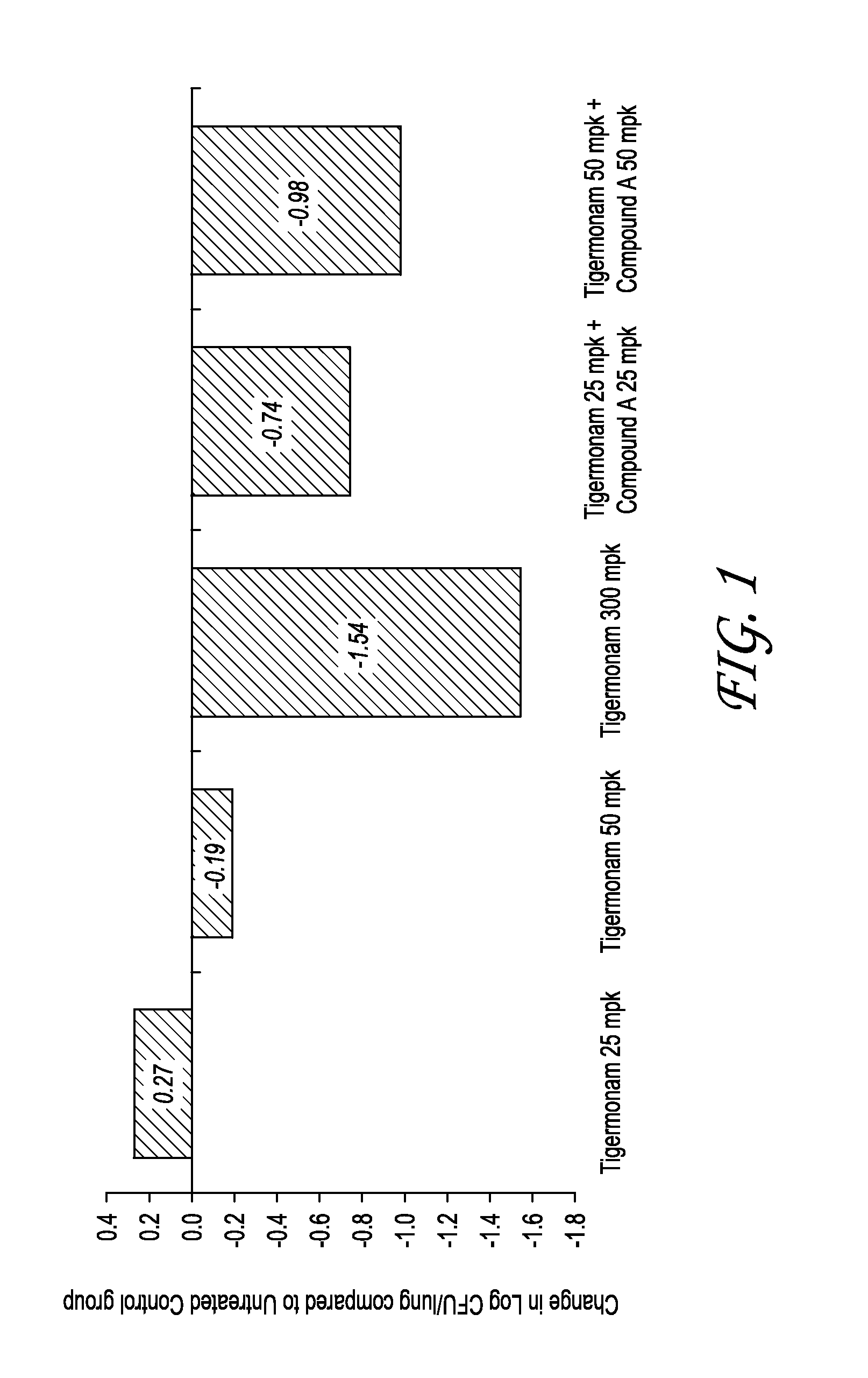
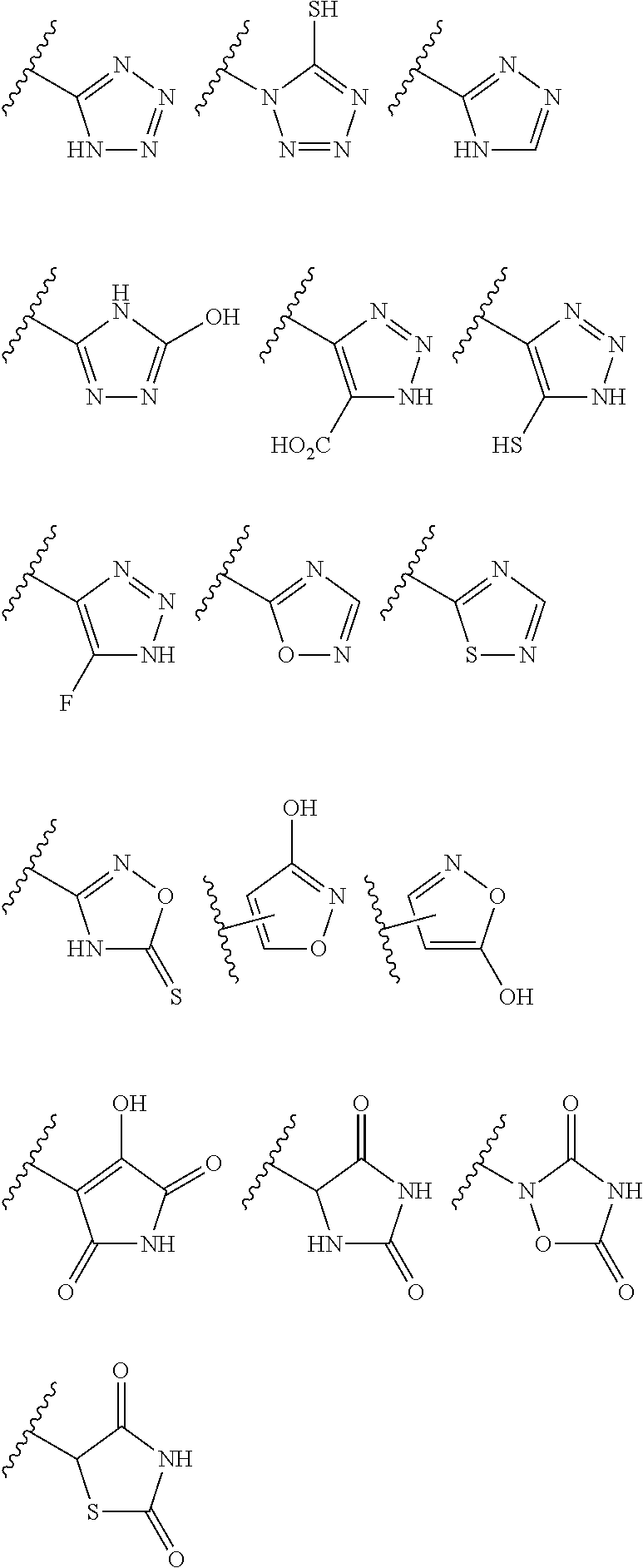
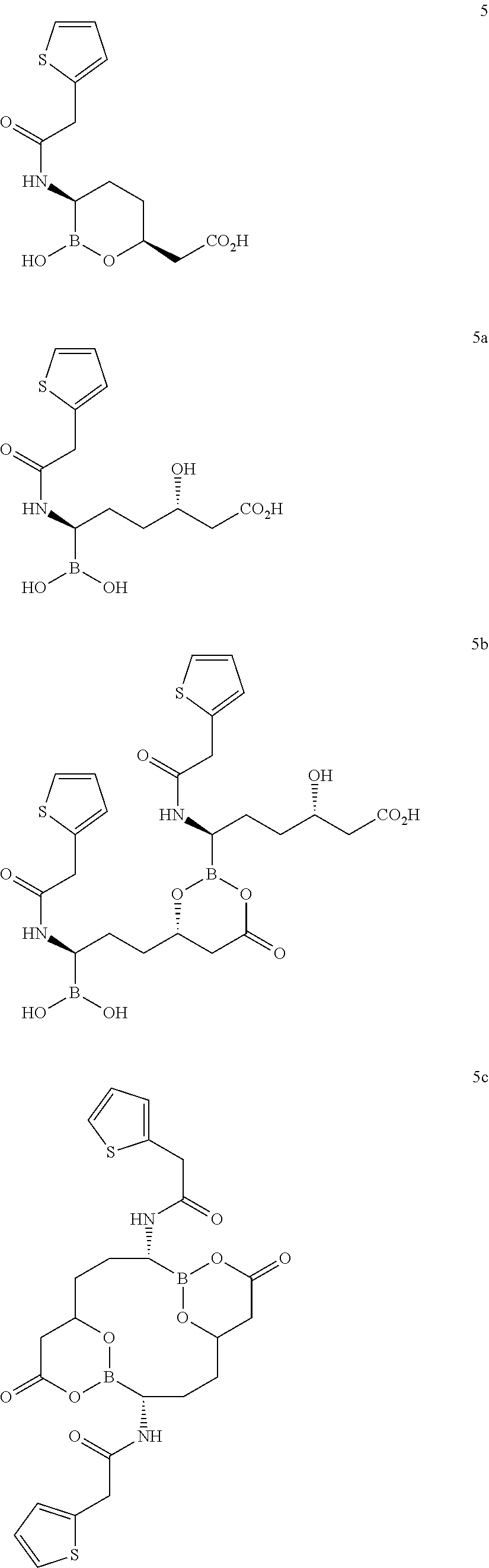
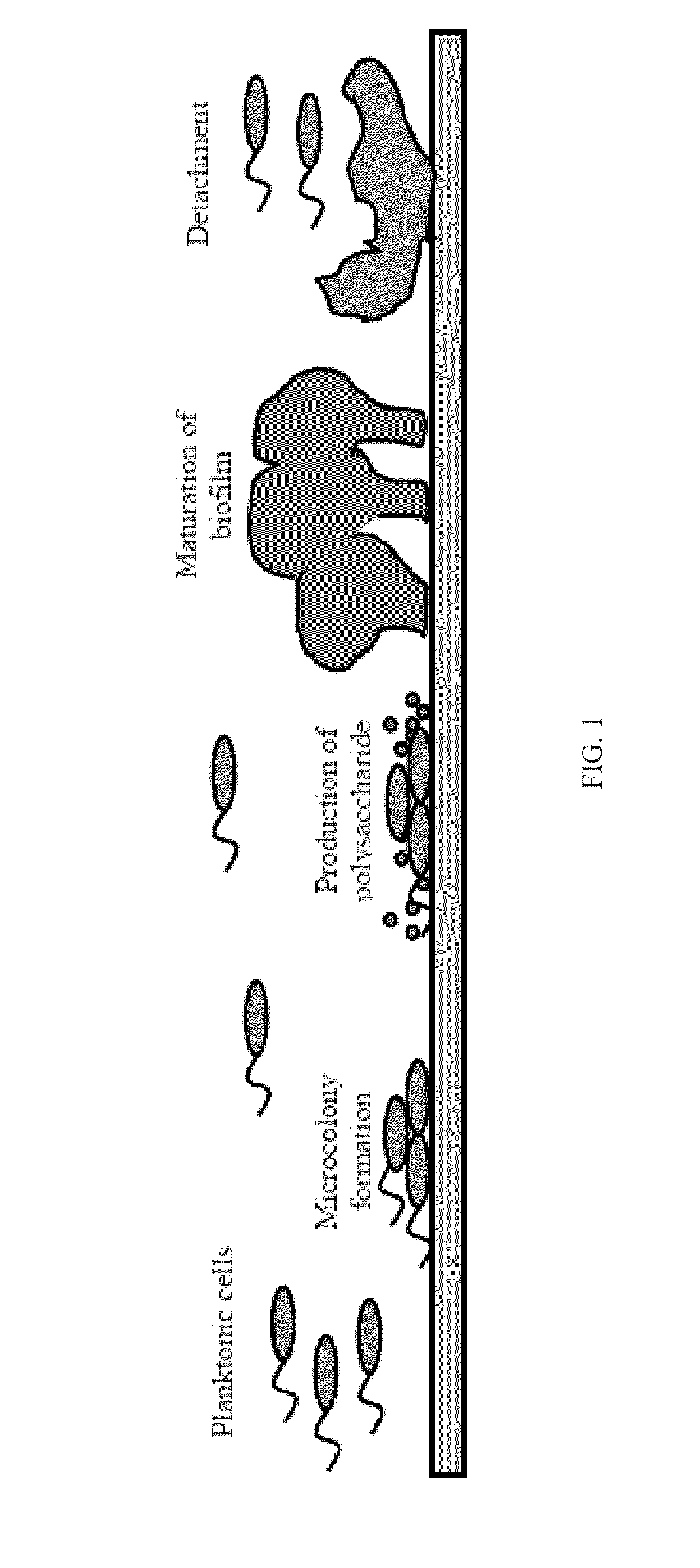
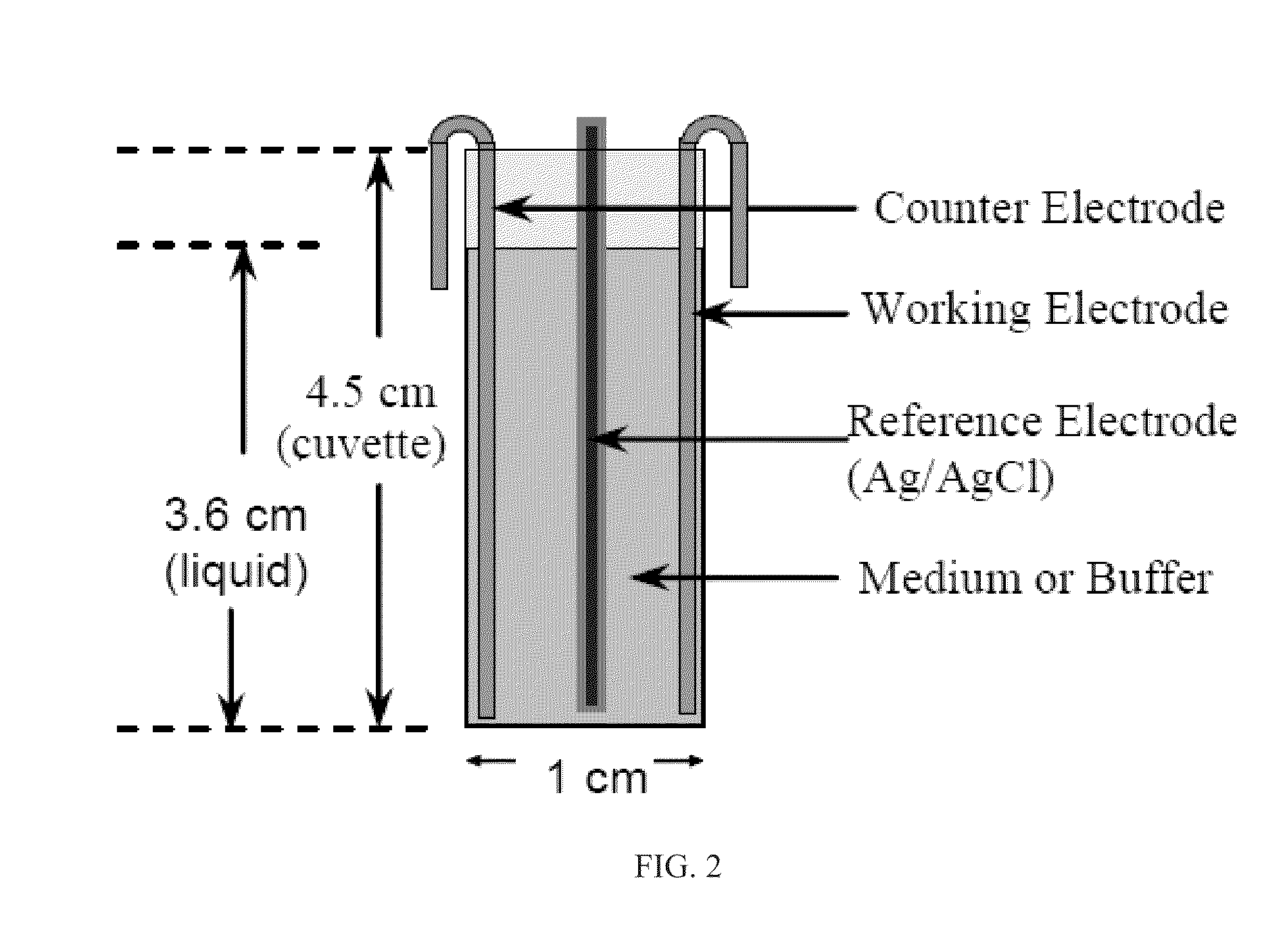
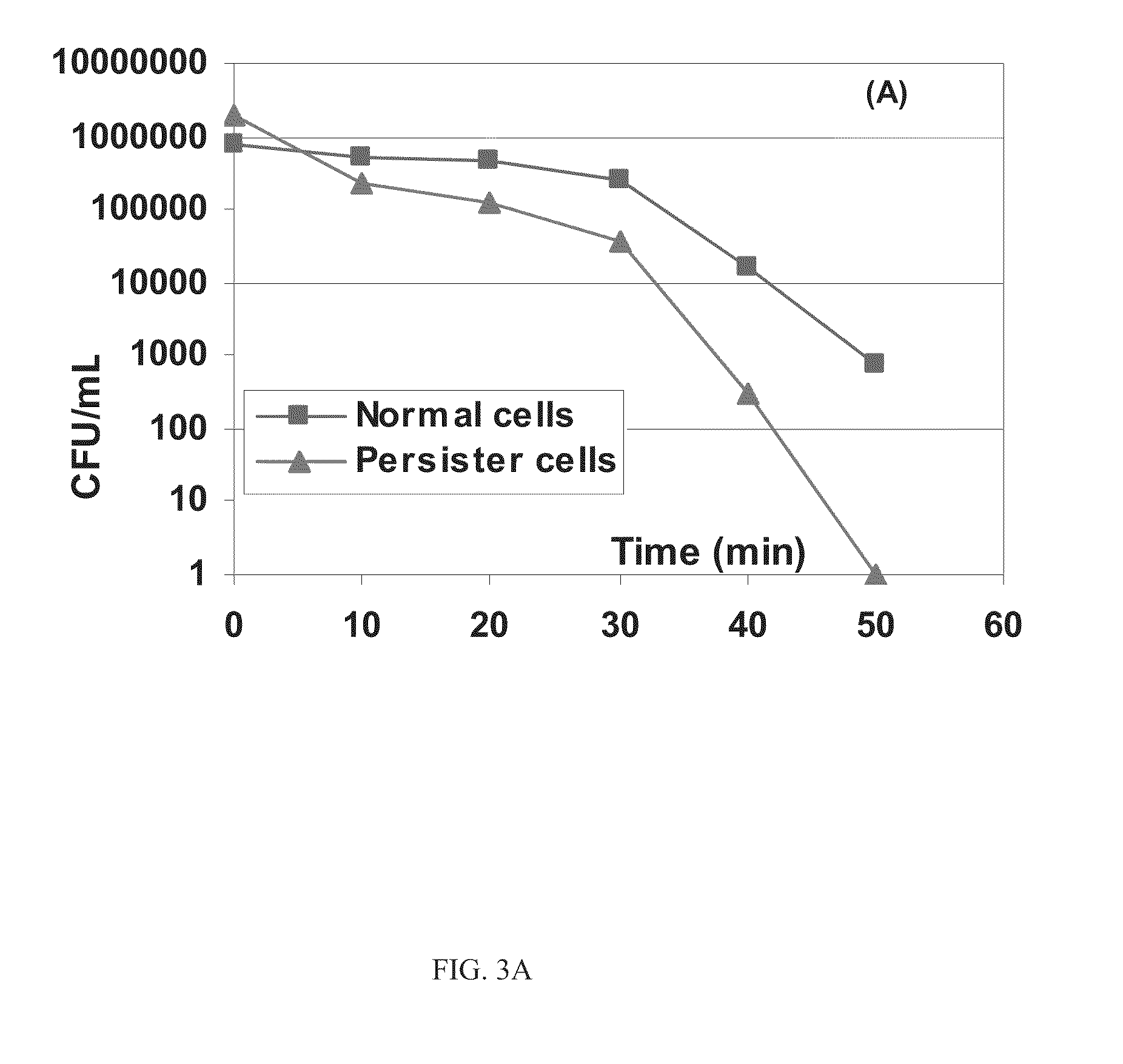
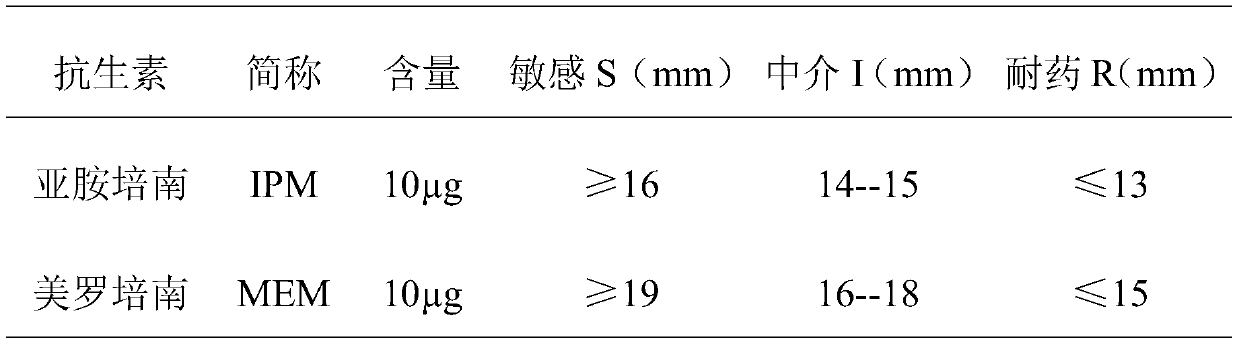
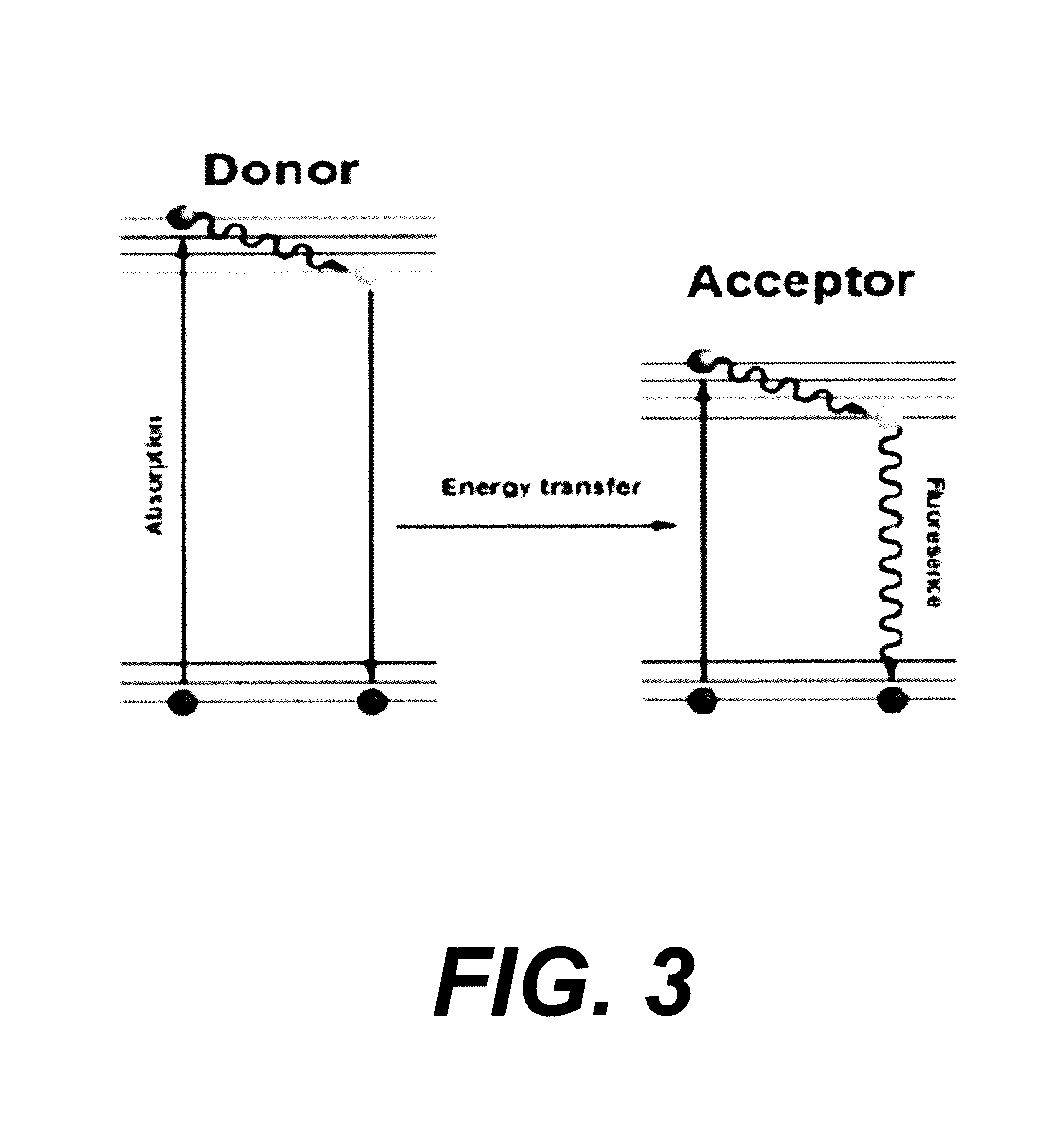
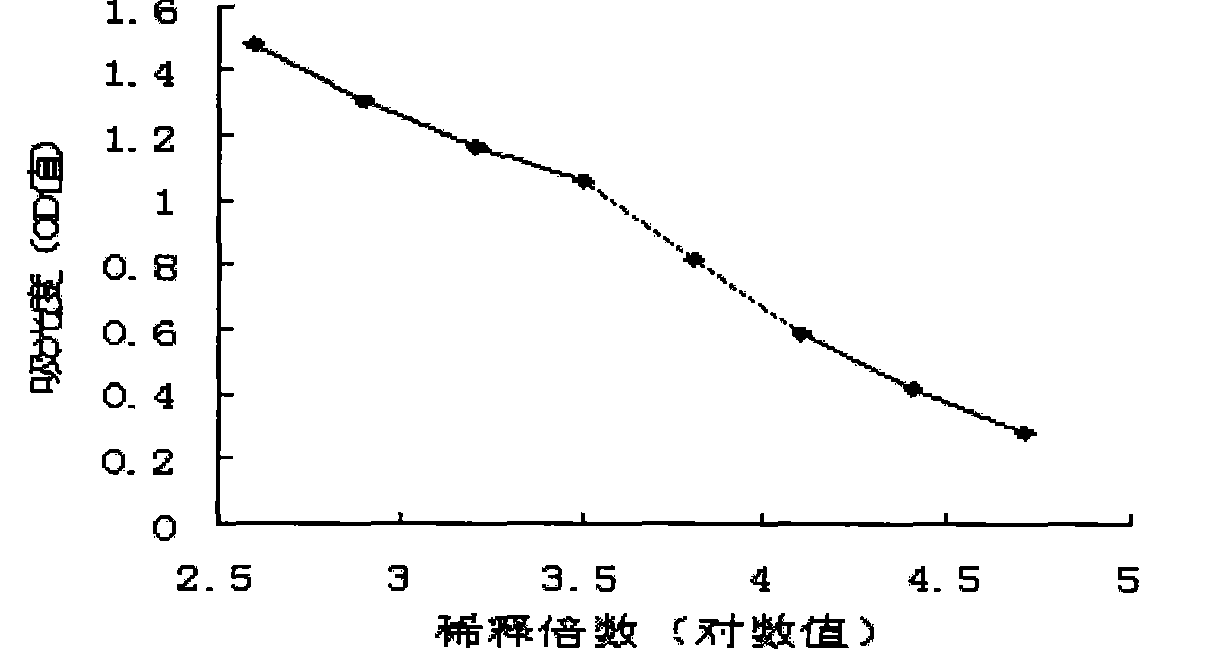
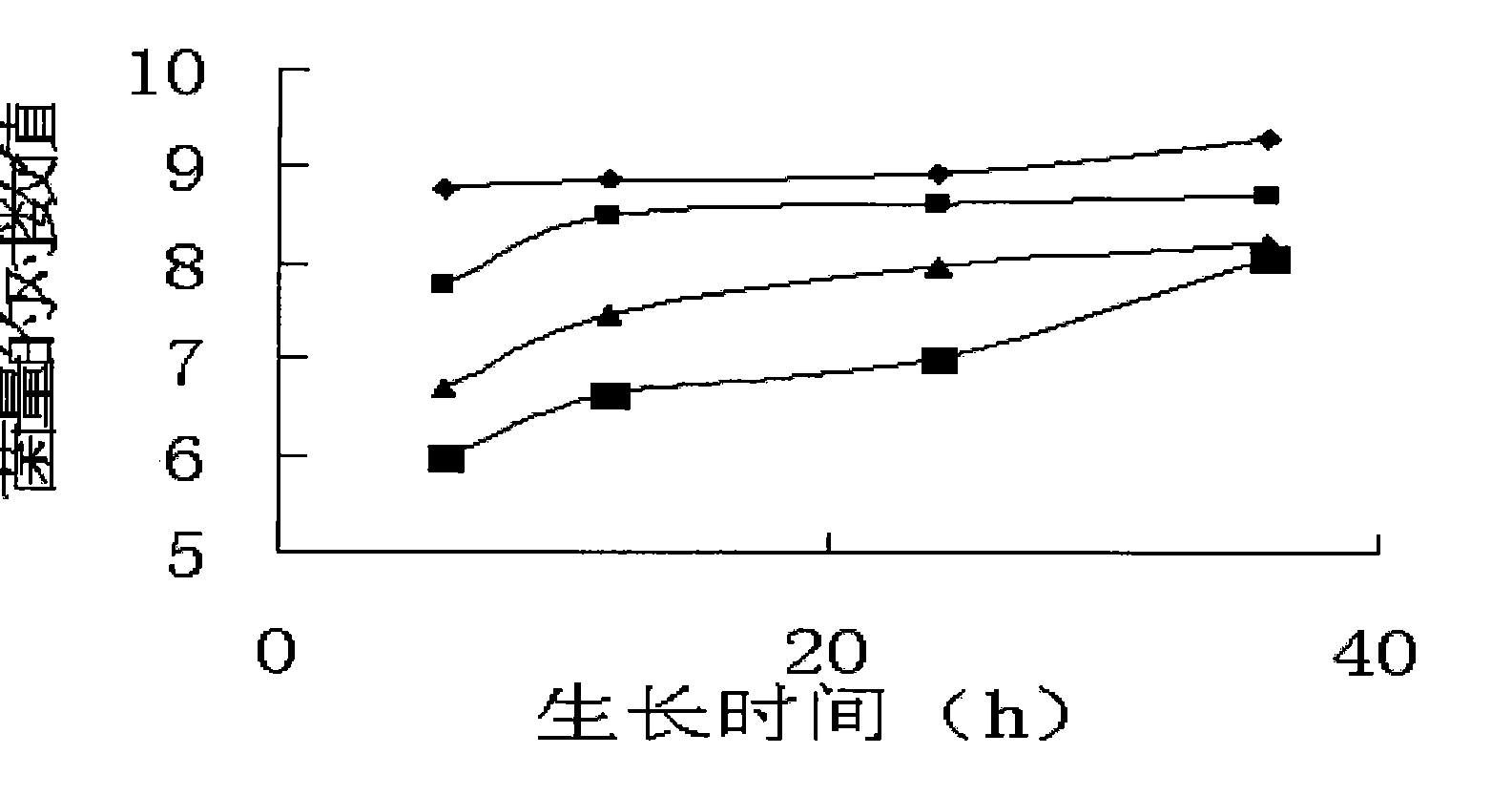
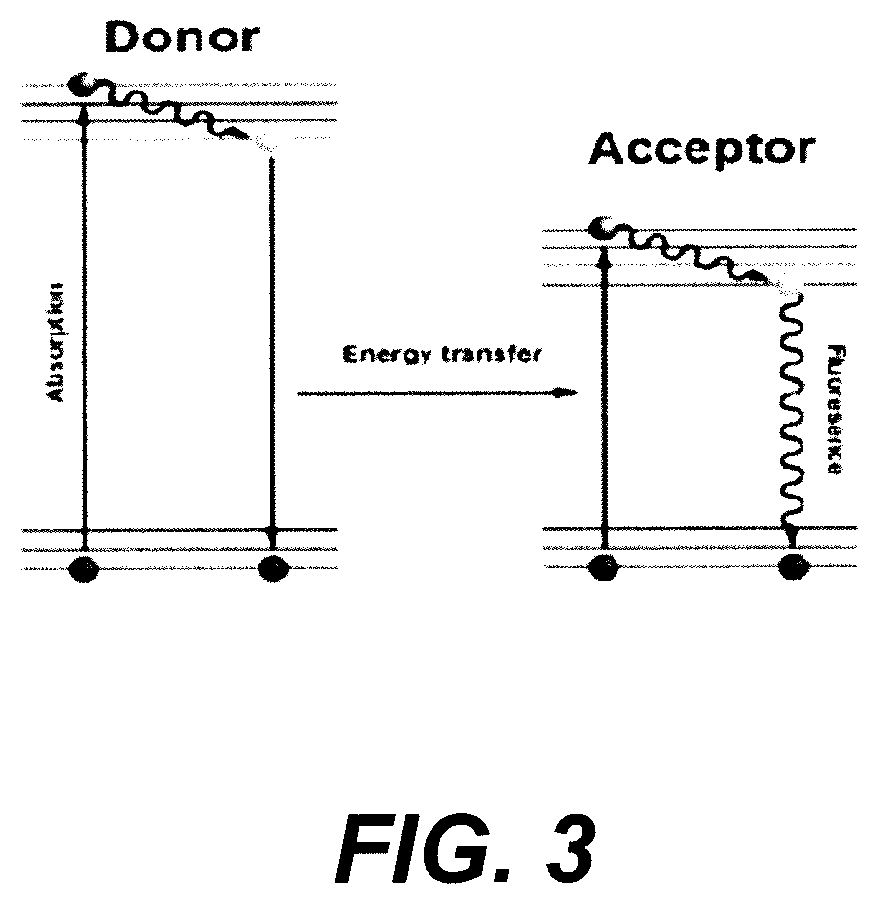
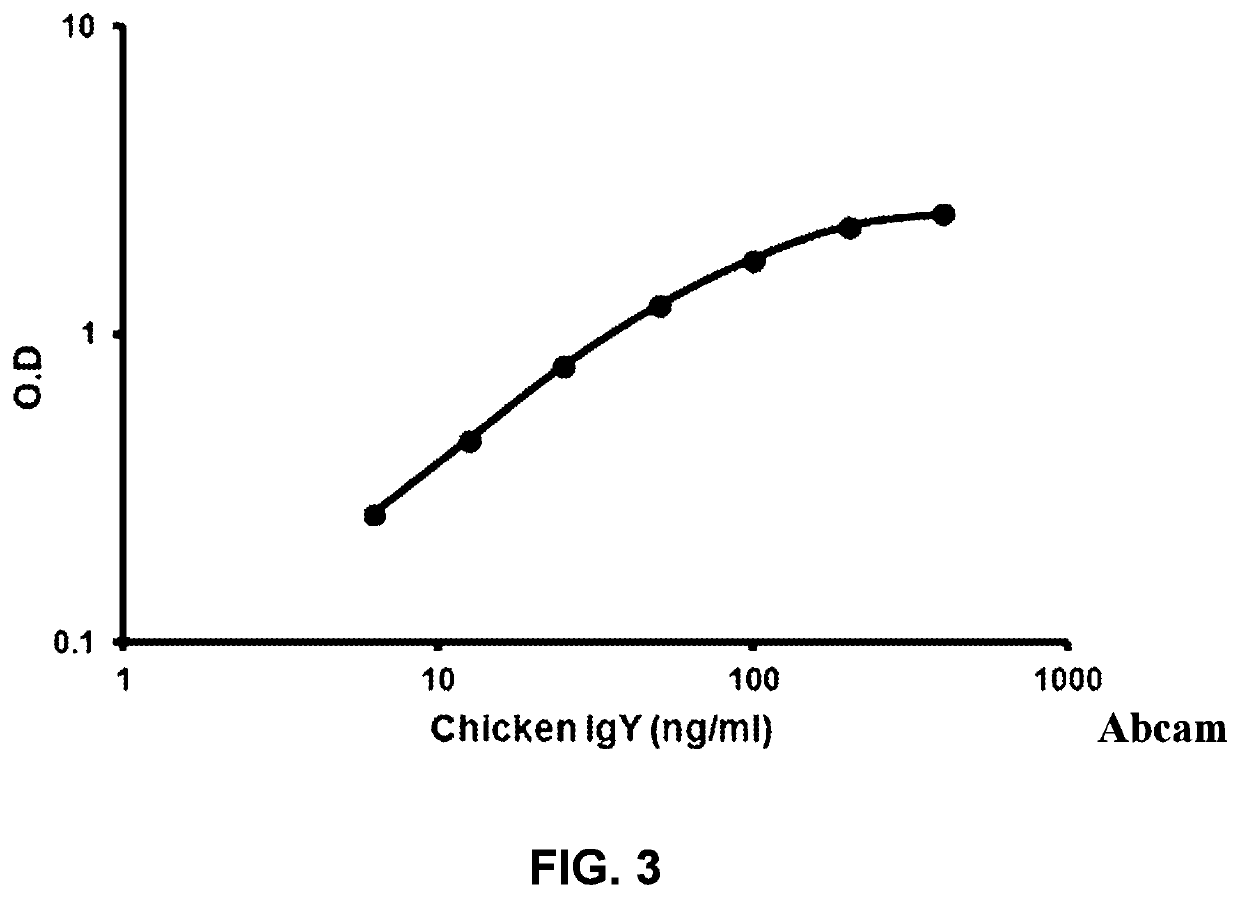
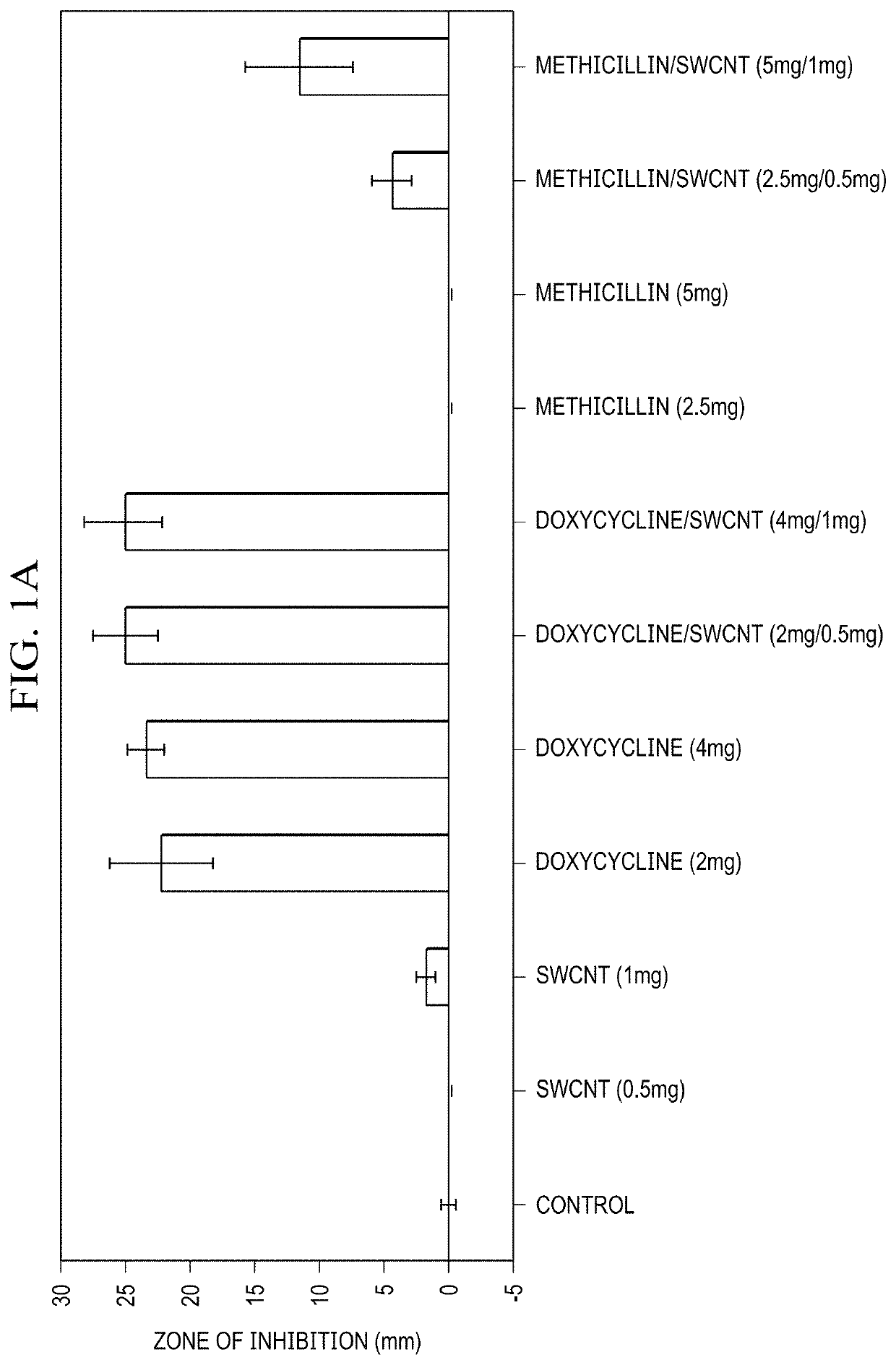
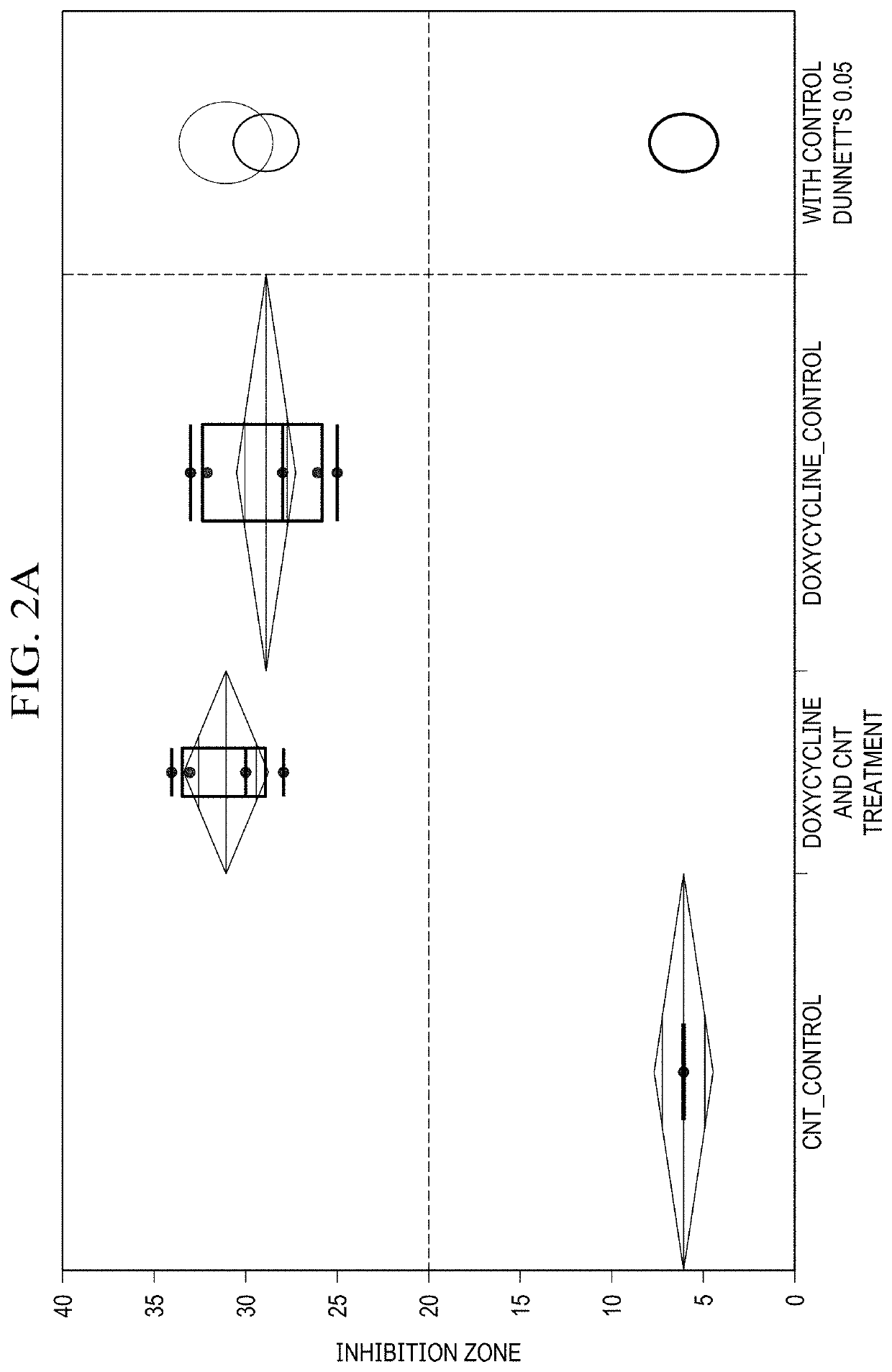
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Resistant infection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compositions and methods for enhancing drug sensitivity and treating drug resistant infections and diseases
InactiveUS20060286574A1Improve therapeutic indexReduce systemic toxicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicroorganismChemotherapeutic drugs
The present invention provides compositions useful in treating drug-resistant microorganisms and cells, as well as related methods of identifying and using such compositions. In addition, the present invention includes compositions useful in enhancing the sensitivity of both drug-resistant and drug-sensitive microorganisms and cells to microbicidal and cytotoxic agents, including antibiotics and chemotherapeutic drugs. Methods of identifying these compositions, as well as methods of using these agents in treating both drug-resistant and drug-sensitive diseases and conditions are further provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
Methods of treating bacterial infections
The present invention relates to compounds, compositions and methods for treating bacterial infections. Embodiments of the present invention include antibiotics and β-lactamase inhibitors to treat resistant infections.
