℃, and the second stage separation condensation temperature is controlled at -125 ℃; after secondary condensation, boron trifluoride liquid is obtained; a sample is detected by gas chromatogra...
Embodiment 3
[0042]The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the molar ratio of diborane and fluorine gas is controlled to be 1:10.0, and the mass ratio of diborane is 1.4%; in the specific reaction process, the flow rate of diborane is adjusted to 0.8g Enter the above-mentioned fluorination reactor after / h, the fluorine-containing mixed gas (the mass percentage of fluorine gas is 70%, and the rest is nitrogen), adjust the flow rate to 55.0g / h, enter the fluorination reactor as described in Example 1 conditioned response;
[0043] The obtained mixed gas is pressurized to a pressure of 0.25 MPa, followed by the first-stage condensation separation and the second-stage condensation separation, wherein the condensation temperature of the first-stage separation is controlled at -25°C, and the condensation temperature of the second-stage separation is controlled at -25°C. At -125° C.; after secondary condensation, boron trifluoride liquid is obtained; a sample is detected by gas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com