Streptomyces albus pd9-pld3 and application thereof in production of epsilon-polylysine
A pd9-pld3, Streptomyces albicans technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, bacteria, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as limited yield, and achieve the effect of increasing yield and increasing stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
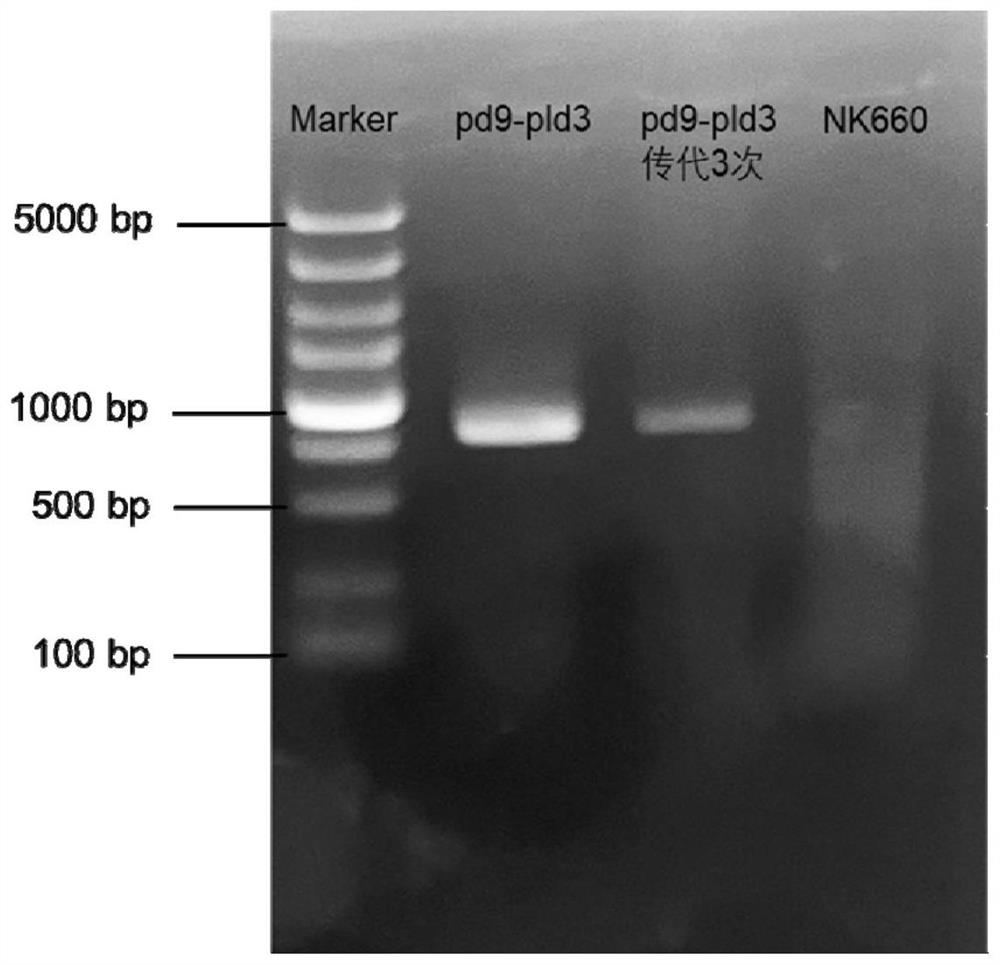
[0029] Embodiment 1, the construction of genetically engineered bacteria
[0030] 1. Construction of p152-dCas9 inhibitory plasmid
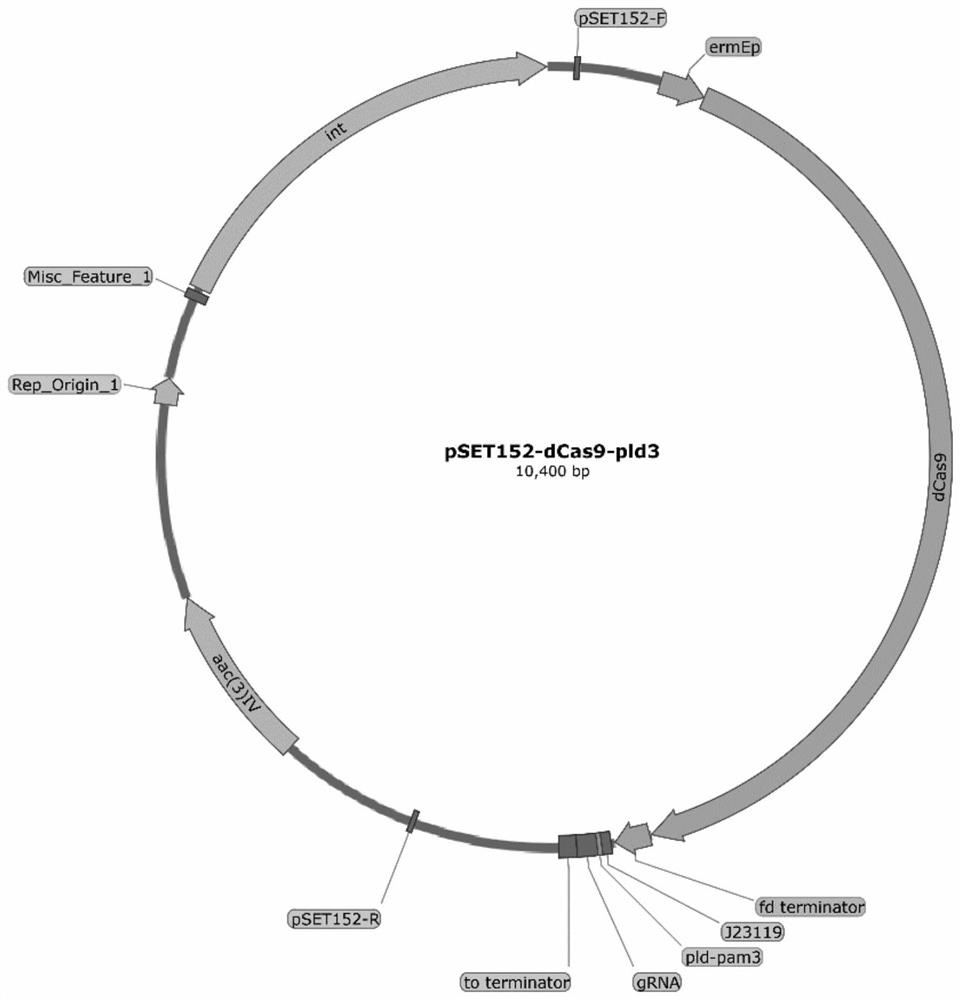
[0031] Use the integrated plasmid pSET152 as the backbone of the p152-dCas9 suppressor plasmid, such as figure 1 As shown, the expression of the dCas9 gene in this plasmid is driven by the strong constitutive promoter ermE*p and terminated by the fd terminator; the sgRNA is transcribed from the promoter j23119 from E. coli and terminated by the TO terminator. The dCas9 gene is derived from the Cas9 nuclease with point mutations in the HNH domain and RuvC domain (D10A and H840A), respectively.
[0032] The 668-688bp of the target gene ε-poly-L-lysine degrading enzyme (pld) gene sequence was selected as the N20 sequence of the PAM site, the sequence is:
[0033] gggctgaccgcgttgatcac (SEQ IN NO: 1).
[0034] The primers for plasmid construction were designed as follows:
[0035] pld-dcas9-pam3F:
[0036] cctaggtataatactagtgggctgaccgcgttgatcacgt...