Owner:REMPEX PHARM INC
Immunoloregulation type DNA vaccine capable of preventing Eimeria necatrix
InactiveCN101422605AGood immune protectionEffective immune protectionGenetic material ingredientsAntiparasitic agentsAntigenEmoia loyaltiensis
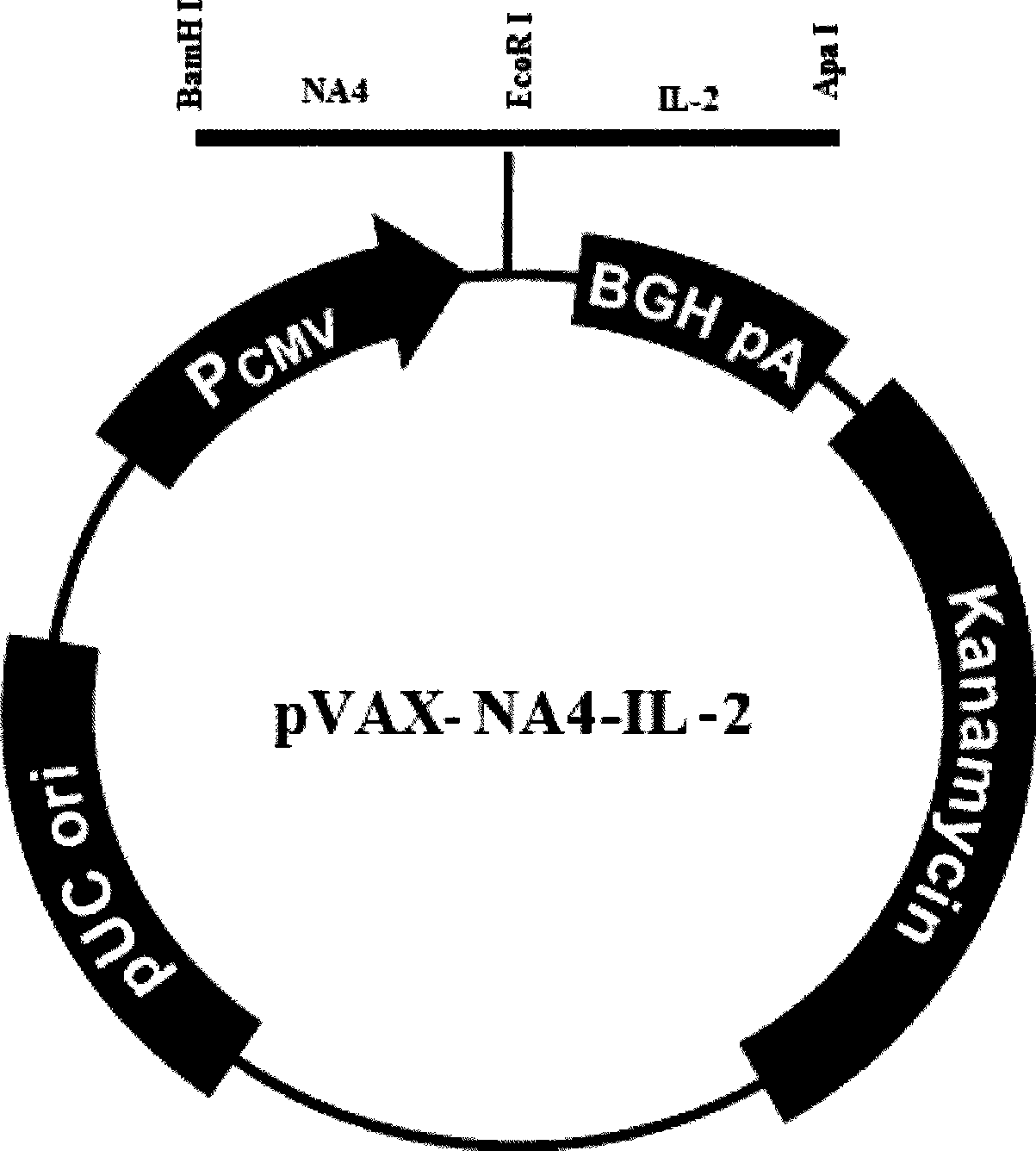
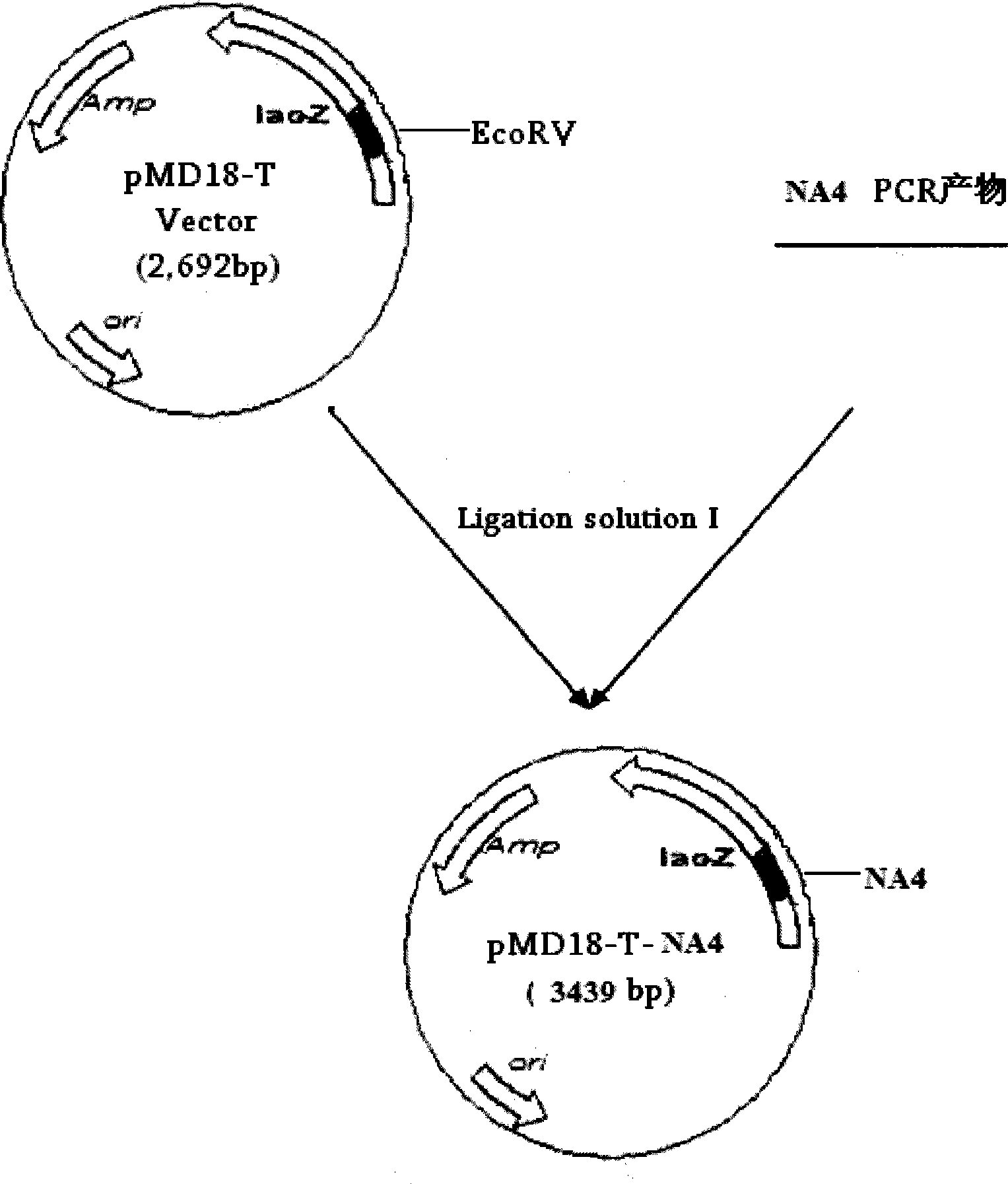
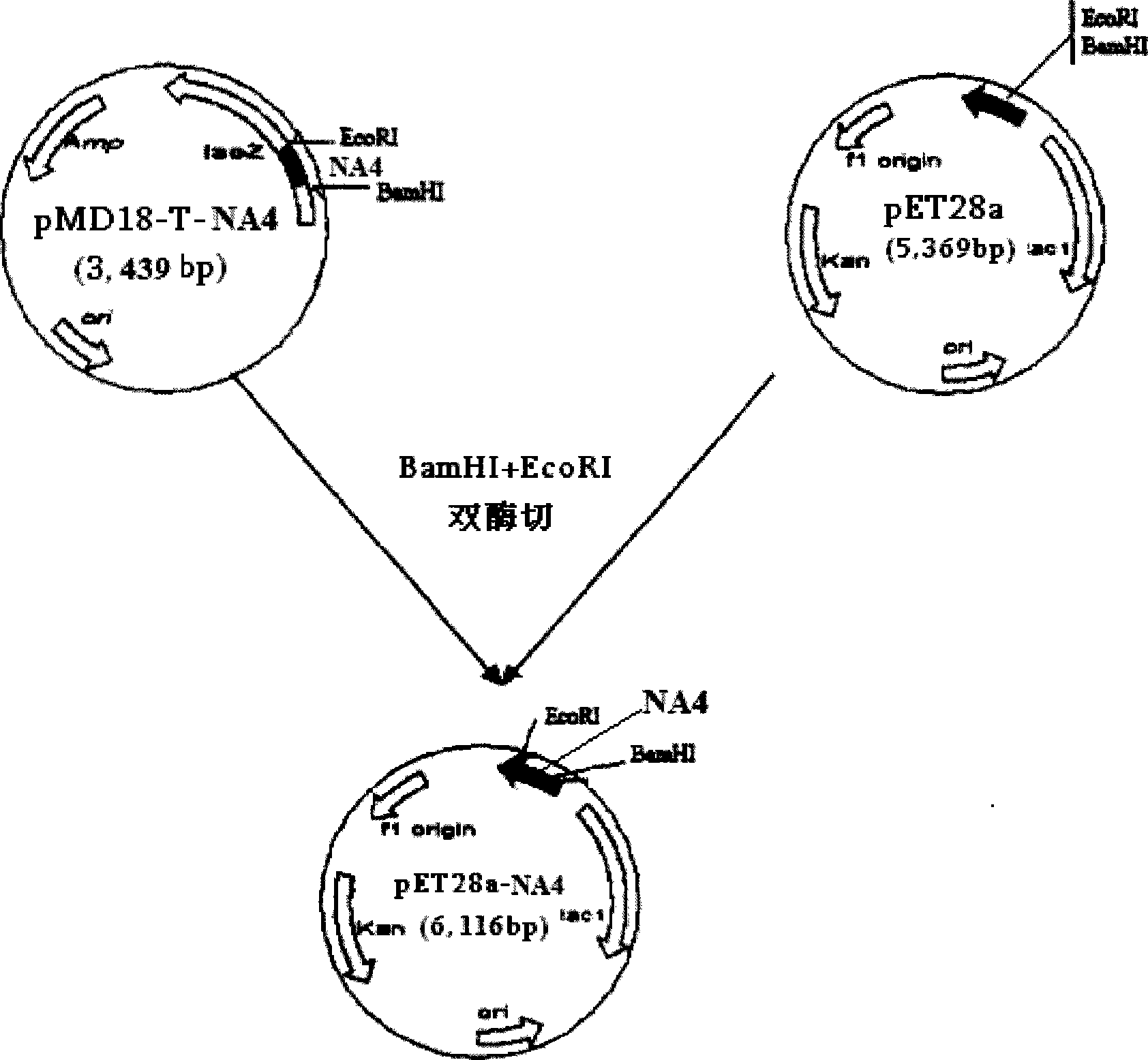
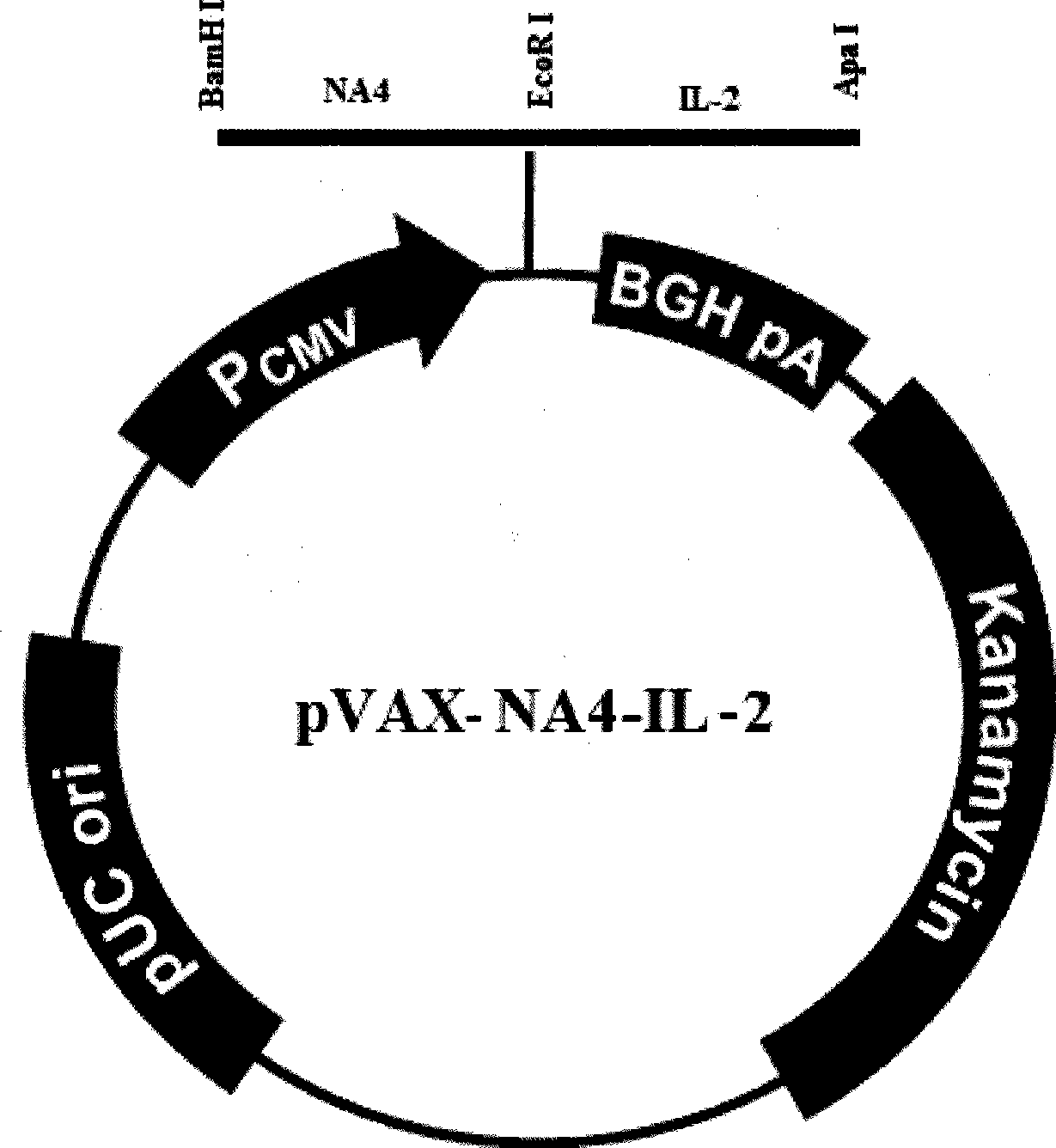
The invention relates to a chicken toxic Eimeria acervulina immunoregulation type DNA vaccine, which belongs to the technical field of biological veterinary medicines. The molecular biology technology is used for connecting toxic Eimeria sporozoite surface antigen NA4 genes and chIL-2 genes in series to construct a fusion expressing carrier pVAX-LDH-IL-2. The vaccine comprises the inserted toxic Eimeria sporozoite surface antigen NA4 genes and the chIL-2 genes. The vaccine comprises a plurality of T cell immune response elements, and has the advantages of high safety, long keeping time in bodies, simple preparation, good heat stability, convenient storage and transportation, time saving and labor saving when in use and the like, thus preventing and curing chicken coccidiosis effectively. Tests prove that the immunoregulation type DNA vaccine pVAX-NA4-IL-2 has good immune protection effect in coccidian resistant infections.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
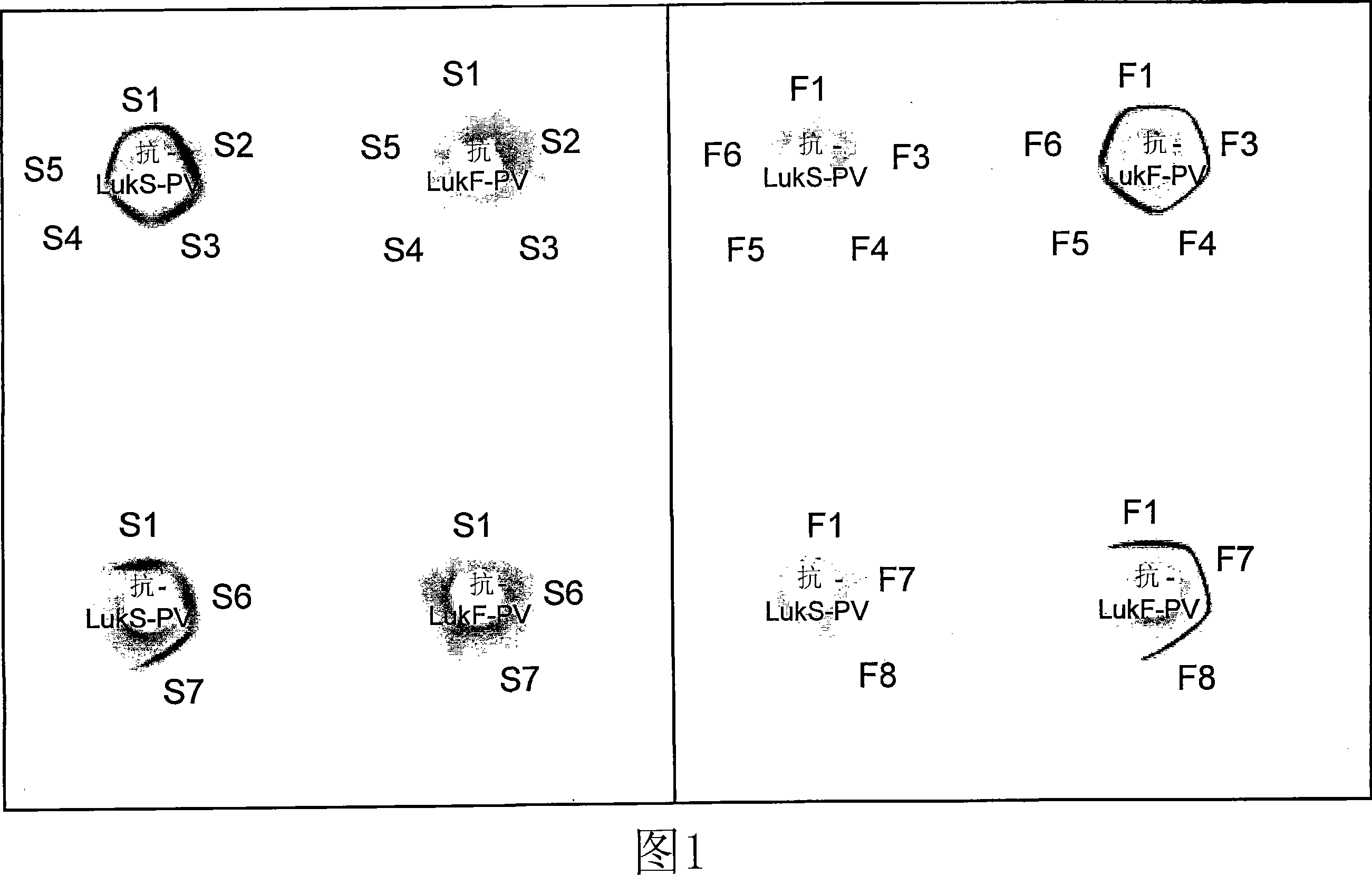
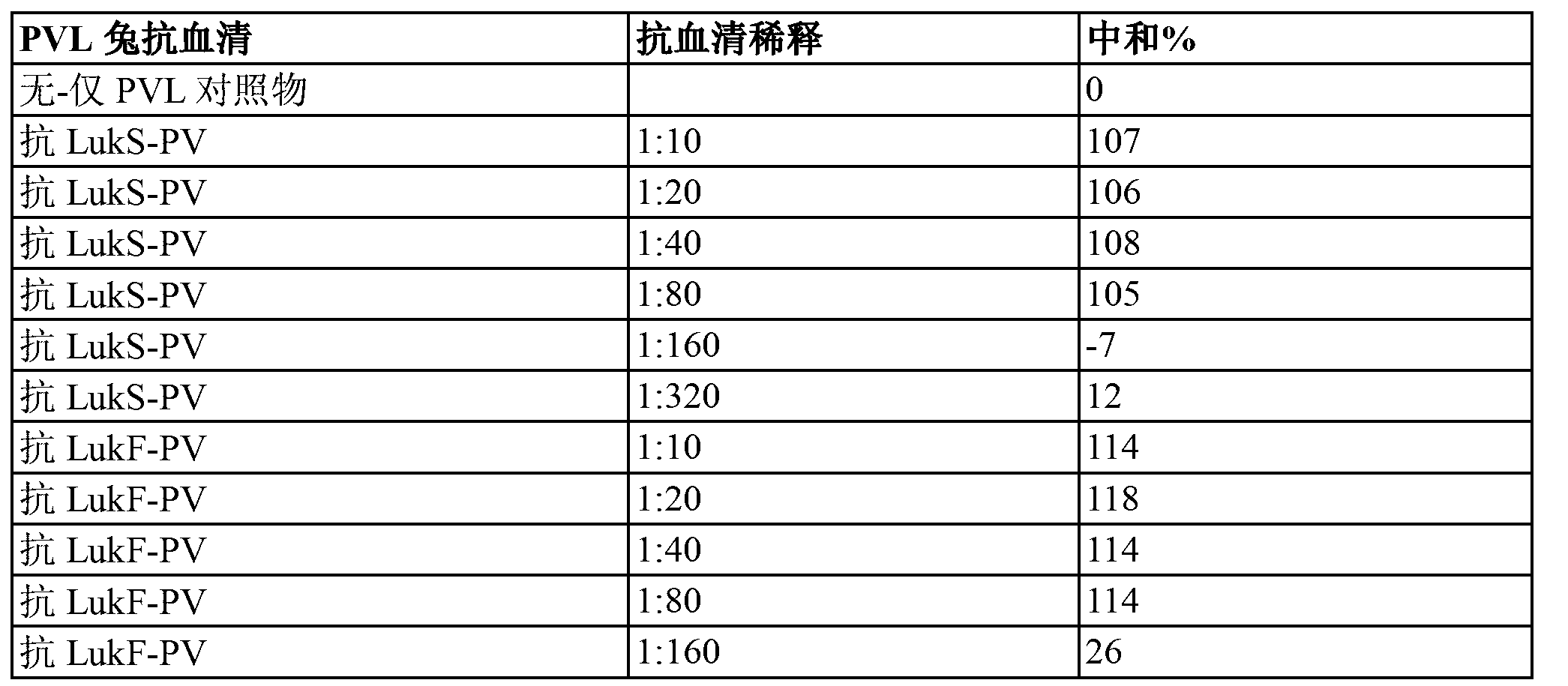
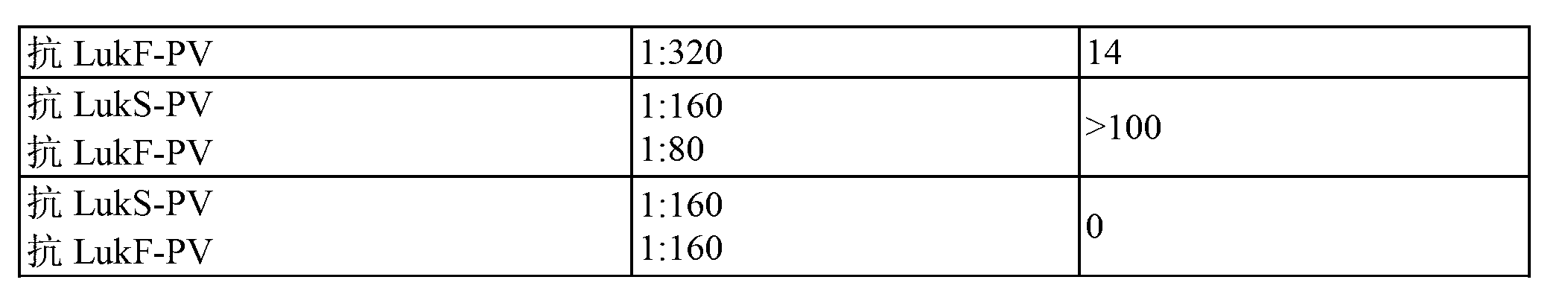
Use of PANTON-VALENTINE leukocidin for treating and preventing staphylococcus infections
InactiveCN101218252AAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaAntigenStaphylococcus cohnii
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for treating Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) infections. In particular, the present invention provides vaccines comprising a Panton- Valentine Leukocidin (PVL) antigen, antibodies which bind a PVL antigen and compositions containing the same, methods of making such compositions and methods for treating S. aureus infections, including those that are community acquired methicillin-resistant infections. The present invention also provides PVL antibodies, including PVL antibodies specific for a single PVL subunit, and PVL antigens, including conjugated and mutated PVL antigens.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
System And Method For Controlling Bacterial Cells With Weak Electric Currents
ActiveUS20110143413A1Eliminate effectiveGood curative effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiocideAntibiotic YWeak current
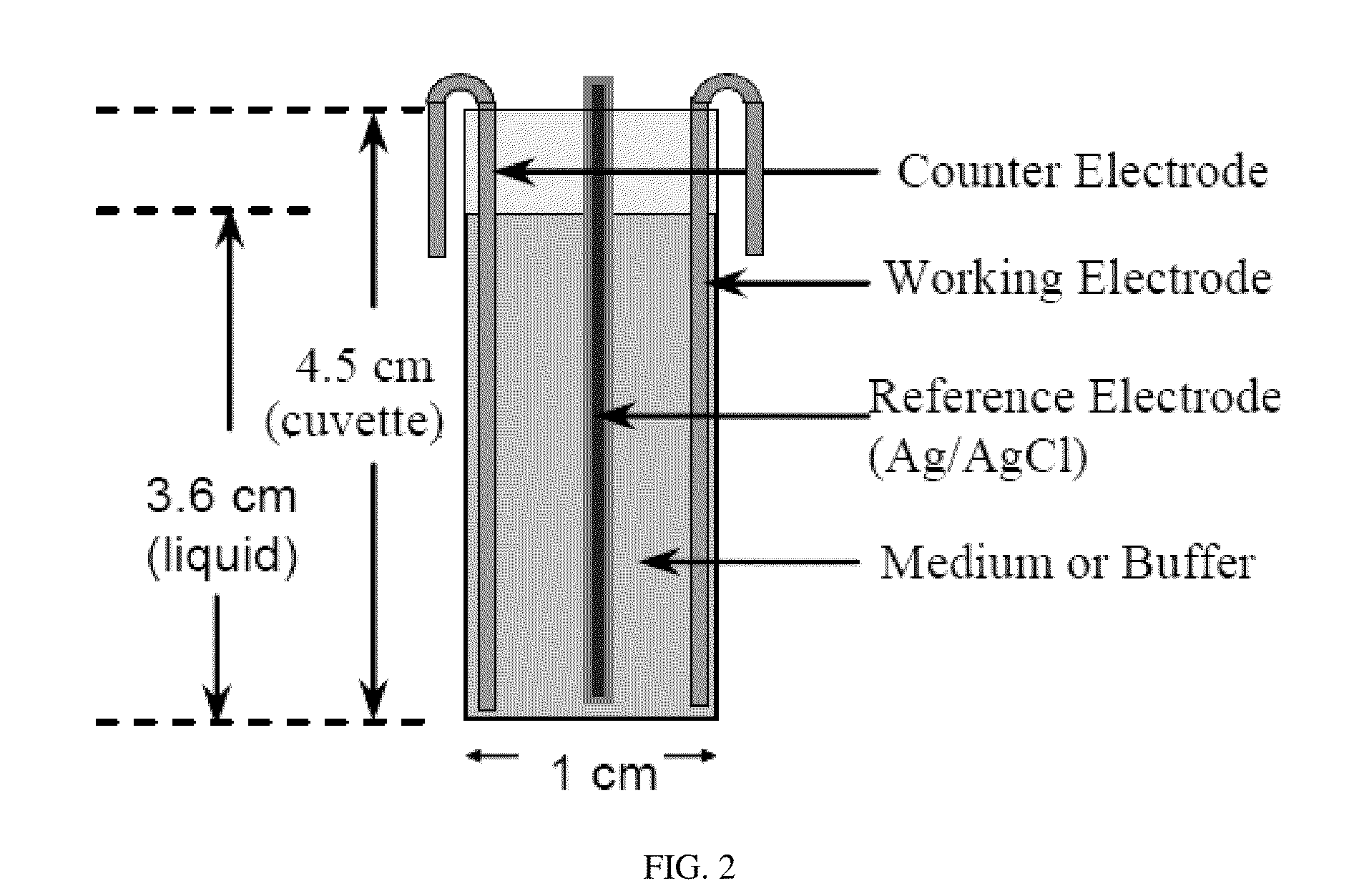
A system and method for treating bacterial cells with an electrochemical process, alone or in combination with antibiotics. Weak electric currents are used to effectively eliminate bacterial cells. The method may be adapted for novel therapies of chronic infections and strategies to control persistent biofouling. The system has broad spectrum applications in treating chronic and drug resistant infections, such as those caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Mycobacterium tuberculosis and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and may also be used for decontamination of medical devices.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
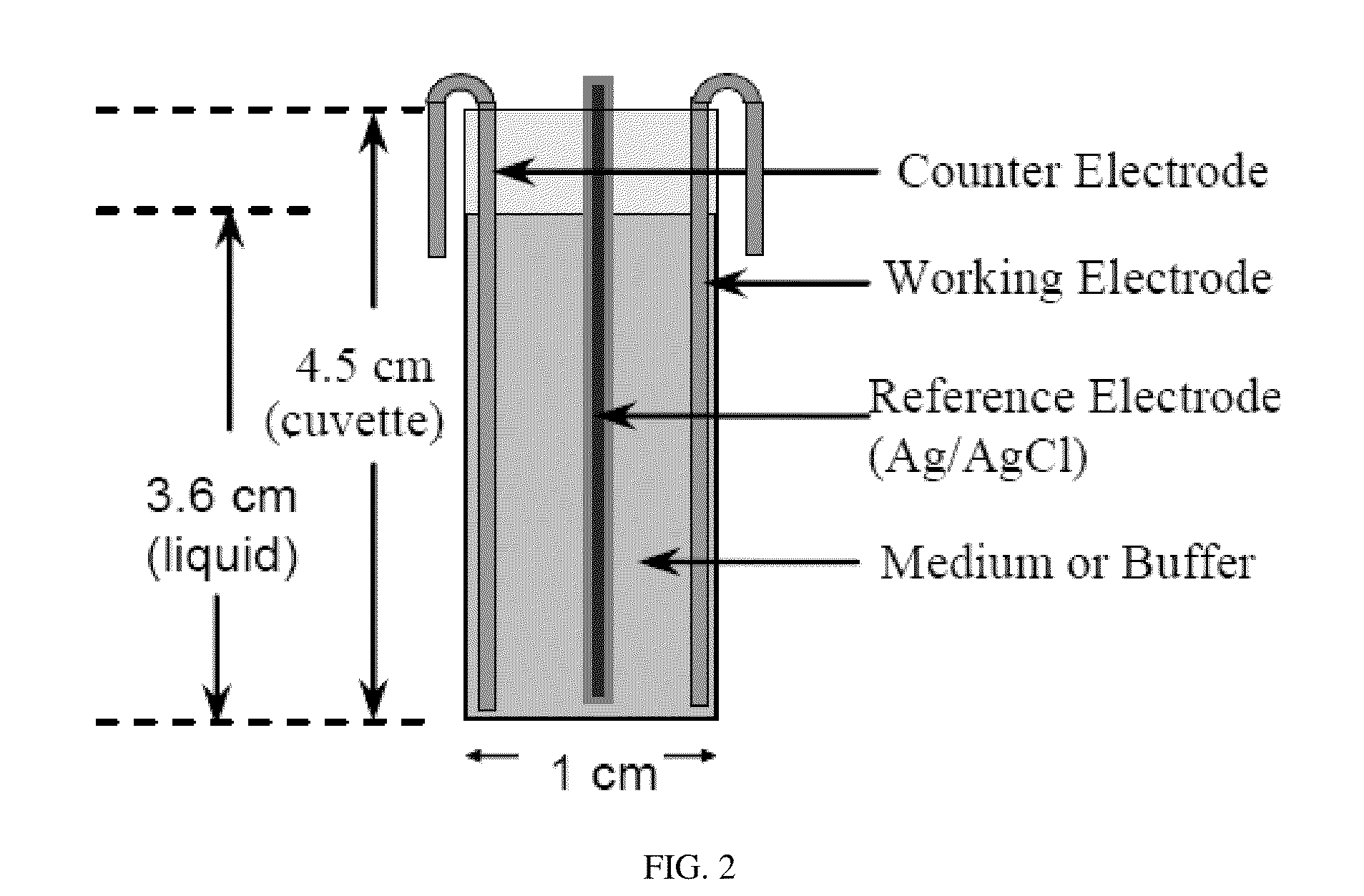
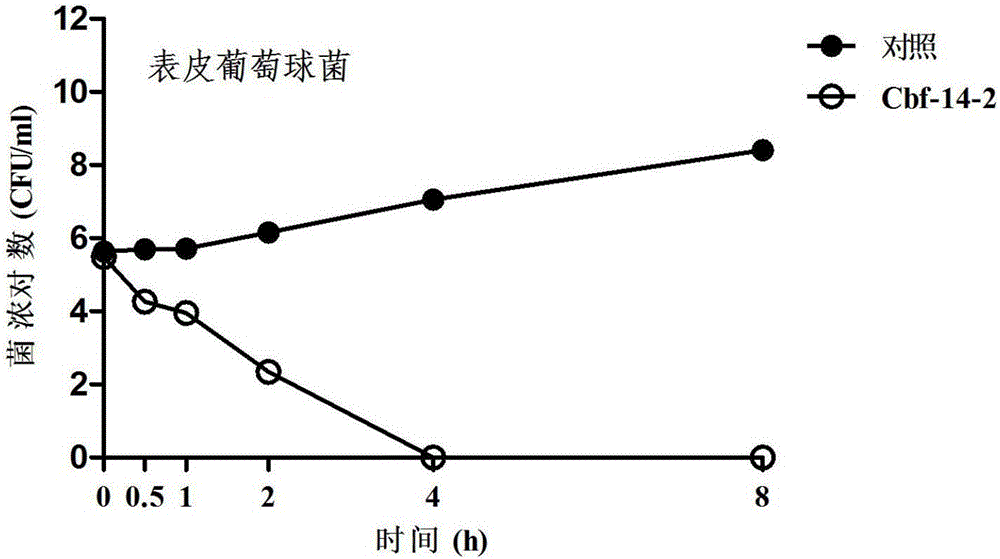
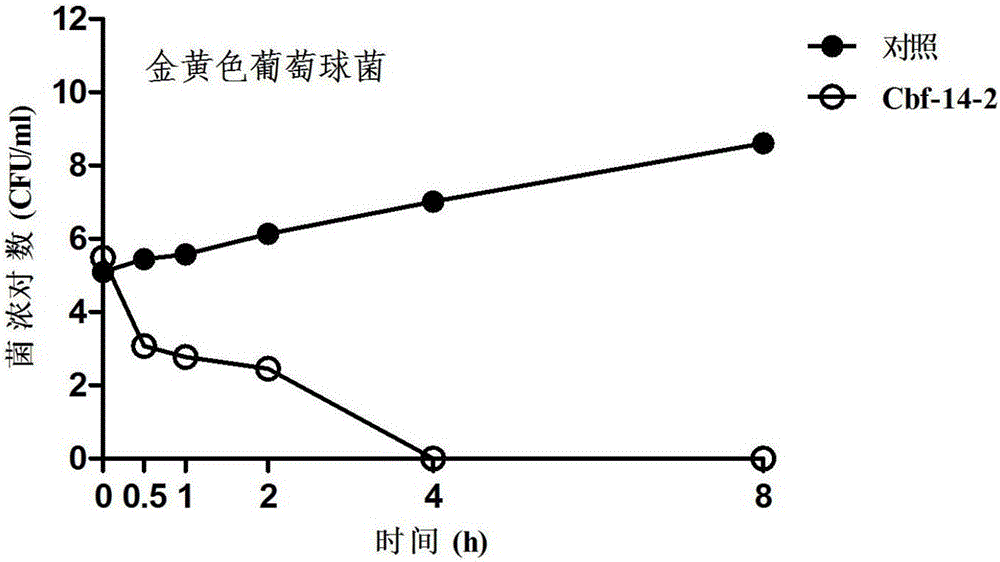
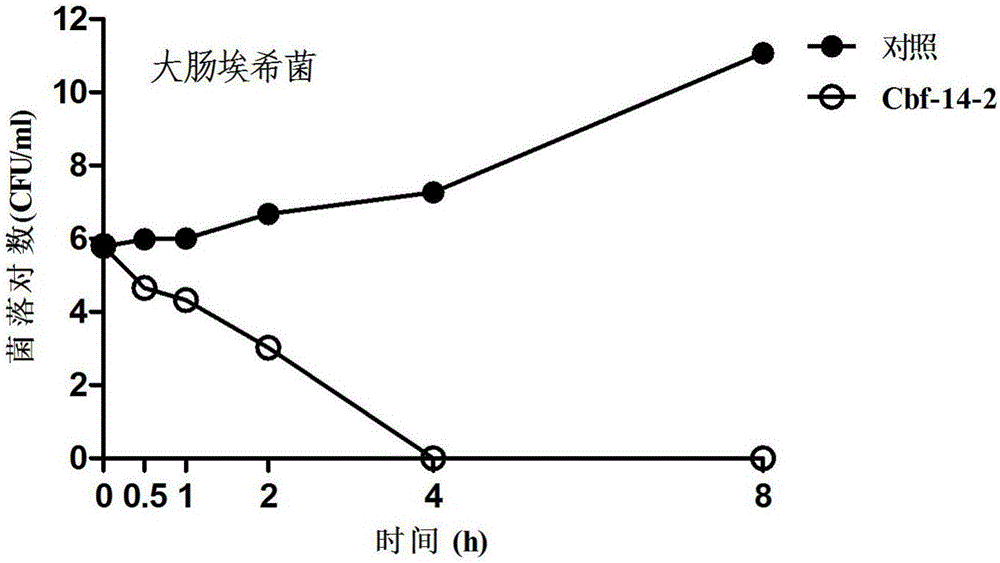
Anti-drug resistant infection polypeptide Cbf-14-2 and application thereof
ActiveCN106543271ALow hemolytic activityLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntimicrobial peptidesAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to the technical field of polypeptide drugs in biochemistry, in particular to a polypeptide and application thereof. An unnatural amino acid is introduced according to an antimicrobial peptide Cbf-14 to obtain the polypeptide Cbf-14-2 having the high inhibiting activity on drug-resistant bacteria. An amino acid sequence of the antibacterial polypeptide is shown as SEQ ID: NO:1. An in-vitro antibacterial activity research shows that the polypeptide Cbf-14-2 has a more remarkable killing effect on clinic drug-resistant bacteria compared with a parent peptide Cbf-14. An in-vivo bacteremia model research shows that the polypeptide Cbf-14-2 can remarkably improve the survival rate of a rat suffering from bacteremia, the weight of the rat suffering from the bacteremia is protected, the bacterium concentration of the polypeptide in blood is reduced, and meanwhile the polypeptide has the very good treating effect on lung tissue infection inflammation caused by drug-resistant strains. The polypeptide Cbf-14-2 has very small toxicity to mammalian cells.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV +1
