Resinous crosslinking agents and rubbers crosslinked with resinous crosslinking agents
A resin cross-linking agent and resin technology are applied in the field of resin cross-linking agent and rubber cross-linked with the resin cross-linking agent, which can solve the problems of corrosion of metal molds and corrosion of metal parts, and achieve small permanent compression deformation. High tear strength, the effect of shortening the necessary time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
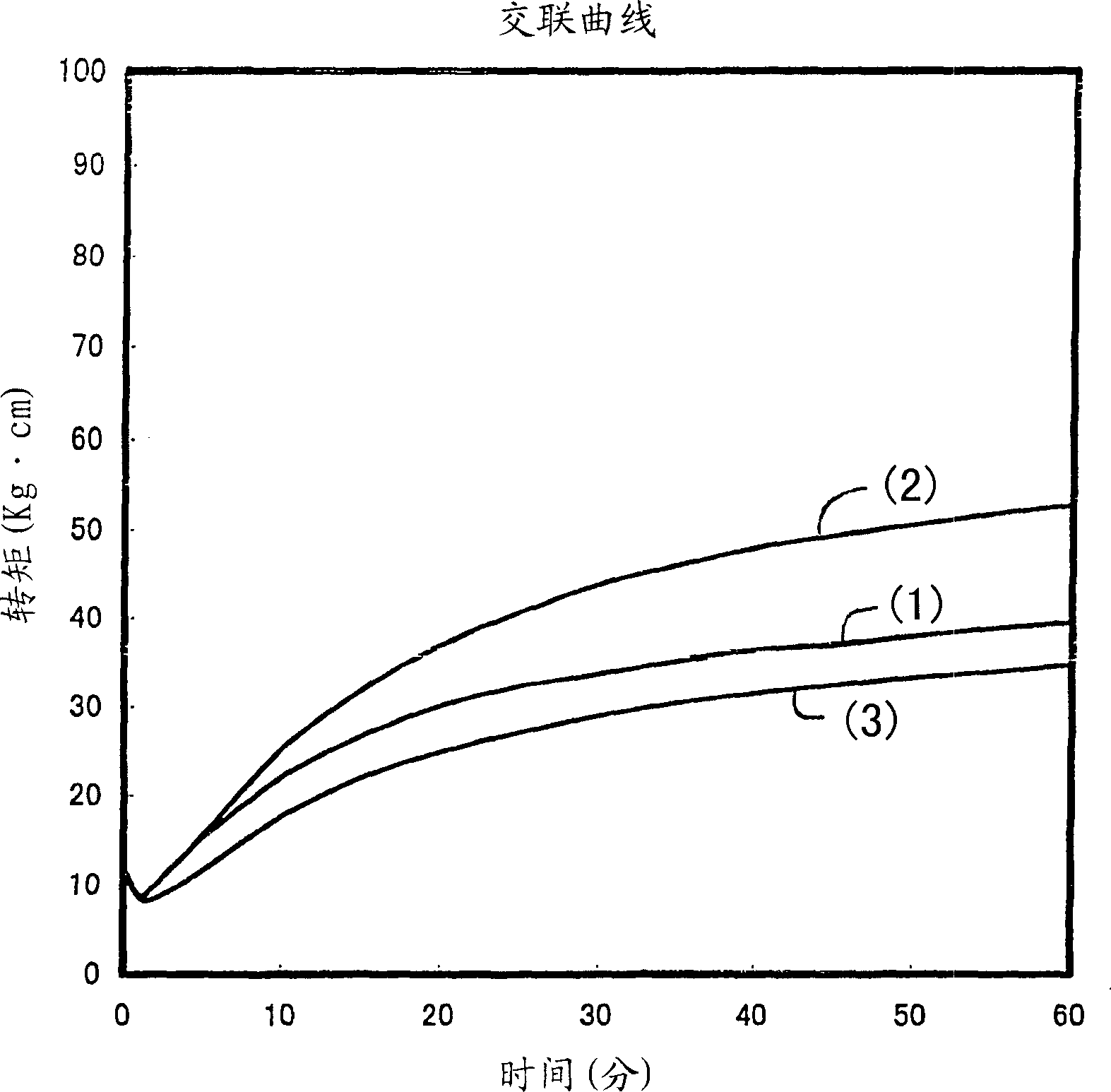
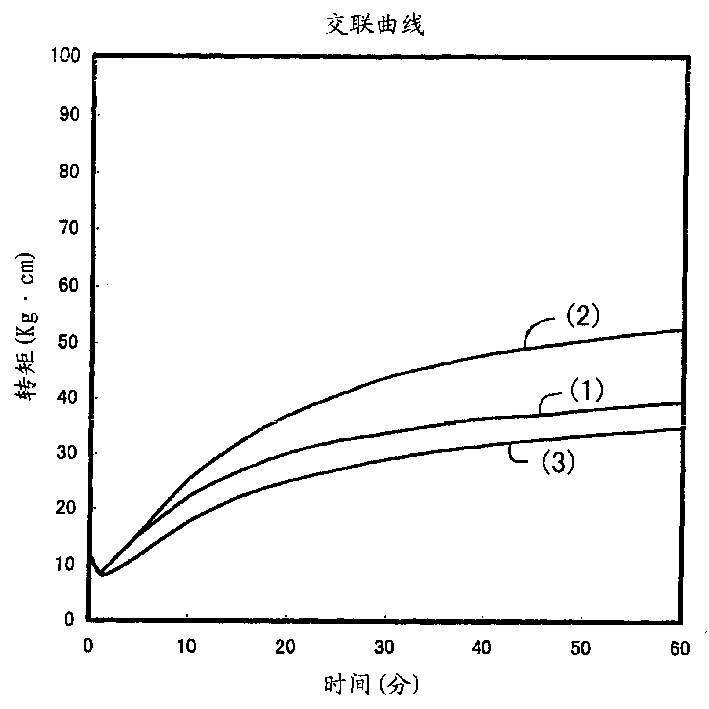
[0040] Contains 80% by weight of Tatsukiro-L 201 (manufactured by Tagoka Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., resole type alkylphenol-formaldehyde co-condensation resin) and 20% by weight of Sumikanol-L 610 (manufactured by Sumitomo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., novolac 15 parts by weight of Resin Crosslinking Agent A (alkylphenol-formaldehyde co-condensation resin) and 100 parts by weight of Polysa-Butyl 365 (butyl rubber manufactured by Polysa Corporation), 50 parts by weight of SRF carbon, 1 part by weight of stearic acid, and 5 parts by weight of zinc oxide was blended, and pressure crosslinking was performed at 200° C. for 35 minutes, and the following rubber physical properties were measured. Table 1 shows the results.
[0041] Hardness: According to JIS K6253, it measured using a type-A duro rebound hardness tester.
[0042] Compression set (%): Measured after 125 hours at 125° C. according to JIS K6262.
