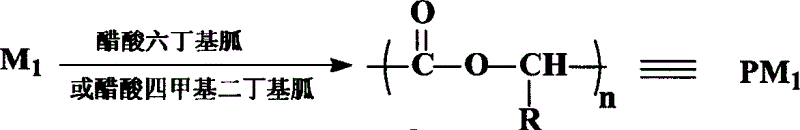Process of snthesizing medical biological degradative material by acetic acid organic guanidine as catalast
A technology of biodegradable materials and process methods, which is applied in the field of synthesis of medical biodegradable polyester polymers, can solve problems such as inability to remove tin-containing catalysts, cytotoxicity, and hidden dangers of safety, and achieve high yield and molecular weight distribution. Narrow, good polymer quality effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] In the reactor, 144 grams of lactide were charged, and 45.5 mg of hexabutylguanidine acetate catalyst was added according to monomer: catalyst=10000: 1 (molar ratio). Vacuumize the reactor, then replace it with nitrogen and repeat the operation three times, close the reactor under vacuum, heat the reactor slowly, and react at a constant temperature (110-120° C.) for 72 hours. After stopping the reaction, the reactor was cooled to room temperature, and then acetone was added to dissolve the polymer in the reactor. Deionized water was then added to precipitate the polymer. The water phase was filtered off, and finally the precipitate was dried in a vacuum oven at 50° C. for 24 hours under vacuum to obtain a white powdery solid with a yield of 99%. The polymer molecular weight is 2.0~4.0×10 4 , PDI≤1.20.
Embodiment 2
[0018] 144 grams of lactide were charged into the reactor, and 28.7 mg of tetramethyldibutylguanidine acetate catalyst was added according to monomer:catalyst=10000:1 (molar ratio). Vacuumize the reactor, then replace it with nitrogen and repeat the operation three times, close the reactor under vacuum, heat the reactor slowly, and react at a constant temperature (110-120° C.) for 72 hours. After stopping the reaction, the reactor was cooled to room temperature, and then acetone was added to dissolve the polymer in the reactor. Deionized water was then added to precipitate the polymer. The water phase was filtered off, and finally the precipitate was dried in a vacuum oven at 50° C. for 24 hours under vacuum to obtain a white powdery solid with a yield of 96.5%. The polymer molecular weight is 2.0~4.0×10 4 , PDI≤1.20.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com