System And Method For Controlling Bacterial Persister Cells With Weak Electric Currents
ActiveUS20110034406A1Eliminate effectiveGood curative effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOrganic active ingredientsBiofoulingWeak current
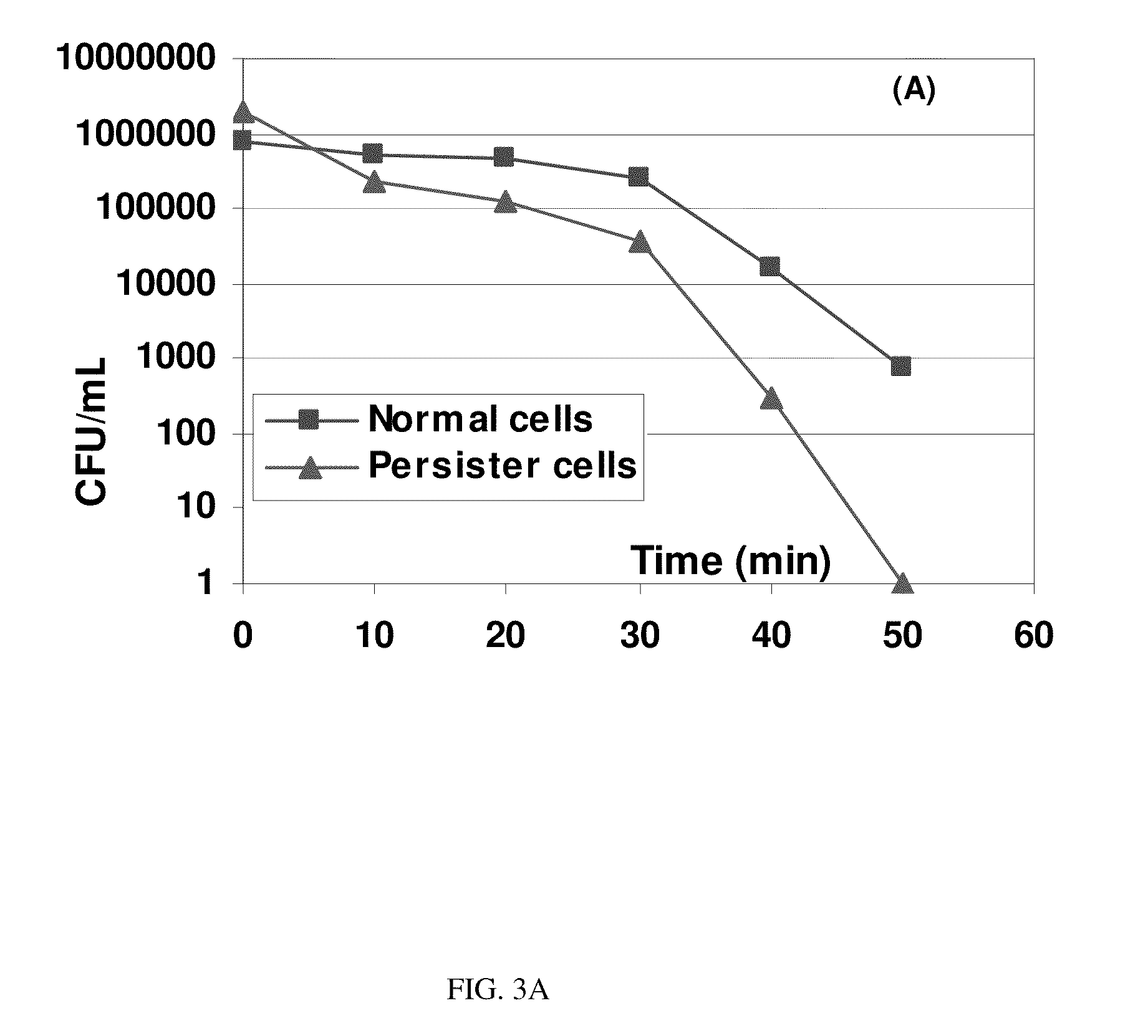
A system and method for treating persister cells with an electrochemical process, alone or in combination with antibiotics. Weak electric currents are used to effectively eliminate persister cells and the efficacy can be further improved through synergistic effects with antibiotics. The method may be adapted for novel therapies of chronic infections and strategies to control persistent biofouling. The system has a broad spectrum applications in treating chronic and drug resistant infections, such as those caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Mycobacterium tuberculosis and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and may also be used for decontamination of medical devices.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
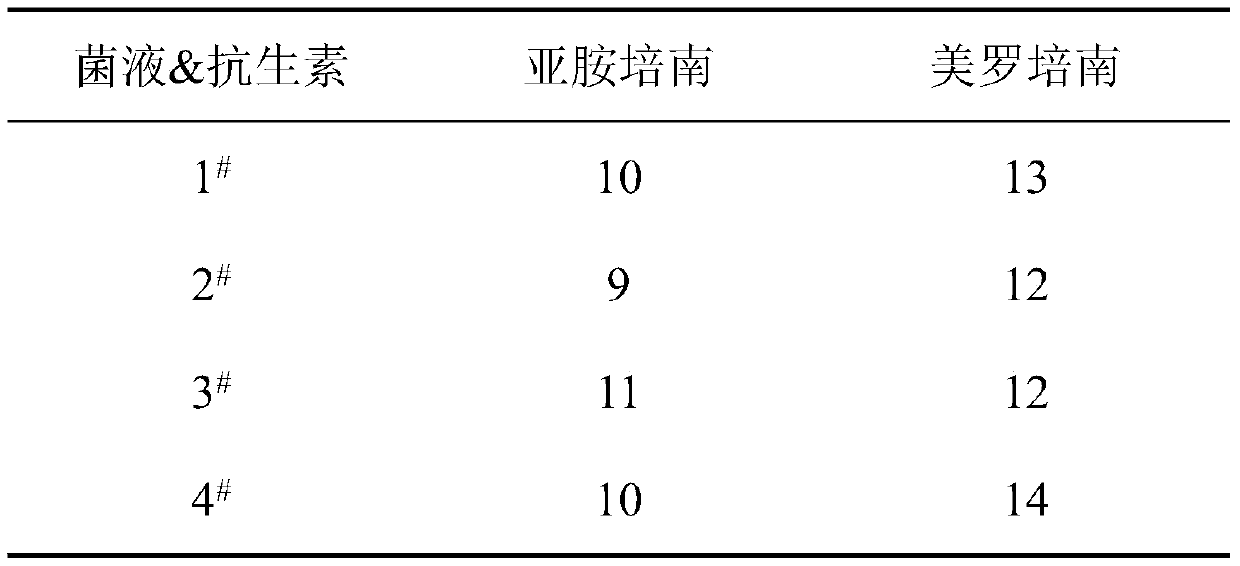
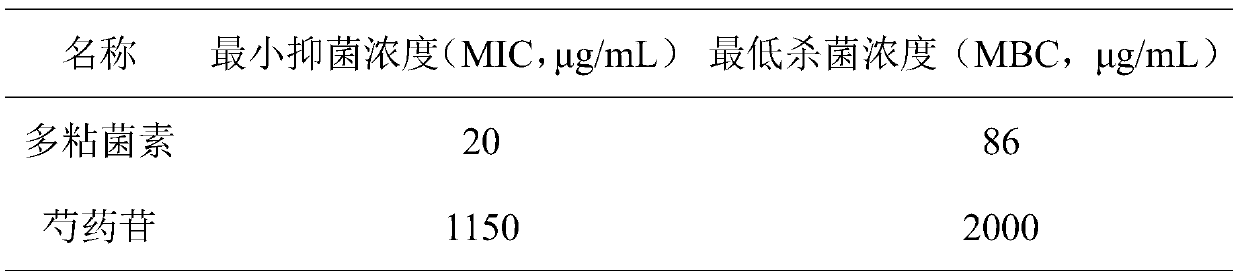
Application of paeoniflorin in inhibition of growth of carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae
InactiveCN110251526AGreat application valueMitigate or resolve drug-resistant infectionsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCarbapenem resistantResistant infection
The invention discloses application of paeoniflorin in inhibition of growth of carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae. According to the fact that paeoniflorin has a good in-vitro killing effect on human klebsiella pneumoniae capable of resisting imipenem and meropenem, growth of carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae can be inhibited, the minimum bactericidal concentration is 2 mg / mL, and the minimum bacteriostatic concentration is 1.15 mg / mL. The invention provides an inhibitory effect of paeoniflorin on carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae. According to the invention, the problem of drug-resistant infection of carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae can be effectively relieved or solved, the mortality is reduced, a new idea is provided for inhibiting the human carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae, and the method has important practical significance.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
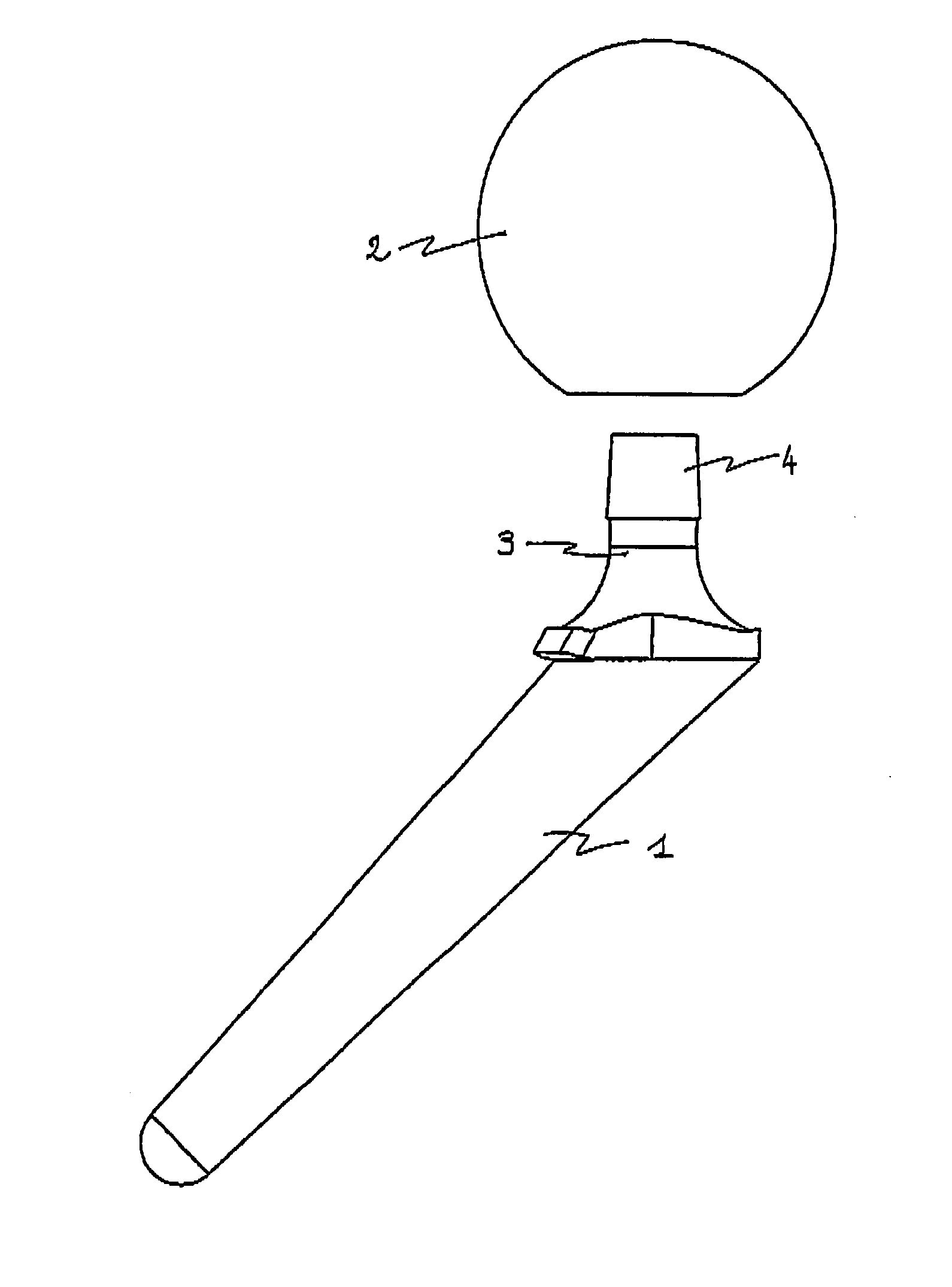
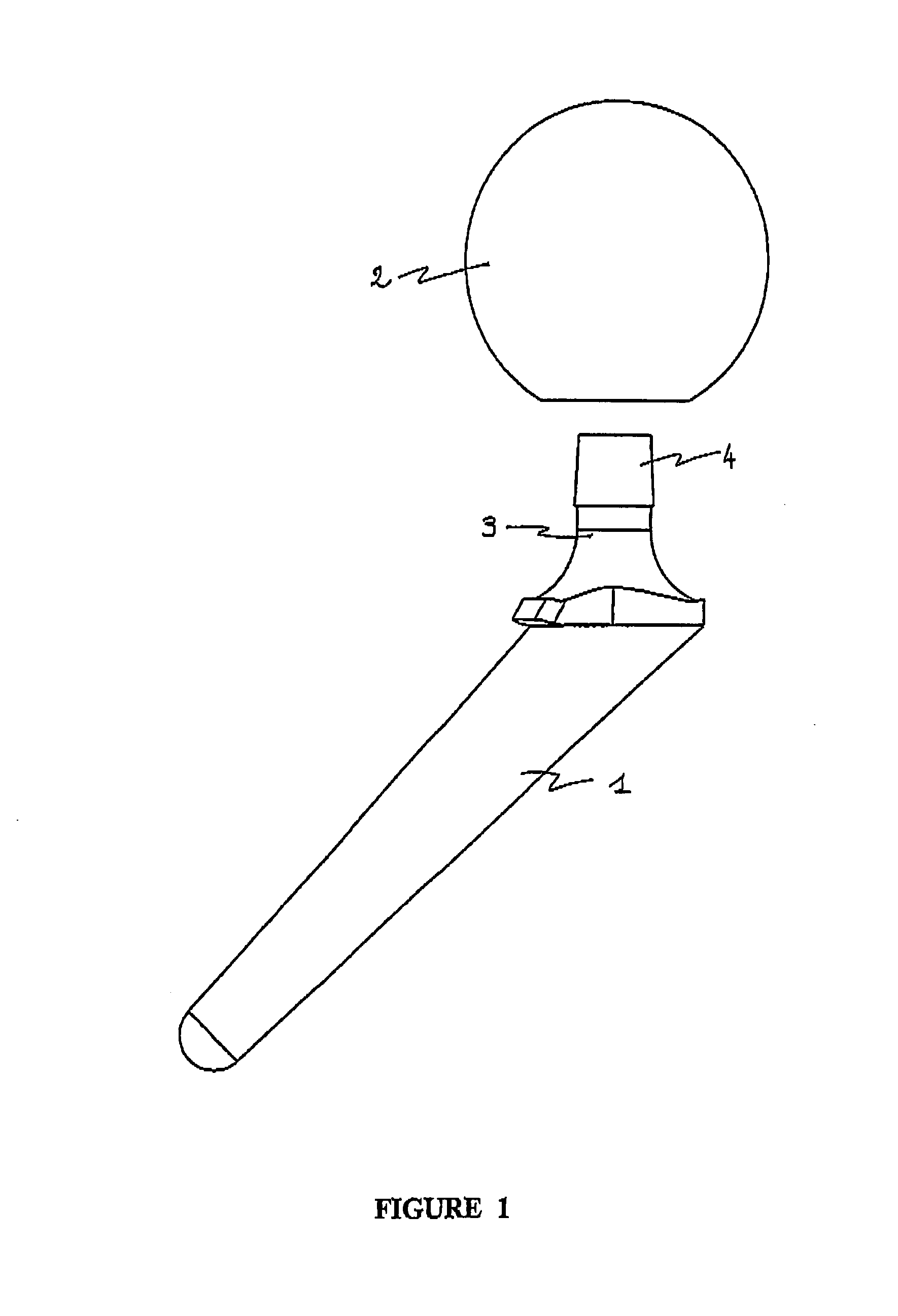
Temporary implant incorporating two active ingredients
ActiveUS8449621B2Without lengthening technological processReduce manufacturing costBone implantJoint implantsAntibiotic YBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
A ready-for-use polymer cement spacer device for the replacement of a permanent joint prosthesis during a two-stage replacement, includes a shank includes for attachment for placing to the supporting bone and a head in the joint region. The spacer device includes two complementary members incorporating rigid members for assembly between them, the first member being loaded with a first active substance and the second member being loaded with a second active substance. The first and second active substances are preferably antibiotics, selected from gentamycin, trobamycin, vancomycin, erythromycin, fucidin, tetracycline or other suitable antibiotics. The temporary joint implant maintains a suitable space for the time necessary for the operation of replacing a permanent prosthesis to prevent tissues from occupying the space released by removal of the permanent prosthesis and ensures effective treatment of resistant infections by local treatment of the joint area through at least two different active substances.
Owner:TEKNIMED SAS
System and method for controlling bacterial persister cells with weak electric currents
ActiveUS8569027B2Eliminate effectiveGood curative effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOrganic active ingredientsAntibiotic YBiofouling
A system and method for treating persister cells with an electrochemical process, alone or in combination with antibiotics. Weak electric currents are used to effectively eliminate persister cells and the efficacy can be further improved through synergistic effects with antibiotics. The method may be adapted for novel therapies of chronic infections and strategies to control persistent biofouling. The system has a broad spectrum applications in treating chronic and drug resistant infections, such as those caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Mycobacterium tuberculosis and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and may also be used for decontamination of medical devices.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