Embodiment 2
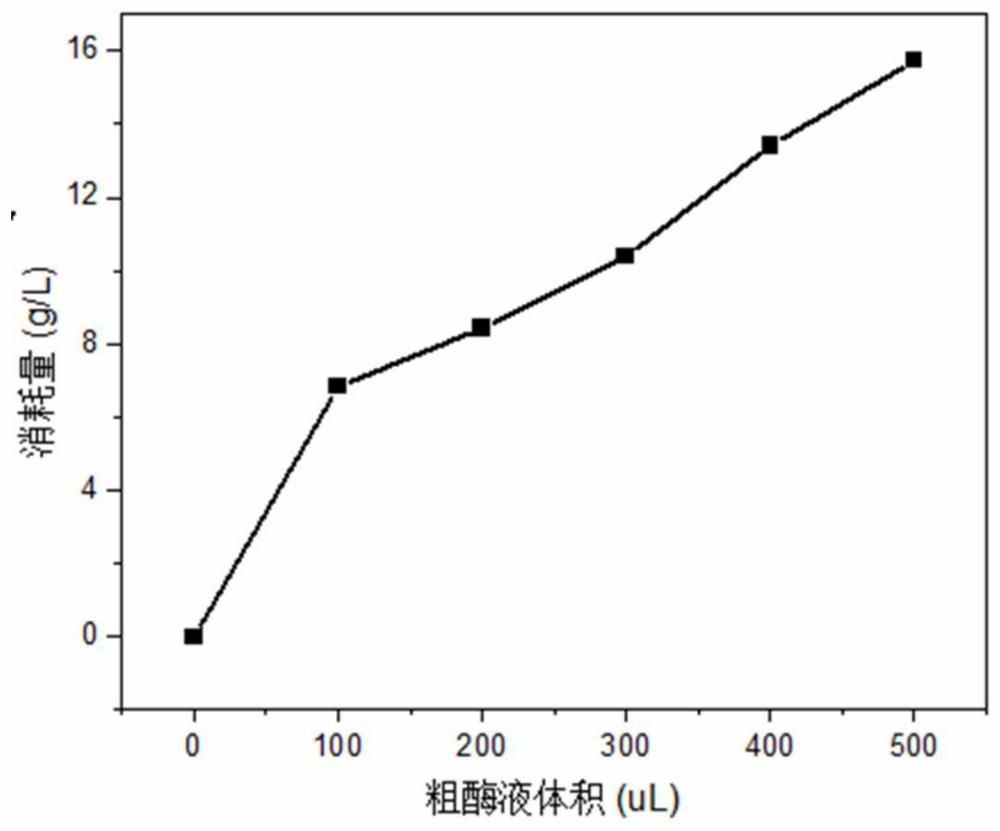
[0052] Example 2. Determination of ε-polylysine degrading enzyme enzymatic activity
[0053] Since the ε-polylysine degrading enzyme is located on the cell membrane, the fermentation broth of Streptomyces albulus pd9-pld3 obtained by the method of Example 1 was crushed to prepare a crude enzyme liquid, and ε-polylysine was added. Amino acid was used as the substrate, and the reaction was carried out at 30 °C and pH=7 for 60 min. The degradation amount of ε-polylysine was determined by HPLC to calculate the degradation rate, and the degradation rate was used to reflect the ε-polylysine. Relative activity of lysine-degrading enzymes.
[0054] The method for HPLC determination of ε-polylysine content is:
[0055] The fermentation broth obtained from the fermentation culture was sampled, centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 15 minutes, the bacteria were separated, and filtered to obtain a clear filtrate; the filtrate was diluted to an appropriate number, and the production of ε-polylysi...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Embodiment 3, the formula optimization of shake flask fermentation experiment
[0059] The shake-flask fermentation recipe of Streptomyces albulus pd9-pld3 obtained by the method of Example 1 for producing ε-polylysine by shake-flask fermentation was optimized.
[0060] A large number of literatures show that the accumulation of ε-polylysine is closely related to pH during the fermentation of Streptomyces albicans. In the shake flask experiment, due to the inability to accurately control the pH, in order to avoid the rapid pH drop due to consumption of glucose by Streptomyces albicans, which will affect the accumulation and enrichment of the strain, and then affect the final production of ε-polylysine, we used Add CaCO to the medium 3 to slow down the rate of pH drop during shake flask fermentation.
[0061] Using Streptomyces albulus pd9-pld3 fermentation medium M3G as the starting medium, CaCO 3 The addition ratios were set to 0%, 0.2%, 0.5%, and 0.8%, respectively...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com