[0043] Cross-linking speed: The rubber blend is measured at 180° C. usin...
Embodiment 2
[0045]Resin crosslinking agent B18 parts by weight and 100 parts by weight of Polysa- ・Buchiru 365, 50 parts by weight of SRF carbon, 1 part by weight of stearic acid, and 5 parts by weight of zinc oxide were blended, and after pressure crosslinking was carried out at 200°C for 35 minutes, the hardness and compression permanent were measured in the same manner as in Example 1. deformation, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0046] In addition, the crosslinking speed was measured in the same manner as in Example 1. Its crosslinking curve is as figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0052] [Synthesis of Resin Crosslinking Agent A]
[0053] After replacing the 1-liter glass flask with nitrogen, 315 g of p-tert-octylphenol, 35 g of m-cresol, and 275 g of 37% formaldehyde aqueous solution were added, and the internal temperature was raised to about 40° C. while stirring slowly. Next, 13.8 g of a 47% caustic soda aqueous solution was added dropwise to start the reaction, and the reaction was carried out at 90 to 95° C. for 1 hour. Then, 67 ml of pure water and 275 ml of toluene were added, and the reaction solution was cooled and neutralized with hydrochloric acid. Next, oil-water separation was performed, and the condensed resin in the oil layer was recovered using a rotary evaporator to obtain about 350 g of a co-condensed resin (resin crosslinking agent A).