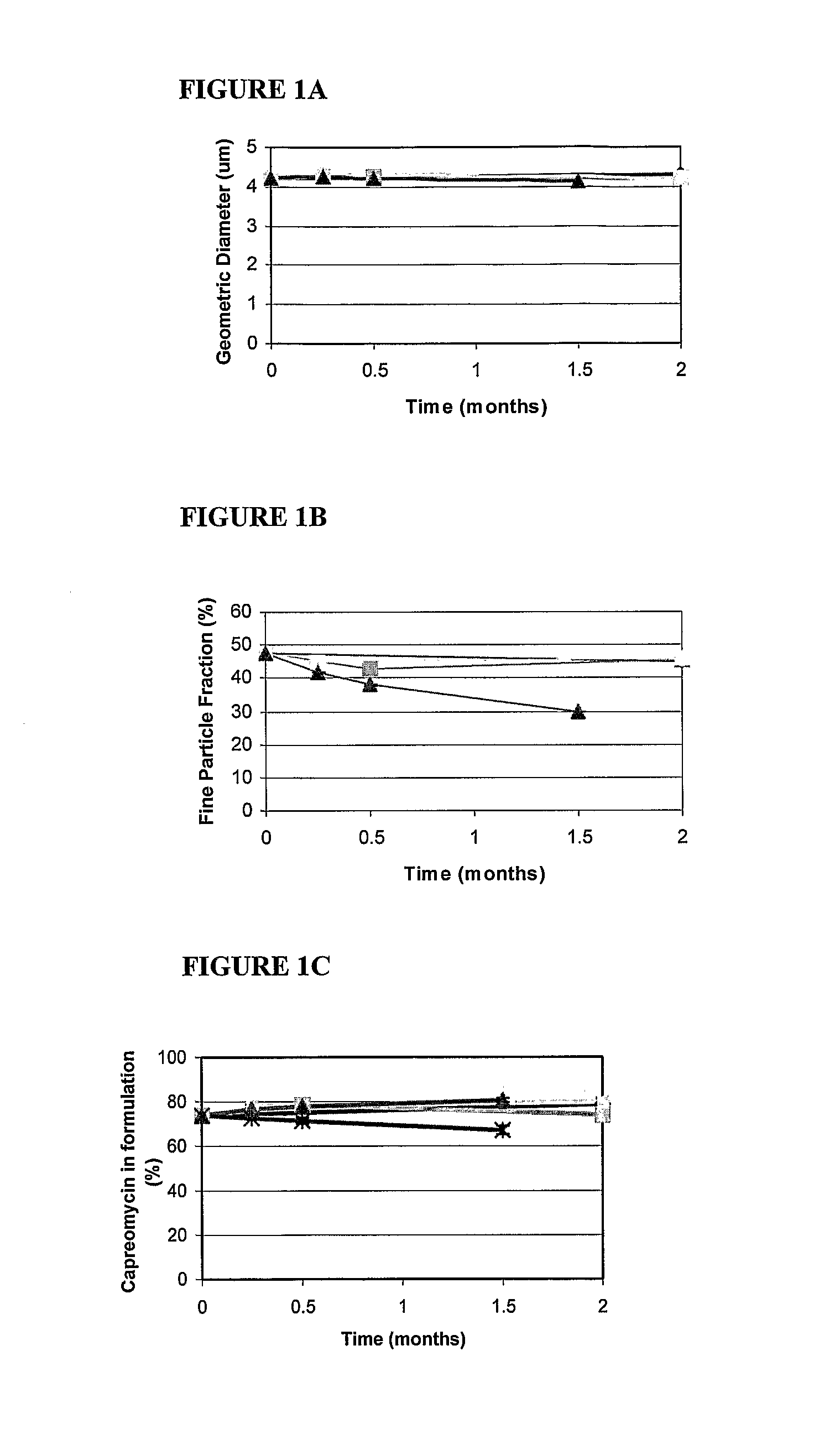
Particles for Treatment of Pulmonary Infection
InactiveUS20080213373A1Maintain good propertiesImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryPulmonary infectionMeningococcal meningitis
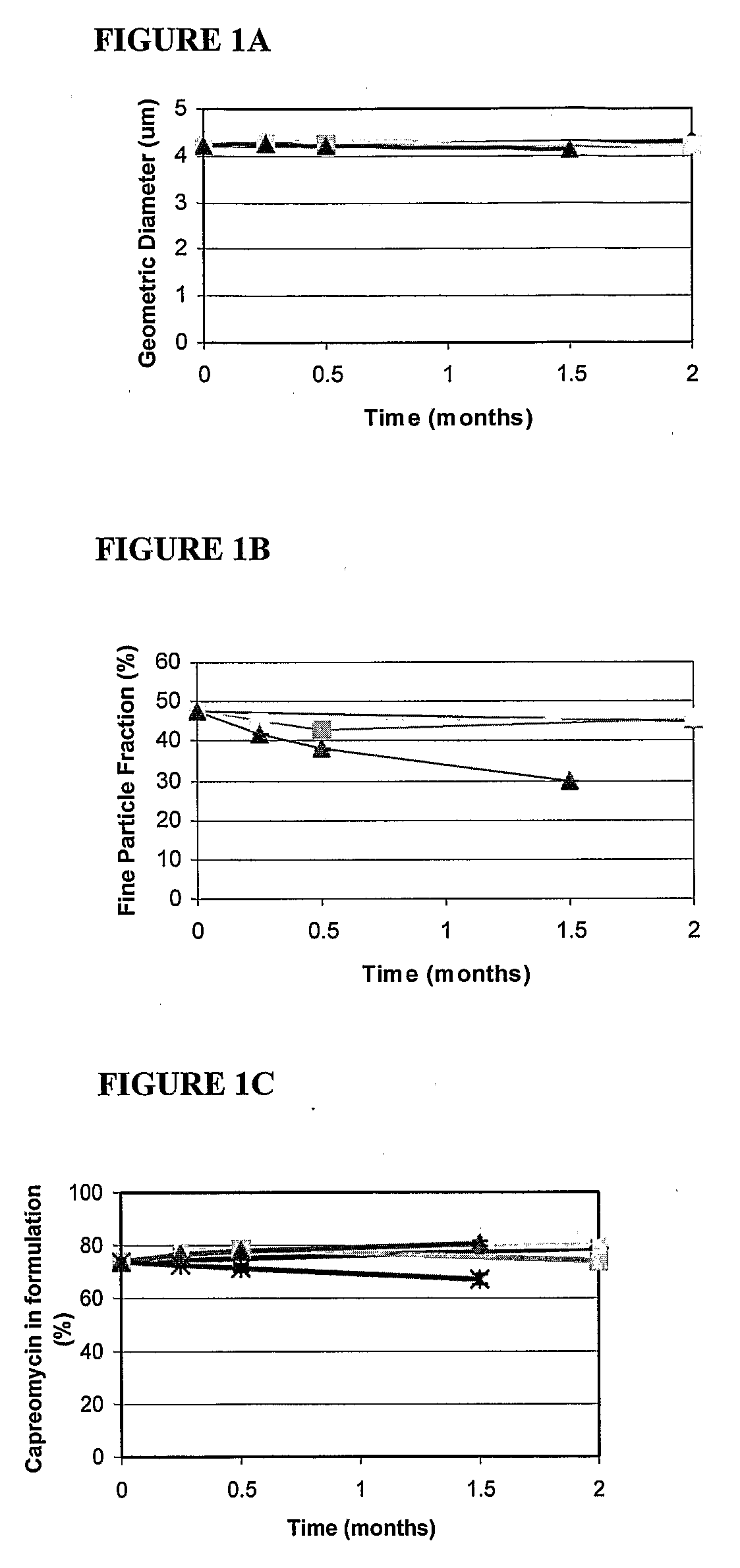
Formulations have been developed to treat or reduce the spread of respiratory infections, especially chronic or drug resistant infections, particularly tuberculosis (TB), severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), meningococcal meningitis, Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza, and small pox. Formulations include a drug or vaccine in the form of a microparticle, nanoparticle, or aggregate of nanoparticles, and, optionally, a carrier, which can be delivered by inhalation. Giving the drugs via an inhaler sidesteps the problems associated with oral or injectable drugs by bypassing the stomach and liver, and delivering the medication directly into the lungs. In one embodiment, the particle containing the agent is a large porous aerosol particle (LPPs). In another embodiment, the particles are nanoparticles, which can be administered as porous nanoparticle aggregates with micron diameters that disperse into nanoparticles following administration. Optionally, the nanoparticles are coated, such as with a surfactant or protein coating. The formulation may be administered as a powder or administered as a solution or via an enteral or non-pulmonary parenteral route of administration. The formulation is preferably administered as a pulmonary formulation. In the preferred embodiment for treatment of TB, the vaccine is a BCG vaccine that is stable at room temperature, or is an antibiotic effective against TB, such as capreomycin or PA-824, loaded at a very high percentage into the microparticles or nanoparticles. In one embodiment, a patient is treated with formulations delivering both antibiotic and vaccine.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
System and method for controlling bacterial cells with weak electric currents
ActiveUS8663914B2Eliminate effectiveGood curative effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiocideWeak currentAntibiotic Y
A system and method for treating bacterial cells with an electrochemical process, alone or in combination with antibiotics. Weak electric currents are used to effectively eliminate bacterial cells. The method may be adapted for novel therapies of chronic infections and strategies to control persistent biofouling. The system has broad spectrum applications in treating chronic and drug resistant infections, such as those caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Mycobacterium tuberculosis and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and may also be used for decontamination of medical devices.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
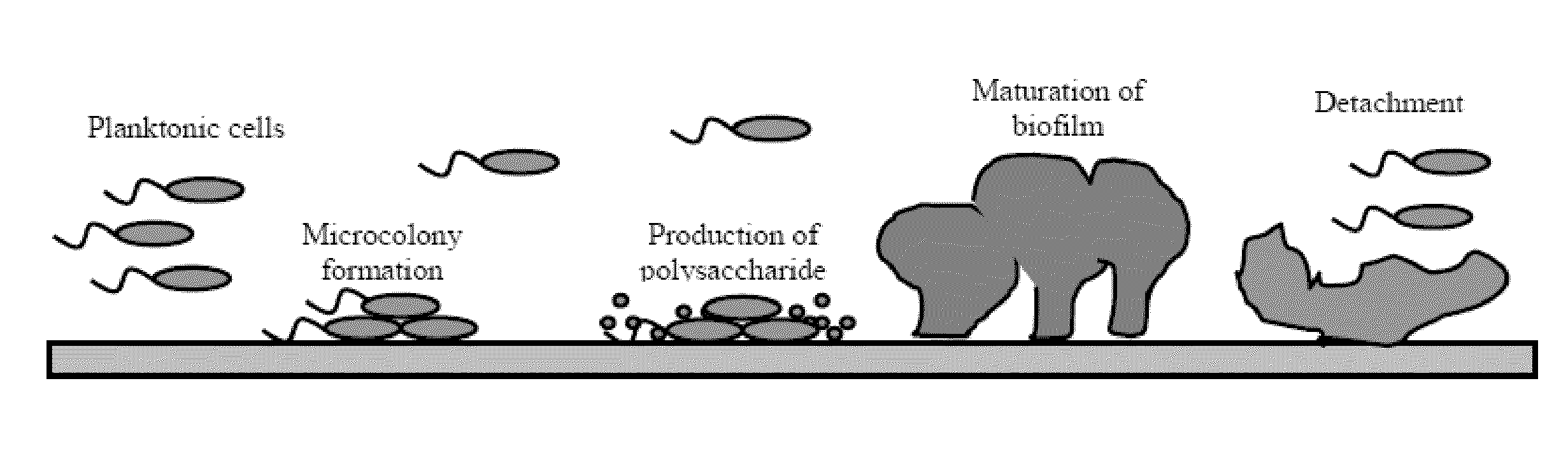
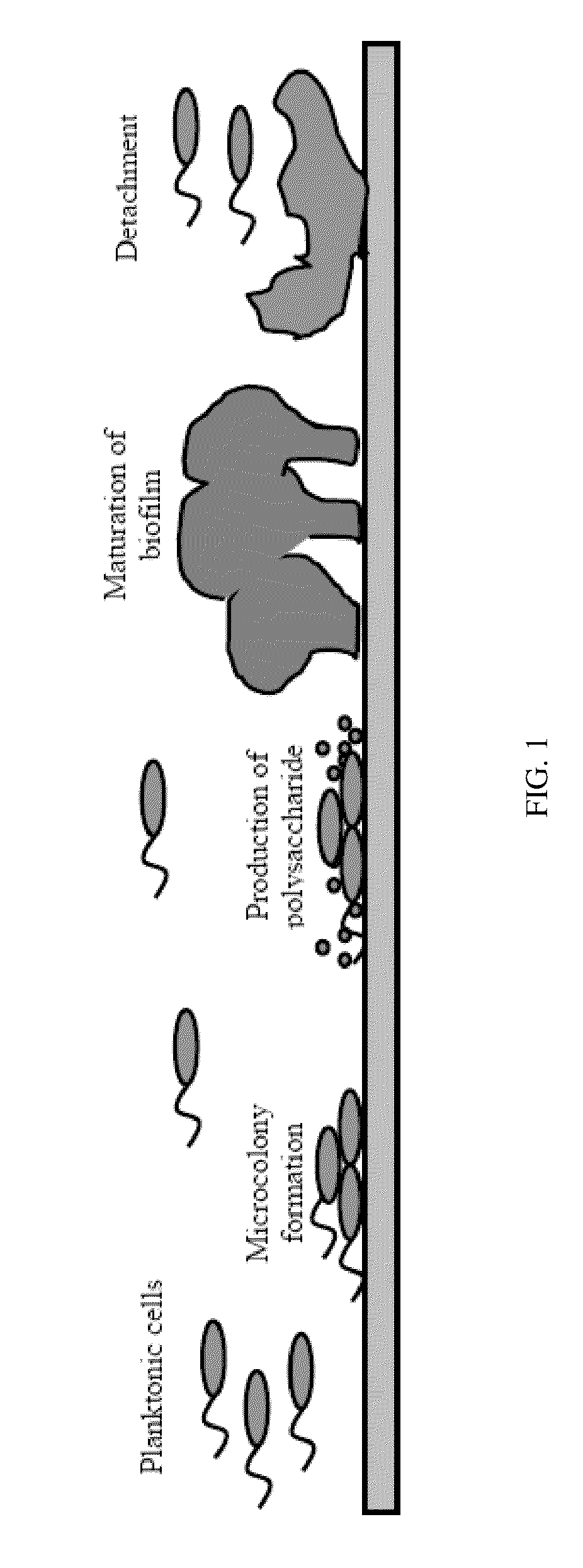
Application of agastache rugosus volatile oil to suppression of growth of drug-resistant escherichia coli
ActiveCN106138197AGrowth inhibitionMitigate or resolve drug-resistant infectionsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliBiofilm
The invention discloses application of agastache rugosus volatile oil to suppression of growth of drug-resistant escherichia coli. A single chemical component, i.e. pulegone, is obtained from an agastache rugosus volatile oil to achieve a better in vitro suppression effect on the growth of human-derived drug-resistant escherichia coli, i.e. human-derived ESBLs-producing escherichia coli. The application has the beneficial effects that the first research on the effect of the agastache rugosus volatile oil on the drug-resistant escherichia coli finds that the growth of the drug-resistant escherichia coli can be suppressed; a main component serving as a drug-resistant suppressing agent is screened from the agastache rugosus volatile oil and then researched; data show that the main monomer component, i.e. the pulegone, of the agastache rugosus volatile oil can suppress the growth of the ESBLs-producing escherichia coli and affect the formation of a biofilm so as to relieve or avoid the drug-resistant infection of the escherichia coli and reduce the fatality rate; a new idea is brought up to solve and treat the human-derived ESBLs-producing escherichia coli; and the application has a great research significance.
