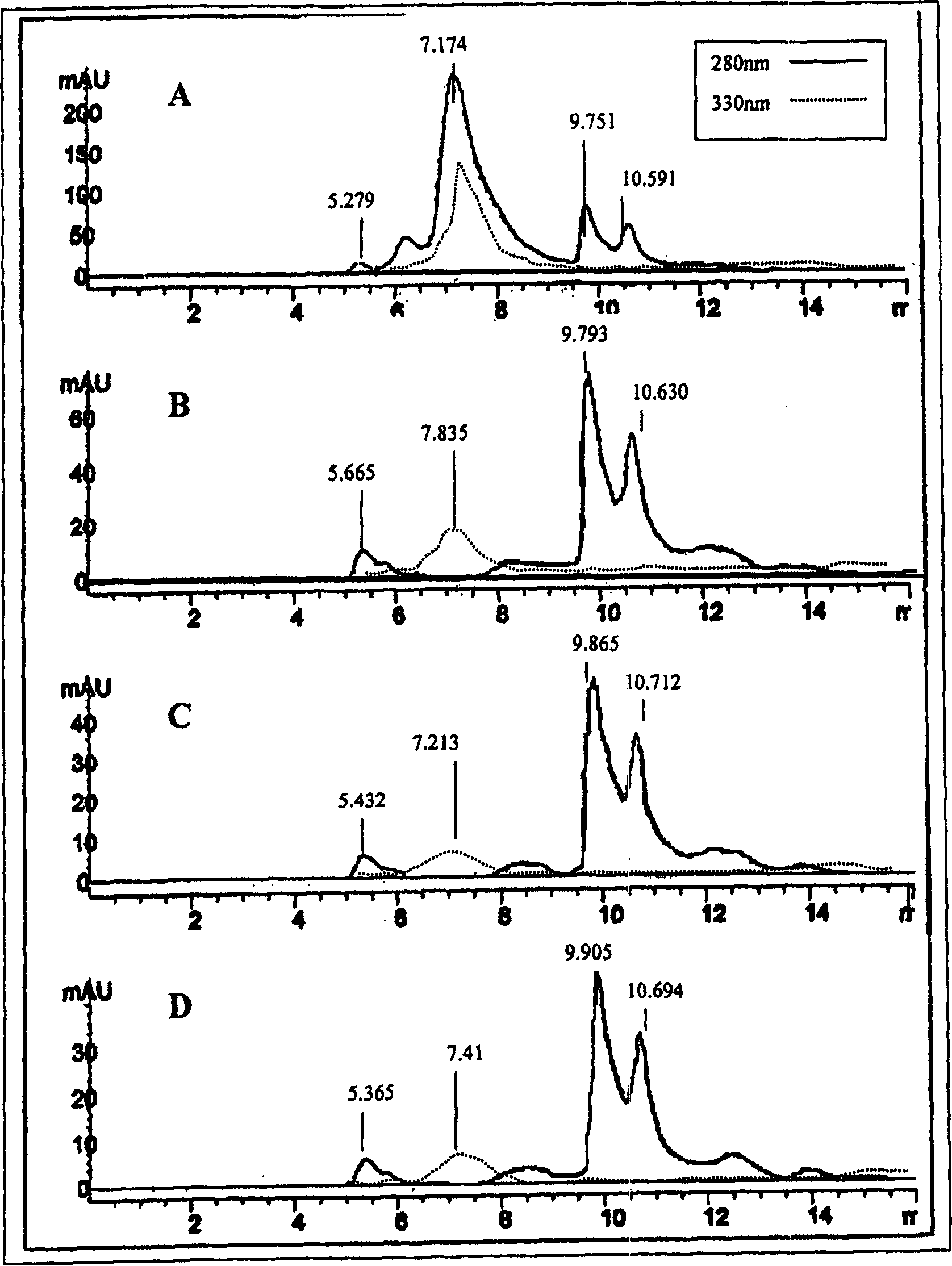
Use of lactalapoprotein in prevention and treatment of microbial or virus infection
A technology of prosthetic protein and milk, which is applied in the direction of antiviral agents, anti-infective drugs, hydrolyzed protein components, etc., to achieve the effect of preventing dental caries and inhibiting adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0130] Embodiment 1: Preparation of whey free fatty acid and whey apoprotein
[0131]Lactose-free whey powder (Carbelac 80 from Carbery Dairy) was used as starting material. Carbelac80 is a typical 100% whey, and the typical Carbelac80 contains 0% skim milk, 80% protein, 5% moisture, 8% fat and 3% dust. 30 g of this starting material were dissolved in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 6.8 in a final volume of 1 liter. To this was added 1 g of a suitable composition of various esterases (mainly lipases, but also amylases and proteases), eg "crude extract of type II esterase from porcine pancreas" available from Sigma. The mixture was incubated at 37°C for 18 hours; heat-treated at 60°C for 10 minutes to inactivate the enzyme; and spray dried.
