Reference voltage generating circuit and voltage amplifier adopting same
A technology of voltage amplifiers and reference voltages, applied to amplifiers with semiconductor devices/discharge tubes, DC-coupled DC amplifiers, amplifiers, etc., can solve problems such as large time delays, and achieve low power consumption and simple configuration.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
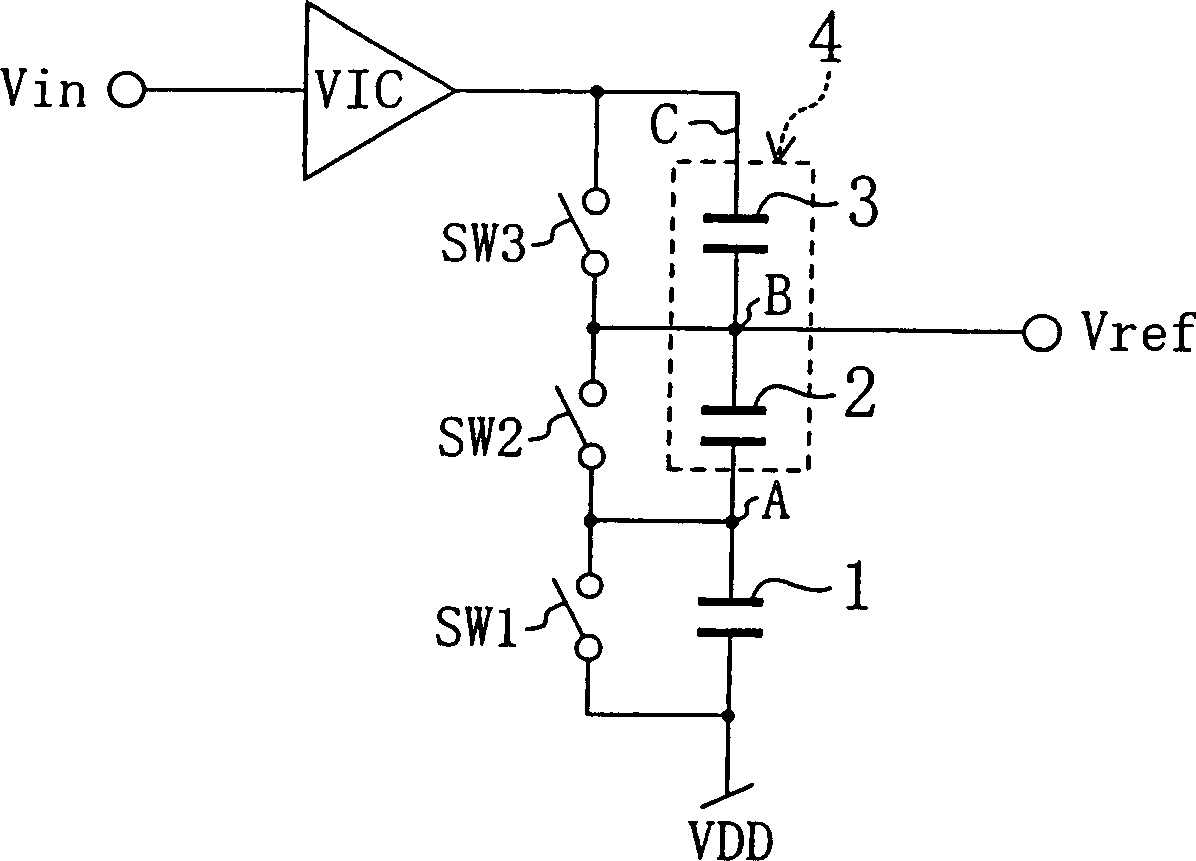
[0065] figure 1 The reference voltage generating circuit according to the inventions 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 of the first embodiment is shown.
[0066] In this figure, one end of the first capacitor 1 is grounded (here, a predetermined voltage VDD, which functions as a minimum value holding circuit). The other end is connected in series with a capacitor row 4 formed by connecting the second and third capacitors 2 and 3 in series. The switches SW1 to SW3 are connected in parallel with the two ends of the capacitors 1 to 3 respectively, and play the role of removing the electric charge. In addition, VIC is a voltage-to-current conversion circuit, which inputs an input voltage signal Vin on its input side, and is connected to a circuit in which the first capacitor 1 and the capacitor row 4 are connected in series on its output side, and functions until the input voltage Vin is connected to the output The capacitors 1 to 3 are charged (or discharged) until the voltages are equal.