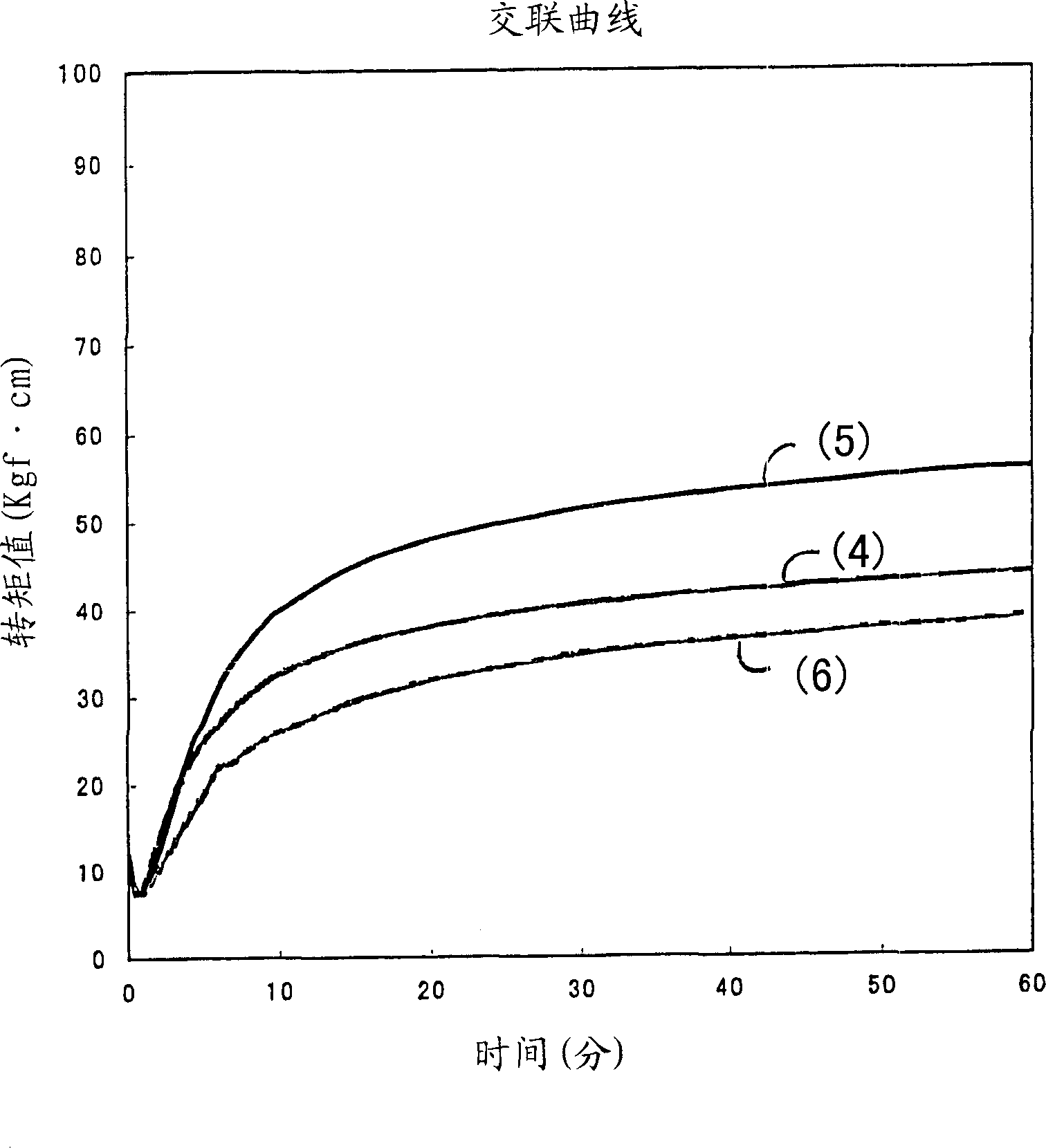
[0054] [Crosslinking of butyl rubber using resin crosslinking agent A]
[0055] Using the blend composition shown in Table 2, pressure crosslinking was performed at 200° C. for 35 minutes. For this...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com