Method for producing d-biotin
A technology of biotin and synthesis method, applied in the direction of organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of long synthesis route and low total yield, and achieve the effect of simple operation, high yield and shortened process route
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
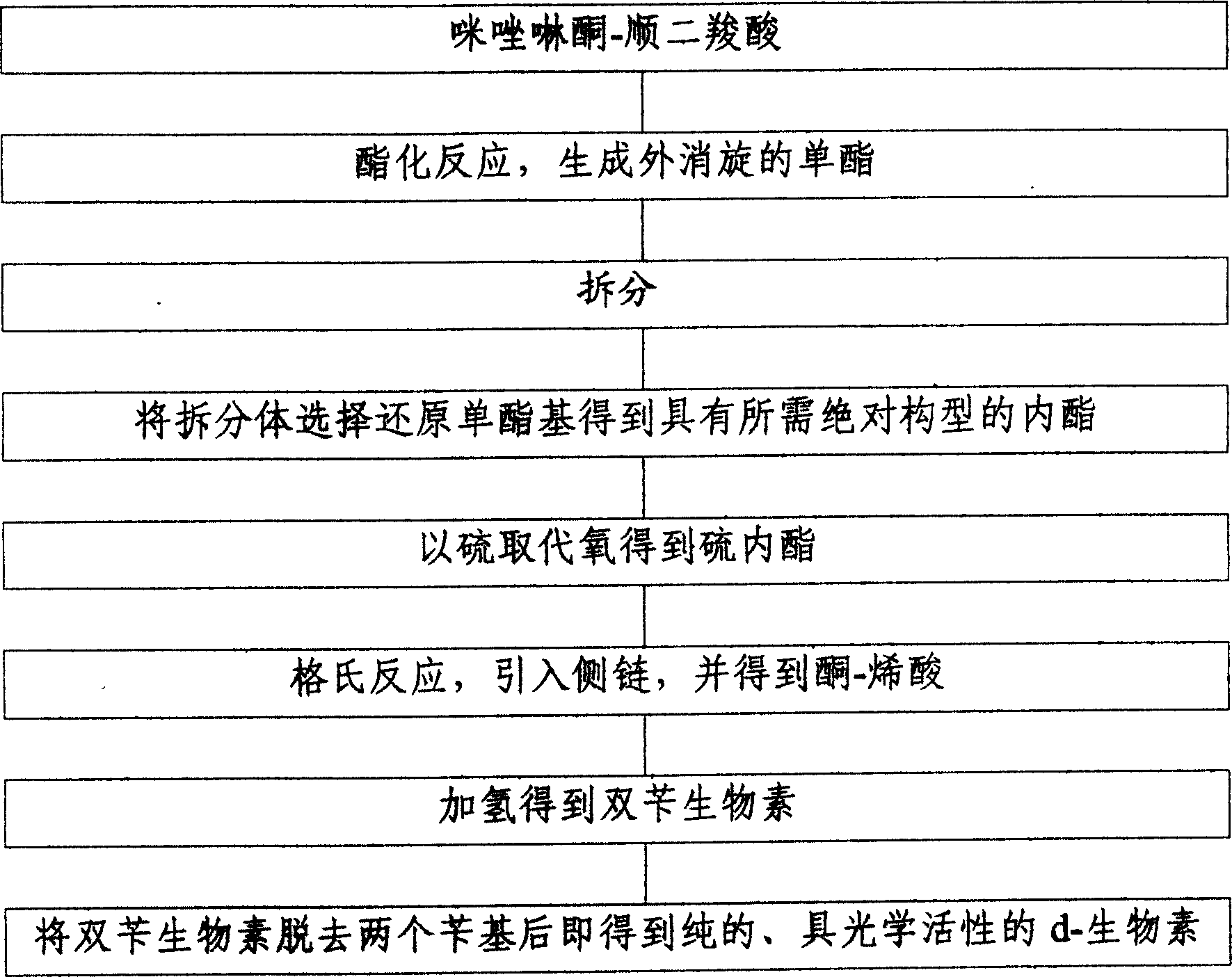
[0018] The present invention utilizes imidazolinone-cis-dicarboxylic acid with concentrated sulfuric acid as a catalyst to generate racemic monoester through esterification reaction with methanol, splits it with right amine, and selectively reduces the monoester group with sodium borohydride Obtain the lactone with the desired absolute configuration, then replace the oxygen with sulfur in potassium ethyl thioacetate to obtain the thiolactone, then use the Grignard reaction to introduce the side chain, and obtain (3aR, 6aR) by carbon dioxide and concentrated sulfuric acid -1,3-dibenzyltetrahydro-1H-thieno[3.4-d]imidazol-2-(3H)-one-enoic acid, then use palladium-carbon as a catalyst to hydrogenate dibenzyl biotin, and then in The pure, optically active d-biotin can be obtained after removing two benzyl groups in hot hydrobromic acid.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com