[0132] Other suitable esterases include, but are not limited to, the commercial products "Palatase" and "Novozyme" from Novo Nordisk (Copenhagen, Denmark), when the two enzymes are mixed 50:50 (w / w) and 1 g is added per 30 g In lacto...
Embodiment 2
[0167] The growth inhibitory properties of standard formulations against fresh clinical isolates of C. albicans were evaluated using the growth assay described above in the Methods and Materials. The analysis was performed in a microtiter format, with quadruplicate assays for each concentration tested. Yeast growth was monitored over 20 hours at 600 nm and the results are shown in FIG. 6 . The standard formulation (5 mg / ml) showed almost 90% growth inhibition relative to the control to which 0 mg / ml standard formulation was added. The results for the standard formulation at 1 mg / ml were in between.
[0168] A similar analysis process is adopted, except that the substance to be tested is added after 5 hours of normal yeast growth, which is called interference analysis herein. The concentration range of standard preparations added is 0-8mg / ml. The detection concentration was set in this way to ensure that when the preheated (to 37°C) solution to be tested was added, the dilut...
Embodiment 3
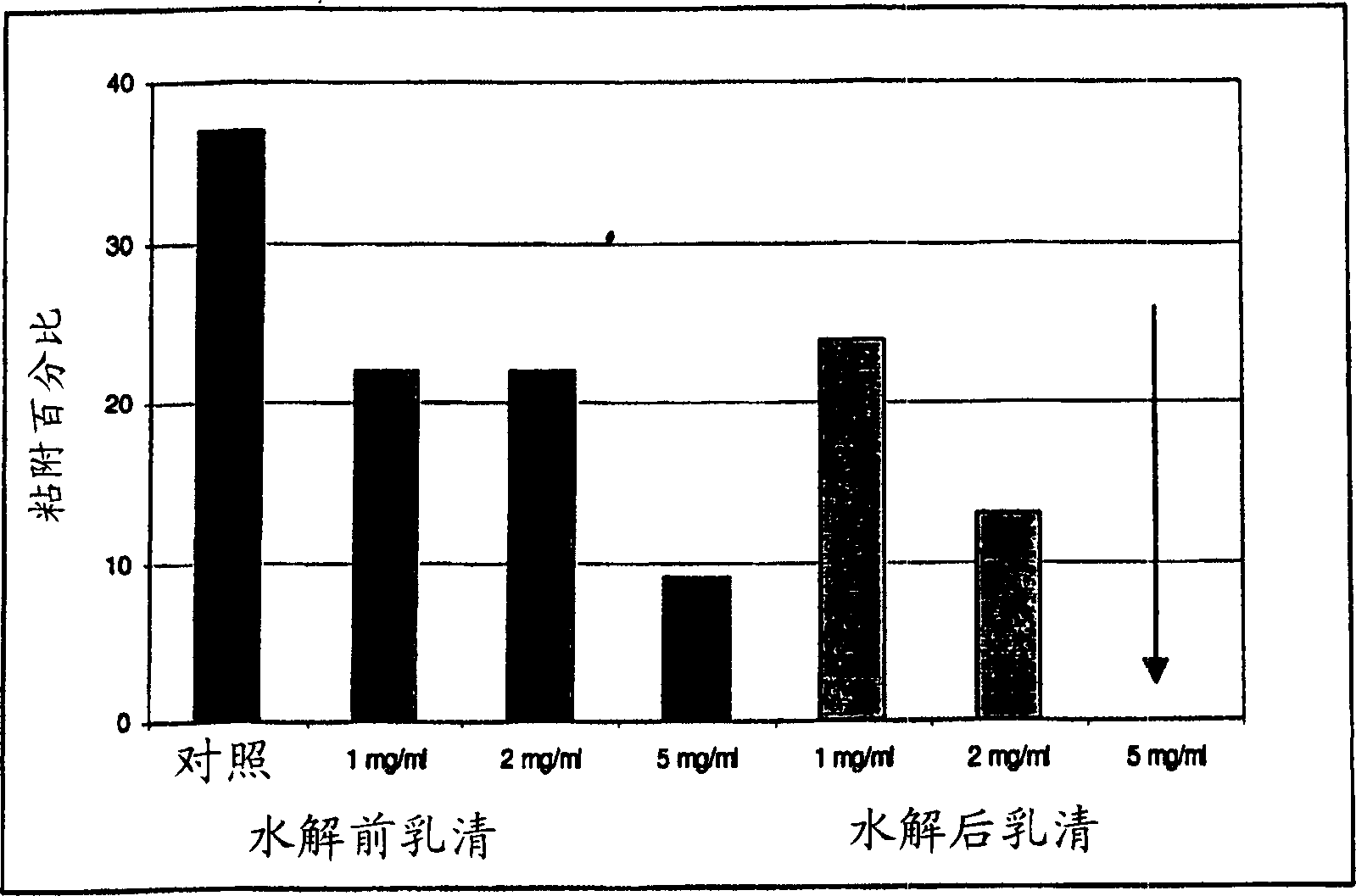
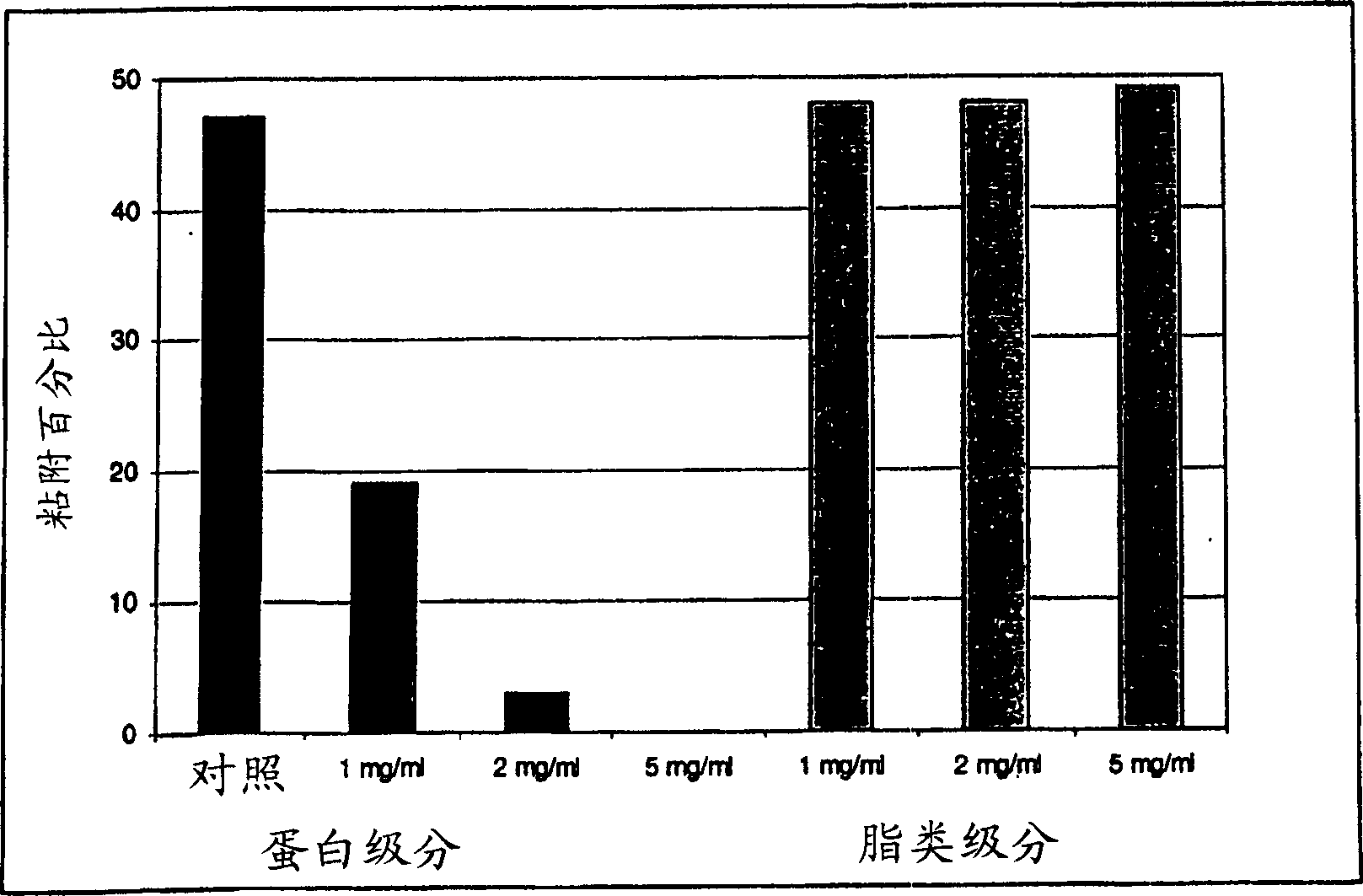
[0170] Standard formulations inhibited adhesion in addition to inhibiting growth. Adhesion assay methods are described above in Methods and Materials. Using the same formulation as in Example 2, its inhibitory effect on the adhesion of the same fresh clinical isolate of Candida albicans to oral epithelial cells is shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9 .
[0171] In Figure 8, yeast cells have been exposed to the standard formulation for 10 minutes prior to the addition of oral epithelial cells. In Figure 9, oral epithelial cells have been exposed to the standard formulation for 10 minutes before adding the yeast suspension.
[0172] The "control" in both assays represents the adhesion achieved under the test conditions in the absence of inhibitory substances; 41% and 35%, respectively. Addition of 1 mg / ml standard formulation to Candida pretreatment reduced adhesion to 20% (53% inhibition), while addition of the same concentration of standard formulation to oral epithelial cell pret...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com