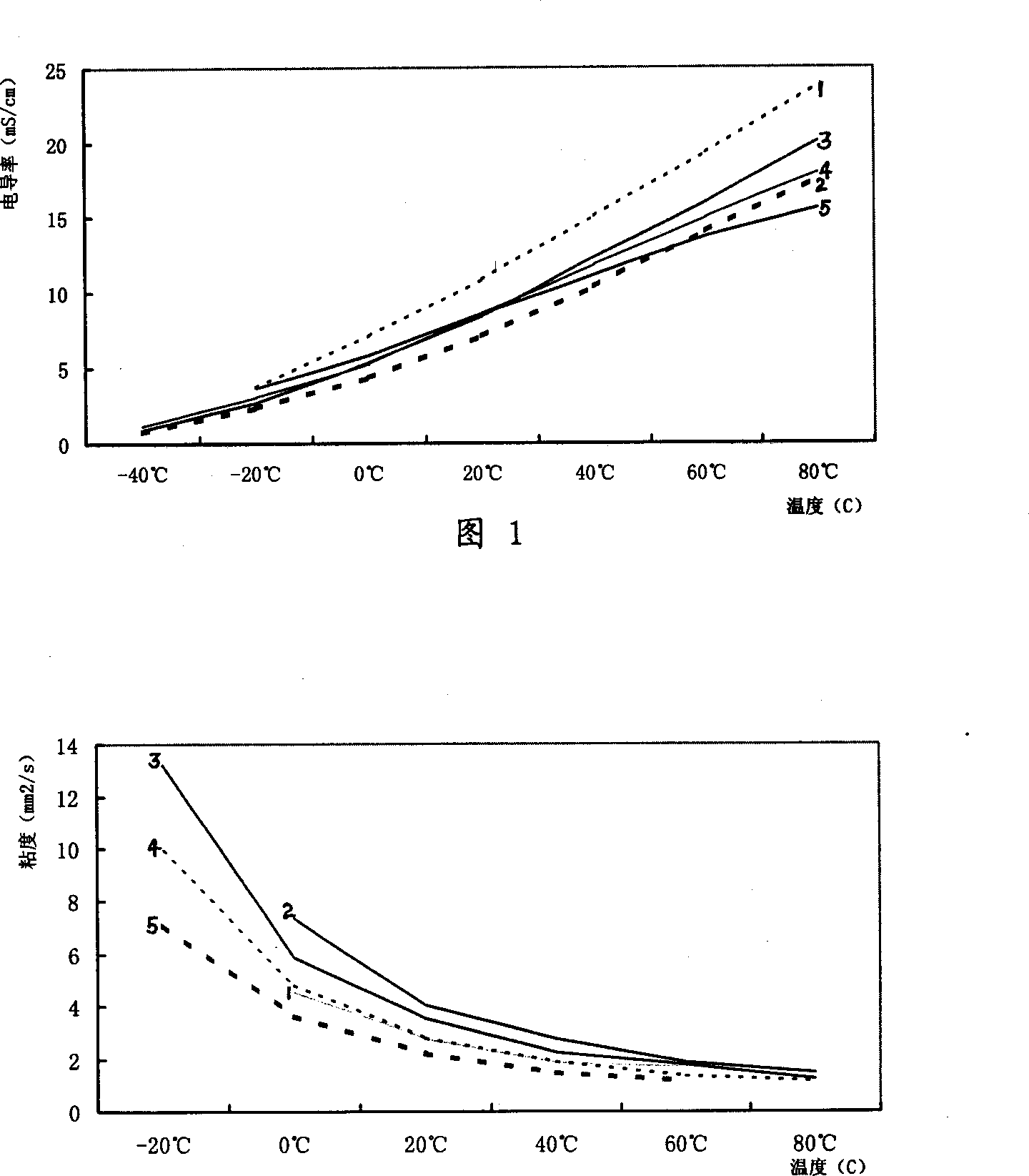
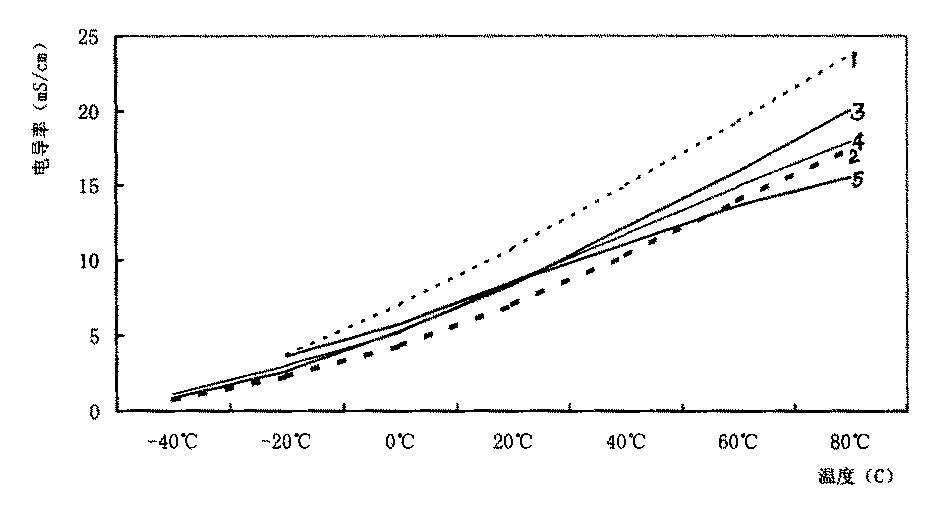
Lithium secondary cell electrolyte
A lithium secondary battery and electrolyte technology, applied in secondary batteries, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of decreased discharge capacity, interference with electrochemical reactions, and impact on battery electrode cycle life and charge-discharge efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Prepare 1 mole lithium hexafluorophosphate electrolyte of EC / DEC, EC / DMC, EC / DEC / DMC, EC / EMC, EC / DMC / EMC, PC / DEC / DMC and other systems in a dry box with a moisture content of less than 20ppm. The electrolyte is injected into a lithium secondary battery with a positive electrode lithium cobalt compound and a negative electrode carbon. The battery is charged with a constant current (1CA) at room temperature (20°C) until it reaches 4.2V, and then continues to charge at a constant voltage of 4.2V. 4 hours. This was followed by discharge at a constant current (1CA). Continue to discharge until the final voltage is 2.7V. The charging and discharging cycle was repeated 300 times, and the charging and discharging capacity, efficiency and cycle life were measured.
[0035] The evaluation results of the battery are shown in Table 2
[0036]
[0037] After 300 charge-discharge cycles, the discharge capacity is more than 84.5% of the initial discharge capacity.
Embodiment 2
[0039] In a dry box with a water content of less than 20ppm, prepare 1 mole lithium hexafluorophosphate electrolytes of EC / DEC, EC / DMC, EC / DEC / DMC, EC / EMC, EC / DMC / EMC, PC / DEC / DMC and other systems, respectively Add 0.01-10% sulfur-containing compound, and inject each electrolyte solution into a lithium secondary battery with a positive electrode lithium cobalt compound and a negative electrode carbon, and charge the battery with a constant current (1CA) at room temperature (20°C) until it reaches 4.2 V, and then continue to charge for 4 hours at a constant voltage of 4.2V. This was followed by discharge at a constant current (1CA). Continue to discharge until the final voltage is 2.7V. The charging and discharging cycle was repeated 300 times, and the charging and discharging capacity, efficiency and cycle life were measured.
[0040] The evaluation results of the battery are shown in Table 3
[0041]
[0042] After 300 charge-discharge cycles, the discharge capac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com