Owner:XINJIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Use of panton-valentine leukocidin for treating and preventing staphylococcus infections
InactiveCN102698261AAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaWhite blood cellStaphylococcal infections
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for treating Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) infections. In particular, the present invention provides vaccines comprising a Panton- Valentine Leukocidin (PVL) antigen, antibodies which bind a PVL antigen and compositions containing the same, methods of making such compositions and methods for treating S. aureus infections, including those that are community acquired methicillin-resistant infections. The present invention also provides PVL antibodies, including PVL antibodies specific for a single PVL subunit, and PVL antigens, including conjugated and mutated PVL antigens.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
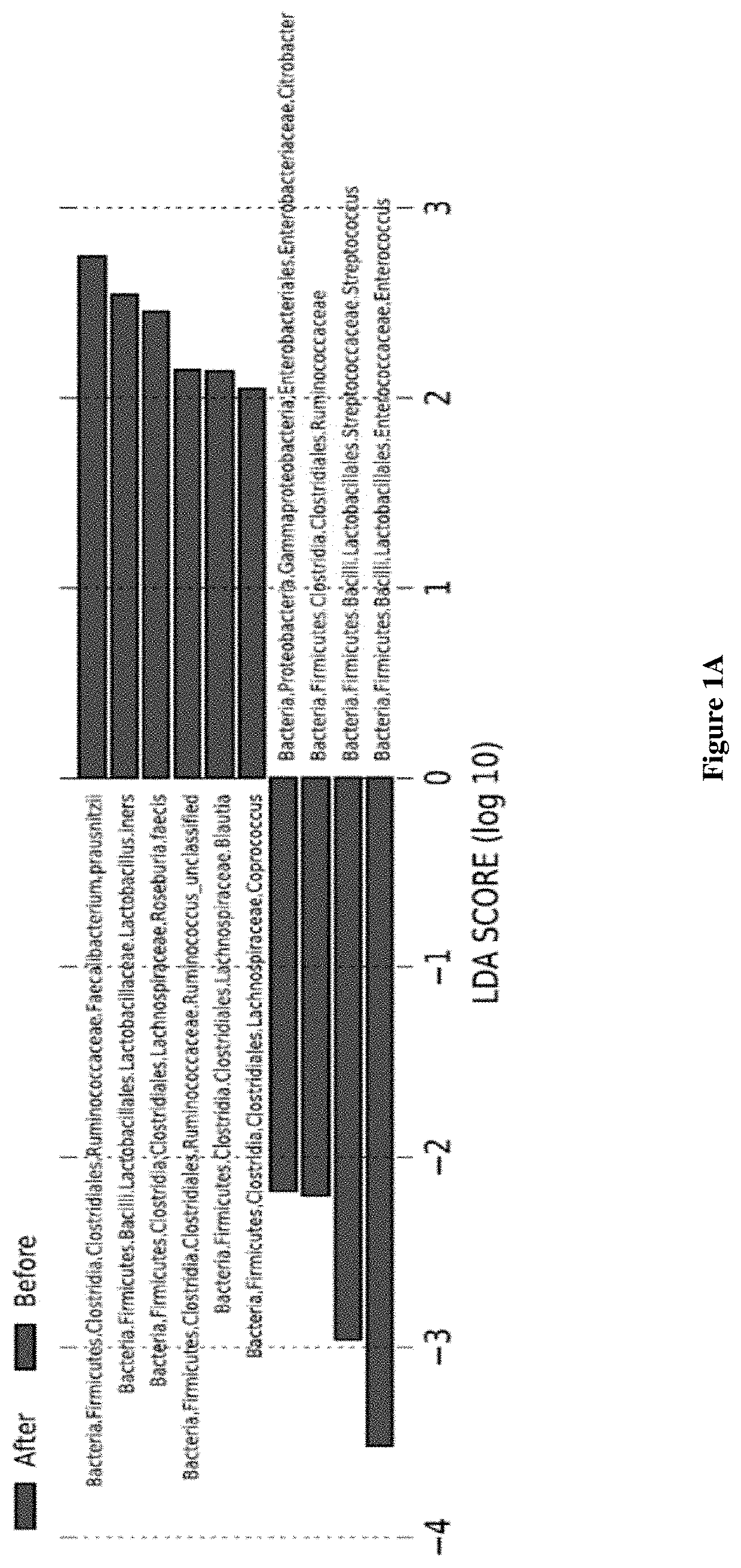
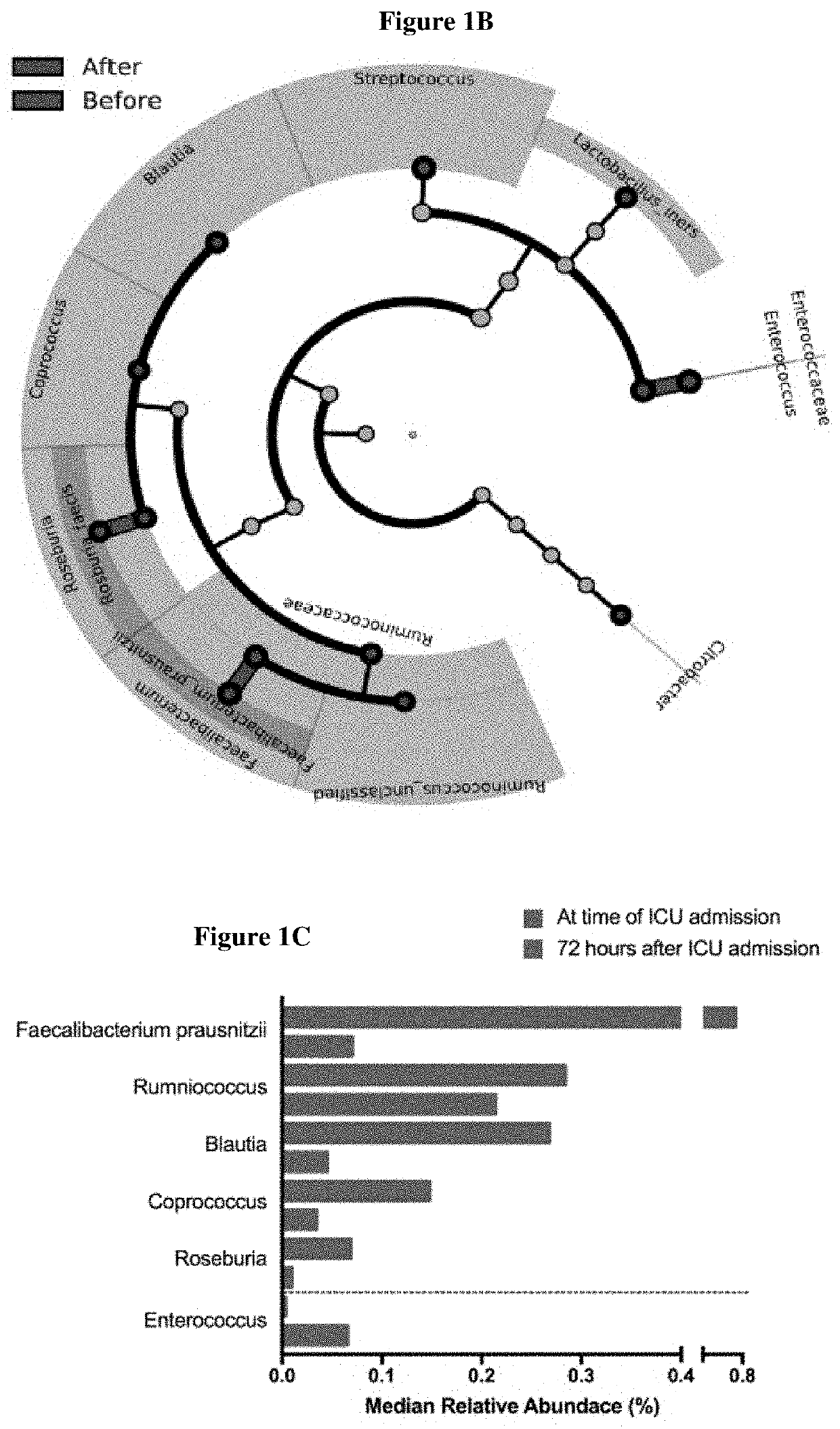
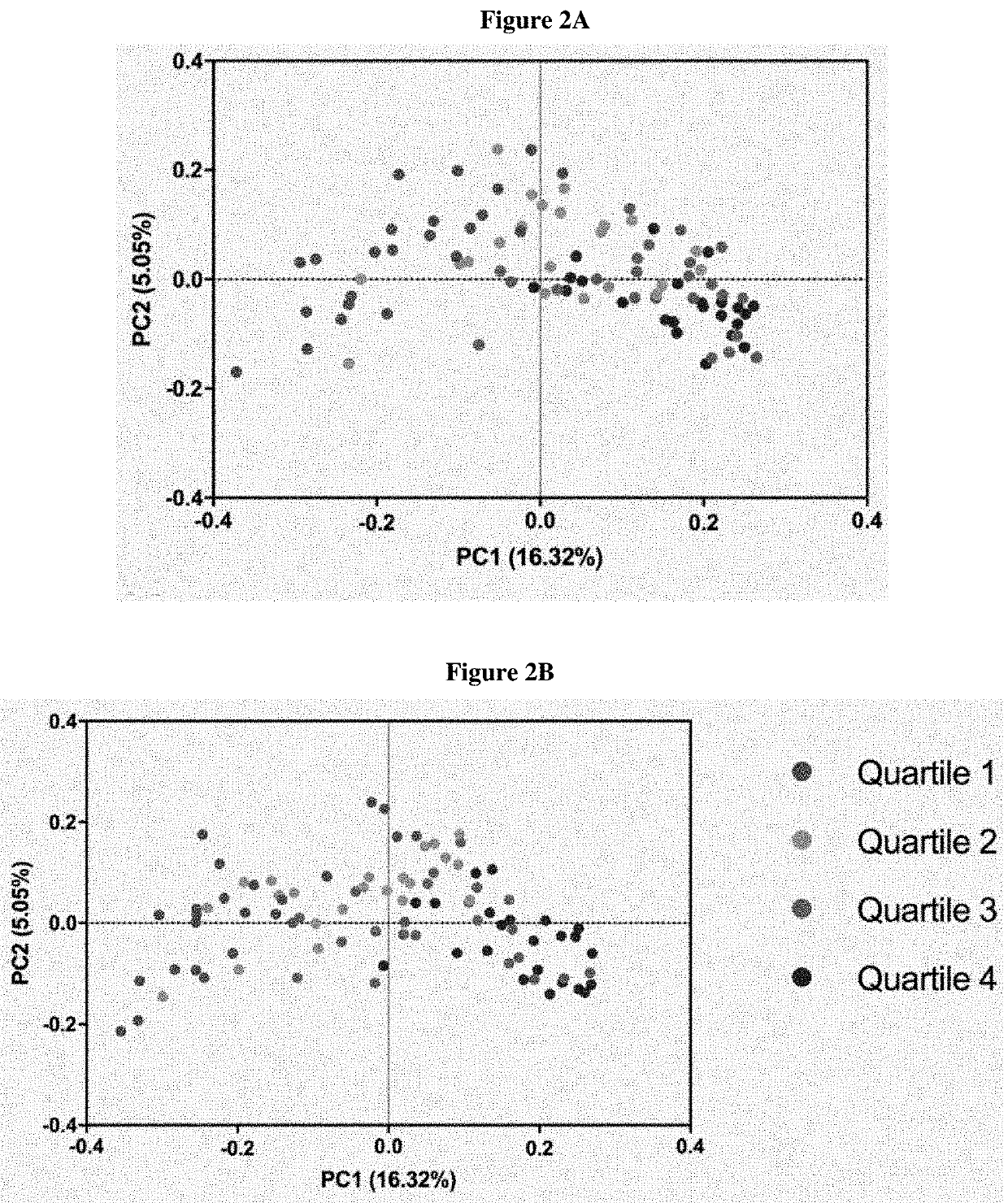
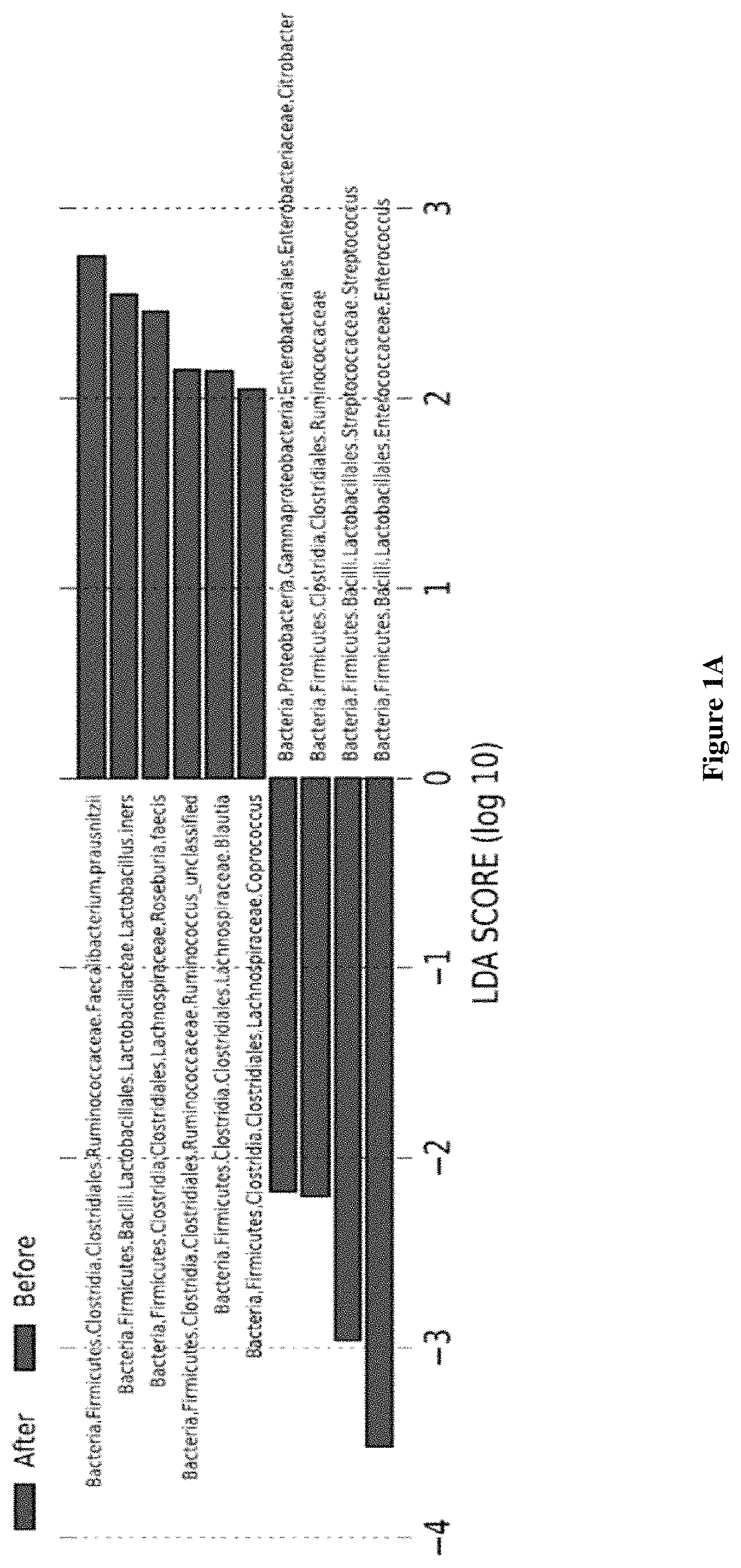
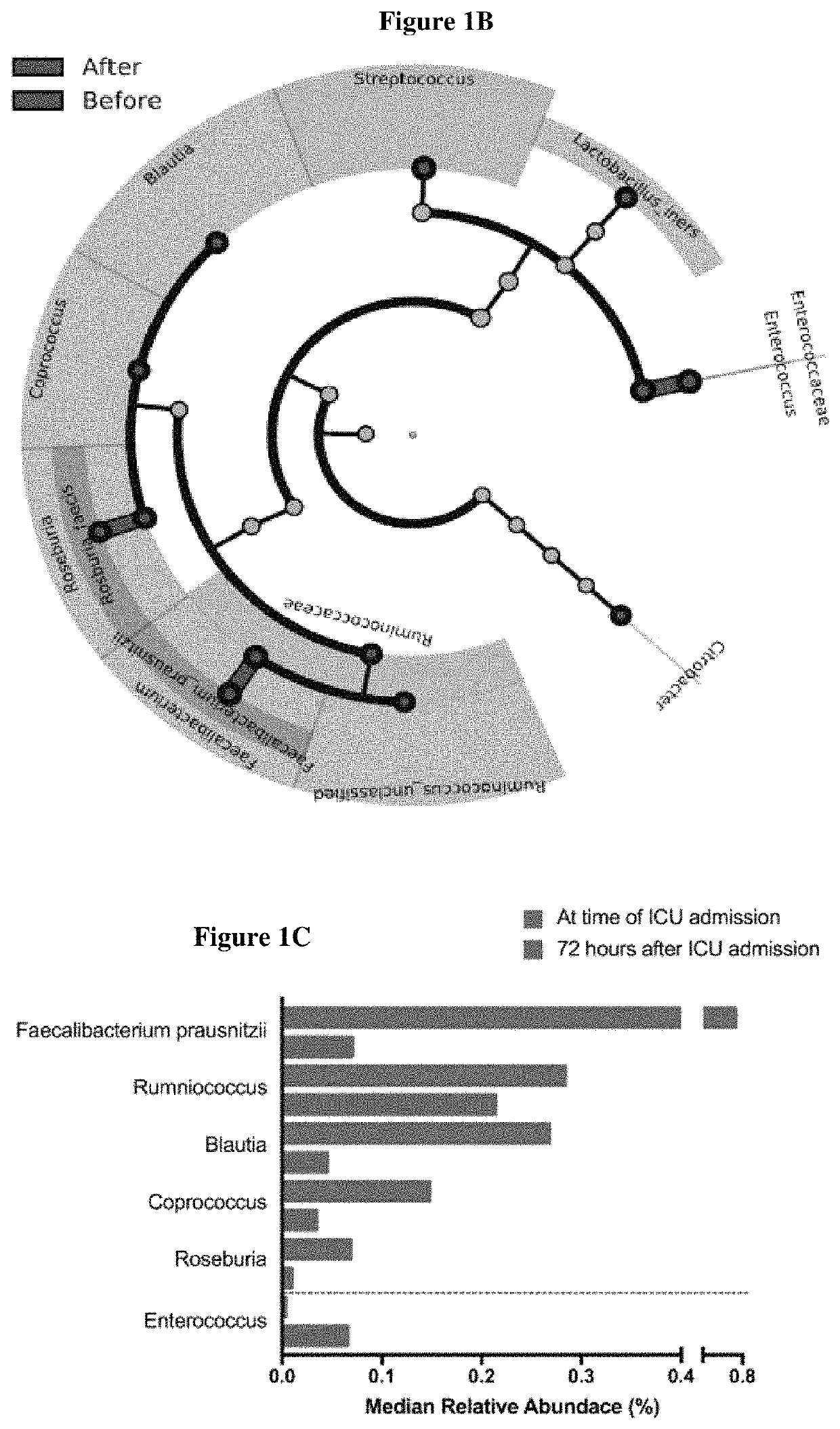
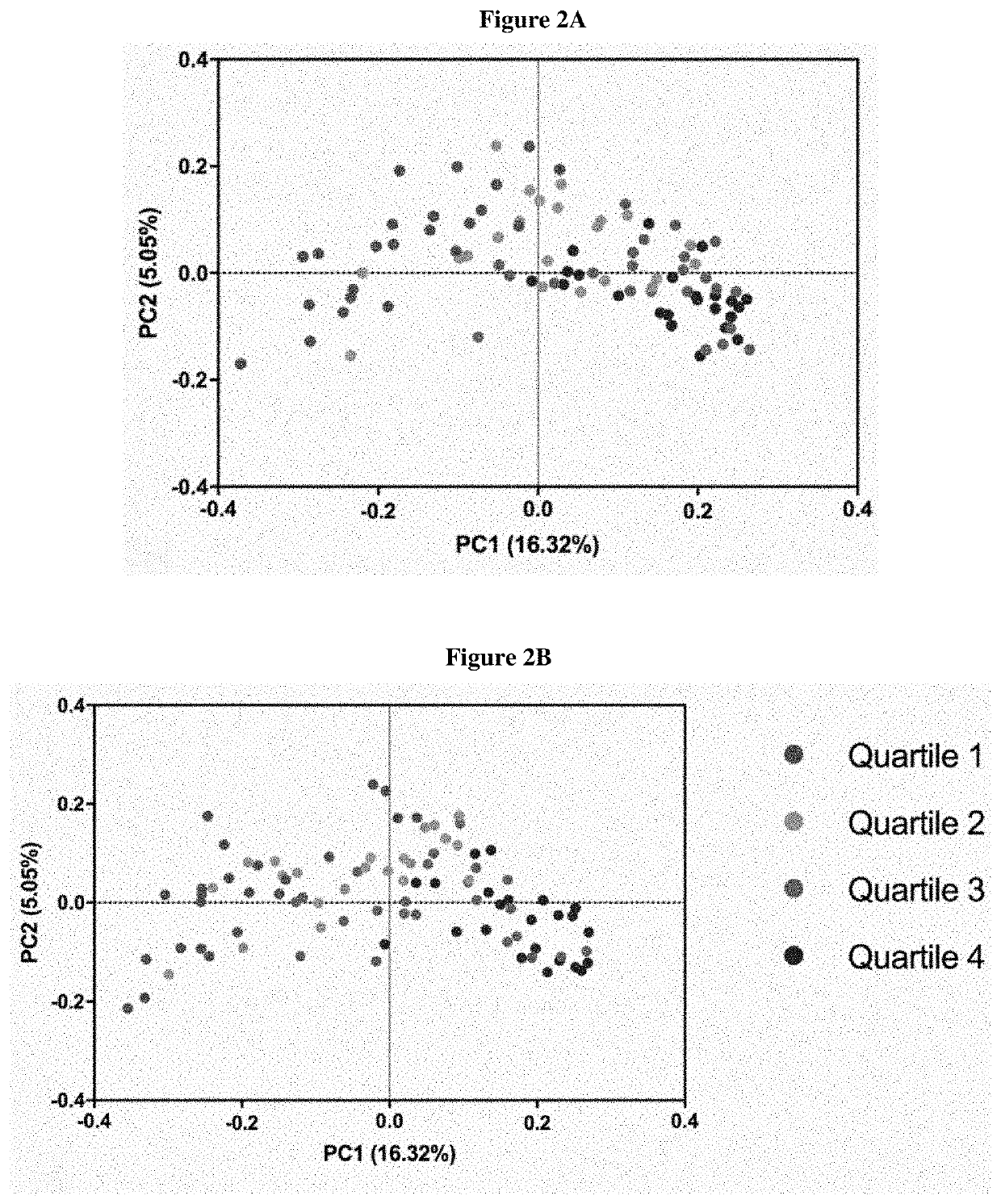
Inulin for preventing antibiotic resistant infection and pathogen colonization
The present disclosure provides for methods and compositions for the treatment and prevention of antibiotic-resistant infections or pathogen colonization in critically ill patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) or in other populations at high risk for such infections.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Inulin for preventing antibiotic resistant infection and pathogen colonization
The present disclosure provides for methods and compositions for the treatment and prevention of antibiotic-resistant infections or pathogen colonization in critically ill patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) or in other populations at high risk for such infections.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Composition, Preparation Method And Evaluation Of A Complex Immunogen Named I-SPGA For Production Of Immunological Active Proteins (IAP)
ActiveUS20210121552A1Increased antibody coupling powerEasy to combineBacterial antigen ingredientsEgg immunoglobulinsPotentiatorResistant infection
The present invention relates to the composition and method of preparing an immunogen designated as I-spga consisting of a complex antigen prepared from 18 to 26 species of pathogenic microorganisms isolated from patients, inactivated with binary ethyleneamine (BEI) and formalin, diluted in a SPGA immunopotentiator mixed with QS-21 adjuvant. By inoculating the hens with the I-spga immunogen, hyperimmune eggs (Immunospga) are obtained which contain immunologically active proteins specific to the 18-26 antigens used for immunization. The immune response of the hens is specific to the used antigens by amplification of the antigenic signal by the SPGA immunopotentiator and due to a special immunization program that allows the immune system to act complex and intense: The I-spga complex antigen contains 18-26 microorganisms isolated from patients, bacterial bodies, components from bodies obtained by ultrasonography, cilia, exotoxins, endotoxins, spores, viruses, fungi or yeasts. This pathogenic material is inactivated with BEI and formalin. The I-spga antigen is of three types. The standard I-spga antigen is composed of 18 to 24 antibiotic-resistant bacterial species isolated from patients in Romania. The specific I-spga complex antigen is composed of the I-spga complex antigen containing a mixture of 7-9 strains from a single species of bacteria, fungi or yeasts isolated from patients in Romania mixed with SPGA and QS-21, used for inoculation of hens previously immunized with standard I-spga antigen. The personalized I-spga antigen is composed of patient-derived pathological material containing cellular debris and pathogenic germs inactivated with BEI and formalin and mixed with SPGA and QS-21 and is used to immunize hens previously immunized with the standard I-spga antigen. This now patented technology encompasses a new generation of biological products in which the immune response of the hens to different groups of parenterally inoculated antigens at different time intervals is overlapping. Chicken response is uniform and additional administration of immunogens and SPGA as an immunopotentiator amplifies the antigenic signal and immune response. The I-spga immunogen as well as the immune response contain two markers, G and A, which identify the I-spga antigen used for immunization against the antigens used to produce the Imunoinstant group bio-preparations or similar products. The I-spga immunogen is used to immunize the hens for obtaining immunologically active proteins that can be used to treat immune deficiencies, psoriasis, epidermolysis bullosa, other dermatitises, nosocomial infections, antibiotic-resistant infections in the urinary system of children and grownups.
