PH-responsive nano-iron-based sustained-release material, preparation method and application
A slow-release material and nano-iron technology, applied in the field of uranium-contaminated groundwater remediation, can solve problems such as weak biological activity, single structure, weakened remediation effectiveness and sustainability, and achieve the effect of improving easy agglomeration and increasing electron selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
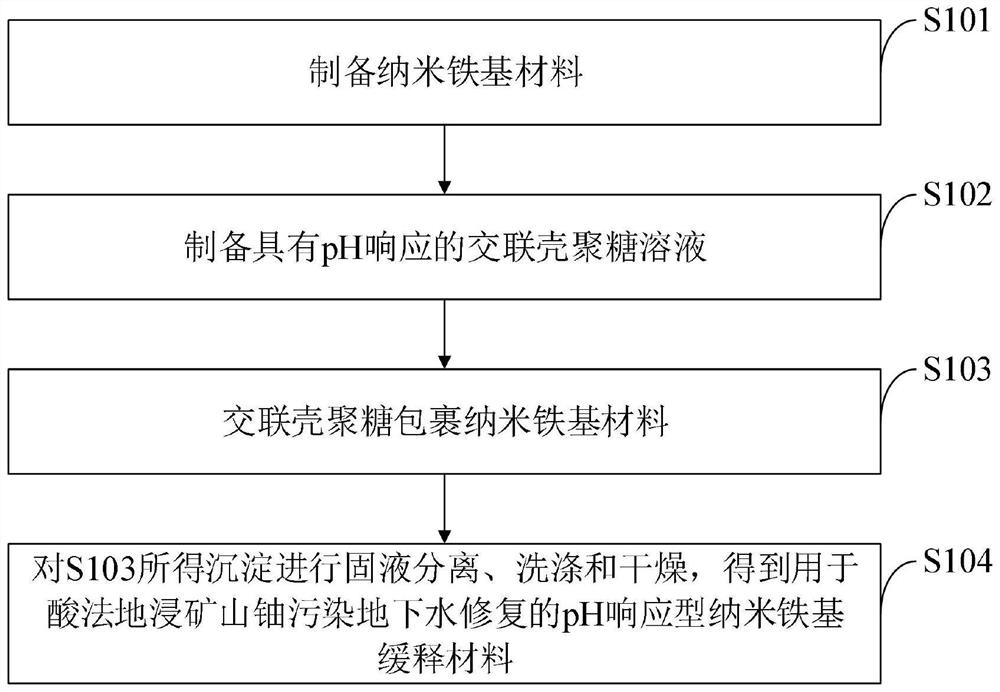
[0037] like figure 1 As shown, the preparation method of the pH-responsive nano-iron-based sustained-release material provided by the embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0038] S101, preparing a nano-iron-based material;
[0039] S102, preparing a pH-responsive cross-linked chitosan solution;
[0040] S103, cross-linked chitosan encapsulates nano-iron-based materials;
[0041] S104 , performing solid-liquid separation, washing and drying on the precipitate obtained in S103 to obtain a pH-responsive nano-iron-based slow-release material for remediation of uranium-contaminated groundwater in an acid in-situ leaching mine.
Embodiment 1
[0044] The preparation method of the pH-responsive nano-iron-based sustained-release material provided in the embodiment of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0045] (1) Weigh 0.01mol of ferric chloride and dissolve it in 1L of deionized water, stir with nitrogen for 30min, add 0.001mol of carboxymethyl cellulose, then dropwise add 100mL of 0.4mol / L NaHB to the above solution 4 The solution was added dropwise within 10 min, and the solution was continuously stirred for 2 h to obtain the carboxymethyl cellulose modified nano-zero valent iron solution. The carboxymethyl cellulose modified nano-zero valent iron is separated, washed three times with oxygen-free deionized water and oxygen-free ethanol, and then blown dry with nitrogen to obtain carboxymethyl cellulose modified nano-zero valent iron powder.
[0046] (2) Use 1% HCl to prepare 50ml of 5.0g / L chitosan solution, prepare 10mL of 5.0g / L sodium tripolyphosphate solution, and add the sodium tripolyphosph...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The preparation method of the pH-responsive nano-iron-based sustained-release material provided in the embodiment of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0051] (1) Weigh 0.01mol of ferric sulfate and dissolve it in 1L of deionized water, stir with nitrogen for 30min, add 0.0005mol of carboxymethyl cellulose, and then dropwise add 100mL of 0.4mol / L NaHB to the above solution 4 The solution was added dropwise within 10 min, and the solution was continuously stirred for 2 h to obtain the carboxymethyl cellulose modified nano-zero valent iron solution. The carboxymethyl cellulose modified nano-zero valent iron is separated, washed three times with oxygen-free deionized water and oxygen-free ethanol, and then blown dry with nitrogen to obtain carboxymethyl cellulose modified nano-zero valent iron powder.
[0052] (2) Use 1% HCl to prepare 50ml of 2.5g / L chitosan solution, configure 10mL of 2.5g / L sodium tripolyphosphate solution, and add the sodium tripoly...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com