Thin film transistors with self aligned light dosed resource structure and their manufacture
A thin film transistor, lightly doped drain technology, applied in transistors, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as low yield and inability to improve complex processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
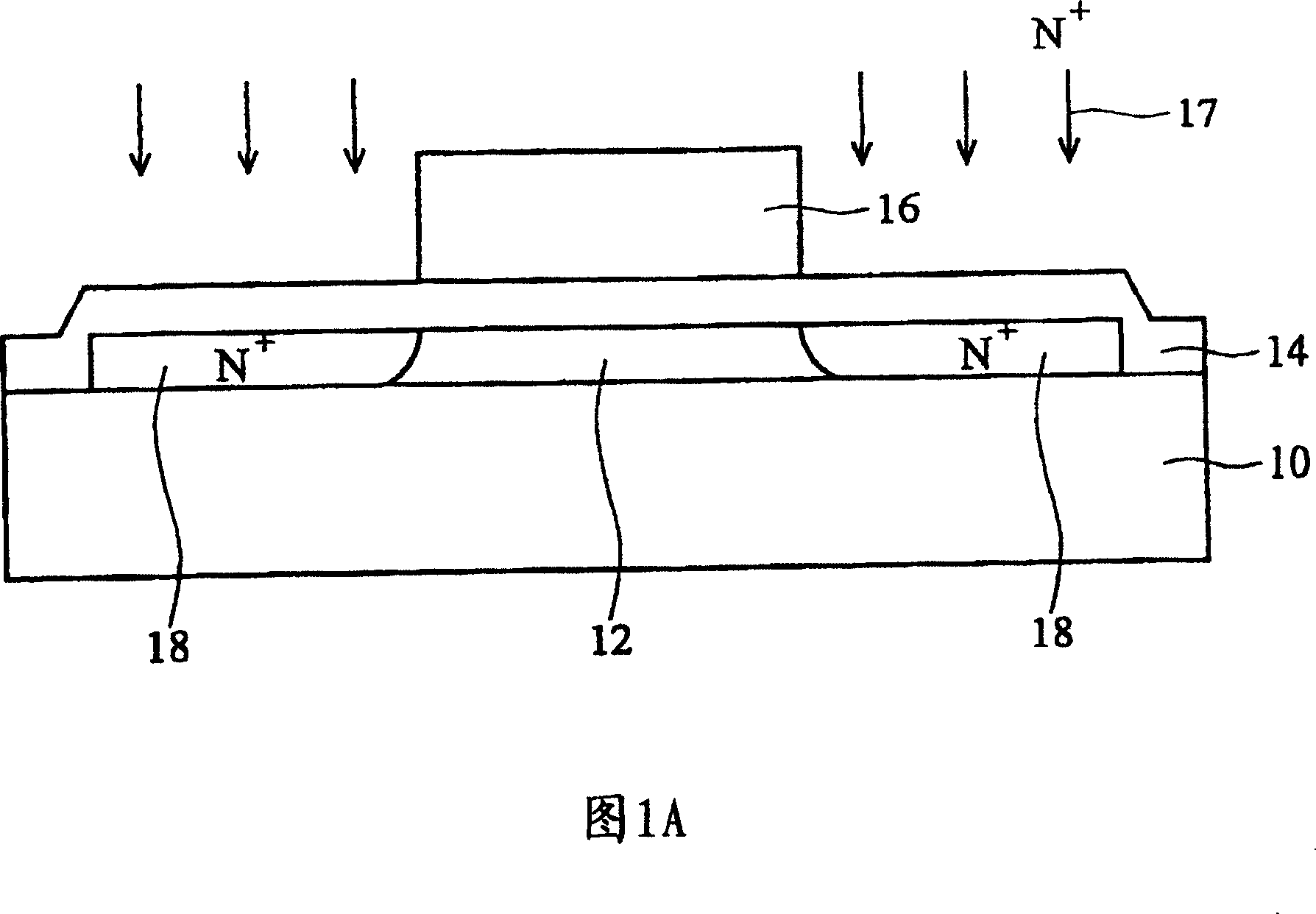
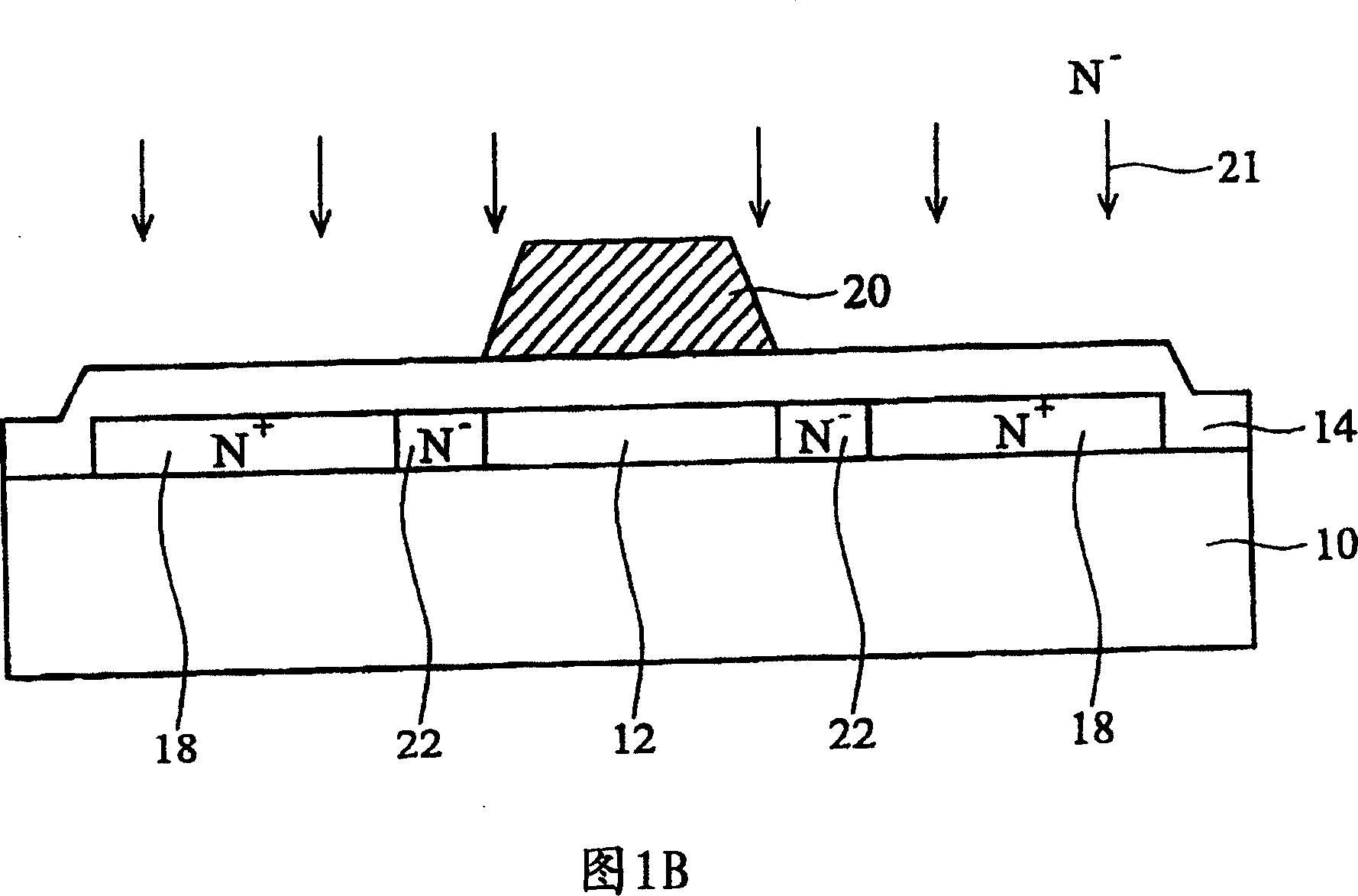
[0061] As shown in FIG. 3 , it shows a schematic cross-sectional view of the self-aligned LDD structure of the thin film transistor according to the first embodiment of the present invention. A buffer layer 52 , an effective layer 54 , a gate insulating layer 56 and a gate layer 58 are sequentially fabricated on a substrate 50 . The substrate 50 is preferably a transparent insulating substrate, such as a glass substrate. The buffer layer 52 is preferably a dielectric material layer, such as a silicon oxide layer, and its purpose is to help the effective layer 54 to be formed on the substrate 50 . The active layer 54 is preferably a semiconductor silicon layer, such as a polysilicon layer. The gate insulating layer 56 is preferably a silicon oxide layer, a silicon nitride layer, a silicon oxynitride layer or a combination thereof. The gate layer 58 is preferably a conductive material layer, such as a metal layer and a polysilicon layer.
[0062] The structural features of th...
