Method for preparing mineral type potassium-magnesium-silicon slow-release fertilizer from nephrite tailings
A slow-release fertilizer and tailings technology, applied in application, fertilization device, fertilizer mixture, etc., can solve the problems of low fertilizer use efficiency and the accumulation of lost fertilizer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] S1: First prepare the raw materials, 3.30 parts of nephrite tailings, 0.1 part of quartz sand and 3.77 parts of potassium carbonate, and use clean water to wash the prepared raw materials. After the raw materials are cleaned, use a dryer to remove the nephrite tailings, quartz sand and Potassium carbonate drying;
[0022] S2: Put the designed raw material components into the ball mill, take out the powder after mixing for 5 minutes, and conduct sampling inspection on the taken out powder. Raw materials with larger particles;
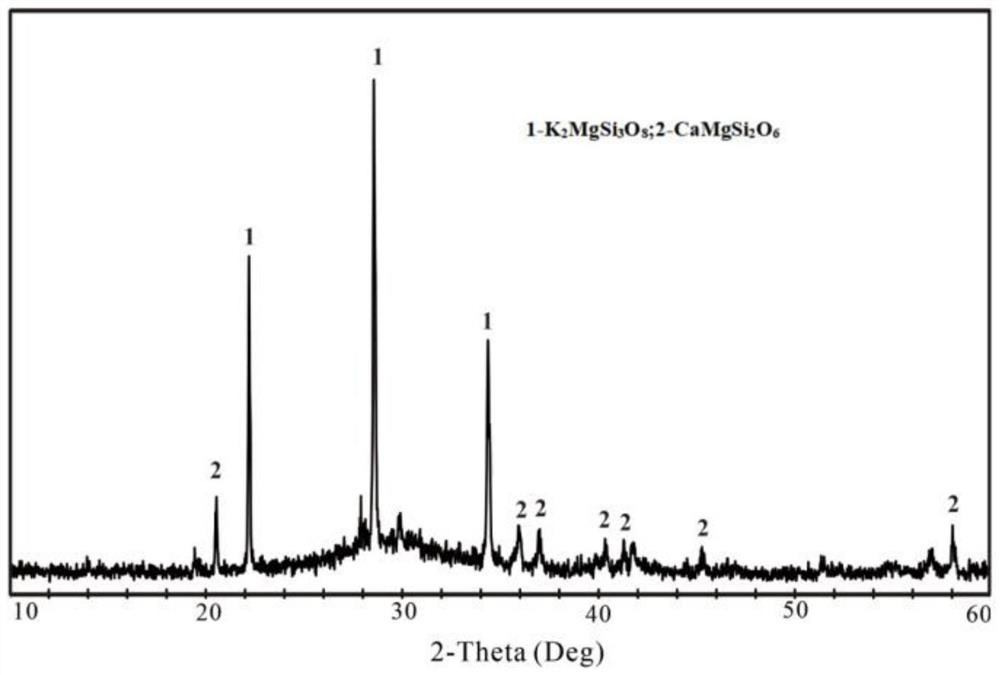
[0023] S3: Put the treated powder into an alumina dry pot, and put it into a high-temperature melting furnace for sintering. After sintering, take out the sintered sample, control the sintering temperature at 850°C, control the holding time at 2h, and use X The sintered samples were analyzed by a ray powder crystal diffraction device;
[0024] S4: The sintered sample is pulverized, and sample particles are produced by a granulator, and the produ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] S1: First prepare the raw materials, 4 parts of nephrite tailings, 3 parts of quartz sand and 4.5 parts of potassium carbonate, and wash the prepared raw materials with clean water. After the raw materials are cleaned, use a dryer to remove the nephrite tailings and quartz sand. dried with potassium carbonate;
[0027] S2: Put the designed raw material components into the ball mill, take out the powder after mixing for 6 minutes, and conduct sampling inspection on the taken out powder. Raw materials with larger particles;
[0028] S3: Put the treated powder into an alumina dry pot, and put it into a high-temperature melting furnace for sintering. After sintering, take out the sintered sample, control the sintering temperature at 900°C, control the holding time at 2.5h, and use The sintered samples were analyzed by X-ray powder crystal diffraction device;
[0029] S4: The sintered sample is pulverized, and sample particles are produced by a granulator, and the produced...
Embodiment 3
[0031] S1: First prepare the raw materials, 5.00 parts of nephrite tailings, 3.04 parts of quartz sand and 5.72 parts of potassium carbonate, and wash the prepared raw materials with clean water. After the raw materials are cleaned, use a dryer to remove the nephrite tailings and quartz sand. dried with potassium carbonate;
[0032] S2: Put the designed raw material components into the ball mill, take out the powder after mixing for 7 minutes, and conduct sampling inspection on the taken out powder. Raw materials with larger particles;
[0033] S3: Put the treated powder into an alumina dry pot, and put it into a high-temperature melting furnace for sintering. After sintering, take out the sintered sample. The sintered samples were analyzed using an X-ray powder crystal diffraction apparatus;
[0034] S4: The sintered sample is pulverized, and sample particles are produced by a granulator, and the produced sample particles are weighed and packaged.
[0035] Combined with th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com