[...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
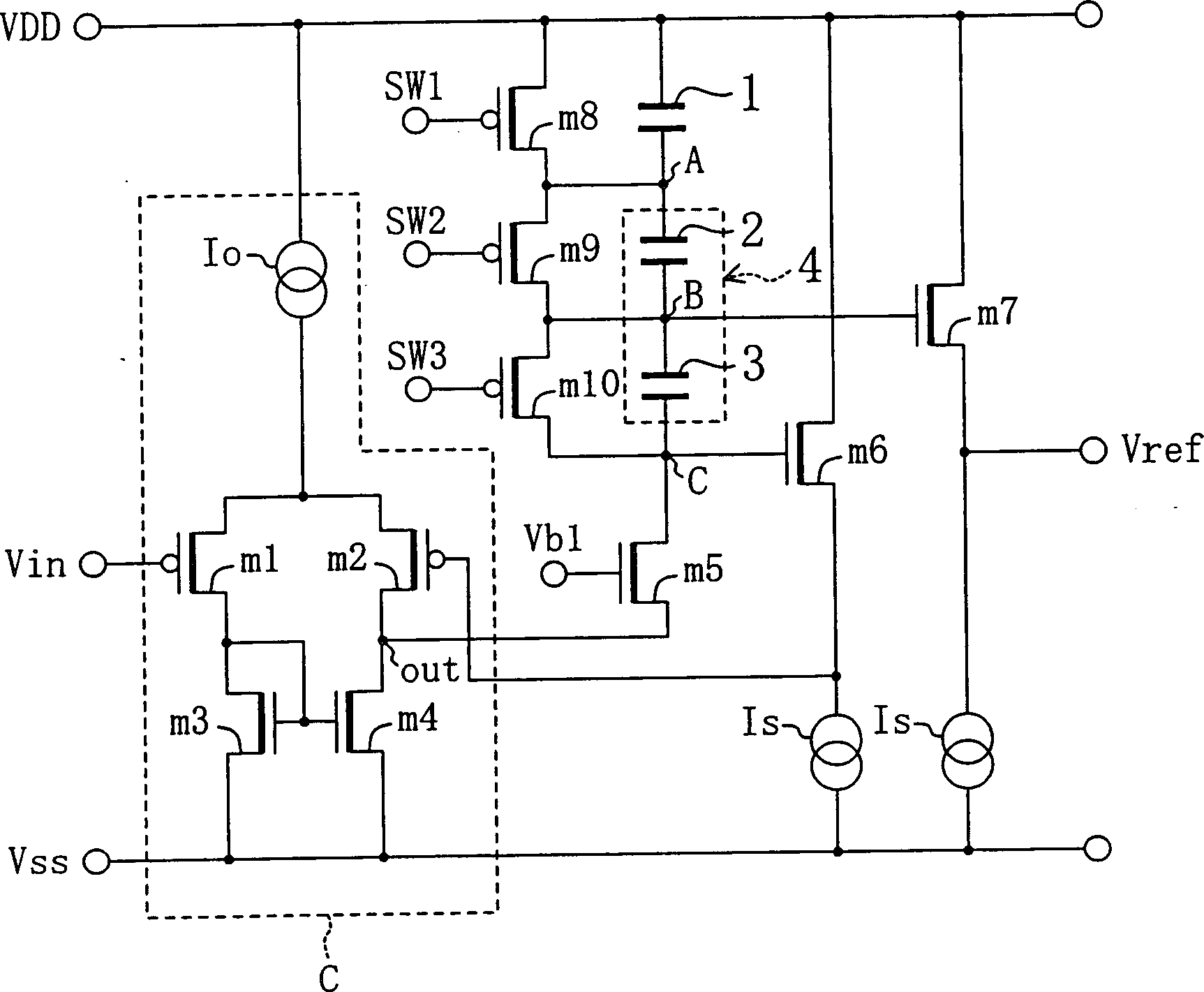
[0089] figure 2 A reference voltage generating circuit according to the invention described in the sixth embodiment of the present invention is shown.
[0090] figure 2 The reference voltage generating circuit, included in the figure 1 The illustrated first capacitor 1 , second and third capacitors 2 and 3 are connected in series to form a capacitor row 4 and a voltage-current conversion circuit C. It further includes a gate-cathode transistor m5 as a unidirectional conduction element that can only pass current in one direction, an NMOS source follower transistor m6 as a buffer circuit, a PMOS transistor m8 connected in parallel with the first capacitor 1 as a first reset circuit, PMOS transistors m9 and m10 as second reset circuits are connected in parallel with the second and third capacitors 2 and 3, respectively.