Owner:FANTANA RAUL SORIN +1
Biophotonic compositions for treating skin and soft tissue wounds having either or both non-resistant and resistant infections
ActiveUS20190022219A1Less stressLess discomfortAntibacterial agentsPhotodynamic therapyPaper documentDocument preparation
The present document describes methods and uses of biophotonic compositions which comprise at least one oxidant and at least one chromophore capable of activating the oxidant, in association with a pharmacologically acceptable carrier for use in the treatment of skin and soft tissue wounds that have either or both non-resistant and resistant infections.
Owner:VETOQUINOL SA
Pseudomonas aeruginosa resisting Fab' fragment
InactiveCN101186648BIncrease productionGood potencyAntibacterial agentsEgg immunoglobulinsBiochemistrySpecific antibody
The invention provides a specific antibody of bacillus pyocyaneus, in particular to a bacillus pyocyaneus resistant Fab' fragment, which is extracted from the egg of laying hens immunized via bacillus pyocyaneus antigen, with high yield, better effect, stable physicochemical property, high specificity, simple preparation, better repeatability, and industrialization production support. The inventive bacillus pyocyaneus resistant Fab' fragment can significantly resist the growth of bacillus pyocyaneus, by external measurement, which can be used to prepare the drug treating bacillus pyocyaneus resistant infection.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Immunoloregulation type DNA vaccine capable of preventing Eimeria necatrix
InactiveCN101422605BGood immune protectionEffective immune protectionGenetic material ingredientsAntiparasitic agentsAntigenEmoia loyaltiensis
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
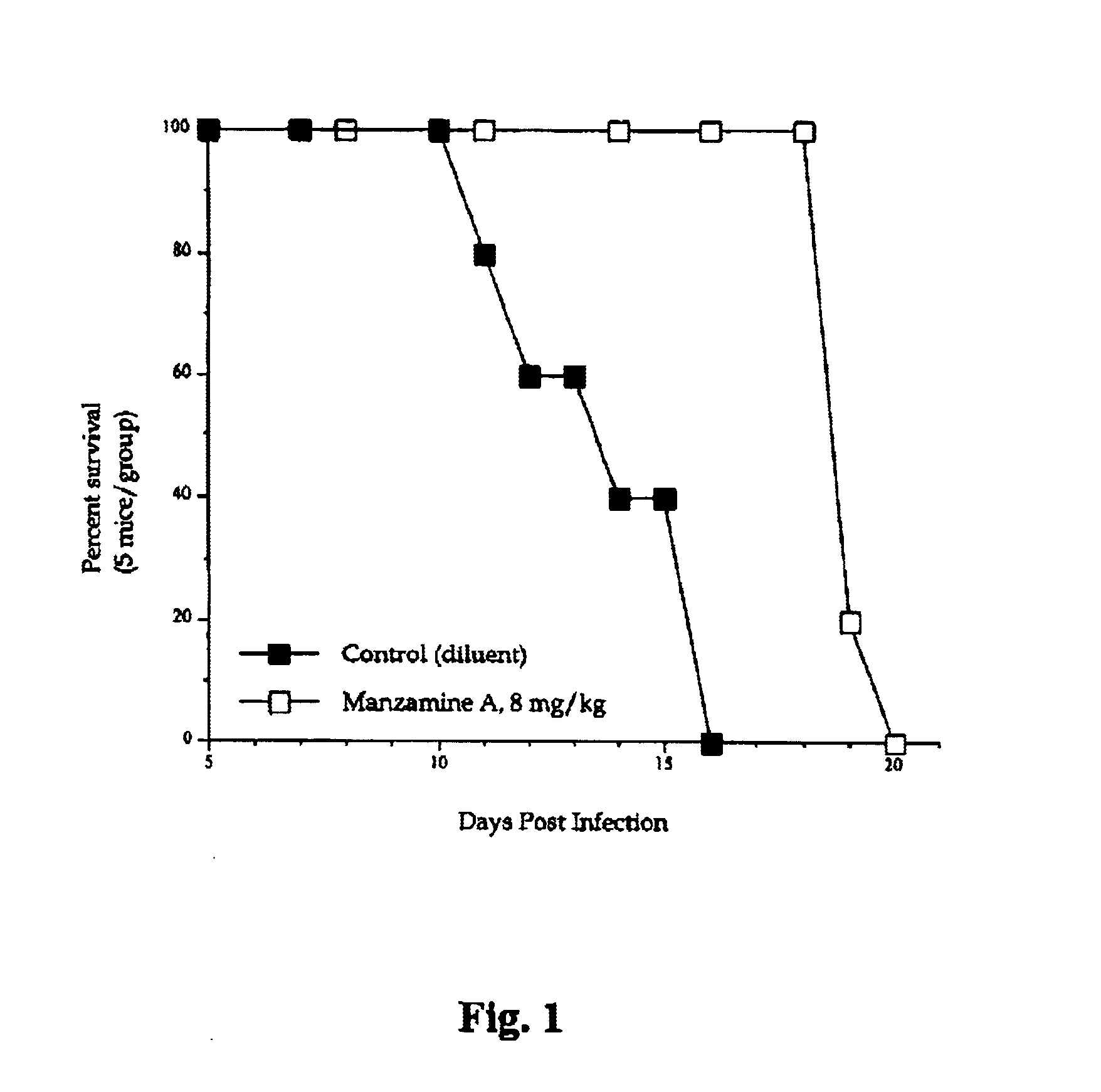
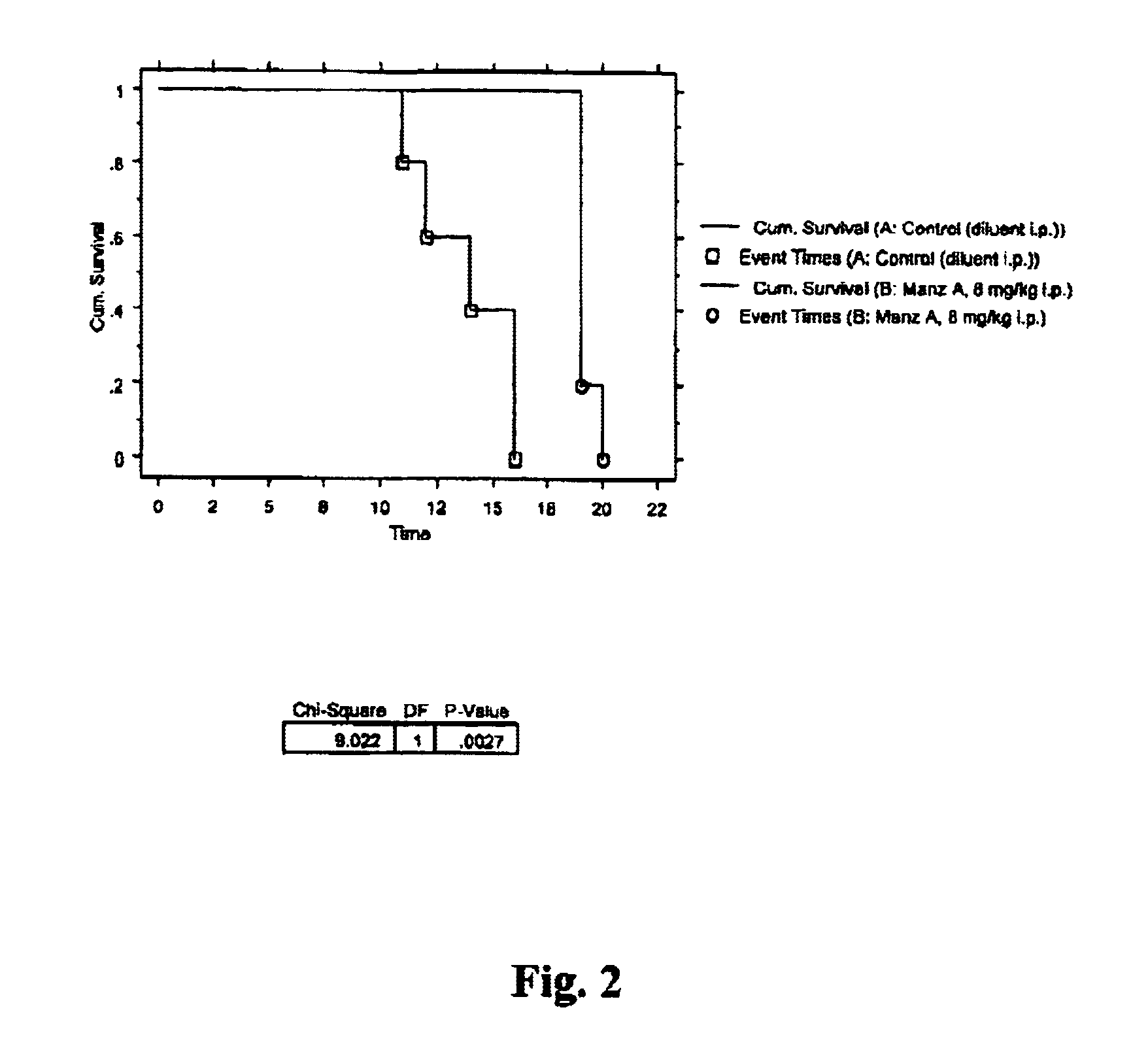
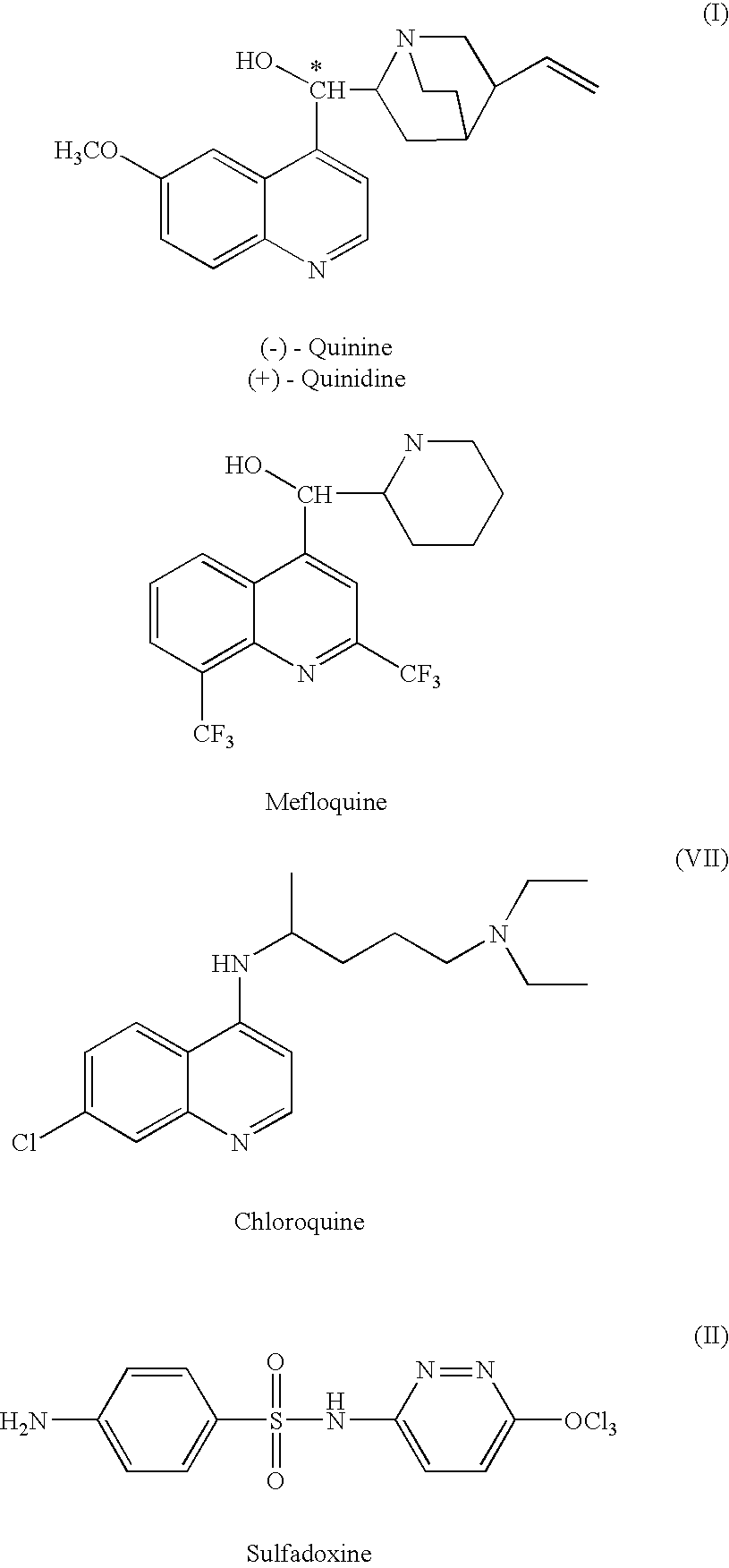
Manzamines for treatment of drug resistant infection
InactiveUS6900195B2High activityLess cytotoxicAntibacterial agentsBiocideInfective disorderResistant infection
A method of treating an infectious disease or condition in a subject in need of such treatment is disclosed. The method comprises administering to a subject an effective amount of a manzamine, manzamine derivative or analog or an optical isomer or racemate or tautomer thereof or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSISSIPPI
Particles for treatment of pulmonary infection
InactiveUS8846607B2Maintain good propertiesImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryPulmonary infectionMeningococcal meningitis
Formulations have been developed to treat or reduce the spread of respiratory infections, especially chronic or drug resistant infections, particularly tuberculosis (TB), severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), meningococcal meningitis, Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza, and small pox. Formulations include a drug or vaccine in the form of a microparticle, nanoparticle, or aggregate of nanoparticles, and, optionally, a carrier, which can be delivered by inhalation. Giving the drugs via an inhaler sidesteps the problems associated with oral or injectable drugs by bypassing the stomach and liver, and delivering the medication directly into the lungs. In one embodiment, the particle containing the agent is a large porous aerosol particle (LPPs). In another embodiment, the particles are nanoparticles, which can be administered as porous nanoparticle aggregates with micron diameters that disperse into nanoparticles following administration. Optionally, the nanoparticles are coated, such as with a surfactant or protein coating. The formulation may be administered as a powder or administered as a solution or via an enteral or non-pulmonary parenteral route of administration. The formulation is preferably administered as a pulmonary formulation. In the preferred embodiment for treatment of TB, the vaccine is a BCG vaccine that is stable at room temperature, or is an antibiotic effective against TB, such as capreomycin or PA-824, loaded at a very high percentage into the microparticles or nanoparticles. In one embodiment, a patient is treated with formulations delivering both antibiotic and vaccine.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
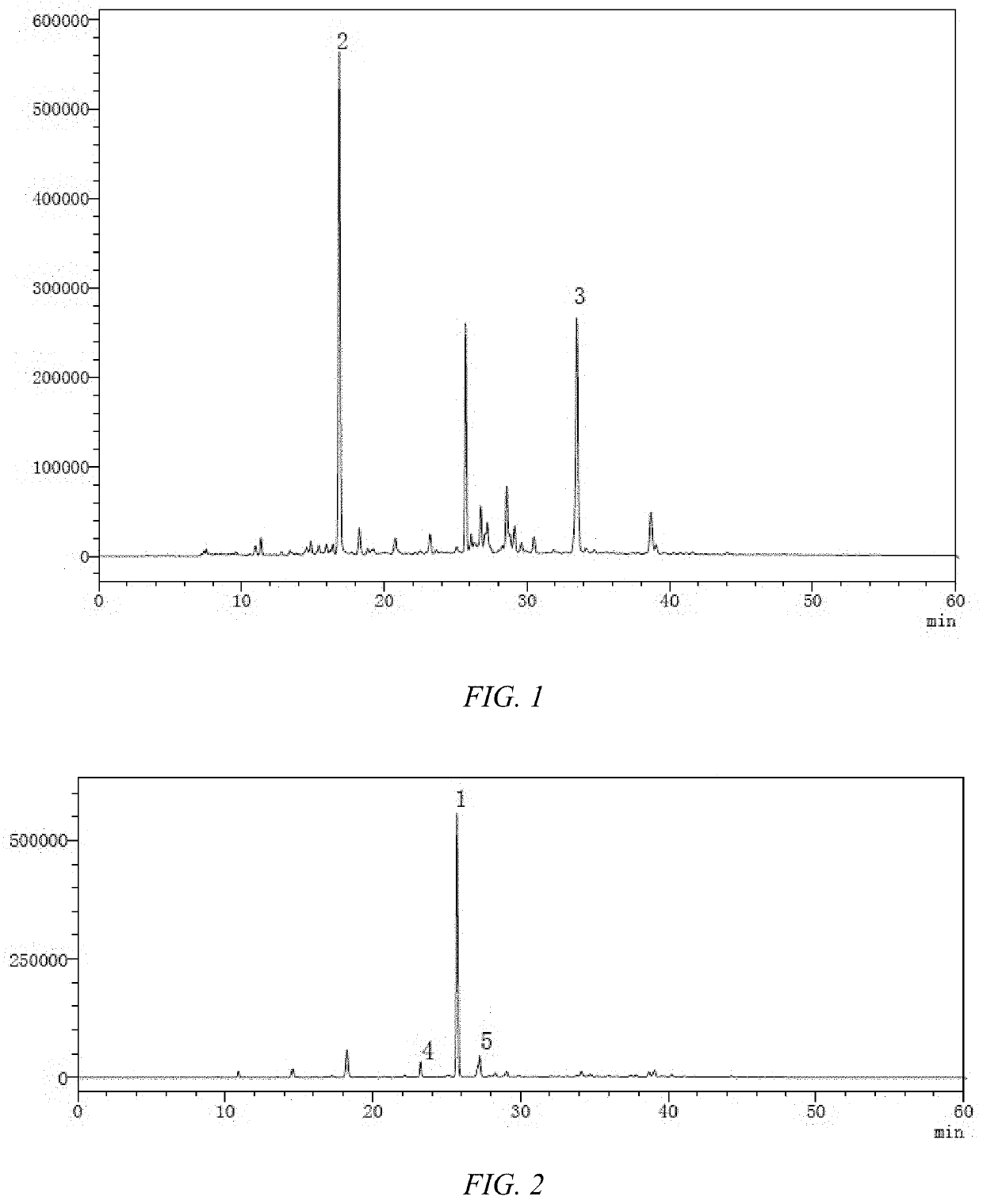
Syringa pubescens seed extract, its preparation and application in antibiotic-resistant infections
A Syringa microphylla seed extract includes the following components by weight based on a total weight of the Syringa microphylla seed extract: 0.4944-0.7142 mg / g of echinacoside, 6.624-7.617 mg / g of oleuropein, 0.4276-0.6309 mg / g of verbascoside, 3.927-4.684 mg / g of syringin, and 4.505-5.250 mg / g of forsythiaside B. A method of preparing the Syringa microphylla seed extract is disclosed. A composition for treating antibiotic-resistant infections that includes the Syringa microphylla seed extract is also disclosed.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
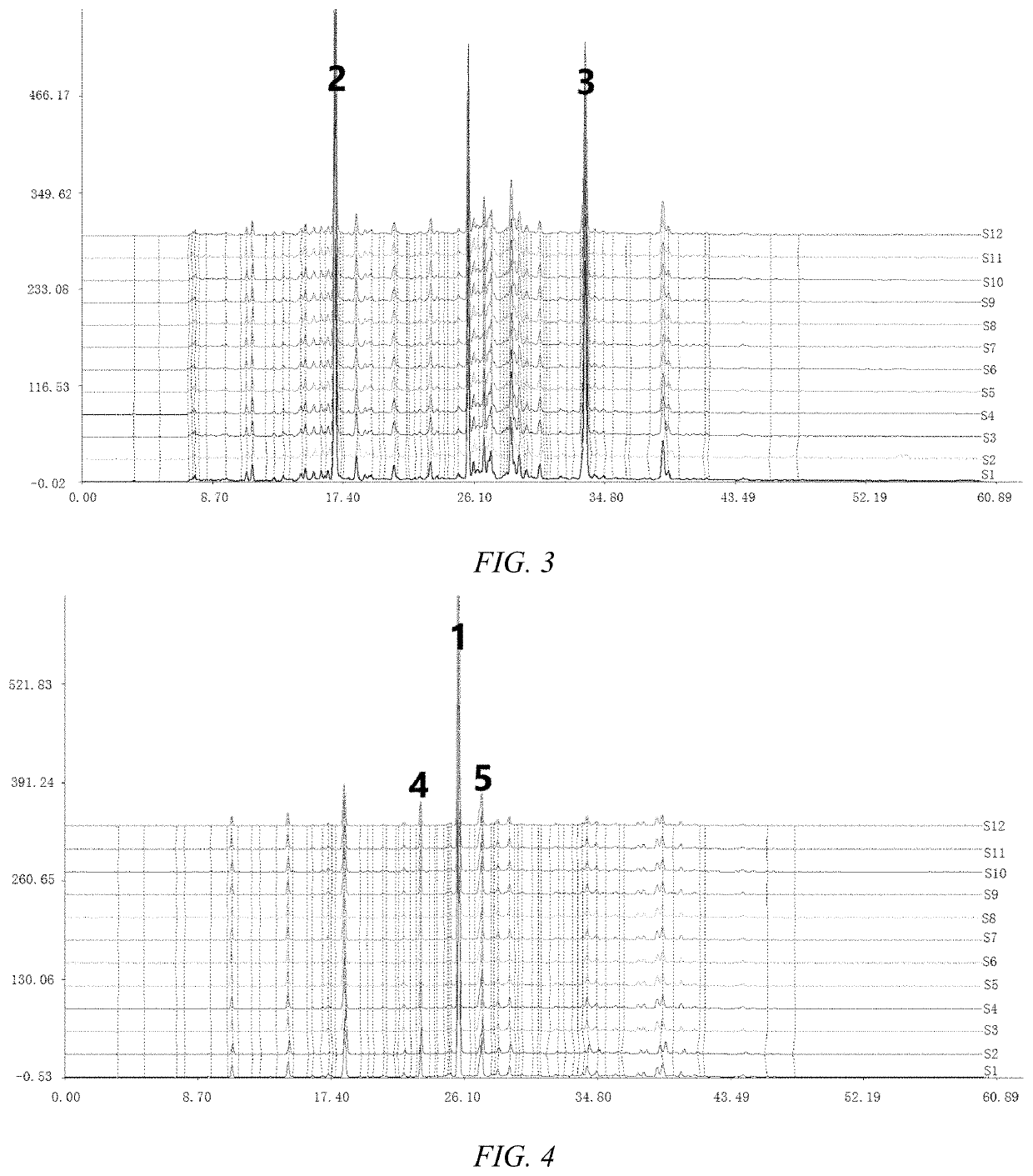
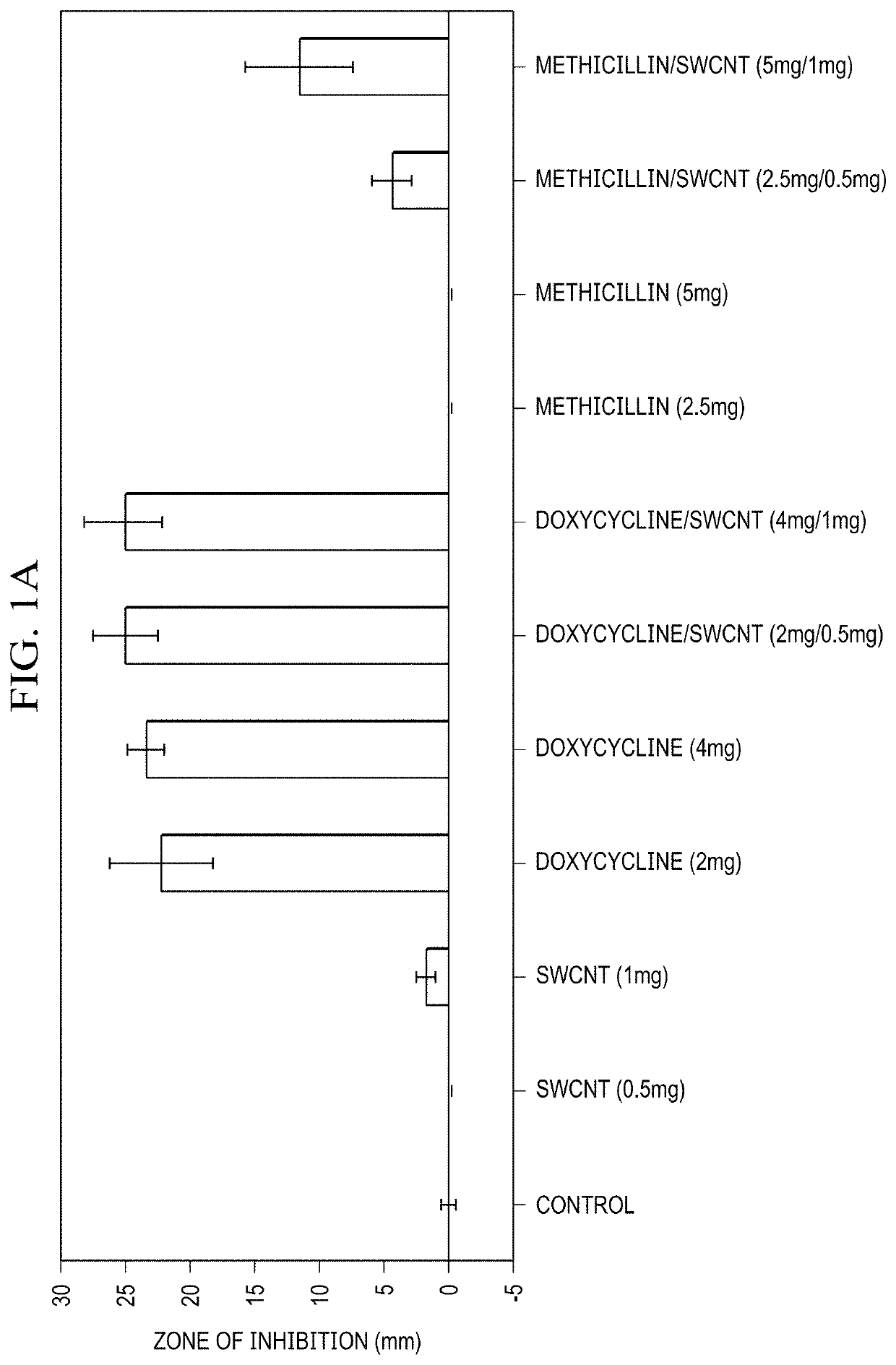
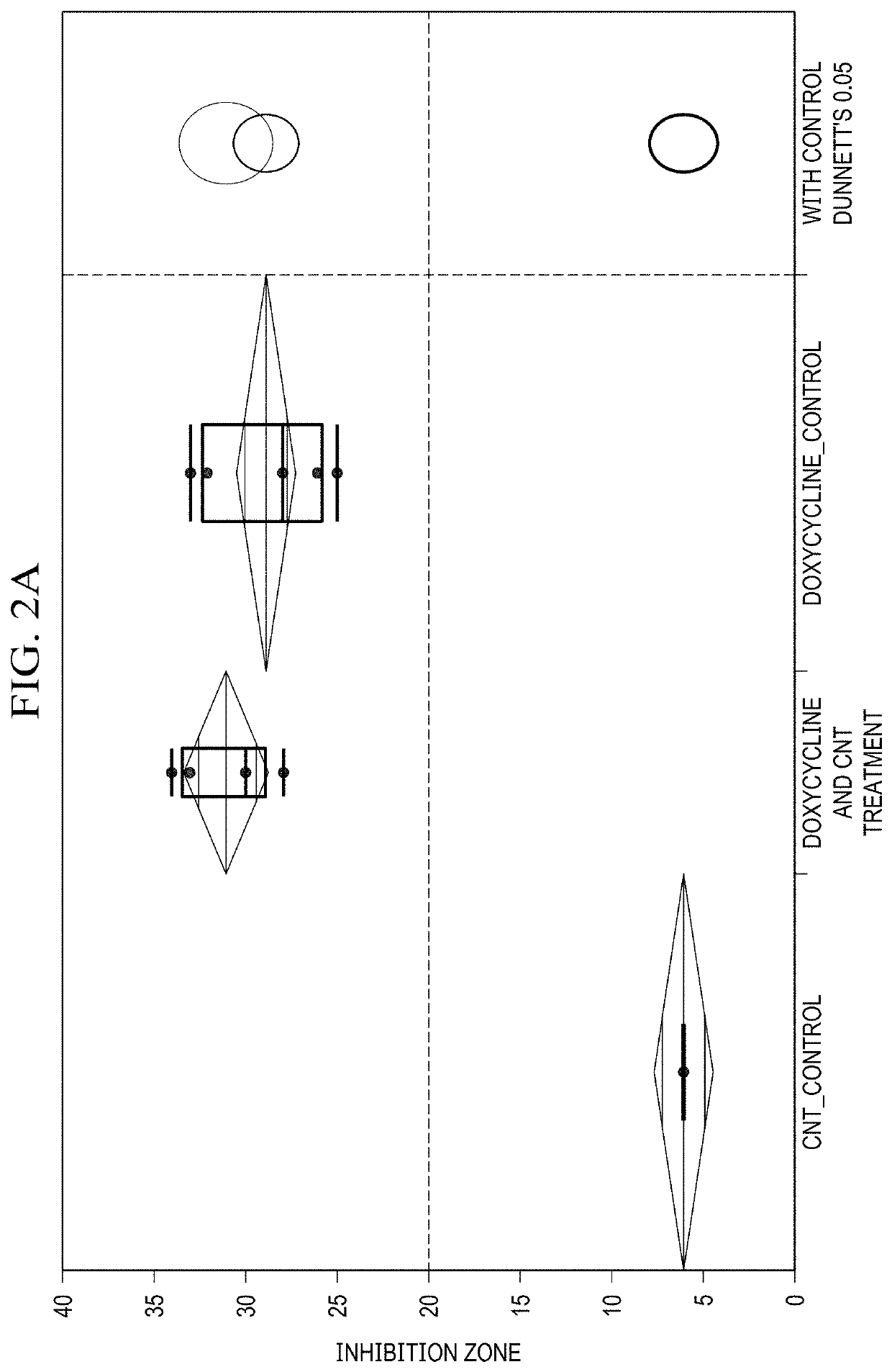
Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Assisted Antibiotic Delivery and Imaging Techniques
ActiveUS20190343765A1Reduce deliveryHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsTetracycline active ingredientsChemical LinkageAntibiotic resistance
A new route is shown for at delivery in fighting drug resistant infections. Nanotubes and antibiotics and complexed non-covalently, with no chemical bonding, but through adsorption of antibiotics onto the nanotube surface governed by sufficiently strong molecular attraction between hydrophobic systems of the two. This allows the antibiotics to be freed from the nanotubes more easily as they reach the cell membrane. When antibiotics are introduced with nanotubes in this manner, bacterial resistance is mitigated by nanotube transport potentially into the membrane of the bacteria. Nanotubes used in this way help to overcome antibiotic resistance
Owner:TEXAS CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
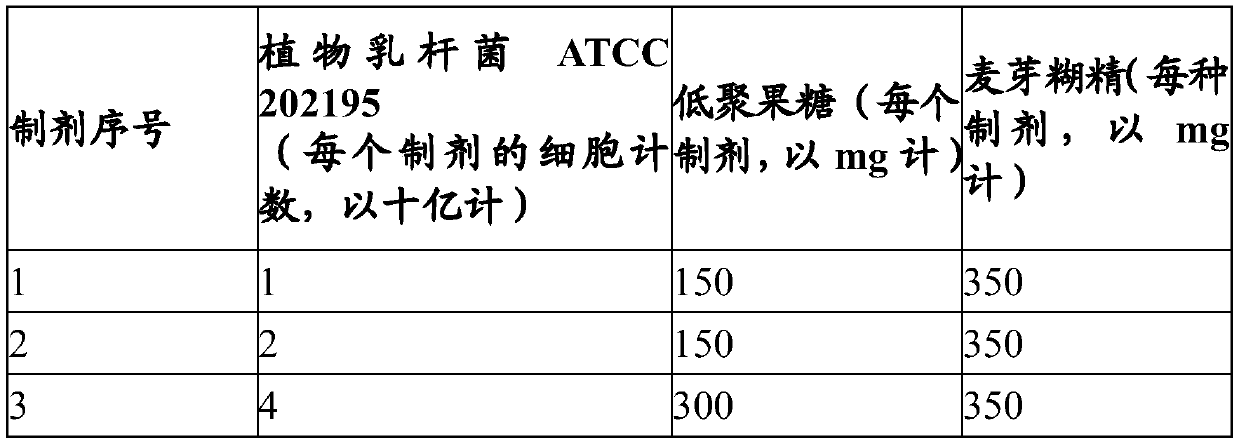
A pharmaceutical composition comprising a probiotic and a prebiotic to prevent acquisition of or treat drug resistant infections
PendingCN111491643APromote maturityImprove comfortAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical drugMicrobiology
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising a probiotic and a prebiotic for preventing acquisition of and / or alleviating symptoms associated with an infection caused by an Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBL) producing organism and other drug resistant pathogens. More particularly, the pharmaceutical composition comprises at least one Lactillobacillus specie(s) as aprobiotic and at least one oligosaccharide as a prebiotic. The present invention further provides a method of preventing acquisition of and / or treating an infection caused by Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBL) producing bacteria and other drug resistant pathogens, comprising administering an effective amount of a pharmaceutical composition comprising a probiotic and a prebiotic to a subjectin need thereof.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Biophotonic compositions for treating skin and soft tissue wounds having either or both non-resistant and resistant infections