no. 2 example
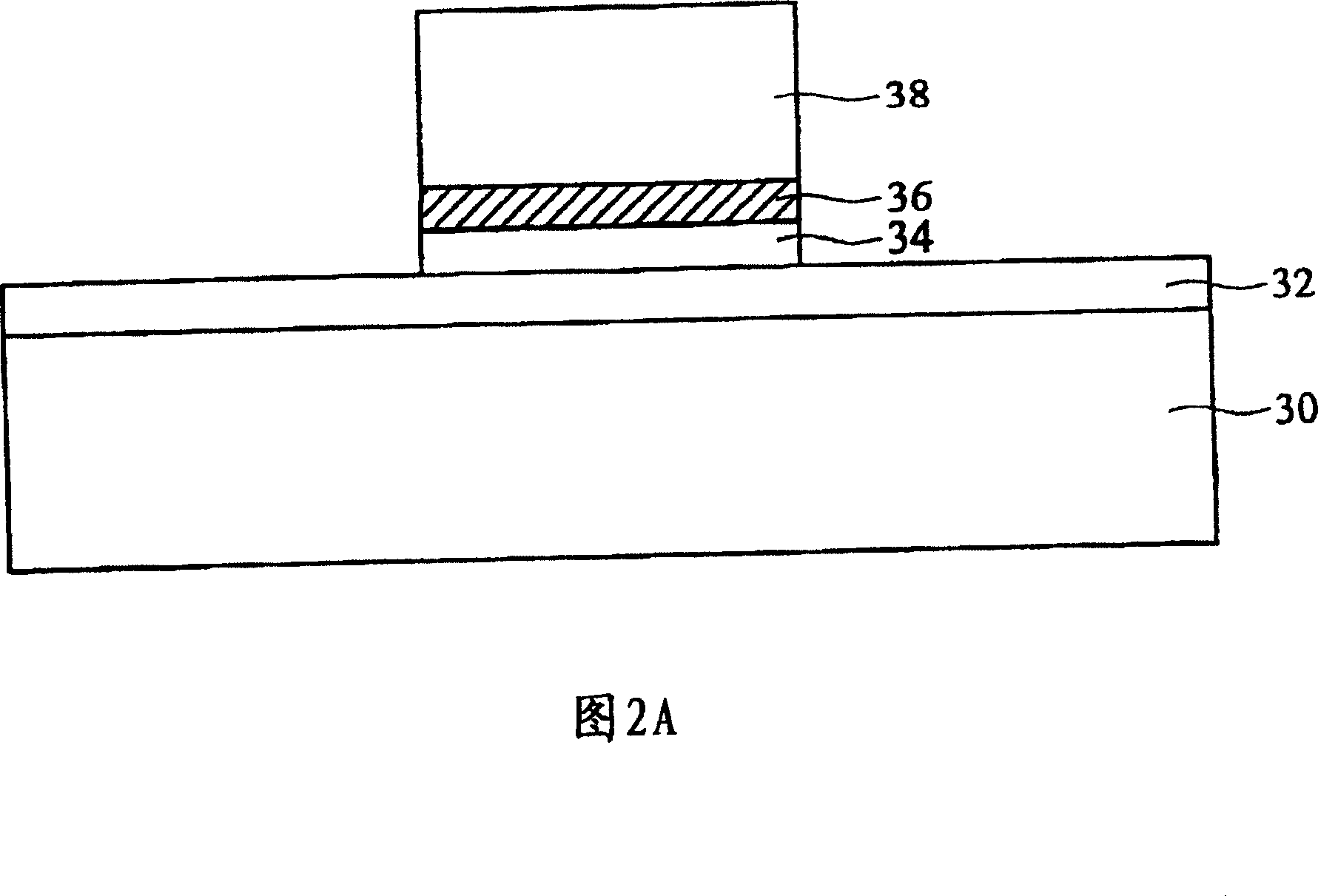
[0070] As shown in FIG. 4A and FIG. 4B , they are schematic cross-sectional views of the self-aligned LDD structure of the thin film transistor according to the second embodiment of the present invention. The components and structural features of the thin film transistor of the second embodiment are substantially the same as those described in the first embodiment, and the similarities will not be described again. The difference is that the gate insulating layer 56 of the second embodiment is composed of a first insulating layer 55 and a second insulating layer 57, wherein the first insulating layer 55 is preferably a silicon oxide layer, a A silicon nitride layer, a silicon oxynitride layer or a combination thereof, the second insulating layer 57 is preferably a silicon oxide layer, a silicon nitride layer, a silicon oxynitride layer or a combination thereof.
[0071] A central region 56 a , two shielding regions 56 b and two extension regions 56 c are defined on the gate ins...
no. 3 example
[0075] 5A to 5F , which are schematic cross-sectional views showing a method for manufacturing a self-aligned LDD structure of a thin film transistor according to a third embodiment of the present invention.
[0076] The manufacturing method of the thin film transistor of the present invention can be applied to a P-type thin film transistor or an N-type thin film transistor. The following takes the thin film transistor of the first embodiment as an example to describe the manufacturing method of the self-aligned LDD structure in detail.
[0077] First, as shown in FIG. 5A , a substrate 50 is provided, and a buffer layer 52 is deposited on the substrate 50 , and then an effective layer 54 is formed on the buffer layer 54 . The substrate 50 is preferably a transparent insulating substrate, such as a glass substrate. The buffer layer 52 is preferably a dielectric material layer, such as a silicon oxide layer, and its purpose is to help the effective layer 54 to be formed on the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com