[0091] The voltage-to-current conversion circuit C is biased by a bias current source Io, and is composed of a differential circuit composed of source-conn...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
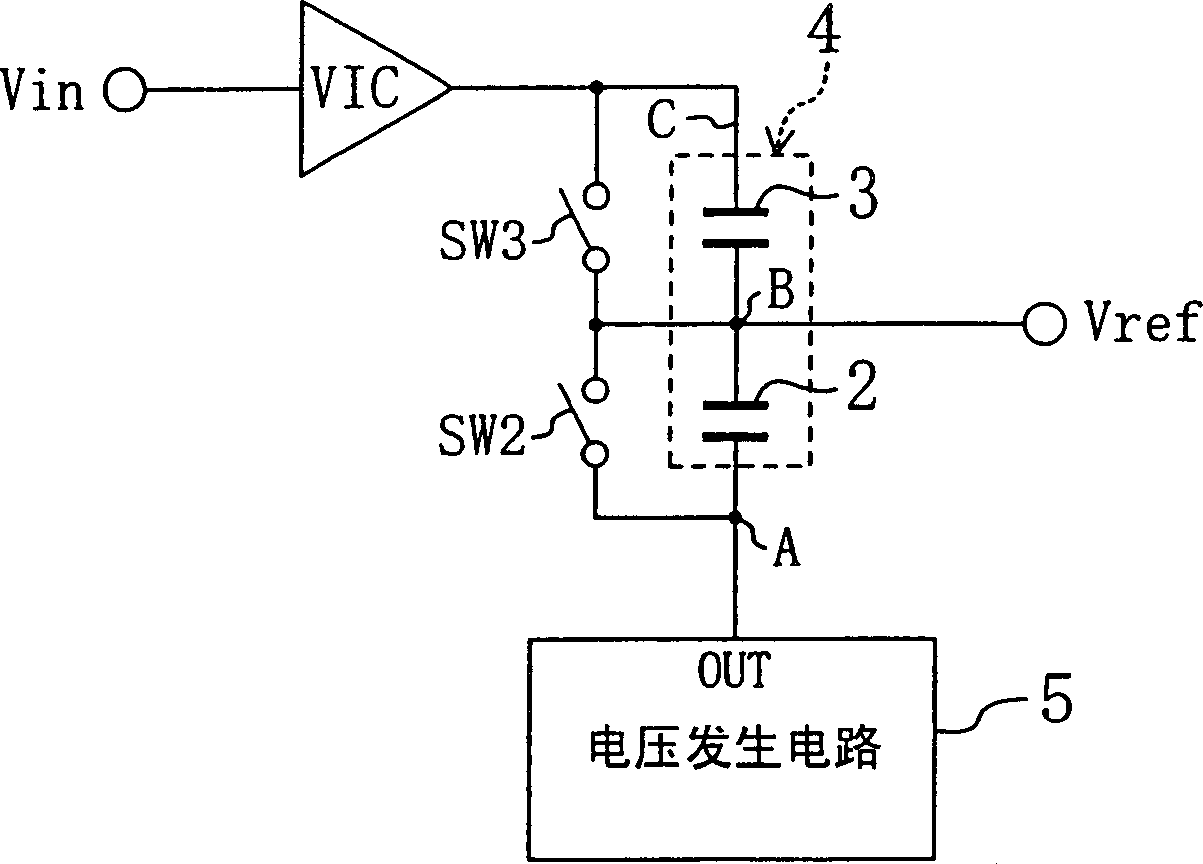
[0097] image 3 The reference voltage generating circuit of the inventions 7, 8, and 9 according to the third embodiment is shown. In the present embodiment, a voltage generating circuit 5 is provided, and the voltage generating circuit 5 is used instead of the first capacitor 1 and the switch SW1 of the above-described first embodiment.
[0098] That is, the reference voltage generating circuit in the figure includes a capacitor row 4 in which two capacitors 2 and 3 are connected in series, two switches SW2 and SW3 connected in parallel with the capacitors 2 and 3, a voltage-current conversion circuit VIC, and A voltage generating circuit 5 that generates a given voltage. The output terminal of the voltage generating circuit 5 is connected to one end of the capacitor 2 of the capacitor array 4 described above. The voltage of the connection node B of the two capacitors 2 and 3 of the capacitor row 4 is output as the reference voltage Vref. Also in the present embodiment, si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com