Bismuth blended germanium base optical glass
An optical glass and germanium-based technology, which is applied in the field of bismuth-doped germanium-based optical glass and its preparation, can solve the problems such as difficult connection of crystal materials to communication systems, electronic bottlenecks, and restriction of the number of optical fiber wavelength channels.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the embodiments and accompanying drawings, but the protection scope of the present invention should not be limited thereby.
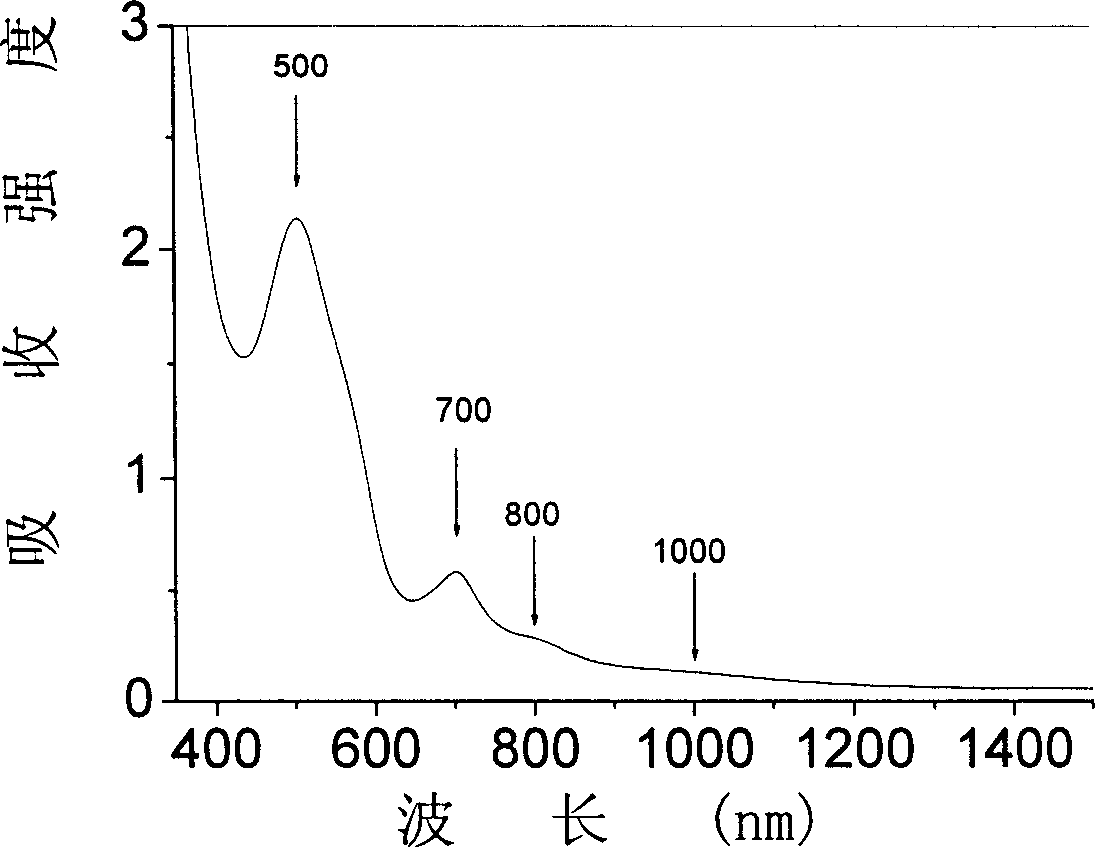
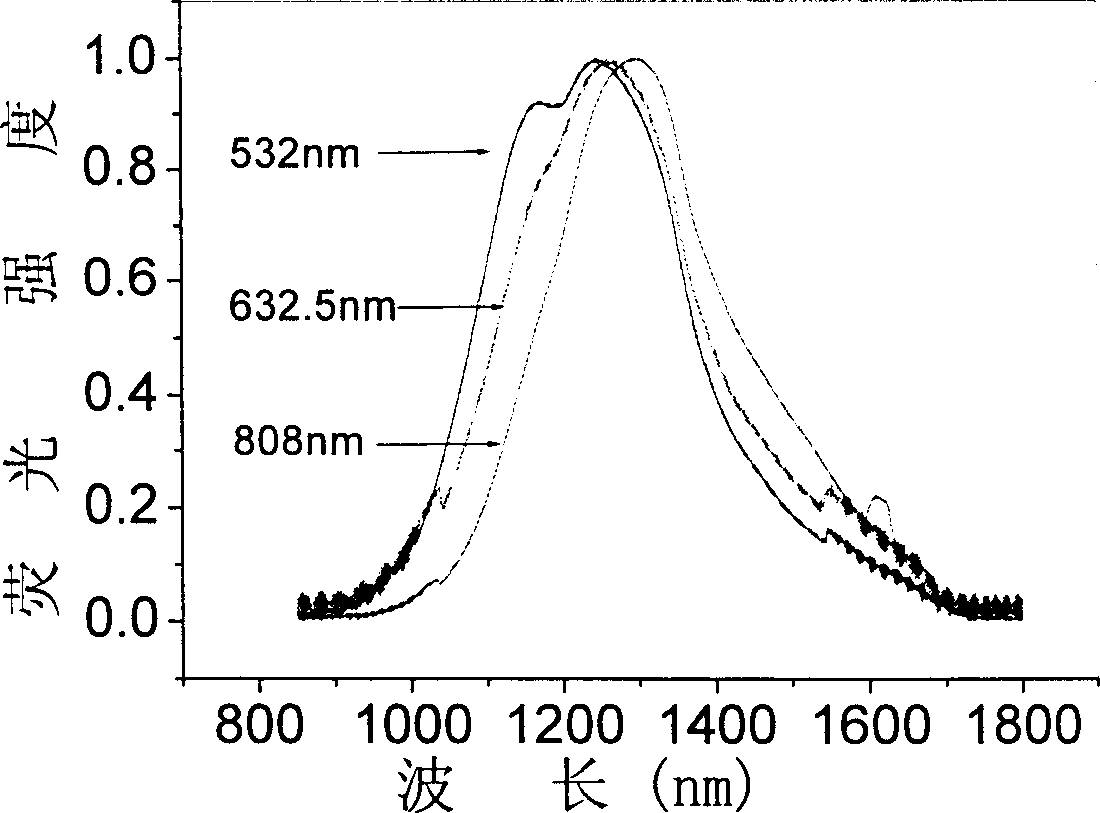
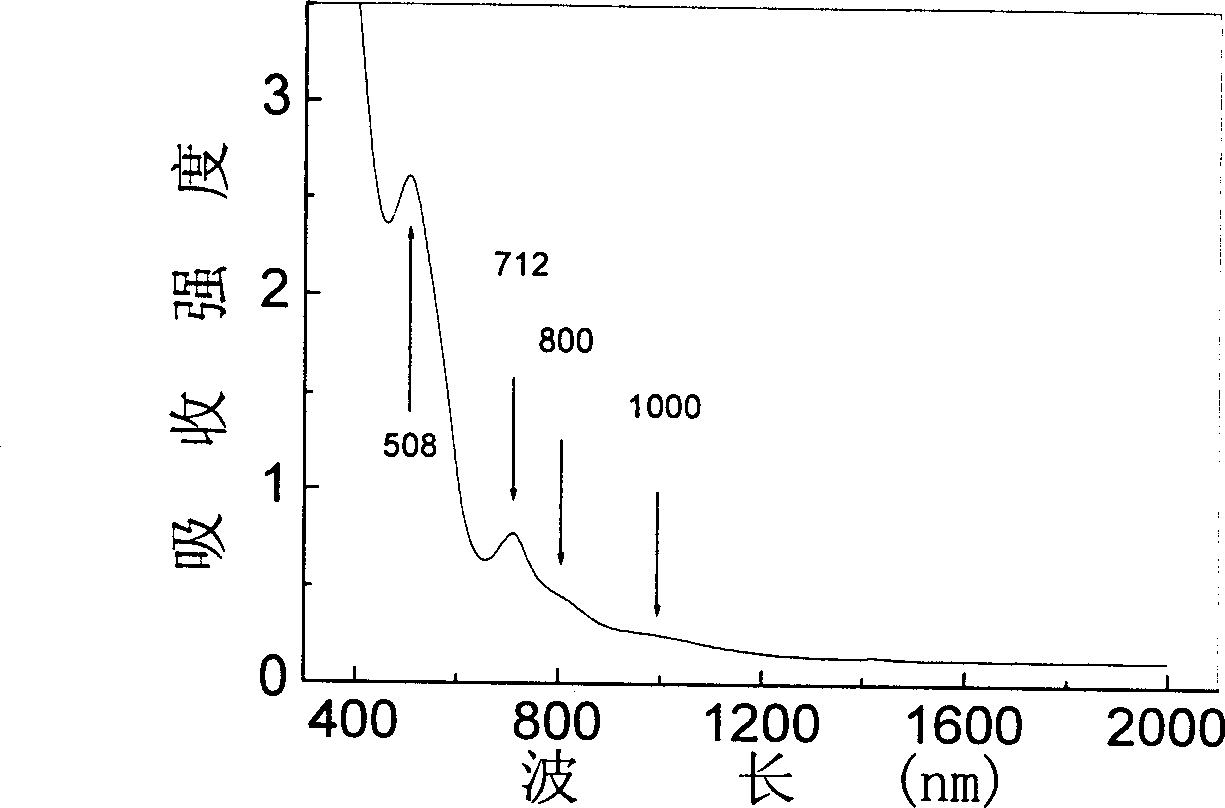
[0030] Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4 have listed M=Al in the glass composition of the present invention respectively 2 o 3 , Ta 2 o 5 , Ga 2 o 3 , B 2 o 3 Composition and molar percentage thereof of four groups of examples, the color of corresponding glass, fluorescence position and half maximum width thereof, the test result of fluorescence lifetime, wherein embodiment 1, 4, 21, 24, 31, 34, 41 and 44 are comparative example.
[0031] Example group 1
[0032] The preparation method is as follows: Weigh about 20g of the ingredients according to the ratio in Table 1, grind them in an agate mortar for half an hour, then pre-fire at 500°C for 7 hours, take them out and grind them, and then melt them at 1550°C for 2 hours, so that In order to completely eliminat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com