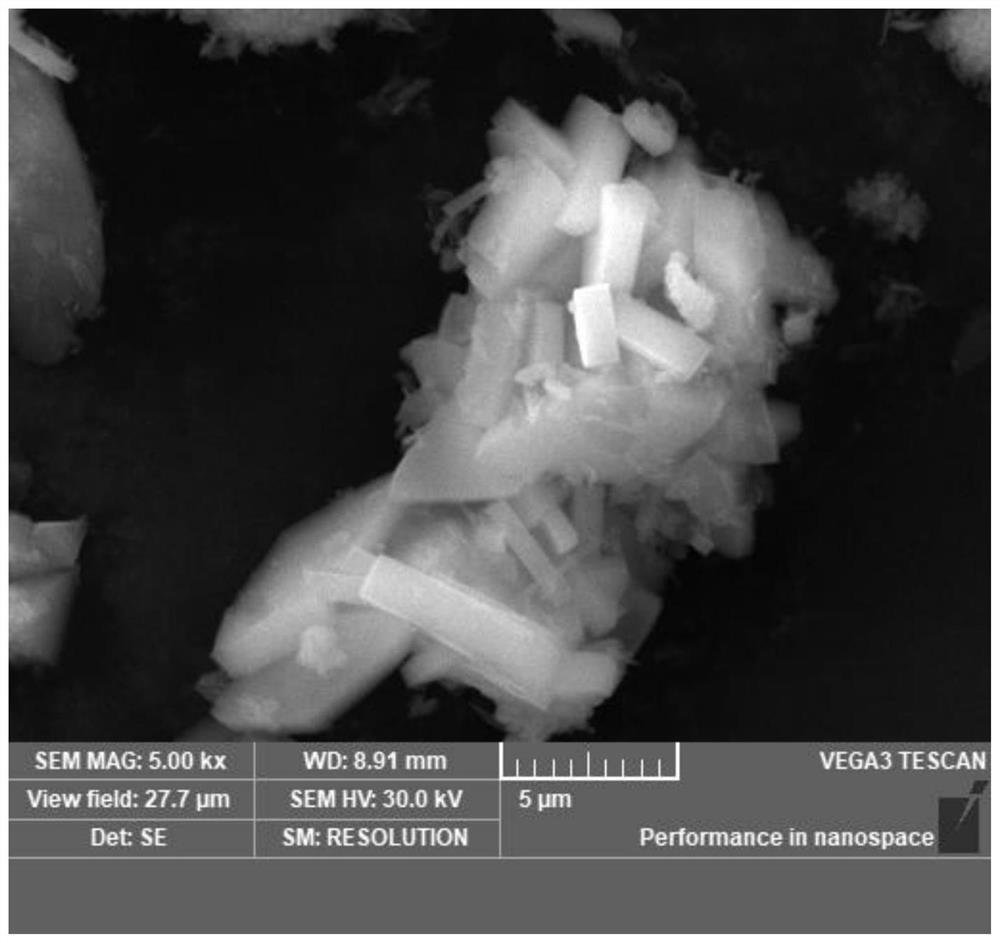
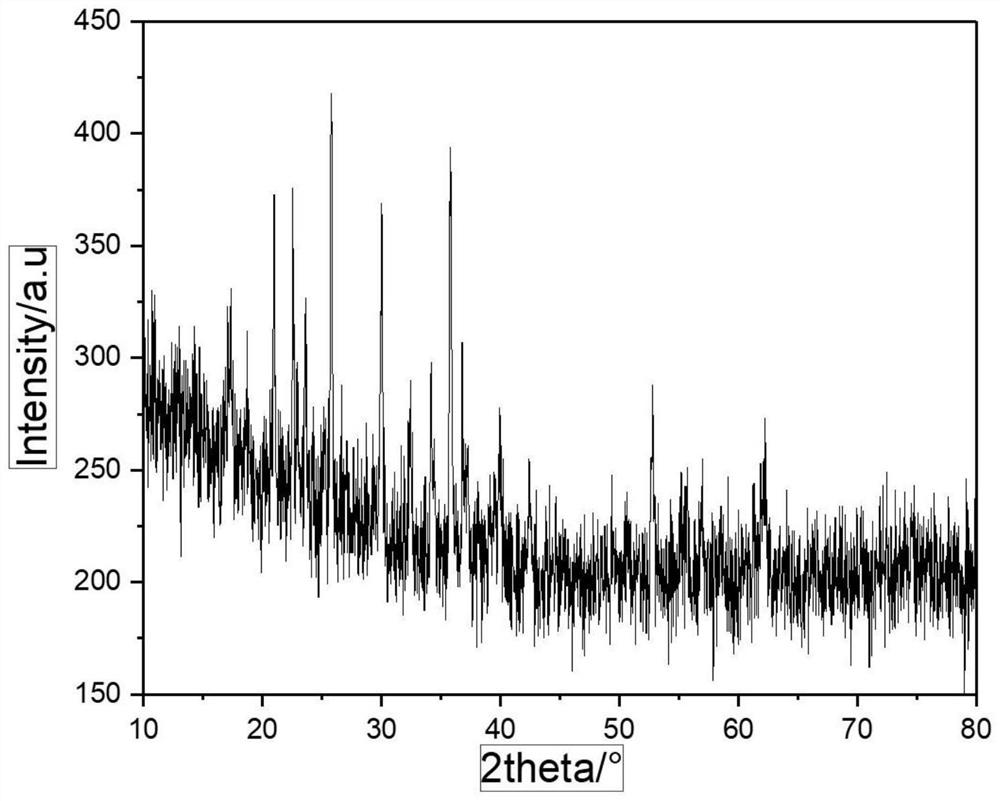
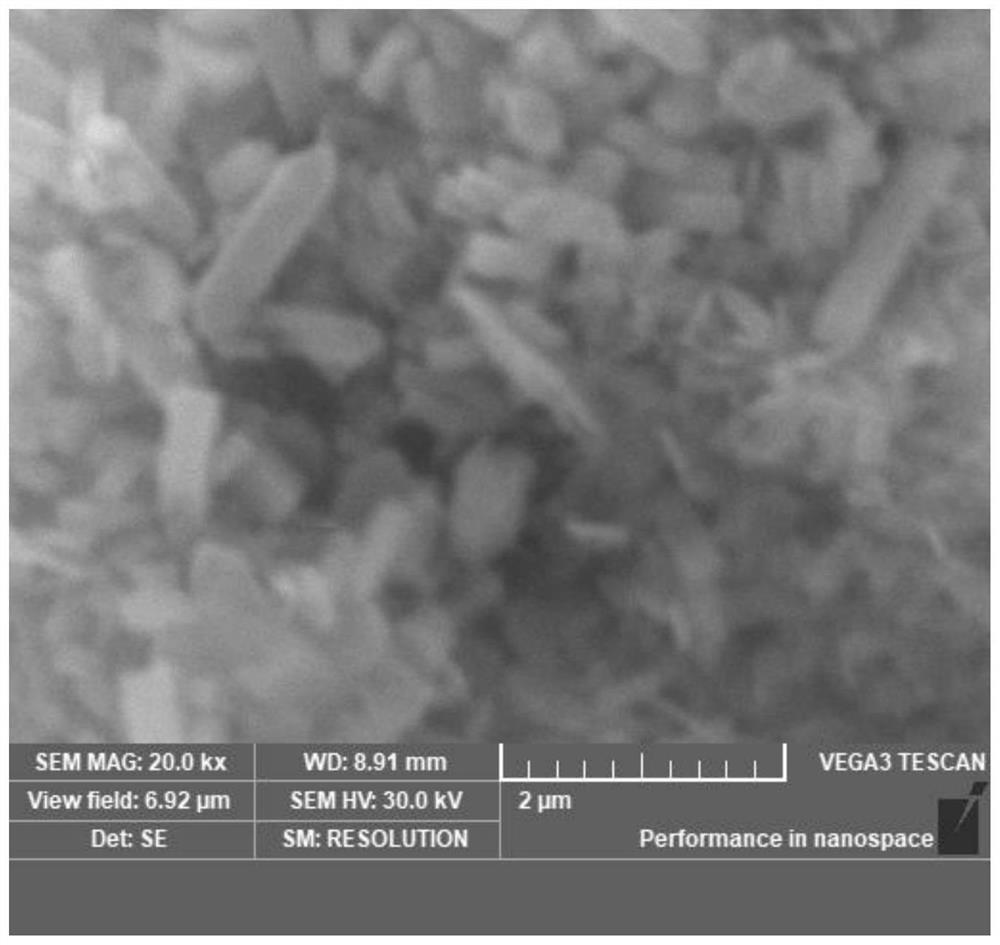
Low-temperature hydrothermal method for preparing nano lithium iron phosphate
A lithium iron phosphate and lithium phosphate technology, applied in nanotechnology, nanotechnology, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problem of low equipment requirements, and achieve the effect of reducing equipment requirements, reducing equipment investment, and improving production safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Weigh 21g of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate and dissolve it in 70ml of deionized water; add the corresponding lithium phosphate according to the ratio of iron, phosphorus and lithium elements as 1:1:3, and transfer it to the liner of the hydrothermal kettle after sonicating for 30 minutes; after sealing Incubate at 110°C for 10h; cool down naturally to room temperature after the incubation; wash with deionized water and filter until the filtrate is neutral; place the filter cake in an oven at 120°C to dry the nanolithium iron phosphate for 10h. Finally, lithium in lithium iron phosphate: iron: phosphorus = 1:0.95:1.01.
Embodiment example 2
[0035] Weigh 28g of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate and dissolve it in 70ml of deionized water; add the corresponding lithium phosphate according to the ratio of iron, phosphorus and lithium elements as 1:1:3, and transfer it to the liner of the hydrothermal kettle after 40 minutes of ultrasonication; after sealing Incubate at 100°C for 10h; cool down naturally to room temperature after the incubation; wash and filter with deionized water until the filtrate is neutral; place the filter cake in an oven at 120°C to dry the nanolithium iron phosphate for 10h. Lithium: iron: phosphorus = 1:0.98:0.99 in the final lithium iron phosphate.
Embodiment example 3
[0037] Weigh 18g of ferric nitrate and dissolve it in 70ml of deionized water; add the corresponding lithium phosphate according to the ratio of iron, phosphorus, and lithium elements as 1:1:3, and transfer it to the liner of the hydrothermal kettle after sonicating for 30 minutes; seal it and place it at 90 Incubate in ℃ for 10h; after the incubation, cool down to room temperature naturally; use deionized water to wash and filter until the filtrate is neutral; place the filter cake in an oven at 120 ℃ to dry the nanolithium iron phosphate for 10h. Lithium: iron: phosphorus = 1:0.99:1.03 in the final lithium iron phosphate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com