ActiveUS11382977B2Less stressLess discomfortAntibacterial agentsPhotodynamic therapyPharmacometricsDermatology
The present document describes methods and uses of biophotonic compositions which comprise at least one oxidant and at least one chromophore capable of activating the oxidant, in association with a pharmacologically acceptable carrier for use in the treatment of skin and soft tissue wounds that have either or both non-resistant and resistant infections.
Owner:VETOQUINOL SA
Pseudomonas aeruginosa resisting Fab' fragment
InactiveCN101186648AIncrease productionGood potencyAntibacterial agentsMilk immunoglobulinsBiochemistrySpecific antibody
The invention provides a specific antibody of bacillus pyocyaneus, in particular to a bacillus pyocyaneus resistant Fab' fragment, which is extracted from the egg of laying hens immunized via bacillus pyocyaneus antigen, with high yield, better effect, stable physicochemical property, high specificity, simple preparation, better repeatability, and industrialization production support. The inventive bacillus pyocyaneus resistant Fab' fragment can significantly resist the growth of bacillus pyocyaneus, by external measurement, which can be used to prepare the drug treating bacillus pyocyaneus resistant infection.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Composition, preparation method and evaluation of a complex immunogen named I-SPGA for production of immunological active proteins (IAP)
ActiveUS11458196B2Increase coupling powerHigh affinityBacterial antigen ingredientsEgg immunoglobulinsPotentiatorResistant infection
The present invention relates to the composition and method of preparing an immunogen designated as I-spga consisting of a complex antigen prepared from 18 to 26 species of pathogenic microorganisms isolated from patients, inactivated with binary ethyleneamine (BEI) and formalin, diluted in a SPGA immunopotentiator mixed with QS-21 adjuvant. By inoculating the hens with the I-spga immunogen, hyperimmune eggs (Immunospga) are obtained which contain immunologically active proteins specific to the 18-26 antigens used for immunization. The immune response of the hens is specific to the used antigens by amplification of the antigenic signal by the SPGA immunopotentiator and due to a special immunization program that allows the immune system to act complex and intense: The I-spga complex antigen contains 18-26 microorganisms isolated from patients, bacterial bodies, components from bodies obtained by ultrasonography, cilia, exotoxins, endotoxins, spores, viruses, fungi or yeasts. This pathogenic material is inactivated with BEI and formalin. The I-spga antigen is of three types. The standard I-spga antigen is composed of 18 to 24 antibiotic-resistant bacterial species isolated from patients in Romania. The specific I-spga complex antigen is composed of the I-spga complex antigen containing a mixture of 7-9 strains from a single species of bacteria, fungi or yeasts isolated from patients in Romania mixed with SPGA and QS-21, used for inoculation of hens previously immunized with standard I-spga antigen. The personalized I-spga antigen is composed of patient-derived pathological material containing cellular debris and pathogenic germs inactivated with BEI and formalin and mixed with SPGA and QS-21 and is used to immunize hens previously immunized with the standard I-spga antigen. This now patented technology encompasses a new generation of biological products in which the immune response of the hens to different groups of parenterally inoculated antigens at different time intervals is overlapping. Chicken response is uniform and additional administration of immunogens and SPGA as an immunopotentiator amplifies the antigenic signal and immune response. The I-spga immunogen as well as the immune response contain two markers, G and A, which identify the I-spga antigen used for immunization against the antigens used to produce the Imunoinstant group bio-preparations or similar products. The I-spga immunogen is used to immunize the hens for obtaining immunologically active proteins that can be used to treat immune deficiencies, psoriasis, epidermolysis bullosa, other dermatitises, nosocomial infections, antibiotic-resistant infections in the urinary system of children and grownups.
Owner:FANTANA RAUL SORIN +1
Single-walled carbon nanotube-assisted antibiotic delivery and imaging techniques
ActiveUS10898434B2Reduce deliveryHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsTetracycline active ingredientsAntibiotic resistanceCell membrane
A new route is shown for at delivery in fighting drug resistant infections. Nanotubes and antibiotics and complexed non-covalently, with no chemical bonding, but through adsorption of antibiotics onto the nanotube surface governed by sufficiently strong molecular attraction between hydrophobic systems of the two. This allows the antibiotics to be freed from the nanotubes more easily as they reach the cell membrane. When antibiotics are introduced with nanotubes in this manner, bacterial resistance is mitigated by nanotube transport potentially into the membrane of the bacteria. Nanotubes used in this way help to overcome antibiotic resistance.
Owner:TEXAS CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
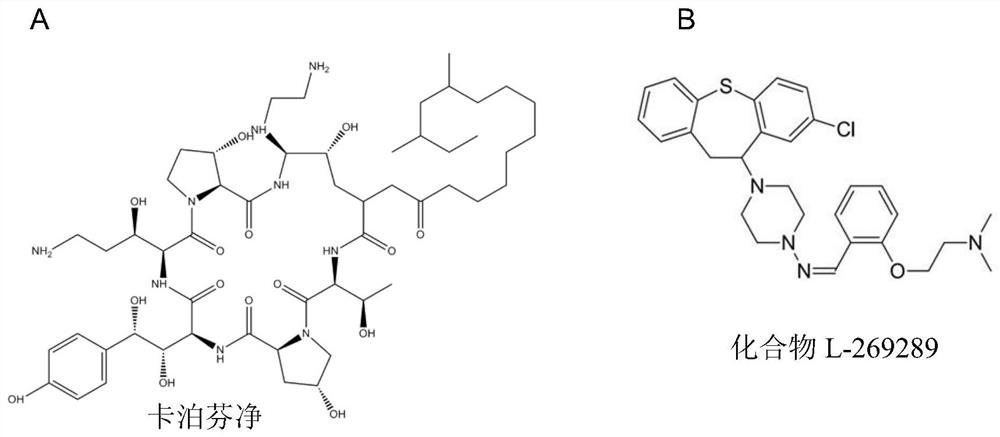
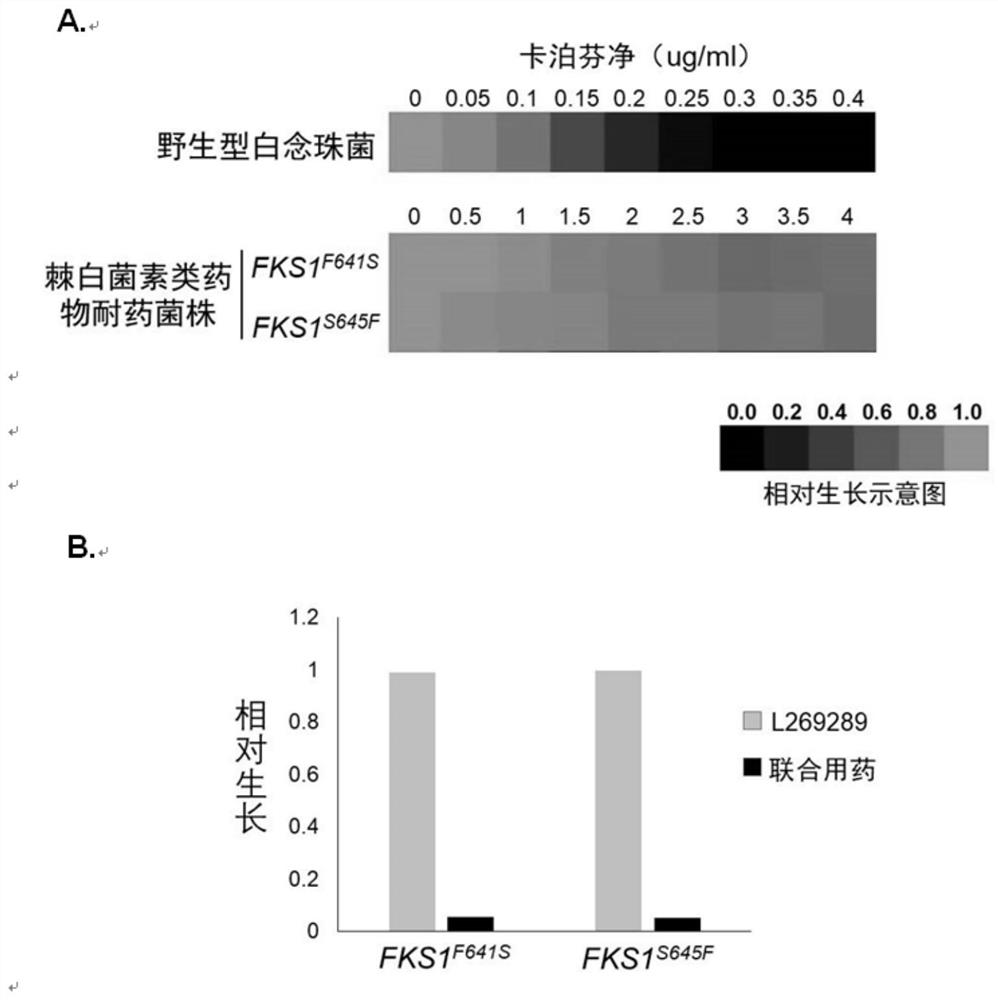
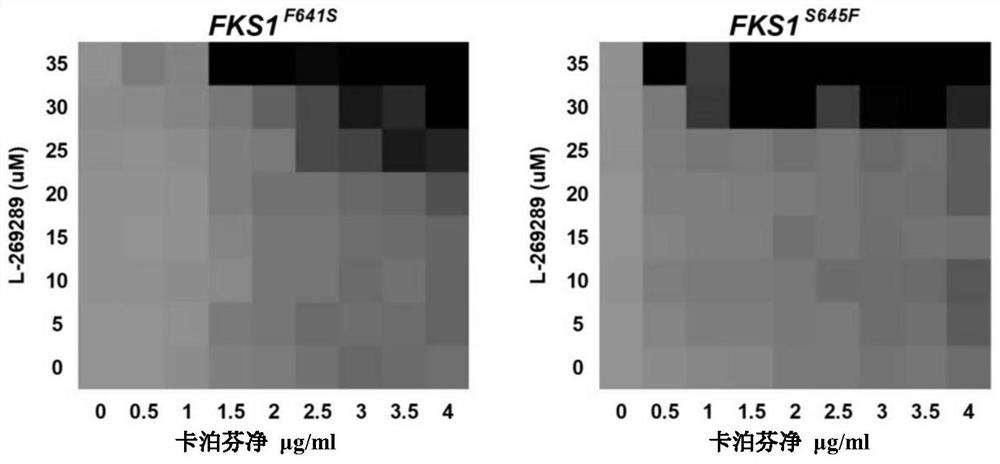
A kind of pharmaceutical composition and application thereof for Candida albicans echinocandins drug-resistant bacteria
ActiveCN110859950BEfficient killingFor invasive infectionOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsEchinocandinResistant bacteria
The invention belongs to the field of medicaments, and in particular relates to a pharmaceutical composition for treating invasive infection of Candida albicans echinocandin drug-resistant bacteria and application thereof. The active component of the pharmaceutical composition is composed of caspofungin and compound L-269289, and in vitro inhibits Echinocandin drug-resistant strains of Candida albicans, the caspofungin and compound L-269289 The mass ratio is 1:3~1:36; for the treatment of the invasive infection of Candida albicans echinocandins drug-resistant strains to mice, the mass ratio of the caspofungin and the compound L-269289 is 1:10. The present invention has verified in vitro experiments that the combined use of caspofungin and compound L‑269289 can effectively kill echinocandin drug-resistant strains of Candida albicans, and is suitable for treating echinocandin drugs of Candida albicans Invasive infection of mice by drug-resistant strains.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com